
Combined DNA Index System
Encyclopedia
The Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) is a DNA database
funded by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation
(FBI). It is a computer system that stores DNA profiles created by federal, state, and local crime laboratories
in the United States, with the ability to search the database to assist in the identification
of suspects in crimes.
) which developed guidelines for standards of practice in the United States and Canadian crime laboratories as they began DNA testing in the late 1980s.
TWGDAM was sponsored by the FBI Laboratory
which hosted several scientific meetings a year at Quantico, Virginia
, to accelerate development of laboratory guidelines and peer-reviewed papers to support forensic DNA testing which was, to some, an unproven forensic tool. TWGDAM completed a white paper in October 1989 which provided conceptual and operational concepts for a Combined DNA Index System to share DNA profiles among crime laboratories similarly to automated fingerprint identification which had become commonplace in law enforcement during the 1980s.
The FBI Laboratory began a pilot project with six state and local crime laboratories to develop software to support each laboratory's DNA testing and allow sharing of DNA profiles with other crime laboratories.
The DNA Identification Act of 1994 formally authorized the FBI to operate CODIS and set national standards for forensic DNA testing. The TWGDAM guidelines served as interim standards until recommendations were provided by a DNA Advisory Board required under the Act. Although the Act was passed in 1994, CODIS did not become fully operational until 1998.
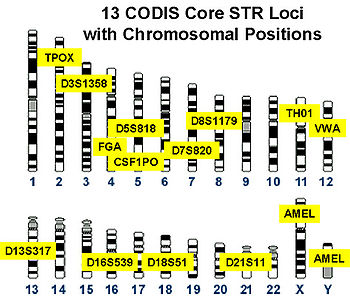 CODIS identifies 13 markers, plus Amelogenin
CODIS identifies 13 markers, plus Amelogenin
(AMEL) to determine sex:
These markers do not overlap with the ones commonly used for genealogical DNA test
ing. Some may be indicative of genetic diseases.
Originally, CODIS consisted of the Convicted Offender Index and the Forensic Index, but in recent years, the Arrestee Index, the Missing or Unidentified Persons Index, and the Missing Persons Reference Index have been added. The Convicted Offender Index contains profiles of individuals convicted of crimes. State law governs which specific crimes are eligible for CODIS. (All 50 states have passed DNA legislation authorizing the collection of DNA profiles from convicted offenders for submission to CODIS.) The Forensic Index contains profiles developed from biological material found at crime-scenes.
CODIS has a matching algorithm that searches the various indexes against one another according to strict rules that protect personal privacy. For solving rapes and homicides, for example, CODIS searches the Forensic Index against itself and against the Offender Index. A Forensic to Forensic match provides an investigative lead that connects two or more previously unlinked cases. A Forensic to Offender match actually provides a suspect for an otherwise unsolved case. It is important to note that the CODIS matching algorithm only produces a list of candidate matches. Each candidate match is confirmed or refuted by a Qualified DNA Analyst. (To become Qualified, a DNA Analyst must meet specific education and experience requirements and undergo semi-annual proficiency tests administered by a third party.)
CODIS databases exist at the local, state, and national levels. This tiered architecture allows crime laboratories to control their own data—each laboratory decides which profiles it will share with the rest of the country. As of 2006, approximately 180 laboratories in all 50 states participate in CODIS. At the national level, the National DNA Index System, or NDIS, is operated by the FBI at an undisclosed location.
in the world, surpassing the United Kingdom National DNA Database, which consisted of an estimated 3,976,090 profiles as of June 2007. As of the same date, CODIS has produced over 49,400 matches to requests, assisting in more than 50,343 investigations.
By October 2008, the US National DNA Index (NDIS) has grown to over 241,685 forensic profiles and 6,384,379 offender profiles. As of July 2009, CODIS has produced over 94,000 hits assisting in more than 93,000 investigations.
The growing public approval of DNA databases has seen the creation and expansion of many states' own DNA databases. California currently maintains the third largest DNA database in the world. Political measures such as California Proposition 69 (2004), which increased the scope of the DNA database, have already met with a significant increase in numbers of investigations aided.
In order to decrease the number of irrelevant matches at NDIS, the Convicted Offender Index requires all 13 CODIS STR
s to be present for a profile upload. Forensic profiles only require 10 of the STRs to be present for an upload.
, all suspects arrested for a felony, as well as some individuals convicted of misdemeanors, will have their DNA collected starting in 2009. In addition to this, all members of the US Armed Services who are convicted at a Special court martial and above are ordered to provide DNA samples, even if their crime has no civilian equivalent (for example adultery
).
Currently, the ACLU is concerned with the increased use of collecting DNA from arrested suspects rather than DNA testing for convicted felons. Along with the ACLU, civil libertarians oppose the use of a DNA database for privacy
concerns as well as possible institutionalized discrimination policies in collection.
, NCIS
, Numb3rs
, Criminal Minds
, Law & Order: SVU, and Dexter
, the investigators often match DNA with the CODIS database.
DNA database
A DNA database or DNA databank is a database of DNA data. A DNA database can be used in the analysis of genetic diseases, genetic fingerprinting for criminology, or genetic genealogy. DNA databases may be public or private. These databases do not normally hold DNA except for a short time...
funded by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation
Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation is an agency of the United States Department of Justice that serves as both a federal criminal investigative body and an internal intelligence agency . The FBI has investigative jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crime...
(FBI). It is a computer system that stores DNA profiles created by federal, state, and local crime laboratories
Crime Lab
A crime laboratory - often shortened to crime lab - is a scientific laboratory, using primarily forensic science for the purpose of examining evidence from criminal cases.- Lab personnel :A typical crime lab has two sets of personnel:...
in the United States, with the ability to search the database to assist in the identification
Identification
Identification or Identify may refer to:* Body identification* Combat Identification* Eyewitness identification* Forensic identification* Gender identity* Hazard Identification...
of suspects in crimes.
Origins
CODIS was an outgrowth of the Technical Working Group on DNA Analysis Methods (TWGDAM, now SWGDAMScientific Working Group
Since the early 1990s, the US FBI Laboratory has sponsored Scientific Working Groups to improve discipline practices and create mutual agreements between federal, state, and local forensic community partners...
) which developed guidelines for standards of practice in the United States and Canadian crime laboratories as they began DNA testing in the late 1980s.
TWGDAM was sponsored by the FBI Laboratory
FBI Laboratory
The FBI Laboratory is a division within the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation that provides forensic analysis support services to the FBI, as well as to state and local law enforcement agencies free of charge. The lab is currently located at Marine Corps Base Quantico in Quantico,...
which hosted several scientific meetings a year at Quantico, Virginia
Quantico, Virginia
- Demographics :As of the census of 2000, there are 561 people, 295 households, and 107 families living in the town. The population density is . There are 359 housing units at an average density of .-Racial composition:...
, to accelerate development of laboratory guidelines and peer-reviewed papers to support forensic DNA testing which was, to some, an unproven forensic tool. TWGDAM completed a white paper in October 1989 which provided conceptual and operational concepts for a Combined DNA Index System to share DNA profiles among crime laboratories similarly to automated fingerprint identification which had become commonplace in law enforcement during the 1980s.
The FBI Laboratory began a pilot project with six state and local crime laboratories to develop software to support each laboratory's DNA testing and allow sharing of DNA profiles with other crime laboratories.
The DNA Identification Act of 1994 formally authorized the FBI to operate CODIS and set national standards for forensic DNA testing. The TWGDAM guidelines served as interim standards until recommendations were provided by a DNA Advisory Board required under the Act. Although the Act was passed in 1994, CODIS did not become fully operational until 1998.
Markers

Amelogenin
Amelogenin is a protein found in developing tooth enamel, and it belongs to a family of extracellular matrix proteins. Developing enamel contains about 30% protein, and 90% of this is amelogenins...
(AMEL) to determine sex:
- CSF1PO
- D3S1358
- D5s818
- D7s820
- D8S1179
- D13s317
- D16s539
- D18s51
- D21s11
- FGA
- THO1
- TPOX
- vWA
These markers do not overlap with the ones commonly used for genealogical DNA test
Genealogical DNA test
A genealogical DNA test examines the nucleotides at specific locations on a person's DNA for genetic genealogy purposes. The test results are not meant to have any informative medical value and do not determine specific genetic diseases or disorders ; they are intended only to give genealogical...
ing. Some may be indicative of genetic diseases.
Indexes and database structure
CODIS is an index of pointers to assist US public crime laboratories to compare and exchange DNA profiles. A record in the CODIS database, known as a CODIS DNA profile, consists of an individual's DNA profile, together with the sample's identifier and an identifier of the laboratory responsible for the profile. CODIS is not a criminal history database, like the National Crime Information Center (NCIC), and does not contain any personal identity information, such as names, dates of birth, and social security numbers.Originally, CODIS consisted of the Convicted Offender Index and the Forensic Index, but in recent years, the Arrestee Index, the Missing or Unidentified Persons Index, and the Missing Persons Reference Index have been added. The Convicted Offender Index contains profiles of individuals convicted of crimes. State law governs which specific crimes are eligible for CODIS. (All 50 states have passed DNA legislation authorizing the collection of DNA profiles from convicted offenders for submission to CODIS.) The Forensic Index contains profiles developed from biological material found at crime-scenes.
CODIS has a matching algorithm that searches the various indexes against one another according to strict rules that protect personal privacy. For solving rapes and homicides, for example, CODIS searches the Forensic Index against itself and against the Offender Index. A Forensic to Forensic match provides an investigative lead that connects two or more previously unlinked cases. A Forensic to Offender match actually provides a suspect for an otherwise unsolved case. It is important to note that the CODIS matching algorithm only produces a list of candidate matches. Each candidate match is confirmed or refuted by a Qualified DNA Analyst. (To become Qualified, a DNA Analyst must meet specific education and experience requirements and undergo semi-annual proficiency tests administered by a third party.)
CODIS databases exist at the local, state, and national levels. This tiered architecture allows crime laboratories to control their own data—each laboratory decides which profiles it will share with the rest of the country. As of 2006, approximately 180 laboratories in all 50 states participate in CODIS. At the national level, the National DNA Index System, or NDIS, is operated by the FBI at an undisclosed location.
Relative size
As of October 2007, CODIS held 194,785 forensic profiles and 5,070,473 offender profiles, making it the largest DNA databaseDNA database
A DNA database or DNA databank is a database of DNA data. A DNA database can be used in the analysis of genetic diseases, genetic fingerprinting for criminology, or genetic genealogy. DNA databases may be public or private. These databases do not normally hold DNA except for a short time...
in the world, surpassing the United Kingdom National DNA Database, which consisted of an estimated 3,976,090 profiles as of June 2007. As of the same date, CODIS has produced over 49,400 matches to requests, assisting in more than 50,343 investigations.
By October 2008, the US National DNA Index (NDIS) has grown to over 241,685 forensic profiles and 6,384,379 offender profiles. As of July 2009, CODIS has produced over 94,000 hits assisting in more than 93,000 investigations.
The growing public approval of DNA databases has seen the creation and expansion of many states' own DNA databases. California currently maintains the third largest DNA database in the world. Political measures such as California Proposition 69 (2004), which increased the scope of the DNA database, have already met with a significant increase in numbers of investigations aided.
In order to decrease the number of irrelevant matches at NDIS, the Convicted Offender Index requires all 13 CODIS STR
Short tandem repeat
A short tandem repeat in DNA occurs when a pattern of two or more nucleotides are repeated and the repeated sequences are directly adjacent to each other. The pattern can range in length from 2 to 5 base pairs and is typically in the non-coding intron region...
s to be present for a profile upload. Forensic profiles only require 10 of the STRs to be present for an upload.
Privacy concerns
The CODIS database originally was primarily used to collect DNA of convicted sex offenders. Over time, this has expanded. Currently all fifty states have mandatory DNA collection from certain felony offenses such as sexual assault and homicide, and 47 states collect DNA from all convicted felons. Other states have gone further in collecting DNA samples from juveniles and all suspects arrested. In California, as a result of Proposition 69 in 2004California Proposition 69 (2004)
California Proposition 69, the DNA Initiative, was a successful 2004 California ballot proposition that allows for the collection of DNA samples from all felons and from people who have been arrested for certain crimes...
, all suspects arrested for a felony, as well as some individuals convicted of misdemeanors, will have their DNA collected starting in 2009. In addition to this, all members of the US Armed Services who are convicted at a Special court martial and above are ordered to provide DNA samples, even if their crime has no civilian equivalent (for example adultery
Adultery
Adultery is sexual infidelity to one's spouse, and is a form of extramarital sex. It originally referred only to sex between a woman who was married and a person other than her spouse. Even in cases of separation from one's spouse, an extramarital affair is still considered adultery.Adultery is...
).
Currently, the ACLU is concerned with the increased use of collecting DNA from arrested suspects rather than DNA testing for convicted felons. Along with the ACLU, civil libertarians oppose the use of a DNA database for privacy
Privacy
Privacy is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves and thereby reveal themselves selectively...
concerns as well as possible institutionalized discrimination policies in collection.
In popular culture
In forensics television series such as CSI, BonesBones (TV series)
Bones is an American crime drama television series that premiered on the Fox Network on September 13, 2005. The show is based on forensic anthropology and forensic archaeology, with each episode focusing on an FBI case file concerning the mystery behind human remains brought by FBI Special Agent...
, NCIS
NCIS (TV series)
NCIS, formerly known as NCIS: Naval Criminal Investigative Service, is an American police procedural drama television series revolving around a fictional team of special agents from the Naval Criminal Investigative Service, which conducts criminal investigations involving the U.S...
, Numb3rs
NUMB3RS
Numb3rs is an American television drama which premiered on CBS on January 23, 2005, and concluded on March 12, 2010. The series was created by Nicolas Falacci and Cheryl Heuton, and follows FBI Special Agent Don Eppes and his mathematical genius brother, Charlie Eppes , who helps Don solve crimes...
, Criminal Minds
Criminal Minds
Criminal Minds is an American police procedural drama that premiered September 22, 2005, on CBS. The series follows a team of profilers from the FBI's Behavioral Analysis Unit based in Quantico, Virginia. The BAU is part of the FBI National Center for the Analysis of Violent Crime...
, Law & Order: SVU, and Dexter
Dexter (TV series)
Dexter is an American television drama series, which debuted on Showtime on October 1, 2006. The sixth season premiered on October 2, 2011. The series centers on Dexter Morgan , a bloodstain pattern analyst for the Miami Metro Police Department who moonlights as a serial killer...
, the investigators often match DNA with the CODIS database.
See also
- Debbie Smith ActDebbie Smith ActThe Debbie Smith Act of 2004 provides United States federal government grants to eligible states and units of local government to conduct DNA analyses of backlogged DNA samples collected from victims and criminal offenders. The Act expands the Combined DNA Index System and provides legal...
- Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification SystemIntegrated Automated Fingerprint Identification SystemThe Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System is a national automated fingerprint identification and criminal history system maintained by the Federal Bureau of Investigation . IAFIS provides automated fingerprint search capabilities, latent searching capability, electronic image...
(IAFIS)
External links
- CODIS homepage
- "ACLU Warns of Privacy Abuses in Government Plan to Expand DNA Databases". ACLU. March 1, 1999.
- A Not So Perfect Match, CBSCBSCBS Broadcasting Inc. is a major US commercial broadcasting television network, which started as a radio network. The name is derived from the initials of the network's former name, Columbia Broadcasting System. The network is sometimes referred to as the "Eye Network" in reference to the shape of...
, 2007 - "Anne Pressly: Detailed Cases and Informed Opinions On DNA". December 4, 2008.
- "DNA didn't prove anything, as it only had five points out of 13. Juror Explains Verdict In Double Murder". November 13, 2008. (As of 20111024, this appears to be a dead link.)

