
Soviet Empire
Encyclopedia
During the Cold War
, the informal term "Soviet Empire" referred to the Soviet Union
's influence over a number of smaller nations who were nominally independent but subject to direct military force if they tried to leave the Soviet system; see Hungarian Revolution of 1956 and Prague Spring
.
Though the Soviet Union was not ruled by an emperor
and declared itself anti-imperialist
, critics argue that it exhibited tendencies common to historic empires. Some scholars hold that the Soviet Union was a hybrid entity containing elements common to both multinational empires and nation states. It has also been argued that the USSR practiced colonialism
as did other imperial powers.
Over time the number of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union
varied. After 1956 the Soviet Union included the following 15 republics.
(which in turn included several autonomous republics)
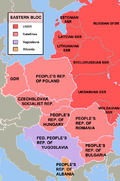 These countries were the closest allies of the Soviet Union. They were members of the Comecon
These countries were the closest allies of the Soviet Union. They were members of the Comecon
, a Soviet-led economic community founded in 1949. In addition, the ones located in Eastern Europe were also members of the Warsaw Pact
. They were sometimes called the Eastern bloc
in English and were widely viewed as Soviet satellite state
s.
Bulgaria Czechoslovakia
Hungary
Mongolia Poland
Romania
North Vietnam
/Vietnam
(after 1975) Albania (ended participation in Comecon after 1961 due to Sino-Soviet Split)
 North Korea was a Soviet ally, but always followed a highly isolationist
North Korea was a Soviet ally, but always followed a highly isolationist
foreign policy and therefore it did not join the Comecon
or any other international organization of Communist states.
had pro-Soviet governments during the Cold War. In the political terminology of the Soviet Union, these were "countries moving along the socialist road of development", as opposed to the more advanced "countries of developed socialism", which were mostly located in Easten Europe, but also included Vietnam and Cuba. Most received some aid, either military or economic, from the Soviet Union, and were influenced by it to varying degrees. Sometimes, their support for the Soviet Union eventually stopped, for various reasons; in some cases the pro-Soviet government lost power, in other cases the pro-Soviet forces were overthrown by military coups promoted by the United States
(such as in Chile
), in some cases the pro-Soviet forces gained power by military
aid from the Soviet Union (such as in Vietnam
), while in other cases the same government remained in power but changed its relations with the Soviet Union.
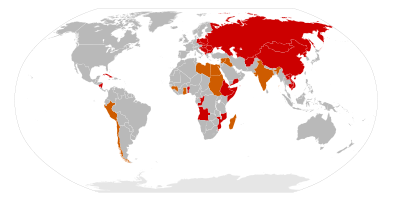 Some of these countries were not Communist states. They are marked in italic.
Some of these countries were not Communist states. They are marked in italic.
(Informbiro 1948) Albania (following the Sino-Soviet split) (following the Sino-Soviet split) Somali Democratic Republic
(1977–1991, due to the Ogaden War
)
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
, the informal term "Soviet Empire" referred to the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
's influence over a number of smaller nations who were nominally independent but subject to direct military force if they tried to leave the Soviet system; see Hungarian Revolution of 1956 and Prague Spring
Prague Spring
The Prague Spring was a period of political liberalization in Czechoslovakia during the era of its domination by the Soviet Union after World War II...
.
Though the Soviet Union was not ruled by an emperor
Emperor
An emperor is a monarch, usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife or a woman who rules in her own right...
and declared itself anti-imperialist
Anti-imperialism
Anti-imperialism, strictly speaking, is a term that may be applied to a movement opposed to any form of colonialism or imperialism. Anti-imperialism includes opposition to wars of conquest, particularly of non-contiguous territory or people with a different language or culture; it also includes...
, critics argue that it exhibited tendencies common to historic empires. Some scholars hold that the Soviet Union was a hybrid entity containing elements common to both multinational empires and nation states. It has also been argued that the USSR practiced colonialism
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
as did other imperial powers.
 Member states of the Soviet Union
Member states of the Soviet Union
Over time the number of the constituent republics of the Soviet UnionRepublics of the Soviet Union
The Republics of the Soviet Union or the Union Republics of the Soviet Union were ethnically-based administrative units that were subordinated directly to the Government of the Soviet Union...
varied. After 1956 the Soviet Union included the following 15 republics.
(which in turn included several autonomous republics)
 Members of Comecon
Members of Comecon


Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance , 1949–1991, was an economic organisation under hegemony of Soviet Union comprising the countries of the Eastern Bloc along with a number of communist states elsewhere in the world...
, a Soviet-led economic community founded in 1949. In addition, the ones located in Eastern Europe were also members of the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
. They were sometimes called the Eastern bloc
Eastern bloc
The term Eastern Bloc or Communist Bloc refers to the former communist states of Eastern and Central Europe, generally the Soviet Union and the countries of the Warsaw Pact...
in English and were widely viewed as Soviet satellite state
Satellite state
A satellite state is a political term that refers to a country that is formally independent, but under heavy political and economic influence or control by another country...
s.
Bulgaria Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic
The Czechoslovak Socialist Republic was the official name of Czechoslovakia from 1960 until end of 1989 , a Soviet satellite state of the Eastern Bloc....
Hungary
People's Republic of Hungary
The People's Republic of Hungary or Hungarian People's Republic was the official state name of Hungary from 1949 to 1989 during its Communist period under the guidance of the Soviet Union. The state remained in existence until 1989 when opposition forces consolidated in forcing the regime to...
Mongolia Poland
People's Republic of Poland
The People's Republic of Poland was the official name of Poland from 1952 to 1990. Although the Soviet Union took control of the country immediately after the liberation from Nazi Germany in 1944, the name of the state was not changed until eight years later...
Romania
Communist Romania
Communist Romania was the period in Romanian history when that country was a Soviet-aligned communist state in the Eastern Bloc, with the dominant role of Romanian Communist Party enshrined in its successive constitutions...
North Vietnam
North Vietnam
The Democratic Republic of Vietnam , was a communist state that ruled the northern half of Vietnam from 1954 until 1976 following the Geneva Conference and laid claim to all of Vietnam from 1945 to 1954 during the First Indochina War, during which they controlled pockets of territory throughout...
/Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
(after 1975) Albania (ended participation in Comecon after 1961 due to Sino-Soviet Split)
 North Korea was a Soviet ally, but always followed a highly isolationist
North Korea was a Soviet ally, but always followed a highly isolationistIsolationism
Isolationism is the policy or doctrine of isolating one's country from the affairs of other nations by declining to enter into alliances, foreign economic commitments, international agreements, etc., seeking to devote the entire efforts of one's country to its own advancement and remain at peace by...
foreign policy and therefore it did not join the Comecon
Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance , 1949–1991, was an economic organisation under hegemony of Soviet Union comprising the countries of the Eastern Bloc along with a number of communist states elsewhere in the world...
or any other international organization of Communist states.
Soviet involvement in the Third World
A large number of countries in the Third WorldThird World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either capitalism and NATO , or communism and the Soviet Union...
had pro-Soviet governments during the Cold War. In the political terminology of the Soviet Union, these were "countries moving along the socialist road of development", as opposed to the more advanced "countries of developed socialism", which were mostly located in Easten Europe, but also included Vietnam and Cuba. Most received some aid, either military or economic, from the Soviet Union, and were influenced by it to varying degrees. Sometimes, their support for the Soviet Union eventually stopped, for various reasons; in some cases the pro-Soviet government lost power, in other cases the pro-Soviet forces were overthrown by military coups promoted by the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
(such as in Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
), in some cases the pro-Soviet forces gained power by military
Military
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
aid from the Soviet Union (such as in Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
), while in other cases the same government remained in power but changed its relations with the Soviet Union.

-
 Egypt (1954–1973)
Egypt (1954–1973) -
 Syria (1955–1991)
Syria (1955–1991) -
 Iraq (1958–1961)
Iraq (1958–1961) -
 Guinea (1960–1978) (1961–1977)
Guinea (1960–1978) (1961–1977) -
 Ghana (1964–1966)
Ghana (1964–1966) -
 Peru (1968–1975)
Peru (1968–1975) -
 Sudan (1968–1972)
Sudan (1968–1972) -
 Libya (1969–1991) People's Republic of the CongoPeople's Republic of the CongoThe People's Republic of the Congo was a self-declared Marxist-Leninist socialist state that was established in 1970 in the Republic of the Congo...
Libya (1969–1991) People's Republic of the CongoPeople's Republic of the CongoThe People's Republic of the Congo was a self-declared Marxist-Leninist socialist state that was established in 1970 in the Republic of the Congo...
(1969–1991) -
 Chile (1970–1973) People's Democratic Republic of YemenPeople's Democratic Republic of YemenThe People's Democratic Republic of Yemen — also referred to as South Yemen, Democratic Yemen or Yemen — was a socialist republic in the present-day southern and eastern Provinces of Yemen...
Chile (1970–1973) People's Democratic Republic of YemenPeople's Democratic Republic of YemenThe People's Democratic Republic of Yemen — also referred to as South Yemen, Democratic Yemen or Yemen — was a socialist republic in the present-day southern and eastern Provinces of Yemen...
(1969–1990) -
 Uganda (1966–1971)
Uganda (1966–1971) -
 Madagascar (1972-1991) People's Democratic Republic of EthiopiaPeople's Democratic Republic of EthiopiaThe People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia was the official name of Ethiopia from 1987 to 1991, as established by the Communist government of Mengistu Haile Mariam and the Workers' Party of Ethiopia...
Madagascar (1972-1991) People's Democratic Republic of EthiopiaPeople's Democratic Republic of EthiopiaThe People's Democratic Republic of Ethiopia was the official name of Ethiopia from 1987 to 1991, as established by the Communist government of Mengistu Haile Mariam and the Workers' Party of Ethiopia...
(1974–1991) (1975–1991) (1975–1979) People's Republic of MozambiquePeople's Republic of MozambiqueThe People's Republic of Mozambique , was a self-declared socialist state that lasted from June 25, 1975 through December 1, 1990, becoming the present day Republic of Mozambique.After gaining independence from Portugal in 1975, the People's Republic of Mozambique was established shortly...
(1975–1990) People's Republic of AngolaPeople's Republic of AngolaThe People's Republic of Angola was a self-declared socialist state that was established in 1975 after it was granted independence from Portugal, akin to the situation in Mozambique. The newly-founded nation enjoyed friendly relations with the Soviet Union, Cuba, and the People's Republic of...
(1977–1991) Democratic Republic of AfghanistanDemocratic Republic of AfghanistanThe Democratic Republic of Afghanistan was a government of Afghanistan between 1978 and 1992. It was both ideologically close to and economically dependent on the Soviet Union, and was a major belligerent of the Afghan Civil War.- Saur Revolution :...
(1978–1991) (1979-1983) -
 Nicaragua (1979–1990) People's Republic of Kampuchea (1979–1989)
Nicaragua (1979–1990) People's Republic of Kampuchea (1979–1989)
Communist states opposed to the Soviet Union
Some Communist states were openly opposed to the Soviet Union and many of its policies. Though their forms of government may have been similar, they were completely sovereign from the USSR and held only formal ties. Relations were often tense, sometimes even to the point of armed conflict.(Informbiro 1948) Albania (following the Sino-Soviet split) (following the Sino-Soviet split) Somali Democratic Republic
Somali Democratic Republic
The Somali Democratic Republic was the name that the communist regime of former President of Somalia Major General Mohamed Siad Barre gave to Somalia after seizing power during a bloodless coup d'état in 1969...
(1977–1991, due to the Ogaden War
Ogaden War
The Ogaden War was a conventional conflict between Somalia and Ethiopia in 1977 and 1978 over the Ogaden region of Ethiopia. In a notable illustration of the nature of Cold War alliances, the Soviet Union switched from supplying aid to Somalia to supporting Ethiopia, which had previously been...
)
See also
- Index of Soviet Union-related articles
- American imperialism
- CominformCominformFounded in 1947, Cominform is the common name for what was officially referred to as the Information Bureau of the Communist and Workers' Parties...
- ImperialismImperialismImperialism, as defined by Dictionary of Human Geography, is "the creation and/or maintenance of an unequal economic, cultural, and territorial relationships, usually between states and often in the form of an empire, based on domination and subordination." The imperialism of the last 500 years,...
- Evil EmpireEvil empireThe phrase evil empire was applied to the Soviet Union especially by U.S. President Ronald Reagan, who took an aggressive, hard-line stance that favored matching and exceeding the Soviet Union's strategic and global military capabilities, in calling for a rollback strategy that would, in his words,...
- Communist stateCommunist stateA communist state is a state with a form of government characterized by single-party rule or dominant-party rule of a communist party and a professed allegiance to a Leninist or Marxist-Leninist communist ideology as the guiding principle of the state...
- Sino-Soviet splitSino-Soviet splitIn political science, the term Sino–Soviet split denotes the worsening of political and ideologic relations between the People's Republic of China and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics during the Cold War...
- Soviet republicRepublics of the Soviet UnionThe Republics of the Soviet Union or the Union Republics of the Soviet Union were ethnically-based administrative units that were subordinated directly to the Government of the Soviet Union...

