Communist state
Encyclopedia
State (polity)
A state is an organized political community, living under a government. States may be sovereign and may enjoy a monopoly on the legal initiation of force and are not dependent on, or subject to any other power or state. Many states are federated states which participate in a federal union...
with a form of government
Form of government
A form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
characterized by single-party rule
Single-party state
A single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a type of party system government in which a single political party forms the government and no other parties are permitted to run candidates for election...
or dominant-party rule
Dominant-party system
A dominant-party system, or one-party dominant system, is a system where there is "a category of parties/political organizations that have successively won election victories and whose future defeat cannot be envisaged or is unlikely for the foreseeable future." A wide range of parties have been...
of a communist party
Communist party
A political party described as a Communist party includes those that advocate the application of the social principles of communism through a communist form of government...
and a professed allegiance to a Leninist or Marxist-Leninist communist
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
ideology as the guiding principle of the state. According to this principle public ownership of all means of production by the Communist party
Communist party
A political party described as a Communist party includes those that advocate the application of the social principles of communism through a communist form of government...
-run state is necessary for the possibility to further the interest of the working class. According to Marxist-Leninists, a multi-party state allows parties to represent interests of subgroups instead of the coherent whole, and because it allows private fortune, it allows private fortune to distort the political decision-making.
In practice, the so-called Communist states do not refer to themselves as Communist states. They constitutionally identify themselves as socialist state
Socialist state
A socialist state generally refers to any state constitutionally dedicated to the construction of a socialist society. It is closely related to the political strategy of "state socialism", a set of ideologies and policies that believe a socialist economy can be established through government...
s or Workers' states. The primary goal of these states, and their justification for single-party rule, is to guide their respective countries in the process of constructing socialism
Socialism
Socialism is an economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and cooperative management of the economy; or a political philosophy advocating such a system. "Social ownership" may refer to any one of, or a combination of, the following: cooperative enterprises,...
.
Communist states may have several legal political parties
Political party
A political party is a political organization that typically seeks to influence government policy, usually by nominating their own candidates and trying to seat them in political office. Parties participate in electoral campaigns, educational outreach or protest actions...
, but the communist party is usually granted a special or dominant role in government, often by statute
Statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs a state, city, or county. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. The word is often used to distinguish law made by legislative bodies from case law, decided by courts, and regulations...
or under the constitution
Constitution
A constitution is a set of fundamental principles or established precedents according to which a state or other organization is governed. These rules together make up, i.e. constitute, what the entity is...
. Consequently, the institutions of the state and of the communist party become intimately entwined, such as in the development of parallel institutions.
In the 20th century, most communist states adopted planned economies
Planned economy
A planned economy is an economic system in which decisions regarding production and investment are embodied in a plan formulated by a central authority, usually by a government agency...
. However, there were exceptions: The Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
during the 1920s and late 1980s and Yugoslavia
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was the Yugoslav state that existed from the abolition of the Yugoslav monarchy until it was dissolved in 1992 amid the Yugoslav Wars. It was a socialist state and a federation made up of six socialist republics: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia,...
after World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
allowed limited markets and a degree of worker self-management, while China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
and Laos
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
introduced far-reaching market reforms after the 1980s.
The fundamental concepts of communist states often diverge from the original socio-economic ideologies from which they develop. As a result, many adherents of these ideologies often oppose the political systems commonly associated with these states. For example, activists describing themselves as Trotskyists or communists were often opposed to the communist states of the 20th century, claiming either that they have nothing to do with 'real' communism or that the ideology of such states has reached a point of irrevocable corruption
Political corruption
Political corruption is the use of legislated powers by government officials for illegitimate private gain. Misuse of government power for other purposes, such as repression of political opponents and general police brutality, is not considered political corruption. Neither are illegal acts by...
.
Types of communist states
While historically almost all claim lineage to MarxistMarxism
Marxism is an economic and sociopolitical worldview and method of socioeconomic inquiry that centers upon a materialist interpretation of history, a dialectical view of social change, and an analysis and critique of the development of capitalism. Marxism was pioneered in the early to mid 19th...
thought, there are many varieties of communist states, with indigenous adaptions. For Marxist-Leninists
Marxism-Leninism
Marxism–Leninism is a communist ideology, officially based upon the theories of Marxism and Vladimir Lenin, that promotes the development and creation of a international communist society through the leadership of a vanguard party over a revolutionary socialist state that represents a dictatorship...
, the state and the communist party claim to act in accordance with the wishes of the industrial working class
Working class
Working class is a term used in the social sciences and in ordinary conversation to describe those employed in lower tier jobs , often extending to those in unemployment or otherwise possessing below-average incomes...
.
For Maoists
Maoism
Maoism, also known as the Mao Zedong Thought , is claimed by Maoists as an anti-Revisionist form of Marxist communist theory, derived from the teachings of the Chinese political leader Mao Zedong . Developed during the 1950s and 1960s, it was widely applied as the political and military guiding...
, the state and party claim to act in accordance to the peasantry. Under Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping was a Chinese politician, statesman, and diplomat. As leader of the Communist Party of China, Deng was a reformer who led China towards a market economy...
, the People's Republic of China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
proclaimed a policy of "socialism with Chinese characteristics". In most communist states, governments assert that they represent the democratic
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
dictatorship of the proletariat
Dictatorship of the proletariat
In Marxist socio-political thought, the dictatorship of the proletariat refers to a socialist state in which the proletariat, or the working class, have control of political power. The term, coined by Joseph Weydemeyer, was adopted by the founders of Marxism, Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, in the...
.
These "Communist states" often don't claim to have achieved socialism or communism in their countries; rather, they claim to be building and working toward the establishment of socialism in their countries. For example, the preamble to the Socialist Republic of Vietnam's constitution states that Vietnam only entered a transition stage between capitalism and socialism after the country was re-unified under the Communist party in 1976, and the 1992 Constitution of the Republic of Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
states that the role of the Communist Party is to "guide the common effort toward the goals and construction of socialism".
Alternative names that states adhering to an officially "communist" ideology may assign themselves is socialist state
Socialist state
A socialist state generally refers to any state constitutionally dedicated to the construction of a socialist society. It is closely related to the political strategy of "state socialism", a set of ideologies and policies that believe a socialist economy can be established through government...
or socialist republic. This is because these nations have not yet transcended capitalism
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
or state capitalism
State capitalism
The term State capitalism has various meanings, but is usually described as commercial economic activity undertaken by the state with management of the productive forces in a capitalist manner, even if the state is nominally socialist. State capitalism is usually characterized by the dominance or...
and progressed toward pure communism in the Marxist sense, which can only be achieved once capitalism exhausts itself.
State institutions
Communist states share similar institutions, which are organized on the premise that the communist party is a vanguard of the proletariatVanguard party
A vanguard party is a political party at the forefront of a mass action, movement, or revolution. The idea of a vanguard party has its origins in the Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels...
and represents the long-term interests of the people. The doctrine of democratic centralism
Democratic centralism
Democratic centralism is the name given to the principles of internal organization used by Leninist political parties, and the term is sometimes used as a synonym for any Leninist policy inside a political party...
, which was developed by Lenin as a set of principles to be used in the internal affairs of the communist party, is extended to society at large.
According to democratic centralism, all leaders must be elected by the people and all proposals must be debated openly, but, once a decision has been reached, all people have a duty to obey that decision and all debate should end. When used within a political party, democratic centralism is meant to prevent factionalism and splits. When applied to an entire state, democratic centralism creates a one-party system
Single-party state
A single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a type of party system government in which a single political party forms the government and no other parties are permitted to run candidates for election...
.
The constitutions of most communist states describe their political system as a form of democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
. Thus, they recognize the sovereignty of the people as embodied in a series of representative
Representative democracy
Representative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
parliament
Parliament
A parliament is a legislature, especially in those countries whose system of government is based on the Westminster system modeled after that of the United Kingdom. The name is derived from the French , the action of parler : a parlement is a discussion. The term came to mean a meeting at which...
ary institutions. Communist states do not have a separation of powers
Separation of powers
The separation of powers, often imprecisely used interchangeably with the trias politica principle, is a model for the governance of a state. The model was first developed in ancient Greece and came into widespread use by the Roman Republic as part of the unmodified Constitution of the Roman Republic...
; instead, they have one national legislative body (such as the Supreme Soviet
Supreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union was the Supreme Soviet in the Soviet Union and the only one with the power to pass constitutional amendments...
in the Soviet Union) which is considered the highest organ of state power and which is legally superior to the executive and judicial branches of government.
Such national legislative politics in communist states often have a similar structure to the parliaments that exist in liberal republics, with two significant differences: first, the deputies elected to these national legislative bodies are not expected to represent the interests of any particular constituency, but the long-term interests of the people as a whole; second, against Marx's advice, the legislative bodies of communist states are not in permanent session. Rather, they convene once or several times per year in sessions which usually last only a few days.
When the national legislative body is not in session, its powers are transferred to a smaller council (often called a presidium
Presidium
The presidium or praesidium is the name for the heading organ of various legislative and organizational bodies.-Historical usage:...
) which combines legislative and executive power, and, in some communist states (such as the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
before 1990), acts as a collective head of state
Head of State
A head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
. In some systems, the presidium is composed of important communist party members who vote the resolutions of the communist party into law.
State social institutions
Another feature of communist states is the existence of numerous state-sponsored social organizations (trade unionTrade union
A trade union, trades union or labor union is an organization of workers that have banded together to achieve common goals such as better working conditions. The trade union, through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members and negotiates labour contracts with...
s, youth organizations, women's organizations, associations of teachers, writers, journalists and other professionals, consumer cooperatives, sports clubs, etc.) which are integrated into the political system.
In some communist states, representatives of these organizations are guaranteed a certain number of seats on the national legislative bodies. In all communist states, the social organizations are expected to promote social unity and cohesion, to serve as a link between the government and society, and to provide a forum for recruitment of new communist party members.
Political power
Historically, the political organization of many communist states has been dominated by a single-party monopoly. Some communist regimes, such as North KoreaNorth Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
, East Germany or the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
The Czechoslovak Socialist Republic was the official name of Czechoslovakia from 1960 until end of 1989 , a Soviet satellite state of the Eastern Bloc....
have or had more than one political party, but all minor parties are or were required to follow the leadership of the communist party. In communist states, the government may not tolerate criticism of policies that have already been implemented in the past or are being implemented in the present.
In addition, communist states are widely seen as being de facto dictatorships by historians and sociologists, as rigged elections have been commonplace under some communist governments. Nevertheless, communist parties have won elections and governed in the context of multi-party democracies
Multi-party system
A multi-party system is a system in which multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government separately or in coalition, e.g.The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition in the United Kingdom formed in 2010. The effective number of parties in a multi-party system is normally...
, without seeking to establish a one-party state. Examples include San Marino
San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino , is a state situated on the Italian Peninsula on the eastern side of the Apennine Mountains. It is an enclave surrounded by Italy. Its size is just over with an estimated population of over 30,000. Its capital is the City of San Marino...
, Republic of Nicaragua
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
, Republic of Moldova
Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
(since 2001), Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
(presently), and the India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n states of Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
, West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
and Tripura
Tripura
Tripura is a state in North-East India, with an area of . It is the third smallest state of India, according to area. Tripura is surrounded by Bangladesh on the north, south, and west. The Indian states of Assam and Mizoram lie to the east. The capital is Agartala and the main languages spoken are...
. However, for the purposes of this article, these entities do not fall under the definition of communist state.
Objections to use of term
Not every country ruled by a communist party is viewed by left communists and Trotskyists as a communist state, and the term "communist state" has traditionally been used in Western political scientistsPolitical science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
and mass-media to refer to a specific type of one-party state.
Some communists, such left communists, dispute the validity of the term "communist state". In classical Marxism
Marxism
Marxism is an economic and sociopolitical worldview and method of socioeconomic inquiry that centers upon a materialist interpretation of history, a dialectical view of social change, and an analysis and critique of the development of capitalism. Marxism was pioneered in the early to mid 19th...
, communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
is the final phase of history at which time the state would have "withered away" and therefore "communist state" is a contradiction in terms under premises of this theory. Current states are either in the capitalist
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
or socialist
Socialism
Socialism is an economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and cooperative management of the economy; or a political philosophy advocating such a system. "Social ownership" may refer to any one of, or a combination of, the following: cooperative enterprises,...
phase of history making the term "socialist state
Socialist state
A socialist state generally refers to any state constitutionally dedicated to the construction of a socialist society. It is closely related to the political strategy of "state socialism", a set of ideologies and policies that believe a socialist economy can be established through government...
" preferable to many communists and marxist theorists.
Some socialists like left communists oppose the idea of a vanguard party pulling a nation towards communism, and thus the term "socialist state" is liable to cause confusion. Others assert that the role of the communist party (i.e. the vanguard party
Vanguard party
A vanguard party is a political party at the forefront of a mass action, movement, or revolution. The idea of a vanguard party has its origins in the Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels...
) is to pull a nation toward the communist phase of history.
Some Marxists have also opposed the usage of the term "communist state". Their critique may be based on a variety of arguments, but nearly all anti-Stalinist communists argued that the Soviet model did not represent the interests of the working class. As such, Trotskyists
Trotskyism
Trotskyism is the theory of Marxism as advocated by Leon Trotsky. Trotsky considered himself an orthodox Marxist and Bolshevik-Leninist, arguing for the establishment of a vanguard party of the working-class...
referred to the Soviet Union as a "degenerated workers' state
Degenerated workers' state
In Trotskyist political theory the term degenerated workers' state has been used since the 1930s to describe the state of the Soviet Union after Joseph Stalin's consolidation of power in or about 1924...
" and called its satellites
Satellite state
A satellite state is a political term that refers to a country that is formally independent, but under heavy political and economic influence or control by another country...
"deformed workers states".
From the moderate liberal viewpoint
Totalitarian communist regimes have been criticized for their one-partySingle-party state
A single-party state, one-party system or single-party system is a type of party system government in which a single political party forms the government and no other parties are permitted to run candidates for election...
dictatorship
Dictatorship
A dictatorship is defined as an autocratic form of government in which the government is ruled by an individual, the dictator. It has three possible meanings:...
s, totalitarian
Totalitarianism
Totalitarianism is a political system where the state recognizes no limits to its authority and strives to regulate every aspect of public and private life wherever feasible...
control of the economy and society and repression of civil liberties by the Council of Europe
Council of Europe
The Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
, economic focus on heavy industry at the expense of consumer goods, sometimes resulting in shortages of vital products or even famine by Leonard E. Hubbard, and militarism and propaganda to cover up the mistakes of the government by Peter Kenez
Peter Kenez
Peter Kenez is a historian specializing in Russian history and Eastern Europe. He also teaches courses on Soviet cinema and an interdisciplinary course on the Holocaust with literature professor Murray Baumgarten...
.
From the communist and socialist viewpoints
Within the socialist and communist movements themselves, there are a number of criticisms of using the term "communist states". Left communists, Anarchists and some Trotskyists point out the fact that the so-called "communist" or "socialist" states or "people's states" were actually state capitalist and thus cannot be called "socialist".List of current communist states
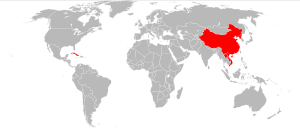
The following countries are one-party states in which the institutions of the ruling communist party and the state have become intertwined; hence they fall under the definition of Communist states. They are listed here together with the year of their founding and their respective ruling parties:Democratic People's Republic of Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
(since 1948); Workers' Party of Korea
Workers' Party of Korea
The Workers' Party of Korea is the ruling Communist party of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea , commonly known as North Korea. It is also called the Korean Workers' Party...
, removed Marxist-Leninism references and officially follows Juche
Juche
Juche or Chuch'e is a Korean word usually translated as "self-reliance." In the Democratic People's Republic of Korea , "Juche" refers specifically to a political thesis of Kim Il-sung, the Juche Idea, that identifies the Korean masses as the masters of the country's development...
. People's Republic of China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
(since 1949); Communist Party of China
Communist Party of China
The Communist Party of China , also known as the Chinese Communist Party , is the founding and ruling political party of the People's Republic of China...
, describes itself as "socialism with Chinese characteristics" Socialist Republic of Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
(since 1976); Communist Party of Vietnam
Communist Party of Vietnam
The Communist Party of Vietnam , formally established in 1930, is the governing party of the nation of Vietnam. It is today the only legal political party in that country. Describing itself as Marxist-Leninist, the CPV is the directing component of a broader group of organizations known as the...
(ruled the Democratic Republic of Vietnam
North Vietnam
The Democratic Republic of Vietnam , was a communist state that ruled the northern half of Vietnam from 1954 until 1976 following the Geneva Conference and laid claim to all of Vietnam from 1945 to 1954 during the First Indochina War, during which they controlled pockets of territory throughout...
since 1954), describes itself "in transition toward socialism in the light of Marxism-Leninism." Republic of Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
(Cuban Revolution
Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution was an armed revolt by Fidel Castro's 26th of July Movement against the regime of Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista between 1953 and 1959. Batista was finally ousted on 1 January 1959, and was replaced by a revolutionary government led by Castro...
in 1959, socialist state declared in 1961); Communist Party of Cuba
Communist Party of Cuba
The Communist Party of Cuba is the governing political party in Cuba. It is a communist party of the Marxist-Leninist model. The Cuban constitution ascribes the role of the Party to be the "leading force of society and of the state"...
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
(since 1975); Lao People's Revolutionary Party
Lao People's Revolutionary Party
The Lao People's Revolutionary Party is a communist political party that has governed Laos since 1975. The policy-making organs are the politburo and the central committee. A party congress, which elects members to the politburo and central committee, is held every five years...
. Laos removed all references to Marxism-Leninism, communism and socialism from its constitution in 1991.
However, in modern times it is questionable how communist these countries really are. While these countries share a similar system of government and ideological roots, they make use of diverse approaches to economic organization and activity. In addition, the various communist states now use different terms to identify themselves and their social systems. The only communist state which still traditionally follows Marxist-Leninist doctrine and maintains a largely planned economy
Planned economy
A planned economy is an economic system in which decisions regarding production and investment are embodied in a plan formulated by a central authority, usually by a government agency...
is Cuba, which describes itself as "a socialist state guided by ideas of Marx, Engels and Lenin and in transition to a communist society". Cuba has adopted some market reforms, but very little in comparison to China, Vietnam, and Laos and is still very heavily a planned economy. North Korea has even more of a planned economy than Cuba, but officially follows Juche instead of Marxist-Leninism.
Democratic states with communist governments
There are multi-party states that currently have communist parties in government. Such states are not considered to be communist states as the countries themselves allow for multiple parties, and do not provide a constitutional role for their communist parties.(since February 2008); Progressive Party of Working People
Progressive Party of Working People
The Progressive Party of Working People is a communist party in Cyprus. It supports an independent, demilitarized and non-aligned Cyprus, and a federal solution of the internal aspect of the Cyprus problem. It places particular emphasis on rapprochement with the Turkish Cypriots. It supported...
(since April 2008); Unified Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist) Moldova
Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
where the Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova was the democratically elected govering party 1998 to 2009. After the July 2009 parliamentary election
Moldovan parliamentary election, July 2009
- Pre-election developments :The country's parliament, elected months earlier, was dissolved by president Vladimir Voronin on 15 June 2009, after it had twice failed to elect a new president....
, the Alliance For European Integration
Alliance for European Integration
The Alliance for European Integration is the ruling coalition in Moldova since the July 2009 election.-Overall context :After April 2009 election and the civil unrest, the climate in Moldova became very polarised. The parliament failed to elect a new president. For this reason, the parliament was...
agreed to create a governing coalition. The Communist party, with three times the support of the next largest party operates currently as a loyal opposition party. Moldova is perhaps the best example of a state
State (polity)
A state is an organized political community, living under a government. States may be sovereign and may enjoy a monopoly on the legal initiation of force and are not dependent on, or subject to any other power or state. Many states are federated states which participate in a federal union...
where there is a large communist party that observes and operates within a democratic state.
Communist parties as part of other ruling coalition
In CyprusCyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
, the ruling Communist party did not come to power by formenting a successful revolution, but rather by being elected to power and thus operate according to the norms of a multi-party system
Multi-party system
A multi-party system is a system in which multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government separately or in coalition, e.g.The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition in the United Kingdom formed in 2010. The effective number of parties in a multi-party system is normally...
.
In Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
, the ruling Communist parties participate in a multi-party coalition government, an alliance of 22 parties that holds 350 seats in the 601-member constituent assembly.
There are also some parties that participate as junior partners in ruling coalitions, as listed below.
Communist Party of Brazil
Communist Party of Brazil
The Communist Party of Brazil is a political party in Brazil. It has national reach and deep penetration in the trade union and students movements. PCdoB dispute with the Brazilian Communist Party the title of "oldest political party in Brazil"...
participates in the ruling coalition
For Brazil to keep on changing
For Brazil to keep on changing is the name of an electoral coalition formed around the democratic socialist Workers' Party in Brazil for the 2010 presidential election. It comprised ten parties from the left and center spectrums: PT, PMDB, PCdoB, PDT, PRB, PR, PSB, PSC, PTC and PTN. On October...
Peruvian Communist Party
Peruvian Communist Party
The Peruvian Communist Party is a communist party in Peru. It was founded in 1928 by José Carlos Mariátegui, under the name Partido Socialista del Perú . In 1930 the name was changed to PCP...
participates in the ruling coalition
Peru Wins
Peru Wins is a left-wing political party in Peru formed as an alliance for the general election, 2011, dominated by the Peruvian Nationalist Party and led by presidential candidate Ollanta Humala.- Constituent Parties :...
South African Communist Party
South African Communist Party
South African Communist Party is a political party in South Africa. It was founded in 1921 as the Communist Party of South Africa by the joining together of the International Socialist League and others under the leadership of Willam H...
participates in the ruling coalition Communist Party of Sri Lanka
Communist Party of Sri Lanka
The Communist Party of Sri Lanka is a communist political party in Sri Lanka. At the last legislative elections, on 2 April 2004, the party was part of the United People's Freedom Alliance that won 45.6% of the popular vote and 105 out of 225 seats....
participates in the ruling coalition
United People's Freedom Alliance
The United People's Freedom Alliance is a political alliance in Sri Lanka. The current leader of the United People's Freedom Alliance is Mahinda Rajapaksa and Susil Premajayantha is the general secretary of UPFA.The alliance was formed by:...
Syrian Communist Party (Bakdash)
Syrian Communist Party (Bakdash)
The Syrian Communist Party is a political party in Syria. The party emerged out of a split in the Syrian Communist Party in 1986, as formed by the anti-Perestroika faction led by Khalid Bakdash...
, Syrian Communist Party (Faisal) participates in the ruling coalition
National Progressive Front
The National Progressive Front , established in 1972, is a coalition of political parties in Syria that support the socialist and Arab nationalist orientation of the government and accept the "leading role in society" of the Arab Socialist Ba’ath Party, .The Front was established by Syrian...
Communist Party of Ukraine
Communist Party of Ukraine
The Communist Party of Ukraine is a political party in Ukraine, currently led by Petro Symonenko.The party fights the Ukrainian national self-determination by identifying any Ukrainian national parties as the National-Fascist ones The Communist Party of Ukraine is a political party in Ukraine,...
participates in the ruling coalition
Azarov Government
The first Azarov Government was appointed on March 11, 2010 as part of the "Stability and Reform" coalition between the Party of Regions, Lytvyn Bloc and the Communist Party of Ukraine in the Verkhovna Rada, Ukraine's parliament...
Communist Party of Uruguay
Communist Party of Uruguay
The Communist Party of Uruguay is a communist political party in Uruguay, created on September 21, 1920. It is a member organisation of the ruling Broad Front.The current PCU secretary-general is ....
participates in the ruling coalition
Broad Front (Uruguay)
The Broad Front is a Uruguayan left-wing coalition of political parties. It is led by Jorge Brovetto. Frente Amplio has close ties with PIT-CNT trade union and the cooperative housing movement.-History:...
See also
- List of socialist countries, which includes a list of current and former communist states.
- List of communist parties
- Soviet EmpireSoviet EmpireDuring the Cold War, the informal term "Soviet Empire" referred to the Soviet Union's influence over a number of smaller nations who were nominally independent but subject to direct military force if they tried to leave the Soviet system; see Hungarian Revolution of 1956 and Prague Spring.Though...
- Criticisms of communist party ruleCriticisms of Communist party ruleCriticisms of communist party rule have been known since the first days of the first communist government in Soviet Russia, established after the October Revolution of 1917.-Background:...

