
Continuous phase modulation
Encyclopedia
Continuous phase modulation (CPM) is a method for modulation
of data commonly used in wireless modem
s. In contrast to other coherent digital phase modulation
techniques where the carrier
phase
abruptly resets to zero at the start of every symbol (e.g. M-PSK
), with CPM the carrier phase is modulated in a
continuous manner. For instance, with QPSK the carrier instantaneously jumps from a sine to a cosine (i.e. a 90 degree phase shift) whenever one of the two message bit
s of the current symbol differs from the two message bits of the previous symbol.
This discontinuity requires a relatively large percentage of the power to occur outside of the intended
band (e.g., high fractional out-of-band
power), leading to poor spectral efficiency
.
Furthermore, CPM is typically implemented as a constant-envelope waveform
, i.e. the transmitted carrier power is constant.
Therefore, CPM is attractive because the phase continuity yields high spectral efficiency, and the constant-envelope
yields excellent power efficiency. The primary drawback is the high implementation complexity required for an optimal receiver.
from the starting value to the final value, over the symbol duration.
The modulation and demodulation
of CPM is complicated by the fact that the initial phase of each symbol is determined by the
cumulative total phase of all previous transmitted symbols, which is known as the phase memory.
Therefore, the optimal receiver cannot make decisions on
any isolated symbol without taking the entire sequence of transmitted symbols into account.
This requires a Maximum Likelihood
Sequence Estimator (MLSE), which is efficiently implemented using the
Viterbi algorithm
.
(MSK) is another name for CPM with an excess bandwidth of 1/2 and a linear phase trajectory.
Although this linear phase trajectory is continuous, it is not smooth since the derivative of the phase is
not continuous. The spectral efficiency of CPM can be further improved by using a smooth phase trajectory.
This is typically accomplished by filtering the phase trajectory prior to modulation, commonly using a Raised Cosine
or a Gaussian filter
. The raised cosine filter has zero crossings offset by exactly one symbol time, and so it can yield a full-response CPM
waveform that prevents Intersymbol Interference (ISI)
.
a certain number of adjacent symbols interfere with each symbol in a controlled manner.
A MLSE must be used to optimally demodulate any signal in the presence of ISI. Whenever
the amount of ISI is known, such as with any partial-response signaling scheme, MLSE can be used to determine the
exact symbol sequence (in the absence of noise). Since the optimal demodulation of full-response CPM already requires MLSE detection, using partial-response signaling requires little additional complexity, but can afford a comparatively smoother
phase trajectory, and thus, even greater spectral efficiency.
One extremely popular form of partial-response CPM is
GMSK, which is used by GSM in most of the world's 2nd generation cell phones. It is also used in 802.11 FHSS, Bluetooth
, and many other proprietary wireless modems.
(FSK), which is itself a special case of analog frequency modulation
. FSK is a method of modulating digital data onto a sinusoidal carrier wave
, encoding the information present in the data to variations in the carrier's instantaneous frequency between one of two frequencies (referred to as the space frequency and mark frequency). In general, a standard FSK signal does not have continuous
phase, as the modulated waveform switches instantaneously between two sinusoids with different frequencies.
As the name suggests, the phase of a CPFSK is in fact continuous; this attribute is desirable for signals that are to be transmitted over a bandlimited
channel, as discontinuities in a signal introduce wideband
frequency components. In addition, some classes of amplifiers exhibit nonlinear behavior when driven with nearly-discontinuous signals; this could have undesired effects on the shape of the transmitted signal.
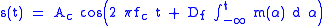
where Ac represents the amplitude of the CPFSK signal, fc is the base carrier frequency
, and Df is a parameter that controls the frequency deviation
of the modulated signal. The integral
located inside of the cosine's argument is what gives the CPFSK signal its continuous phase; an integral over any finitely-valued function (which m(t) is assumed to be) will not contain any discontinuities. If the message signal is assumed to be causal, then the limits on the integral change to a lower bound of zero and a higher bound of t.
Note that this does not mean that m(t) must be continuous; in fact, most ideal digital data waveforms contain discontinuities. However, even a discontinuous message signal will generate a proper CPFSK signal.
Frequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
of data commonly used in wireless modem
Wireless modem
A wireless modem is a type of modulator-demodulator which connects to a wireless network instead of using telephone or cable television lines...
s. In contrast to other coherent digital phase modulation
Phase modulation
Phase modulation is a form of modulation that represents information as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave.Unlike its more popular counterpart, frequency modulation , PM is not very widely used for radio transmissions...
techniques where the carrier
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
phase
abruptly resets to zero at the start of every symbol (e.g. M-PSK
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
), with CPM the carrier phase is modulated in a
continuous manner. For instance, with QPSK the carrier instantaneously jumps from a sine to a cosine (i.e. a 90 degree phase shift) whenever one of the two message bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s of the current symbol differs from the two message bits of the previous symbol.
This discontinuity requires a relatively large percentage of the power to occur outside of the intended
band (e.g., high fractional out-of-band
Out-of-band
The term out-of-band has different uses in communications and telecommunication. In case of out-of-band control signaling, signaling bits are sent in special order in a dedicated signaling frame...
power), leading to poor spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system...
.
Furthermore, CPM is typically implemented as a constant-envelope waveform
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
, i.e. the transmitted carrier power is constant.
Therefore, CPM is attractive because the phase continuity yields high spectral efficiency, and the constant-envelope
yields excellent power efficiency. The primary drawback is the high implementation complexity required for an optimal receiver.
Phase Memory
Each symbol is modulated by gradually changing the phase of the carrierfrom the starting value to the final value, over the symbol duration.
The modulation and demodulation
Demodulation
Demodulation is the act of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a modulated carrier wave.A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave.These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers,...
of CPM is complicated by the fact that the initial phase of each symbol is determined by the
cumulative total phase of all previous transmitted symbols, which is known as the phase memory.
Therefore, the optimal receiver cannot make decisions on
any isolated symbol without taking the entire sequence of transmitted symbols into account.
This requires a Maximum Likelihood
Maximum likelihood
In statistics, maximum-likelihood estimation is a method of estimating the parameters of a statistical model. When applied to a data set and given a statistical model, maximum-likelihood estimation provides estimates for the model's parameters....
Sequence Estimator (MLSE), which is efficiently implemented using the
Viterbi algorithm
Viterbi algorithm
The Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states – called the Viterbi path – that results in a sequence of observed events, especially in the context of Markov information sources, and more generally, hidden Markov models...
.
Phase Trajectory
Minimum-shift keyingMinimum-shift keying
In digital modulation, minimum-shift keying is a type of continuous-phase frequency-shift keying that was developed in the late 1950s and 1960s. Similar to OQPSK, MSK is encoded with bits alternating between quadrature components, with the Q component delayed by half the symbol period. However,...
(MSK) is another name for CPM with an excess bandwidth of 1/2 and a linear phase trajectory.
Although this linear phase trajectory is continuous, it is not smooth since the derivative of the phase is
not continuous. The spectral efficiency of CPM can be further improved by using a smooth phase trajectory.
This is typically accomplished by filtering the phase trajectory prior to modulation, commonly using a Raised Cosine
or a Gaussian filter
Gaussian filter
In electronics and signal processing, a Gaussian filter is a filter whose impulse response is a Gaussian function. Gaussian filters are designed to give no overshoot to a step function input while minimizing the rise and fall time. This behavior is closely connected to the fact that the Gaussian...
. The raised cosine filter has zero crossings offset by exactly one symbol time, and so it can yield a full-response CPM
waveform that prevents Intersymbol Interference (ISI)
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
.
Partial Response CPM
Partial-response signaling, such as duo-binary signaling, is a form of intentional ISI wherea certain number of adjacent symbols interfere with each symbol in a controlled manner.
A MLSE must be used to optimally demodulate any signal in the presence of ISI. Whenever
the amount of ISI is known, such as with any partial-response signaling scheme, MLSE can be used to determine the
exact symbol sequence (in the absence of noise). Since the optimal demodulation of full-response CPM already requires MLSE detection, using partial-response signaling requires little additional complexity, but can afford a comparatively smoother
phase trajectory, and thus, even greater spectral efficiency.
One extremely popular form of partial-response CPM is
GMSK, which is used by GSM in most of the world's 2nd generation cell phones. It is also used in 802.11 FHSS, Bluetooth
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
, and many other proprietary wireless modems.
Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying
Continuous-phase frequency-shift keying (CPFSK) is a commonly-used variation of frequency-shift keyingFrequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK . BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called...
(FSK), which is itself a special case of analog frequency modulation
Frequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
. FSK is a method of modulating digital data onto a sinusoidal carrier wave
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
, encoding the information present in the data to variations in the carrier's instantaneous frequency between one of two frequencies (referred to as the space frequency and mark frequency). In general, a standard FSK signal does not have continuous
Continuous function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function for which, intuitively, "small" changes in the input result in "small" changes in the output. Otherwise, a function is said to be "discontinuous". A continuous function with a continuous inverse function is called "bicontinuous".Continuity of...
phase, as the modulated waveform switches instantaneously between two sinusoids with different frequencies.
As the name suggests, the phase of a CPFSK is in fact continuous; this attribute is desirable for signals that are to be transmitted over a bandlimited
Bandlimited
Bandlimiting is the limiting of a deterministic or stochastic signal's Fourier transform or power spectral density to zero above a certain finite frequency...
channel, as discontinuities in a signal introduce wideband
Wideband
In communications, wideband is a relative term used to describe a wide range of frequencies in a spectrum. A system is typically described as wideband if the message bandwidth significantly exceeds the channel's coherence bandwidth....
frequency components. In addition, some classes of amplifiers exhibit nonlinear behavior when driven with nearly-discontinuous signals; this could have undesired effects on the shape of the transmitted signal.
Theory
If a finitely-valued digital signal to be transmitted (the message) is m(t), then the corresponding CPFSK signal is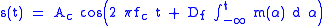
where Ac represents the amplitude of the CPFSK signal, fc is the base carrier frequency
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
, and Df is a parameter that controls the frequency deviation
Frequency deviation
Frequency deviation is used in FM radio to describe the maximum instantaneous difference between an FM modulated frequency and the nominal carrier frequency...
of the modulated signal. The integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
located inside of the cosine's argument is what gives the CPFSK signal its continuous phase; an integral over any finitely-valued function (which m(t) is assumed to be) will not contain any discontinuities. If the message signal is assumed to be causal, then the limits on the integral change to a lower bound of zero and a higher bound of t.
Note that this does not mean that m(t) must be continuous; in fact, most ideal digital data waveforms contain discontinuities. However, even a discontinuous message signal will generate a proper CPFSK signal.

