Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
Encyclopedia
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent
widely used in organic synthesis
. This carbonate ester
reacts with amine
s to give N-tert-butoxycarbonyl or so-called t-BOC derivatives. These derivatives do not behave as amines, which allows certain subsequent transformations to occur that would have otherwise affected the amine functional group
. The t-BOC can later be removed from the amine using acids. Thus, t-BOC serves as a protective group, for instance in solid phase peptide synthesis. It is unreactive to most bases and nucleophile
s, allowing for an orthogonal Fmoc protection.
, carbon dioxide
, phosgene
, using DABCO
as a base:
This route is currently employed commercially by manufacturers in China and India. European and Japanese companies use the reaction of sodium tert-butylate with carbon dioxide, catalysed by p-toluenesulfonic acid
or methanesulfonic acid
. This process involves a distillation of the crude material yielding a very pure grade.
Boc anhydride is also available as a 70% solution in toluene
or THF
. Since boc anhydride is a low-melting solid, having the reagent in a solution simplifies storage and handling.
. Protection of the amine can also be accomplished in acetonitrile
solution using 4-dimethylaminopyridine
(DMAP) as the base.
Removal of the t-BOC in amino acid
s can be accomplished with strong acids such as trifluoroacetic acid
neat or in dichloromethane
, or with HCl
in methanol
. A complication may be the tendency of the t-butyl cation intermediate to alkylate other nucleophiles; scavengers such as anisole
or thioanisole may be used.
(See Maillard reaction
). The first step in this reaction sequence is the formation of the carbamate
from the reaction of the secondary amine with boc anhydride in acetonitrile
with DMAP as a base
.
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
widely used in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
. This carbonate ester
Carbonate ester
A carbonate ester is a functional group in organic chemistry consisting of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is R1OOR2 and they are related to esters R1OR and ethers R1OR2 and also to the inorganic carbonates.Carbonate esters are used as...
reacts with amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s to give N-tert-butoxycarbonyl or so-called t-BOC derivatives. These derivatives do not behave as amines, which allows certain subsequent transformations to occur that would have otherwise affected the amine functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
. The t-BOC can later be removed from the amine using acids. Thus, t-BOC serves as a protective group, for instance in solid phase peptide synthesis. It is unreactive to most bases and nucleophile
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
s, allowing for an orthogonal Fmoc protection.
Preparation
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is inexpensive, so it is usually purchased. Classically, this compound is prepared from tert-butanolTert-Butanol
tert-Butanol, or 2-methyl-2-propanol, is the simplest tertiary alcohol. It is one of the four isomers of butanol. tert-Butanol is a clear liquid with a camphor-like odor. It is very soluble in water and miscible with ethanol and diethyl ether...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
, phosgene
Phosgene
Phosgene is the chemical compound with the formula COCl2. This colorless gas gained infamy as a chemical weapon during World War I. It is also a valued industrial reagent and building block in synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. In low concentrations, its odor resembles...
, using DABCO
DABCO
DABCO or 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane is a chemical compound. It is a polyurethane and Baylis-Hillman reaction catalyst, complexing ligand and Lewis base. It is used to regulate the reaction rate in Flexplay time-limited DVDs by adjusting pH. Antioxidants, like DABCO, are used to improve the...
as a base:
This route is currently employed commercially by manufacturers in China and India. European and Japanese companies use the reaction of sodium tert-butylate with carbon dioxide, catalysed by p-toluenesulfonic acid
P-Toluenesulfonic acid
p-Toluenesulfonic acid or tosylic acid is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO3H. It is a white solid that is soluble in water, alcohols, and other polar organic solvents. The 4-CH3C6H4SO2- group is known as the Tosyl group and is often abbreviated as Ts or Tos...
or methanesulfonic acid
Methanesulfonic acid
Methanesulfonic acid is a colorless liquid with the chemical formula CH3SO3H. It is the simplest of the alkylsulfonic acids. Salts and esters of methanesulfonic acid are known as mesylates. Methanesulfonic acid is used as an acid catalyst in organic reactions because it is non-volatile, strong acid...
. This process involves a distillation of the crude material yielding a very pure grade.
Boc anhydride is also available as a 70% solution in toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
or THF
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity at standard temperature and pressure. This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula 4O. As one of the most polar ethers with a wide liquid range, it is a useful solvent. Its main use, however, is as a precursor...
. Since boc anhydride is a low-melting solid, having the reagent in a solution simplifies storage and handling.
Protection and deprotection of amines
The Boc group can be added to the amine under aqueous conditions using di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in the presence of a base such as sodium bicarbonateSodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Na HCO3. Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda . The natural mineral form is...
. Protection of the amine can also be accomplished in acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
solution using 4-dimethylaminopyridine
4-Dimethylaminopyridine
4-Dimethylaminopyridine is a derivative of pyridine with the chemical formula 2NC5H4N. This colourless solid is a useful nucleophilic catalyst for a variety of reactions such as esterifications with anhydrides, the Baylis-Hillman reaction, hydrosilylations, tritylation, the Steglich...
(DMAP) as the base.
Removal of the t-BOC in amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s can be accomplished with strong acids such as trifluoroacetic acid
Trifluoroacetic acid
Trifluoroacetic acid is the simplest stable perfluorinated carboxylic acid chemical compound, with the formula CF3CO2H. It is a strong carboxylic acid due to the influence of the electronegative trifluoromethyl group. TFA is almost 100,000-fold more acidic than acetic acid...
neat or in dichloromethane
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula CH2Cl2. This colorless, volatile liquid with a moderately sweet aroma is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is miscible with many organic solvents...
, or with HCl
HCL
HCL or HCl can stand for:* Hairy cell leukemia, an uncommon and slowly progressing B cell leukemia* Hardware compatibility list...
in methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
. A complication may be the tendency of the t-butyl cation intermediate to alkylate other nucleophiles; scavengers such as anisole
Anisole
Anisole, or methoxybenzene, is the organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H5. It is a colorless liquid with a smell reminiscent of anise seed, and in fact many of its derivatives are found in natural and artificial fragrances...
or thioanisole may be used.
Other uses
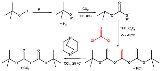
The synthesis of 6-acetyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine, an important bread aroma compound from 2-piperidone was accomplished using t-boc anhydride.(See Maillard reaction
Maillard reaction
The Maillard reaction is a form of nonenzymatic browning similar to caramelization. It results from a chemical reaction between an amino acid and a reducing sugar, usually requiring heat....
). The first step in this reaction sequence is the formation of the carbamate
Carbamate
Carbamates are organic compounds derived from carbamic acid . A carbamate group, carbamate ester, and carbamic acids are functional groups that are inter-related structurally and often are interconverted chemically. Carbamate esters are also called urethanes.-Synthesis:Carbamic acids are derived...
from the reaction of the secondary amine with boc anhydride in acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
with DMAP as a base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
.
External links
- Protection or deprotection conditions - Synthetic protocols from organic-reaction.com



