
Cousin prime
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, cousin primes are prime numbers that differ by four; compare this with twin prime
s, pairs of prime numbers that differ by two, and sexy prime
s, pairs of prime numbers that differ by six.
The cousin primes (sequences and in OEIS) below 1000 are:
, (7, 11), (13, 17), (19, 23), (37, 41), (43, 47), (67, 71), (79, 83), (97, 101), (103, 107), (109, 113), (127, 131), (163, 167), (193, 197), (223, 227), (229, 233), (277, 281), (307, 311), (313, 317), (349, 353), (379, 383), (397, 401), (439, 443), (457, 461), (463,467), (487, 491), (499, 503), (613, 617), (643, 647), (673, 677), (739, 743), (757, 761), (769, 773), (823, 827), (853, 857), (859, 863), (877, 881), (883, 887), (907, 911), (937, 941), (967, 971)
where 9001# is a primorial
. It was found by Ken Davis and has 11594 digits.
The largest known cousin probable prime
is
It has 29629 digits and was found by Angel, Jobling and Augustin. While the first of these numbers has been proven prime, there is no known primality test
to easily determine whether the second number is prime.
It follows from the first Hardy–Littlewood conjecture that cousin primes have the same asymptotic density as twin prime
s. An analogy of Brun's constant for twin primes can be defined for cousin primes, with the initial term (3, 7) omitted:
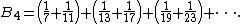
Using cousin primes up to 242, the value of B4 was estimated by Marek Wolf in 1996 as
This constant should not be confused with Brun's constant for prime quadruplets, which is also denoted B4.
of three terms with common difference 4, because 4 > 3 and the two numbers are relatively prime, one of the terms must be divisible by 3. Thus, the only cousin prime triplet is (3, 7, 11) with no longer sequence of cousin primes possible.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, cousin primes are prime numbers that differ by four; compare this with twin prime
Twin prime
A twin prime is a prime number that differs from another prime number by two. Except for the pair , this is the smallest possible difference between two primes. Some examples of twin prime pairs are , , , , and...
s, pairs of prime numbers that differ by two, and sexy prime
Sexy prime
In mathematics, a sexy prime is a prime number that differs from another prime number by six. For example, the numbers 5 and 11 are both sexy primes, because they differ by 6...
s, pairs of prime numbers that differ by six.
The cousin primes (sequences and in OEIS) below 1000 are:
, (7, 11), (13, 17), (19, 23), (37, 41), (43, 47), (67, 71), (79, 83), (97, 101), (103, 107), (109, 113), (127, 131), (163, 167), (193, 197), (223, 227), (229, 233), (277, 281), (307, 311), (313, 317), (349, 353), (379, 383), (397, 401), (439, 443), (457, 461), (463,467), (487, 491), (499, 503), (613, 617), (643, 647), (673, 677), (739, 743), (757, 761), (769, 773), (823, 827), (853, 857), (859, 863), (877, 881), (883, 887), (907, 911), (937, 941), (967, 971)
Properties
the largest known cousin prime was (p, p + 4) for- p = (311778476 · 587502 · 9001# · (587502 · 9001# + 1) + 210)·(587502 · 9001# − 1)/35 + 1
where 9001# is a primorial
Primorial
In mathematics, and more particularly in number theory, primorial is a function from natural numbers to natural numbers similar to the factorial function, but rather than multiplying successive positive integers, only successive prime numbers are multiplied...
. It was found by Ken Davis and has 11594 digits.
The largest known cousin probable prime
Probable prime
In number theory, a probable prime is an integer that satisfies a specific condition also satisfied by all prime numbers. Different types of probable primes have different specific conditions...
is
- 474435381 · 298394 − 1
- 474435381 · 298394 − 5.
It has 29629 digits and was found by Angel, Jobling and Augustin. While the first of these numbers has been proven prime, there is no known primality test
Primality test
A primality test is an algorithm for determining whether an input number is prime. Amongst other fields of mathematics, it is used for cryptography. Unlike integer factorization, primality tests do not generally give prime factors, only stating whether the input number is prime or not...
to easily determine whether the second number is prime.
It follows from the first Hardy–Littlewood conjecture that cousin primes have the same asymptotic density as twin prime
Twin prime
A twin prime is a prime number that differs from another prime number by two. Except for the pair , this is the smallest possible difference between two primes. Some examples of twin prime pairs are , , , , and...
s. An analogy of Brun's constant for twin primes can be defined for cousin primes, with the initial term (3, 7) omitted:
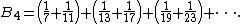
Using cousin primes up to 242, the value of B4 was estimated by Marek Wolf in 1996 as
- B4 ≈ 1.1970449.
This constant should not be confused with Brun's constant for prime quadruplets, which is also denoted B4.
Cousin prime triplets
In an arithmetic progressionArithmetic progression
In mathematics, an arithmetic progression or arithmetic sequence is a sequence of numbers such that the difference between the consecutive terms is constant...
of three terms with common difference 4, because 4 > 3 and the two numbers are relatively prime, one of the terms must be divisible by 3. Thus, the only cousin prime triplet is (3, 7, 11) with no longer sequence of cousin primes possible.

