
Diamond color
Encyclopedia
A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond
is perfectly transparent with no hue
, or color. However, in reality almost no gem-sized natural diamonds are absolutely perfect. The color of a diamond may be affected by chemical impurities
and/or structural defects in the crystal lattice. Depending on the hue and intensity of a diamond's coloration, a diamond's color can either detract from or enhance its value. For example, most white diamonds are discounted in price when more yellow hue is detectable, while intense pink or blue diamonds (such as the Hope Diamond
) can be dramatically more valuable. Out of all colored diamonds, red
diamonds are the rarest. The Aurora Pyramid of Hope displays a spectacular array of naturally colored diamonds, including red diamonds.


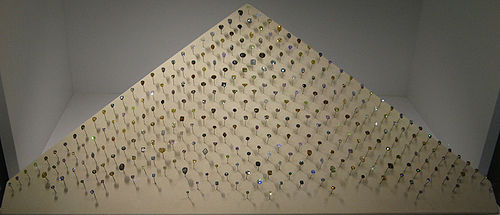 Diamonds occur in a variety of colors — steel gray, white, blue, yellow, orange, red, green, pink to purple, brown, and black, virtually in every color of the rainbow. Colored diamonds contain interstitial impurities or structural defects that cause the coloration, whilst pure diamonds are perfectly transparent and colorless. Diamonds are scientifically classed into two main types and several subtypes, according to the nature of impurities present and how these impurities affect light absorption:
Diamonds occur in a variety of colors — steel gray, white, blue, yellow, orange, red, green, pink to purple, brown, and black, virtually in every color of the rainbow. Colored diamonds contain interstitial impurities or structural defects that cause the coloration, whilst pure diamonds are perfectly transparent and colorless. Diamonds are scientifically classed into two main types and several subtypes, according to the nature of impurities present and how these impurities affect light absorption:
Type I diamonds have nitrogen
atom
s as the main impurity, commonly at a concentration of 0.1%. If the nitrogen atoms are in pairs they do not affect the diamond's color; these are Type IaA. If the nitrogen atoms are in large even-numbered aggregates they impart a yellow to brown tint (Type IaB). About 98% of gem diamonds are type Ia, and most of these are a mixture of IaA and IaB material: these diamonds belong to the Cape series, named after the diamond-rich region formerly known as Cape Province
in South Africa
, whose deposits are largely Type Ia. If the nitrogen atoms are dispersed throughout the crystal in isolated sites (not paired or grouped), they give the stone an intense yellow or occasionally brown
tint (Type Ib); the rare canary diamonds belong to this type, which represents only 0.1% of known natural diamonds. Synthetic diamond containing nitrogen is Type Ib. Type I diamonds absorb in both the infrared
and ultraviolet
region, from 320 nm (3.2E-07 m). They also have a characteristic fluorescence and visible absorption spectrum (see Optical properties of diamond).
Type II diamonds have no measurable nitrogen impurities. Type II diamonds absorb in a different region of the infrared, and transmit in the ultraviolet below 225 nm (2.25E-07 m), unlike Type I diamonds. They also have differing fluorescence characteristics, but no discernible visible absorption spectrum. Type IIa diamond can be colored pink, red, or brown due to structural anomalies arising through plastic deformation during crystal growth—these diamonds are rare (1.8% of gem diamonds), but constitute a large percentage of Australian production. Type IIb diamonds, which account for 0.1% of gem diamonds, are usually light blue due to scattered boron
within the crystal matrix; these diamonds are also semiconductor
s, unlike other diamond types (see Electrical properties of diamond). However, a blue-grey color may also occur in Type Ia diamonds and be unrelated to boron. Also not restricted to type are green diamonds, whose color is derived from exposure to varying quantities of radiation
.
As the diamond trade developed, early diamond grades were introduced by various parties in the diamond trade. Without any co-operative development these early grading systems lacked standard nomenclature, and consistency. Some early grading scales were; I, II, III; A, AA, AAA; A, B, C. Numerous terms developed to describe diamonds of particular colors: golconda, river, jagers, cape, blue white, fine white, and gem blue, "brown".
for example). The scale ranges from D which is totally colorless to Z which is a pale yellow or brown color. Brown diamonds darker than K color are usually described using their letter grade, and a descriptive phrase, for example M Faint Brown. Diamonds with more depth of color than Z color fall into the fancy color diamond range.
Diamond color is graded by comparing a sample stone to a masterstone set of diamonds. Each masterstone is known to exhibit the very least amount of body color that a diamond in that color grade may exhibit. A trained diamond grader compares a diamond of unknown grade against the series of masterstones, assessing where in the range of color the diamond resides. This process occurs in a lighting box, fitted with daylight equivalent lamps, that are UV filtered. Accurate color grading can only be performed with diamond unset, as the comparison with masterstones is done with diamond placed on its table facet and pavilion side facing upwards. When color grading is done in the mounting, the grade is expressed as an estimated color grade and commonly as a range of color. Grading mounted diamonds involves holding the mounted diamonds table close to the table facet of the masterstone and visually comparing the diamond color under the same color conditions as unmounted diamond grading. The resulting grade is typically less accurate, and is therefore espressed as a range of color. While a grading laboratory will possess a complete set of masterstones representing every color grade, the independent grader working in a retail environment works with a smaller subset of masterstones that covers only the typical grade range of color they expect to encounter while grading. A common subset of masterstones would consist of five diamonds in two grade increments, such as an E, G, I, K, and M. The intermediate grades are assessed by the graders judgement.
Diamonds in the normal color range are graded loose, (for example F-G)
Diamonds that rate toward the colorless end of the range are sometimes known as "high-color" diamonds, and those toward the other end, "low-color" diamonds. These terms refer to the relative desirability (as demonstrated by market prices) of color grades, not the intensity of the color itself.
, sapphire
, or emerald
, than they are to the system used for white diamonds.
Faint,
Very Light,
Light,
Fancy Light,
Fancy,
Fancy Dark,
Fancy Intense,
Fancy Deep,
Fancy Vivid.
The terms 'Champagne', 'Cognac' and 'Coffee' refer to different types of brown diamonds. In the diamond processing/dealing industry, the word 'Brown' is considered a killer as far as diamond value goes. Even though champagne is a light yellow color, champagne diamonds are Light Brown. Cognac is usually used to describe a diamond that is Orangish-Brown because cognac is a deep golden-orange color. Coffee is usually used to describe a diamond that is a Deep Brown or Vivid Brown color. Some grading agencies may also describe brown stones as Fancy Yellowish-Brown, Fancy Light Brown, Fancy Intense Brown, etc.
, AGS, and HRD. The accuracy is within ±1 color grade for mounted stones.
The Gran colorimeter was first developed by Paul Gran in 1972 at Gran Computer Industries Ltd.
Diamonds that go out of scale in the rating are known as "fancy color" diamonds. Any light shade of diamond other than light yellow or light brown automatically falls out of the scale. For instance, a pale blue diamond won't get a "G" or "K" color grade, it will get a Faint Blue or Light Blue grade. These diamonds are valued using different criteria than those used for regular diamonds. When the color is rare, the more intensely colored a diamond is, the more valuable it becomes. Another factor that affects the value of Fancy-Colored diamonds is fashion trends. For example, pink diamonds fetched higher prices after Jennifer Lopez
received a pink diamond engagement ring. Extremely low grade quality has not stopped creative merchants, such as Le Vian, from marketing Dark Brown diamonds as so-called "Chocolate Diamonds".
Fancy-colored diamonds such as the deep blue Hope Diamond
are among the most valuable and sought-after diamonds in the world. In 2009 a 7 carats (1.4 g) blue diamond fetched the highest price per carat ever paid for a diamond when it was sold at auction for 10.5 million Swiss francs (US$9.5 million at the time) which is in excess of US$1.3 million per carat.
Diamond (gemstone)
A diamond is one of the best-known and most sought-after gemstones...
is perfectly transparent with no hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
, or color. However, in reality almost no gem-sized natural diamonds are absolutely perfect. The color of a diamond may be affected by chemical impurities
Colors of chemicals
The color of chemicals is a physical property of chemicals that in most cases comes from the excitation of electrons due to an absorption of energy performed by the chemical...
and/or structural defects in the crystal lattice. Depending on the hue and intensity of a diamond's coloration, a diamond's color can either detract from or enhance its value. For example, most white diamonds are discounted in price when more yellow hue is detectable, while intense pink or blue diamonds (such as the Hope Diamond
Hope Diamond
The Hope Diamond, also known as "Le bleu de France" or "Le Bijou du Roi", is a large, , deep-blue diamond, now housed in the Smithsonian Natural History Museum in Washington, D.C. It is blue to the naked eye because of trace amounts of boron within its crystal structure, but exhibits red...
) can be dramatically more valuable. Out of all colored diamonds, red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
diamonds are the rarest. The Aurora Pyramid of Hope displays a spectacular array of naturally colored diamonds, including red diamonds.
Possible colors



Type I diamonds have nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s as the main impurity, commonly at a concentration of 0.1%. If the nitrogen atoms are in pairs they do not affect the diamond's color; these are Type IaA. If the nitrogen atoms are in large even-numbered aggregates they impart a yellow to brown tint (Type IaB). About 98% of gem diamonds are type Ia, and most of these are a mixture of IaA and IaB material: these diamonds belong to the Cape series, named after the diamond-rich region formerly known as Cape Province
Cape Province
The Province of the Cape of Good Hope was a province in the Union of South Africa and subsequently the Republic of South Africa...
in South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, whose deposits are largely Type Ia. If the nitrogen atoms are dispersed throughout the crystal in isolated sites (not paired or grouped), they give the stone an intense yellow or occasionally brown
Brown diamonds
Brown diamonds are the most common color variety of natural diamonds. The brown color makes them less attractive as gemstones and most are used for industrial purposes, however technical advances and improved marketing programs, especially in Australia, have resulted in brown diamonds becoming...
tint (Type Ib); the rare canary diamonds belong to this type, which represents only 0.1% of known natural diamonds. Synthetic diamond containing nitrogen is Type Ib. Type I diamonds absorb in both the infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
region, from 320 nm (3.2E-07 m). They also have a characteristic fluorescence and visible absorption spectrum (see Optical properties of diamond).
Type II diamonds have no measurable nitrogen impurities. Type II diamonds absorb in a different region of the infrared, and transmit in the ultraviolet below 225 nm (2.25E-07 m), unlike Type I diamonds. They also have differing fluorescence characteristics, but no discernible visible absorption spectrum. Type IIa diamond can be colored pink, red, or brown due to structural anomalies arising through plastic deformation during crystal growth—these diamonds are rare (1.8% of gem diamonds), but constitute a large percentage of Australian production. Type IIb diamonds, which account for 0.1% of gem diamonds, are usually light blue due to scattered boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
within the crystal matrix; these diamonds are also semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
s, unlike other diamond types (see Electrical properties of diamond). However, a blue-grey color may also occur in Type Ia diamonds and be unrelated to boron. Also not restricted to type are green diamonds, whose color is derived from exposure to varying quantities of radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
.
Grading white diamonds
The majority of diamonds that are mined are in a range of pale yellow or brown color that is termed the normal color range. Diamonds that are of intense yellow or brown, or any other color are called fancy color diamonds. Diamonds that are of the very highest purity are totally colorless, and appear a bright white. The degree to which diamonds exhibit body color is one of the four value factors by which diamonds are assessed.History of color grading
Color grading of diamonds was performed as a step of sorting rough diamonds for sale by the London Diamond Syndicate.As the diamond trade developed, early diamond grades were introduced by various parties in the diamond trade. Without any co-operative development these early grading systems lacked standard nomenclature, and consistency. Some early grading scales were; I, II, III; A, AA, AAA; A, B, C. Numerous terms developed to describe diamonds of particular colors: golconda, river, jagers, cape, blue white, fine white, and gem blue, "brown".
Grading the normal color range
Refers to a grading scale for diamonds in the normal color range used by internationally recognized laboratories (GIA & IGIIGI
IGI may refer to:* Le Igi is a traditional Samoan guitar tuning style* Indira Gandhi International Airport, Delhi* Interconnector Greece – Italy, a planned natural gas pipeline* International Genealogical Index* Indian Gemmological Institute...
for example). The scale ranges from D which is totally colorless to Z which is a pale yellow or brown color. Brown diamonds darker than K color are usually described using their letter grade, and a descriptive phrase, for example M Faint Brown. Diamonds with more depth of color than Z color fall into the fancy color diamond range.
Diamond color is graded by comparing a sample stone to a masterstone set of diamonds. Each masterstone is known to exhibit the very least amount of body color that a diamond in that color grade may exhibit. A trained diamond grader compares a diamond of unknown grade against the series of masterstones, assessing where in the range of color the diamond resides. This process occurs in a lighting box, fitted with daylight equivalent lamps, that are UV filtered. Accurate color grading can only be performed with diamond unset, as the comparison with masterstones is done with diamond placed on its table facet and pavilion side facing upwards. When color grading is done in the mounting, the grade is expressed as an estimated color grade and commonly as a range of color. Grading mounted diamonds involves holding the mounted diamonds table close to the table facet of the masterstone and visually comparing the diamond color under the same color conditions as unmounted diamond grading. The resulting grade is typically less accurate, and is therefore espressed as a range of color. While a grading laboratory will possess a complete set of masterstones representing every color grade, the independent grader working in a retail environment works with a smaller subset of masterstones that covers only the typical grade range of color they expect to encounter while grading. A common subset of masterstones would consist of five diamonds in two grade increments, such as an E, G, I, K, and M. The intermediate grades are assessed by the graders judgement.
Diamonds in the normal color range are graded loose, (for example F-G)
Diamonds that rate toward the colorless end of the range are sometimes known as "high-color" diamonds, and those toward the other end, "low-color" diamonds. These terms refer to the relative desirability (as demonstrated by market prices) of color grades, not the intensity of the color itself.
Grading fancy color diamonds
Yellow or brown color diamonds having color more intense than "Z", as well as diamonds exhibiting color other than yellow or brown are considered fancy colored diamonds. These diamonds are graded using separate systems which indicate the characteristics of the color, and not just its presence. These color grading systems are more similar to those used for other colored gemstones, such as rubyRuby
A ruby is a pink to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum . The red color is caused mainly by the presence of the element chromium. Its name comes from ruber, Latin for red. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires...
, sapphire
Sapphire
Sapphire is a gemstone variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide , when it is a color other than red or dark pink; in which case the gem would instead be called a ruby, considered to be a different gemstone. Trace amounts of other elements such as iron, titanium, or chromium can give...
, or emerald
Emerald
Emerald is a variety of the mineral beryl colored green by trace amounts of chromium and sometimes vanadium. Beryl has a hardness of 7.5–8 on the 10 point Mohs scale of mineral hardness...
, than they are to the system used for white diamonds.
Colored diamond grading system
Diamond colors more saturated than this scale are known as "fancy color" diamonds. Any light shade of diamond other than Light Yellow or Light Brown automatically falls out of the scale. For instance, a pale blue diamond won't get a "K", "N", or "S" color grade, it will get a Faint Blue, very Light Blue or Light Blue grade. Laboratories use a list of 27 color hues that span the full spectrum for colored gems and diamonds (Red, Orangish-Red, Reddish-Orange, orange, Yellowish-Orange, Yellow-Orange, Orange-Yellow, Orangish-Yellow, Yellow, Greenish-Yellow, Green-Yellow, Yellow-Green, Yellowish-Green, Green, Bluish-Green, Blue-Green, Green-Blue, Greenish-Blue, Blue, Violetish-Blue, Bluish-Violet, Violet, Purple, Reddish-Purple, Red-Purple, Purple-Red, Purplish-Red). A modifying color combination can also be added (e.g., Olive or Brown-Olive) for stones without the purest hues. Additionally, for diamonds the following colors are used: White (which are milky), Black (which are opaque), Gray, Pink, Brown. The saturation of these hues is then described with one of nine descriptors:Faint,
Very Light,
Light,
Fancy Light,
Fancy,
Fancy Dark,
Fancy Intense,
Fancy Deep,
Fancy Vivid.
The terms 'Champagne', 'Cognac' and 'Coffee' refer to different types of brown diamonds. In the diamond processing/dealing industry, the word 'Brown' is considered a killer as far as diamond value goes. Even though champagne is a light yellow color, champagne diamonds are Light Brown. Cognac is usually used to describe a diamond that is Orangish-Brown because cognac is a deep golden-orange color. Coffee is usually used to describe a diamond that is a Deep Brown or Vivid Brown color. Some grading agencies may also describe brown stones as Fancy Yellowish-Brown, Fancy Light Brown, Fancy Intense Brown, etc.
Gran colorimeter
Color can also be determined using a device called the Gran Colorimeter, manufactured by Sarin Technologies. It measures from D to Z to Fancy Intense with an accuracy within ±½ of a color grade on loose stones from 0.25 to 10 carats (50 to 2,000 mg) (as low as 0.15 carat (30 mg) or as high as 20 carats (4 g) with reduced accuracy). The colorimeter provides output in various grading scales including GIA, GEM, IGIIGI
IGI may refer to:* Le Igi is a traditional Samoan guitar tuning style* Indira Gandhi International Airport, Delhi* Interconnector Greece – Italy, a planned natural gas pipeline* International Genealogical Index* Indian Gemmological Institute...
, AGS, and HRD. The accuracy is within ±1 color grade for mounted stones.
The Gran colorimeter was first developed by Paul Gran in 1972 at Gran Computer Industries Ltd.
Value of colored diamonds
Diamonds that enter the Gemological Institute of America's scale are valued according to their clarity and color. For example, a "D" or "E" rated diamond (both grades are considered colorless) is much more valuable than an "R" or "Y" rated diamond (light yellow or brown). This is due to two effects: high-color diamonds are rarer, limiting supply; and the bright white appearance of high-color diamonds is more desired by consumers, increasing demand. Poor color is usually not enough to eliminate the use of diamond as a gemstone: If other gemological characteristics of a stone are good, a low-color diamond can remain more valuable as a gem diamond than an industrial-use diamond, and can see use in diamond jewelry.Diamonds that go out of scale in the rating are known as "fancy color" diamonds. Any light shade of diamond other than light yellow or light brown automatically falls out of the scale. For instance, a pale blue diamond won't get a "G" or "K" color grade, it will get a Faint Blue or Light Blue grade. These diamonds are valued using different criteria than those used for regular diamonds. When the color is rare, the more intensely colored a diamond is, the more valuable it becomes. Another factor that affects the value of Fancy-Colored diamonds is fashion trends. For example, pink diamonds fetched higher prices after Jennifer Lopez
Jennifer Lopez
Jennifer Lynn Lopez is an American actress, singer, record producer, dancer, television personality, and fashion designer. Lopez began her career as a dancer on the television comedy program In Living Color. Subsequently venturing into acting, she gained recognition in the 1995 action-thriller...
received a pink diamond engagement ring. Extremely low grade quality has not stopped creative merchants, such as Le Vian, from marketing Dark Brown diamonds as so-called "Chocolate Diamonds".
Fancy-colored diamonds such as the deep blue Hope Diamond
Hope Diamond
The Hope Diamond, also known as "Le bleu de France" or "Le Bijou du Roi", is a large, , deep-blue diamond, now housed in the Smithsonian Natural History Museum in Washington, D.C. It is blue to the naked eye because of trace amounts of boron within its crystal structure, but exhibits red...
are among the most valuable and sought-after diamonds in the world. In 2009 a 7 carats (1.4 g) blue diamond fetched the highest price per carat ever paid for a diamond when it was sold at auction for 10.5 million Swiss francs (US$9.5 million at the time) which is in excess of US$1.3 million per carat.

