Differential signaling
Encyclopedia
Differential signaling is a method of transmitting information
electrically by means of two complementary signals
sent on two separate wires. The technique can be used for both analog signaling, as in some audio
systems, and digital signaling, as in RS-422, RS-485, Ethernet
(twisted-pair only), PCI Express
and USB. The opposite technique, which is more common but lacks some of the benefits of differential signaling, is called single-ended signaling.
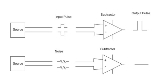
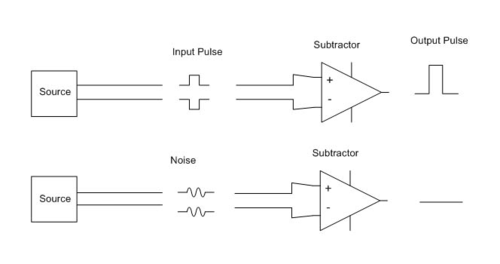 At the end of the connection, the receiving device reads the difference between the two signals. Since the receiver ignores the wires' voltages with respect to ground, small changes in ground potential between transmitter and receiver do not affect the receiver's ability to detect the signal.
At the end of the connection, the receiving device reads the difference between the two signals. Since the receiver ignores the wires' voltages with respect to ground, small changes in ground potential between transmitter and receiver do not affect the receiver's ability to detect the signal.
To see why, consider a single-ended digital system with supply voltage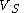 . The high logic level is
. The high logic level is 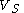 and the low logic level is 0 V. The difference between the two levels is therefore
and the low logic level is 0 V. The difference between the two levels is therefore 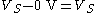 . Now consider a differential system with the same supply voltage. The voltage difference in the high state, where one wire is at
. Now consider a differential system with the same supply voltage. The voltage difference in the high state, where one wire is at  and the other at 0 V, is
and the other at 0 V, is 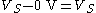 . The voltage difference in the low state, where the voltages on the wires are exchanged, is
. The voltage difference in the low state, where the voltages on the wires are exchanged, is 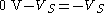 . The difference between high and low logic levels is therefore
. The difference between high and low logic levels is therefore 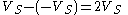 . This is twice the difference of the single-ended system. Supposing that the voltage noise on one wire is uncorrelated to the noise on the other one, the result is that it takes twice as much noise to cause an error with the differential system as with the single-ended system. In other words, the noise immunity is doubled.
. This is twice the difference of the single-ended system. Supposing that the voltage noise on one wire is uncorrelated to the noise on the other one, the result is that it takes twice as much noise to cause an error with the differential system as with the single-ended system. In other words, the noise immunity is doubled.
s. Single-ended signals are still resistant to interference if the lines are balanced and terminated by a differential amplifier. See Balanced line
for more details.
The widely used RS-232
system is an example of single-ended signaling, which uses ±12 V to represent a signal, and anything less than ±3 V to represent the lack of a signal. The high voltage levels give the signals some immunity from noise, since few naturally occurring signals can create that sort of voltage. They also have the advantage of requiring only one wire per signal. However, they also have a serious disadvantage: they cannot run at high speeds. The effects of capacitance
and inductance
, which filter out high-frequency signals, limit the speed. Large voltage swings driving long cables also require significant power from the transmitting end. This problem can be reduced by using smaller voltages, but then the chance of mistaking random environmental noise for a signal becomes much more of a problem. In many instances single-ended designs are not feasible. Another difficulty is the electromagnetic interference that can be generated by a single-ended signaling system which attempts to operate at high speed.
, PECL, LVPECL, current loop
interfaces such as Musical Instrument Digital Interface
(MIDI) hardware, RS-422, RS-485, most Ethernet physical layer
s, USB, Serial ATA
(SATA
), TMDS, FireWire, and HDMI
. LVDS is currently the only scheme that combines low power dissipation with high speed.
Examples of single-ended signaling include RS-232
and PATA.
The lowest-power-dissipation, highest-speed signals in any commercially available system are the on-chip signals in a microprocessor. Those signals are almost always single-ended.
In an electric guitar
, the humbucker
pickup type uses exactly the same principle to avoid power supply hum at the AC frequency.
s, in which one conductor totally screens the other from the environment. All screens (or shields) are combined into a single piece of material to form a common ground
. Differential signaling is used with a balanced pair of conductors. For short cables and low frequencies, the two methods are equivalent, so cheap single-ended circuits with a common ground can be used with cheap cables. As signaling speeds become faster, wires begin to behave as transmission line
s.
, because complete screening is not possible with microstrip
s and chips
in computers, due to geometric constraints and the fact that screening does not work at DC. If a DC power supply line and a low-voltage signal line share the same ground, the power current returning through the ground can induce a significant voltage in it. A low-resistance ground reduces this problem to some extent. A balanced pair of microstrip lines is a convenient solution, because it does not need an additional PCB layer, as a stripline
does. Because each line causes a matching image current in the ground plane, which is required anyway for supplying power, the pair looks like four lines and therefore has a shorter crosstalk distance than a simple isolated pair. In fact, it behaves as well as a twisted pair. Low crosstalk is important when many lines are packed into a small space, as on a typical PCB.
signals. In computer
electronics, "high voltage" normally means 5 volts or more.
SCSI-1 variations included a high voltage differential (HVD) implementation whose maximum cable length was many times that of the single-ended version. SCSI
equipment for example allows a maximum total cable length of 25 meters using HVD, while single-ended SCSI allows a maximum cable length of 1.5 to 6 meters, depending on bus speed. LVD versions of SCSI allow less than 25 m cable length not because of the lower voltage, but because these SCSI standards allow much higher speeds than the older HVD SCSI.
The term high-voltage differential signaling is a generic one that describes a variety of systems. Low-voltage differential signaling or LVDS, on the other hand, is a specific system defined by a TIA/EIA standard.
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
electrically by means of two complementary signals
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
sent on two separate wires. The technique can be used for both analog signaling, as in some audio
Sound recording and reproduction
Sound recording and reproduction is an electrical or mechanical inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording...
systems, and digital signaling, as in RS-422, RS-485, Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
(twisted-pair only), PCI Express
PCI Express
PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
and USB. The opposite technique, which is more common but lacks some of the benefits of differential signaling, is called single-ended signaling.
Tolerance of ground offsets

Suitability for use with low-voltage electronics
In the electronics industry, and particularly in portable and mobile devices, there is a continuing tendency to lower the supply voltage in order to save power and reduce unwanted emitted radiation. A low supply voltage, however, causes problems with signaling because it reduces the noise immunity. Differential signaling helps to reduce these problems because, for a given supply voltage, it gives twice the noise immunity of a single-ended system.To see why, consider a single-ended digital system with supply voltage
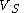 . The high logic level is
. The high logic level is 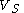 and the low logic level is 0 V. The difference between the two levels is therefore
and the low logic level is 0 V. The difference between the two levels is therefore 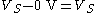 . Now consider a differential system with the same supply voltage. The voltage difference in the high state, where one wire is at
. Now consider a differential system with the same supply voltage. The voltage difference in the high state, where one wire is at  and the other at 0 V, is
and the other at 0 V, is 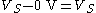 . The voltage difference in the low state, where the voltages on the wires are exchanged, is
. The voltage difference in the low state, where the voltages on the wires are exchanged, is 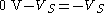 . The difference between high and low logic levels is therefore
. The difference between high and low logic levels is therefore 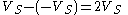 . This is twice the difference of the single-ended system. Supposing that the voltage noise on one wire is uncorrelated to the noise on the other one, the result is that it takes twice as much noise to cause an error with the differential system as with the single-ended system. In other words, the noise immunity is doubled.
. This is twice the difference of the single-ended system. Supposing that the voltage noise on one wire is uncorrelated to the noise on the other one, the result is that it takes twice as much noise to cause an error with the differential system as with the single-ended system. In other words, the noise immunity is doubled.Resistance to electromagnetic interference
This advantage is not actually due to differential signaling itself, but to the common practice of transmitting differential signals on balanced lineBalanced line
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a transmission line consisting of two conductors of the same type, each of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the...
s. Single-ended signals are still resistant to interference if the lines are balanced and terminated by a differential amplifier. See Balanced line
Balanced line
In telecommunications and professional audio, a balanced line or balanced signal pair is a transmission line consisting of two conductors of the same type, each of which have equal impedances along their lengths and equal impedances to ground and to other circuits. The chief advantage of the...
for more details.
Comparison with single-ended signaling
In single-ended signaling, the transmitter generates a single voltage that the receiver compares with a fixed reference voltage, both relative to a common ground connection shared by both ends.The widely used RS-232
RS-232
In telecommunications, RS-232 is the traditional name for a series of standards for serial binary single-ended data and control signals connecting between a DTE and a DCE . It is commonly used in computer serial ports...
system is an example of single-ended signaling, which uses ±12 V to represent a signal, and anything less than ±3 V to represent the lack of a signal. The high voltage levels give the signals some immunity from noise, since few naturally occurring signals can create that sort of voltage. They also have the advantage of requiring only one wire per signal. However, they also have a serious disadvantage: they cannot run at high speeds. The effects of capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
and inductance
Inductance
In electromagnetism and electronics, inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field. Inductors generate an opposing voltage proportional to the rate of change in current in a circuit...
, which filter out high-frequency signals, limit the speed. Large voltage swings driving long cables also require significant power from the transmitting end. This problem can be reduced by using smaller voltages, but then the chance of mistaking random environmental noise for a signal becomes much more of a problem. In many instances single-ended designs are not feasible. Another difficulty is the electromagnetic interference that can be generated by a single-ended signaling system which attempts to operate at high speed.
Examples
Examples of differential signaling include LVDS, differential ECLEmitter coupled logic
In electronics, emitter-coupled logic , is a logic family that achieves high speed by using an overdriven BJT differential amplifier with single-ended input, whose emitter current is limited to avoid the slow saturation region of transistor operation....
, PECL, LVPECL, current loop
Current loop
A current loop describes two different electrical signalling schemes.- Digital :For digital serial communications, a current loop is a communication interface that uses current instead of voltage for signaling...
interfaces such as Musical Instrument Digital Interface
Musical Instrument Digital Interface
MIDI is an industry-standard protocol, first defined in 1982 by Gordon Hall, that enables electronic musical instruments , computers and other electronic equipment to communicate and synchronize with each other...
(MIDI) hardware, RS-422, RS-485, most Ethernet physical layer
Ethernet physical layer
The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer component of the Ethernet family of computer network standards.The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed...
s, USB, Serial ATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
(SATA
Sata
Sata is a traditional dish from the Malaysian state of Terengganu, consisting of spiced fish meat wrapped in banana leaves and cooked on a grill.It is a type of Malaysian fish cake, or otak-otak...
), TMDS, FireWire, and HDMI
HDMI
HDMI is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. It is a digital alternative to consumer analog standards, such as radio frequency coaxial cable, composite video, S-Video, SCART, component video, D-Terminal, or VGA...
. LVDS is currently the only scheme that combines low power dissipation with high speed.
Examples of single-ended signaling include RS-232
RS-232
In telecommunications, RS-232 is the traditional name for a series of standards for serial binary single-ended data and control signals connecting between a DTE and a DCE . It is commonly used in computer serial ports...
and PATA.
The lowest-power-dissipation, highest-speed signals in any commercially available system are the on-chip signals in a microprocessor. Those signals are almost always single-ended.
In an electric guitar
Electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that uses the principle of direct electromagnetic induction to convert vibrations of its metal strings into electric audio signals. The signal generated by an electric guitar is too weak to drive a loudspeaker, so it is amplified before sending it to a loudspeaker...
, the humbucker
Humbucker
A humbucker is a type of electric guitar pickup, first patented by Seth Lover and the Gibson company, that uses two coils, both generating string signal. Humbuckers have higher output than a single coil pickup since both coils are connected in series...
pickup type uses exactly the same principle to avoid power supply hum at the AC frequency.
Transmission lines
The type of transmission line used to connect two devices (chips, modules) dictates the type of signaling to be used. Single-ended signaling is used with coaxial cableCoaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
s, in which one conductor totally screens the other from the environment. All screens (or shields) are combined into a single piece of material to form a common ground
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
. Differential signaling is used with a balanced pair of conductors. For short cables and low frequencies, the two methods are equivalent, so cheap single-ended circuits with a common ground can be used with cheap cables. As signaling speeds become faster, wires begin to behave as transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
s.
Use in computers
Differential signaling is often used in computers to reduce electromagnetic interferenceElectromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
, because complete screening is not possible with microstrip
Microstrip
Microstrip is a type of electrical transmission line which can be fabricated using printed circuit board technology, and is used to convey microwave-frequency signals. It consists of a conducting strip separated from a ground plane by a dielectric layer known as the substrate. Microwave components...
s and chips
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
in computers, due to geometric constraints and the fact that screening does not work at DC. If a DC power supply line and a low-voltage signal line share the same ground, the power current returning through the ground can induce a significant voltage in it. A low-resistance ground reduces this problem to some extent. A balanced pair of microstrip lines is a convenient solution, because it does not need an additional PCB layer, as a stripline
Stripline
Stripline is a transverse electromagnetic transmission line medium, that was invented by Robert M. Barrett of the Air Force Cambridge Research Centre in the 1950s.- Description :...
does. Because each line causes a matching image current in the ground plane, which is required anyway for supplying power, the pair looks like four lines and therefore has a shorter crosstalk distance than a simple isolated pair. In fact, it behaves as well as a twisted pair. Low crosstalk is important when many lines are packed into a small space, as on a typical PCB.
High-voltage differential signaling
High-voltage differential (HVD) signaling uses high-voltageVoltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
signals. In computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
electronics, "high voltage" normally means 5 volts or more.
SCSI-1 variations included a high voltage differential (HVD) implementation whose maximum cable length was many times that of the single-ended version. SCSI
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, and electrical and optical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disks and tape drives, but it...
equipment for example allows a maximum total cable length of 25 meters using HVD, while single-ended SCSI allows a maximum cable length of 1.5 to 6 meters, depending on bus speed. LVD versions of SCSI allow less than 25 m cable length not because of the lower voltage, but because these SCSI standards allow much higher speeds than the older HVD SCSI.
The term high-voltage differential signaling is a generic one that describes a variety of systems. Low-voltage differential signaling or LVDS, on the other hand, is a specific system defined by a TIA/EIA standard.
See also
- Current mode logicCurrent mode logicCurrent mode logic , or source-coupled logic , is a differential digital logic family intended to transmit data at speeds between 312.5 Mbit/s and 3.125 Gbit/s over a standard printed circuit board....
(CML) - Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS)
- Low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic (LVPECL)
- Positive emitter-coupled logic (PECL)
- EIA-422EIA-422RS-422 is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a digital signalling circuit. Differential-mode signals can be sent at rates as high as 10 million bits per second, or may be sent on cables as long as 1200 metres. Some systems directly interconnect using RS 422 signals,...
(RS-422) - Transition Minimized Differential SignalingTransition Minimized Differential SignalingTransition-minimized differential signaling is a technology for transmitting high-speed serial data and is used by the DVI and HDMI video interfaces, as well as other digital communication interfaces....
(TMDS) - Longitudinal voltageLongitudinal voltageIn telecommunication, a longitudinal voltage is a voltage induced or appearing along the length of a transmission medium.Note 1: Longitudinal voltage may be effectively eliminated by using differential amplifiers or receivers that respond only to voltage differences, e.g., those between the wires...
- Differential amplifierDifferential amplifierA differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two voltages but does not amplify the particular voltages.- Theory :Many electronic devices use differential amplifiers internally....
- Differential pairDifferential pairA differential pair is a pair of conductors used for differential signaling. Differential pairs are usually found on a printed circuit board, in cables , and in connectors...
- Twisted pairTwisted pairTwisted pair cabling is a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together for the purposes of canceling out electromagnetic interference from external sources; for instance, electromagnetic radiation from unshielded twisted pair cables, and crosstalk between neighboring pairs...
- Current loopCurrent loopA current loop describes two different electrical signalling schemes.- Digital :For digital serial communications, a current loop is a communication interface that uses current instead of voltage for signaling...
signaling

