Digital Command Control
Encyclopedia
Digital Command Control (DCC) is a standard for a system to operate model railways digitally. When equipped with Digital Command Control, locomotives on the same electrical section of track can be independently controlled.
The DCC protocol is defined by the Digital Command Control Working group of the National Model Railroad Association
(NMRA). The NMRA has trademarked the term DCC, so while the term Digital Command Control is sometimes used to describe any digital model railway control system, strictly speaking it refers to NMRA DCC.
 A DCC command station, in combination with its booster, modulates
A DCC command station, in combination with its booster, modulates
the voltage on the track to encode digital
messages while providing electric power.
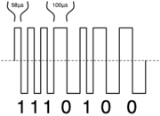
The voltage to the track is a bipolar DC signal. This results in a form of alternating current
, but the DCC signal does not follow a sine wave
. Instead, the command station quickly switches the direction of the DC voltage, resulting in a modulated pulse wave
. The length of time the voltage is applied in each direction provides the method for encoding data. To represent a binary
one, the time is short (nominally 58µs for a half cycle), while a zero is represented by a longer period (nominally at least 100µs for a half cycle).
Each locomotive is equipped with a mobile DCC decoder that takes the signals from the track and, after rectification
, routes power to the motor
as requested. Each decoder is given a unique running number, and will ignore all commands intended for a different decoder, thus providing independent control of locomotives anywhere on the layout, without special wiring requirements. Power can also be routed to lights, smoke
generators, and sound generators. These extra functions can be operated remotely from the DCC controller. Stationary decoders can also receive commands from the controller in a similar way to allow control of turnouts, uncouplers, other operating accessories (such as station announcements) and lights.
In a segment of DCC-powered track, it is possible to power a single analog model locomotive by itself (or in addition to) the DCC equipped engines, depending on the choice of commercially available base systems. The technique is known as zero stretching. Either the high or the low pulse of the zero bits can be extended to make the average voltage (and thus the current) either forward or reverse. However, because the raw power contains a heavy AC component, DC motors heat up much more quickly than they would on DC power, and some motor types (particularly coreless electric motors) can be damaged by a DCC signal.
Elektronik GmbH of Germany in the 1980s for two German model railway manufacturers, Märklin
and Arnold (models)
. The first DCC digital decoders that Lenz produced appeared on the market early 1989 for Arnold (N) and mid 1990 for Märklin (Z, H0 and 1; Digital=). Märklin and Arnold exited the agreement over patent issues, but Lenz has continued to develop the system. In 1992 Stan Ames, who later chaired the NMRA/DCC Working Group, investigated the Märklin/Lenz system as possible candidate for the NMRA/DCC standards. When the NMRA Command Control committee requested submissions from manufacturers for its proposed command control standard in the 1990s, Märklin
and Keller Engineering submitted their systems for evaluation. The committee was impressed by the Märklin/Lenz system and had settled on digital early in the process. The NMRA eventually licensed the protocol from Lenz and extended it. The system was later named DCC. The proposed standard was published in the October 1993 issue of Model Railroader magazine prior to its adoption.
The DCC protocol is the subject of two standard
s published by the NMRA
: S-9.1 specifies the electrical standard, and S-9.2 specifies the communications
standard. Several recommended practices documents are also available.
The DCC protocol defines signal levels and timings on the track. DCC does not specify the protocol used between the DCC command station and other components such as additional throttles. A variety of proprietary standards exist, and in general, command stations from one vendor are not compatible with throttles from another vendor.
systems is the simpler wiring needed to operate more than one locomotive at a time. Before, to operate more than one locomotive independently, the track had to be wired into separate "blocks" with switches selecting which controller powered which block of track. If an operator failed to switch control of a block before his locomotive entered, a short circuit or loss of control was possible. With DCC, many layouts can be wired as a single large block, and each operator can control his locomotive without worrying about crossing a block boundary.
DCC controllers can include an "inertia" simulation, where the locomotive will gradually increase or decrease speeds in a realistic manner without continuous inputs from the operator. Mobile decoders are available which will adjust the power to try to maintain a constant speed, again without burdening the operator. Most DCC controllers allow an operator to set the speed of one locomotive and then quickly select another locomotive to control its speed.
Recent developments include on-board sound modules for locomotives as small as N scale
.
Wiring requirements are generally reduced compared to a conventional DC powered layout. With DCC control of accessories, the wiring is distributed to accessory decoders rather than all being connected to a central control panel. For portable layouts this can greatly reduce the number of inter-board connections- only the DCC signal and any accessory power supplies must cross baseboard joins.
is an open NEM
standard, but the Märklin
-Motorola system is proprietary and used only in Märklin products. From the U.S., the Rail-Lynx system provides power with a fixed voltage to the rails while commands are sent digitally using infrared light. Other systems include the Digital Command System and Trainmaster Command Control
.
Several major manufacturers (including Roco
and Hornby
), have entered the DCC market alongside makers which specialize in it (including Lenz, Digitrax, ESU, ZIMO, Kühn, Tams, North Coast Engineering (NCE), and CVP Products' EasyDCC, Sound Traxx, Lok Sound, and Train Control Systems).
The DCC protocol is defined by the Digital Command Control Working group of the National Model Railroad Association
National Model Railroad Association
The National Model Railroad Association is a non-profit organization for those involved in the hobby or business of model railroading. It was founded in the United States in 1935, and is now active in Canada, Australia, Great Britain, and the Netherlands...
(NMRA). The NMRA has trademarked the term DCC, so while the term Digital Command Control is sometimes used to describe any digital model railway control system, strictly speaking it refers to NMRA DCC.
How DCC works

Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
the voltage on the track to encode digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
messages while providing electric power.
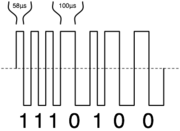
The voltage to the track is a bipolar DC signal. This results in a form of alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
, but the DCC signal does not follow a sine wave
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
. Instead, the command station quickly switches the direction of the DC voltage, resulting in a modulated pulse wave
Pulse wave
A pulse wave or pulse train is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform that is similar to a square wave, but does not have the symmetrical shape associated with a perfect square wave. It is a term common to synthesizer programming, and is a typical waveform available on many synths. The exact shape of...
. The length of time the voltage is applied in each direction provides the method for encoding data. To represent a binary
Binary numeral system
The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, represents numeric values using two symbols, 0 and 1. More specifically, the usual base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2...
one, the time is short (nominally 58µs for a half cycle), while a zero is represented by a longer period (nominally at least 100µs for a half cycle).
Each locomotive is equipped with a mobile DCC decoder that takes the signals from the track and, after rectification
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
, routes power to the motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
as requested. Each decoder is given a unique running number, and will ignore all commands intended for a different decoder, thus providing independent control of locomotives anywhere on the layout, without special wiring requirements. Power can also be routed to lights, smoke
Smoke
Smoke is a collection of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires , but may also be used for pest...
generators, and sound generators. These extra functions can be operated remotely from the DCC controller. Stationary decoders can also receive commands from the controller in a similar way to allow control of turnouts, uncouplers, other operating accessories (such as station announcements) and lights.
In a segment of DCC-powered track, it is possible to power a single analog model locomotive by itself (or in addition to) the DCC equipped engines, depending on the choice of commercially available base systems. The technique is known as zero stretching. Either the high or the low pulse of the zero bits can be extended to make the average voltage (and thus the current) either forward or reverse. However, because the raw power contains a heavy AC component, DC motors heat up much more quickly than they would on DC power, and some motor types (particularly coreless electric motors) can be damaged by a DCC signal.
History and Protocols
The DCC system was originally developed by LenzLenz
Lenz may refer to:* Lantsch/Lenz, the German name of the place in Grisons, Switzerland* Lenz , literary fragment by Georg Büchner* Lenasia, an Indian township in Gauteng, South Africa* Lenz Military Base, a military base in Lenasia, Gauteng...
Elektronik GmbH of Germany in the 1980s for two German model railway manufacturers, Märklin
Märklin
Gebr. Märklin & Cie. GmbH or Märklin is a German toy company. The company was founded in 1859 and is based at Göppingen in Baden-Wurttemberg. Although it originally specialised in doll house accessories, today it is best known for model railways and technical toys...
and Arnold (models)
Arnold (models)
Founded in 1906 by Karl Arnold in Nürnberg, K. Arnold & Co. began its life producing tin toys and related items. They produced an extensive line of model ships, doll house items and other toys. In 1935, K. Arnold & Co. hired Max Ernst as their managing director...
. The first DCC digital decoders that Lenz produced appeared on the market early 1989 for Arnold (N) and mid 1990 for Märklin (Z, H0 and 1; Digital=). Märklin and Arnold exited the agreement over patent issues, but Lenz has continued to develop the system. In 1992 Stan Ames, who later chaired the NMRA/DCC Working Group, investigated the Märklin/Lenz system as possible candidate for the NMRA/DCC standards. When the NMRA Command Control committee requested submissions from manufacturers for its proposed command control standard in the 1990s, Märklin
Märklin
Gebr. Märklin & Cie. GmbH or Märklin is a German toy company. The company was founded in 1859 and is based at Göppingen in Baden-Wurttemberg. Although it originally specialised in doll house accessories, today it is best known for model railways and technical toys...
and Keller Engineering submitted their systems for evaluation. The committee was impressed by the Märklin/Lenz system and had settled on digital early in the process. The NMRA eventually licensed the protocol from Lenz and extended it. The system was later named DCC. The proposed standard was published in the October 1993 issue of Model Railroader magazine prior to its adoption.
The DCC protocol is the subject of two standard
Standardization
Standardization is the process of developing and implementing technical standards.The goals of standardization can be to help with independence of single suppliers , compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality....
s published by the NMRA
National Model Railroad Association
The National Model Railroad Association is a non-profit organization for those involved in the hobby or business of model railroading. It was founded in the United States in 1935, and is now active in Canada, Australia, Great Britain, and the Netherlands...
: S-9.1 specifies the electrical standard, and S-9.2 specifies the communications
Communications protocol
A communications protocol is a system of digital message formats and rules for exchanging those messages in or between computing systems and in telecommunications...
standard. Several recommended practices documents are also available.
The DCC protocol defines signal levels and timings on the track. DCC does not specify the protocol used between the DCC command station and other components such as additional throttles. A variety of proprietary standards exist, and in general, command stations from one vendor are not compatible with throttles from another vendor.
Advantages
The great advantage of using DCC over traditional DCDirect current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
systems is the simpler wiring needed to operate more than one locomotive at a time. Before, to operate more than one locomotive independently, the track had to be wired into separate "blocks" with switches selecting which controller powered which block of track. If an operator failed to switch control of a block before his locomotive entered, a short circuit or loss of control was possible. With DCC, many layouts can be wired as a single large block, and each operator can control his locomotive without worrying about crossing a block boundary.
DCC controllers can include an "inertia" simulation, where the locomotive will gradually increase or decrease speeds in a realistic manner without continuous inputs from the operator. Mobile decoders are available which will adjust the power to try to maintain a constant speed, again without burdening the operator. Most DCC controllers allow an operator to set the speed of one locomotive and then quickly select another locomotive to control its speed.
Recent developments include on-board sound modules for locomotives as small as N scale
N scale
N scale is a popular model railway scale/track gauge. Depending upon the manufacturer , the scale ranges from 1:148 to 1:160. In all cases, the gauge is . The term N gauge refers to the track dimensions, but in the UK in particular N gauge refers to a 1:148 scale with track gauge modelling...
.
Wiring requirements are generally reduced compared to a conventional DC powered layout. With DCC control of accessories, the wiring is distributed to accessory decoders rather than all being connected to a central control panel. For portable layouts this can greatly reduce the number of inter-board connections- only the DCC signal and any accessory power supplies must cross baseboard joins.
Railcom
In 2006 Lenz, together with Kühn, Zimo and Tams, started development of an extension to the DCC protocol to allow a feedback channel from decoders to the command station. This feedback channel can typically be used to signal which train occupies a certain section, but as well to inform the command station of the actual speed of an engine. This feedback channel is known under the name Railcom, and was standardized in 2007 as NMRA RP 9.3.1.Competing Systems
In Europe, SelectrixSelectrix
A number of control systems are available to operate locomotives on model railways. The earlier traditional analog systems where the speed and the direction of a train is controlled by adjusting the voltage on the track are still popular while they have recently given way to control systems based...
is an open NEM
Normen Europäischer Modelleisenbahnen
NEM standards are the standards for model railroads issued by the MOROP. NEM stands for Normen Europäischer Modellbahnen , Normas Europeas de Modelismo or Normes Européennes de Modélisme , the German translating to European Standards for Model Railways)...
standard, but the Märklin
Märklin
Gebr. Märklin & Cie. GmbH or Märklin is a German toy company. The company was founded in 1859 and is based at Göppingen in Baden-Wurttemberg. Although it originally specialised in doll house accessories, today it is best known for model railways and technical toys...
-Motorola system is proprietary and used only in Märklin products. From the U.S., the Rail-Lynx system provides power with a fixed voltage to the rails while commands are sent digitally using infrared light. Other systems include the Digital Command System and Trainmaster Command Control
Trainmaster Command Control
Trainmaster Command is Lionel's electronic control system for O scale 3-rail model trains and toy trains. Conceptually it is similar to Digital Command Control , the industry's open standard used by HO scale and other 2-rail DC trains...
.
Several major manufacturers (including Roco
Roco
Roco, based in Salzburg, Austria, is a manufacturer of model railway equipment.-History:The company was founded in 1960 by Ing. Heinz Rössler and started with a plastic Minitanks series. After export to the USA became successful, the model line was expanded with model trains in H0 scale and the...
and Hornby
Hornby Railways
Hornby Railways is the leading brand of model railway in the United Kingdom. Its roots date back to 1901, when founder Frank Hornby received a patent for his Meccano construction toy. The first clockwork train was produced in 1920. In 1938, Hornby launched its first 00 gauge train...
), have entered the DCC market alongside makers which specialize in it (including Lenz, Digitrax, ESU, ZIMO, Kühn, Tams, North Coast Engineering (NCE), and CVP Products' EasyDCC, Sound Traxx, Lok Sound, and Train Control Systems).
External links
- NMRA Standards and Recommended Practices page
- The NMRA's trademarked DCC logo
- DCC History at the DCCWiki
- The DCCWiki
- Wiring for DCC
- Hornby DCC Product Information Page
- Model Rectifier Corporation - Manufacturer of DCC related products
- Digitrax - Manufacturer of DCC related products, Mobile Decoders, Starter Sets, etc
- Train Control Systems - Manufacturer of DCC related products
- NCE Power Pro System - Manufacturer of DCC related products
- CVP's EasyDCC System - Manufacturer of DCC related products
- OpenDCC - An open project for building your own decoders, command stations etc.

