
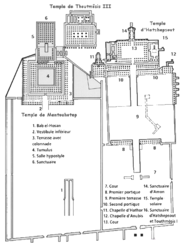
Deir el-Bahri
Encyclopedia

Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
") is a complex of mortuary temple
Mortuary temple
Mortuary temples were temples constructed adjacent to, or in the vicinity of, royal tombs in the Ancient Egypt. The temples were designed to commemorate the reign of the pharaoh by whom they were built, as well as for use by the pharaoh's cult after death.-History:Mortuary temples were built...
s and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor
Luxor
Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt and the capital of Luxor Governorate. The population numbers 487,896 , with an area of approximately . As the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of Thebes, Luxor has frequently been characterized as the "world's greatest open air museum", as the ruins of the temple...
, Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
.
The first monument built at the site was the mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II
Mentuhotep II
Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II was a Pharaoh of the 11th dynasty, the son of Intef III of Egypt and a minor queen called Iah. His own wife was the 'king's mother' Tem. Other wives were Neferu and several secondary wives, one or more who it has been suggested were possibly Nubian, buried in his...
of the Eleventh dynasty
Eleventh dynasty of Egypt
The eleventh dynasty of ancient Egypt was one group of rulers, whose earlier members are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, while the later members are considered part of the Middle Kingdom...
.
During the Eighteenth dynasty
Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt
The eighteenth dynasty of ancient Egypt is perhaps the best known of all the dynasties of ancient Egypt...
, Amenhotep I
Amenhotep I
Amenhotep I was the second Pharaoh of the 18th dynasty of Egypt. His reign is generally dated from 1526 to 1506 BC. He was born to Ahmose I and Ahmose-Nefertari, but had at least two elder brothers, Ahmose-ankh and Ahmose Sapair, and was not expected to inherit the throne...
and Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut also Hatchepsut; meaning Foremost of Noble Ladies;1508–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the eighteenth dynasty of Ancient Egypt...
also built extensively at the site.
Mortuary temple of Nebhepetre Mentuhotep
Mentuhotep II
Nebhepetre Mentuhotep II was a Pharaoh of the 11th dynasty, the son of Intef III of Egypt and a minor queen called Iah. His own wife was the 'king's mother' Tem. Other wives were Neferu and several secondary wives, one or more who it has been suggested were possibly Nubian, buried in his...
, Eleventh Dynasty
Eleventh dynasty of Egypt
The eleventh dynasty of ancient Egypt was one group of rulers, whose earlier members are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, while the later members are considered part of the Middle Kingdom...
king who reunited Egypt at the beginning of the Middle Kingdom
Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the establishment of the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Fourteenth Dynasty, between 2055 BC and 1650 BC, although some writers include the Thirteenth and Fourteenth dynasties in the Second Intermediate...
, built a very unusual funerary complex. His mortuary temple was built on several levels in the great bay at Deir el-Bahari. It was approached by a 16-metre-wide (150-ft) causeway leading from a valley temple which no longer exists.
The mortuary temple itself consists of a forecourt, enclosed by walls on three sides, and a terrace on which stands a large square structure that may represent the primeval mound that arose from the waters of chaos. As the temple faces east, the structure is likely to be connected with the sun cult of Rê
Re
Re, bre, moré is an interjection common to Cypriot Greek, the languages of the Balkans, Turkish, and Venetian, with its "locus... more in the Greek world than elsewhere". It is used in colloquial speech to gain someone's attention, add emphasis, insult, or express surprise or astonishment, like...
and the resurrection of the king.

Statues of the Twelfth Dynasty king Senusret III
Senusret III
Khakhaure Senusret III was a pharaoh of Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC, and was the fifth monarch of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. Among his achievements was the building of the Sisostris Canal...
were found here too.
The inner part of the temple was actually cut into the cliff and consists of a peristyle court, a hypostyle hall and an underground passage leading into the tomb itself. The cult of the dead king centred on the small shrine cut into the rear of the Hypostyle Hall.
The mastaba
Mastaba
A mastaba, or "pr-djt" , is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with outward sloping sides that marked the burial site of many eminent Egyptians of Egypt's ancient period...
-like structure on the terrace is surrounded by a pillared ambulatory along the west wall, where the statue shrines and tombs of several royal wives and daughters were found. These royal princesses were the priestesses of Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
, one of the main ancient Egyptian funerary deities. Although little remained of the king's own burial, six sarcophagi were retrieved from the tombs of the royal ladies (Ashayet, Henhenet, Kawit, Kemsit, Muyet and Sadhe). Each was formed of six slabs, held together at the corners by metal braces and carved in sunken relief. The sarcophagus of Queen Kawit, now in the Cairo Museum, is particularly fine.
The burial shaft and subsequent tunnel descend for 150 meters and end in a burial chamber 45 meters below the court. The chamber held a shrine, which once held the wooden coffin of Nebhepetre Mentuhotep. A great tree-lined court was reached by means of the processional causeway, leading up from the valley temple. Beneath the court, a deep shaft was cut which led to unfinished rooms believed to have been intended originally as the king’s tomb. A wrapped image of the pharaoh was discovered in this area by Howard Carter
Howard Carter
Howard Carter may refer to:* Howard Carter , English archaeologist who discovered Tutankhamun's tomb* Howard Carter , American basketball player...
. The temple complex also held six mortuary chapels and shaft tombs built for the pharaoh's wives and daughters.
Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut

Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut also Hatchepsut; meaning Foremost of Noble Ladies;1508–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the eighteenth dynasty of Ancient Egypt...
. It is a colonnaded structure, which was designed and implemented by Senemut
Senemut
Senenmut was an 18th dynasty ancient Egyptian architect and government official. His name translates literally as "mother's brother."- Family :...
, royal steward and architect of Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut also Hatchepsut; meaning Foremost of Noble Ladies;1508–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the eighteenth dynasty of Ancient Egypt...
(and believed by some to be her lover), to serve for her posthumous worship and to honor the glory of Amun
Amun
Amun, reconstructed Egyptian Yamānu , was a god in Egyptian mythology who in the form of Amun-Ra became the focus of the most complex system of theology in Ancient Egypt...
.
Djeser-Djeseru sits atop a series of colonnaded terraces, reached by long ramps that once were graced with gardens. It is built into a cliff face that rises sharply above it, and is largely considered to be one of the "incomparable monuments of ancient Egypt". It is 97 feet (30 m) tall.
The unusual form of Hatshepsut's temple is explained by the choice of location, in the valley basin of Deir el-Bahari, surrounded by steep cliffs. It was here, in about 2050 BC, that Mentuhotep II, the founder of the Middle Kingdom, laid out his sloping, terrace-shaped mortuary temple. The pillared galleries at either side of the central ramp of the Djeser Djeseru correspond to the pillar positions on two successive levels of the Temple of Mentuhotep.
Today the terraces of Deir el-Bahari only convey a faint impression of the original intentions of Senenmut. Most of the statue ornaments are missing - the statues of Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
in front of the pillars of the upper colonnade, the sphinx
Sphinx
A sphinx is a mythical creature with a lion's body and a human head or a cat head.The sphinx, in Greek tradition, has the haunches of a lion, the wings of a great bird, and the face of a woman. She is mythicised as treacherous and merciless...
avenues in front of the court, and the standing, sitting, and kneeling figures of Hatshepsut; these were destroyed in a posthumous condemnation of this pharaoh. The architecture of the temple has been considerably altered as a result of misguided reconstruction in the early twentieth century A.D.
Architecture

There are three layered terraces reaching 97 feet (30 m) in height. Each ‘story’ is articulated by a double colonnade of square piers, with the exception of the northwest corner of the central terrace, which employs Proto-Doric columns to house the chapel.
These terraces are connected by long ramps which were once surrounded by gardens. The layering of Hatshepsut’s temple corresponds with the classical Theban form, employing pylon
Pylon (architecture)
Pylon is the Greek term for a monumental gateway of an Egyptian temple It consists of two tapering towers, each surmounted by a cornice, joined by a less elevated section which enclosed the entrance between them. The entrance was generally about half the height of the towers...
, courts, hypostyle hall, sun court, chapel
Chapel
A chapel is a building used by Christians as a place of fellowship and worship. It may be part of a larger structure or complex, such as a church, college, hospital, palace, prison or funeral home, located on board a military or commercial ship, or it may be an entirely free-standing building,...
, and sanctuary
Sanctuary
A sanctuary is any place of safety. They may be categorized into human and non-human .- Religious sanctuary :A religious sanctuary can be a sacred place , or a consecrated area of a church or temple around its tabernacle or altar.- Sanctuary as a sacred place :#Sanctuary as a sacred place:#:In...
.
The relief sculpture within Hatshepsut’s temple recites the tale of the divine birth of the pharaoh. The text and pictorial cycle also tell of an expedition to the Land of Punt
Land of Punt
The Land of Punt, also called Pwenet, or Pwene by the ancient Egyptians, was a trading partner known for producing and exporting gold, aromatic resins, African blackwood, ebony, ivory, slaves and wild animals...
, an exotic country on the Red Sea coast.
On either side of the entrance to the sanctuary (shown above) are painted pillars with images of Hathor
Hathor
Hathor , is an Ancient Egyptian goddess who personified the principles of love, beauty, music, motherhood and joy. She was one of the most important and popular deities throughout the history of Ancient Egypt...
as the capitals. Just under the roof is an image of Wadjet
Wadjet
In Egyptian mythology, Wadjet, or the Green One , was originally the ancient local goddess of the city of Dep , which became part of the city that the Egyptians named Per-Wadjet, House of...
, displayed as a bilateral solar symbol, flanked by two other long serpents.
The temple includes an image, shown to the right, of Hatshepsut depicted as male pharaoh giving offerings to Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
, and to their left, an animal skin wound around a tall staff that is a symbol of the god Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
.
While the statues and ornamentation have since been stolen or destroyed, the temple once was home to two statues of Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
, a long avenue lined by sphinx
Sphinx
A sphinx is a mythical creature with a lion's body and a human head or a cat head.The sphinx, in Greek tradition, has the haunches of a lion, the wings of a great bird, and the face of a woman. She is mythicised as treacherous and merciless...
es, as well as many sculptures of pharaoh Hatshepsut in different attitudes – standing, sitting, or kneeling.
Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III
Thutmose III built a temple complex here, dedicated to Amun. Discovered in 1961, it is believed to have been used during the Beautiful festival of the valleyBeautiful festival of the valley
The Beautiful Festival of the Valley was an Ancient Egyptian festival, celebrated annually in Thebes, during the Middle Kingdom period and later....
. Not much is known about the complex, as it was abandoned after sustaining severe damage during a landslide in the latter twentieth Dynasty
Twentieth dynasty of Egypt
The Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth Dynasties of ancient Egypt are often combined under the group title, New Kingdom. This dynasty is considered to be the last one of the New Kingdom of Egypt, and was followed by the Third Intermediate Period....
. After that time it was used a source of building materials and in Christian times became the site of a Coptic cemetery.
Royal and non-royal tombs

Valley of the Kings
The Valley of the Kings , less often called the Valley of the Gates of the Kings , is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th century BC, tombs were constructed for the Pharaohs and powerful nobles of the New Kingdom .The valley stands on the west bank of...
. The bodies had been placed there by Twenty-first Dynasty
Twenty-first dynasty of Egypt
The Twenty-First, Twenty-Second, Twenty-Third, Twenty-Fourth, and Twenty-Fifth Dynasties of ancient Egypt are often combined under the group title, Third Intermediate Period.-Rulers:...
priests, most likely to prevent further desecration and looting. The tomb was probably originally built for priests of the 21st Dynasty, most likely the family of Pinedjem II
Pinedjem II
Pinedjem II was a High Priest of Amun at Thebes in Ancient Egypt from 990 BC to 969 BC and was the de facto ruler of the south of the country. He was married to his sister Isetemkheb D and also to his niece Nesikhons, the daughter of his brother Smendes II...
.
In the cache were found the mummies of Ahmose I
Ahmose I
Ahmose I was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Eighteenth dynasty. He was a member of the Theban royal house, the son of pharaoh Tao II Seqenenre and brother of the last pharaoh of the Seventeenth dynasty, King Kamose...
, along with the Eighteenth and Nineteenth dynasty leaders Amenhotep I
Amenhotep I
Amenhotep I was the second Pharaoh of the 18th dynasty of Egypt. His reign is generally dated from 1526 to 1506 BC. He was born to Ahmose I and Ahmose-Nefertari, but had at least two elder brothers, Ahmose-ankh and Ahmose Sapair, and was not expected to inherit the throne...
, Thutmose I
Thutmose I
Thutmose I was the third Pharaoh of the 18th dynasty of Egypt. He was given the throne after the death of the previous king Amenhotep I. During his reign, he campaigned deep into the Levant and Nubia, pushing the borders of Egypt further than ever before...
, Thutmose II
Thutmose II
Thutmose II was the fourth Pharaoh of the Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt. He built some minor monuments and initiated at least two minor campaigns but did little else during his rule and was probably strongly influenced by his wife, Hatshepsut...
, Thutmose III
Thutmose III
Thutmose III was the sixth Pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. During the first twenty-two years of Thutmose's reign he was co-regent with his stepmother, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh...
, Ramesses I
Ramesses I
Menpehtyre Ramesses I was the founding Pharaoh of Ancient Egypt's 19th dynasty. The dates for his short reign are not completely known but the time-line of late 1292-1290 BC is frequently cited as well as 1295-1294 BC...
, Seti I
Seti I
Menmaatre Seti I was a Pharaoh of Ancient Egypt , the son of Ramesses I and Queen Sitre, and the father of Ramesses II...
, Ramesses II
Ramesses II
Ramesses II , referred to as Ramesses the Great, was the third Egyptian pharaoh of the Nineteenth dynasty. He is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the Egyptian Empire...
, and Ramesses IX
Ramesses IX
Ramesses IX was the eighth king of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt. He was the third longest serving king of this Dynasty after Ramesses III and Ramesses XI...
. In a separate room were found Twenty-first dynasty High Priests
High Priests of Amun at Thebes
While not regarded as a dynasty, the High Priests of Amun at Thebes were nevertheless of such power and influence that they were effectively the rulers of Upper Egypt from 1080 to c.943 BC, after this period their influence declined...
and pharaohs Pinedjem I
Pinedjem I
Pinedjem I was the High Priest of Amun at Thebes in Ancient Egypt from 1070 BC to 1032 BC and the de facto ruler of the south of the country from 1054 BC. He was the son of the High Priest Piankh. However, many Egyptologists today believe that the succession in the Amun priesthood actually ran from...
, Pinedjem II
Pinedjem II
Pinedjem II was a High Priest of Amun at Thebes in Ancient Egypt from 990 BC to 969 BC and was the de facto ruler of the south of the country. He was married to his sister Isetemkheb D and also to his niece Nesikhons, the daughter of his brother Smendes II...
, and Siamun
Siamun
Neterkheperre or Netjerkheperre-setepenamun Siamun was the sixth pharaoh of Egypt during the Twenty-first dynasty. He built extensively in Lower Egypt for a king of the Third Intermediate Period and is regarded as one of the most powerful rulers of this Dynasty after Psusennes I...
. Later on, a cache of 153 reburied mummies of the priests themselves also were found in a tomb at the site.
Private tombs dating from the Middle Kingdom
Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the establishment of the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Fourteenth Dynasty, between 2055 BC and 1650 BC, although some writers include the Thirteenth and Fourteenth dynasties in the Second Intermediate...
through the Ptolemaic period may be found here. There are two most notable private tombs at Deir el-Bahari. The first is that of Meketre
Meketre
The Ancient Egyptian noble Meketre was chancellor and chief steward during the reign of Mentuhotep II and Mentuhotep III, during the Middle Kingdom...
(TT280
TT280
Tomb TT280, located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, is the burial place of the Ancient Egyptian noble Meketre who was chancellor and chief steward during the reign of Mentuhotep II and Mentuhotep III, during the Middle Kingdom...
), which contains many painted wooden funerary models from the Middle Kingdom and the first recorded human-headed canopic jar
Canopic jar
Canopic jars were used by the Ancient Egyptians during the mummification process to store and preserve the viscera of their owner for the afterlife. They were commonly either carved from limestone or were made of pottery...
.
The second, the 'secret' tomb of Senenmut
Senenmut
Senenmut was an 18th dynasty ancient Egyptian architect and government official. His name translates literally as "mother's brother."- Family :...
—the architect and steward who oversaw the construction of the temple for Hatshepsut—was begun in the complex also. Senenmut's tomb was vandalized in antiquity, but some of the relief artwork still is intact. It was meant to be a very large tomb and its corridors are over one hundred yards long, however, it was never finished and Senenmut was not interred there. He has another tomb, not far from Deir el-Bahari, where his body may have been placed, but it, too, was vandalized and robbed.
The discovery of the mummies cache is depicted in the Egyptian movie "The Night of Counting the Years
The Night of Counting the Years
The Night of Counting the Years, a.k.a. The Mummy is a 1969 Egyptian film directed by Shadi Abdel Salam. It was Salam's first feature film. Egyptian critics consistently list it as one of the most important Egyptian films ever made...
" (1969).
Terrorism
In 1997, 58 tourists and four Egyptians were massacred there by Islamist terrorists from Al-Gama'a al-Islamiyya in what has been called the Luxor massacre, causing a reduction of tourism in the area.See also

- Mentuhotep IIMentuhotep IINebhepetre Mentuhotep II was a Pharaoh of the 11th dynasty, the son of Intef III of Egypt and a minor queen called Iah. His own wife was the 'king's mother' Tem. Other wives were Neferu and several secondary wives, one or more who it has been suggested were possibly Nubian, buried in his...
- Valley of the KingsValley of the KingsThe Valley of the Kings , less often called the Valley of the Gates of the Kings , is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th century BC, tombs were constructed for the Pharaohs and powerful nobles of the New Kingdom .The valley stands on the west bank of...
- Thebes, EgyptThebes, EgyptThebes is the Greek name for a city in Ancient Egypt located about 800 km south of the Mediterranean, on the east bank of the river Nile within the modern city of Luxor. The Theban Necropolis is situated nearby on the west bank of the Nile.-History:...
- Thutmose IIIThutmose IIIThutmose III was the sixth Pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. During the first twenty-two years of Thutmose's reign he was co-regent with his stepmother, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh...
- HatshepsutHatshepsutHatshepsut also Hatchepsut; meaning Foremost of Noble Ladies;1508–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the eighteenth dynasty of Ancient Egypt...
- Hatshepsut's temple
External links
- Egypt Index at Bluffton University
- The Cache at Deir el-Bahri Archaeology at About.com
- The Temple Djeser djeseru
- Deir el-Bahri by Marie Parsons

