Dewar-Chatt-Duncanson model
Encyclopedia
The Dewar–Chatt–Duncanson model is a model in organometallic chemistry
which explains the type of chemical bond
ing between an alkene
and a metal (pi-complex) in certain organometallic compounds. The model is named after Michael J. S. Dewar, Joseph Chatt
and L. A. Duncanson.
The pi-acid alkene
donates electron density
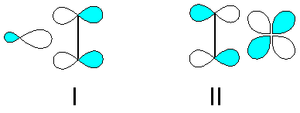
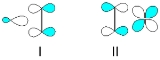
into a metal d-orbital from π-symmetry bonding orbital between the carbon atoms (I). The metal donates electrons back from (a different) filled d-orbital into the empty π* antibonding orbital (II). Both of these effects tend to reduce the carbon-carbon bond order, leading to an elongated C-C distance and a lowering its vibrational frequency.
In Zeise's salt
K[ Pt
Cl3(C2H4)].H2O the C-C bond length
has increased to 134 picometre
s from 133 pm for ethylene
. In the nickel
compound Ni(CH2CH2)(PPh3)2 the value is 143 pm.
The interaction also causes carbon atoms to "rehybridise" from sp2 towards sp3, which is indicated by the bending of the hydrogen atoms on the ethylene back away from the metal. In silico
calculations show that 75% of the binding energy is derived from the forward donation and 25% from backdonation. This model is a specific manifestation of the more general pi backbonding model.
Organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of chemical compounds containing bonds between carbon and a metal. Since many compounds without such bonds are chemically similar, an alternative may be compounds containing metal-element bonds of a largely covalent character...
which explains the type of chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
ing between an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
and a metal (pi-complex) in certain organometallic compounds. The model is named after Michael J. S. Dewar, Joseph Chatt
Joseph Chatt
Joseph Chatt, CBE FRS was a renowned researcher in the area of inorganic and organometallic chemistry. His name is associated with the description of the pi-bond between transition metals and alkenes, the so-called Dewar-Chatt-Duncanson model.Chatt received his Ph.D. at the University of...
and L. A. Duncanson.
The pi-acid alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
donates electron density
Electron density
Electron density is the measure of the probability of an electron being present at a specific location.In molecules, regions of electron density are usually found around the atom, and its bonds...
into a metal d-orbital from π-symmetry bonding orbital between the carbon atoms (I). The metal donates electrons back from (a different) filled d-orbital into the empty π* antibonding orbital (II). Both of these effects tend to reduce the carbon-carbon bond order, leading to an elongated C-C distance and a lowering its vibrational frequency.
In Zeise's salt
Zeise's salt
Zeise's salt, potassium trichloroplatinate, is the chemical compound with the formula KPtCl3]·H2O. The anion of this air-stable, yellow, coordination complex contains an η2-ethylene ligand. The anion features a platinum atom with a square planar geometry.-Preparation:This compound is commercially...
K
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
Cl3(C2H4)].H2O the C-C bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
has increased to 134 picometre
Picometre
A picometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one trillionth, i.e. of a metre, which is the current SI base unit of length...
s from 133 pm for ethylene
Ethylene
Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone...
. In the nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
compound Ni(CH2CH2)(PPh3)2 the value is 143 pm.
The interaction also causes carbon atoms to "rehybridise" from sp2 towards sp3, which is indicated by the bending of the hydrogen atoms on the ethylene back away from the metal. In silico
In silico
In silico is an expression used to mean "performed on computer or via computer simulation." The phrase was coined in 1989 as an analogy to the Latin phrases in vivo and in vitro which are commonly used in biology and refer to experiments done in living organisms and outside of living organisms,...
calculations show that 75% of the binding energy is derived from the forward donation and 25% from backdonation. This model is a specific manifestation of the more general pi backbonding model.