Donor (semiconductors)
Encyclopedia
In semiconductor physics, a donor is a dopant
atom that, when added to a semiconductor
, can form n-type
regions.
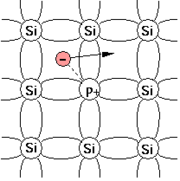 For example, when silicon
For example, when silicon
(Si), having four valence electron
s, needs to be doped as an n-type semiconductor
, elements from group V
like phosphorus
(P) or arsenic
(As) can be used because they have five valence electrons. A dopant with five valence electrons is also called a pentavalent impurity. Other pentavalent dopants are antimony
(Sb) and bismuth
(Bi).
When substituting a Si atom in the crystal lattice, four of the valence electrons of phosphorus form covalent bond
s with the neighbouring Si atoms but the fifth one remains weakly bonded. At room temperature
all the fifth electrons are liberated, can move around the Si crystal and can carry a current, act as charge carrier
s. The initially neutral donor becomes positively charged (ionised).
Dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace impurity element that is inserted into a substance in order to alter the electrical properties or the optical properties of the substance. In the case of crystalline substances, the atoms of the dopant very commonly take the place of elements that...
atom that, when added to a semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
, can form n-type
N-type semiconductor
N-type semiconductors are a type of extrinsic semiconductor where the dopant atoms are capable of providing extra conduction electrons to the host material . This creates an excess of negative electron charge carriers....
regions.

Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
(Si), having four valence electron
Valence electron
In chemistry, valence electrons are the electrons of an atom that can participate in the formation of chemical bonds with other atoms. Valence electrons are the "own" electrons, present in the free neutral atom, that combine with valence electrons of other atoms to form chemical bonds. In a single...
s, needs to be doped as an n-type semiconductor
N-type semiconductor
N-type semiconductors are a type of extrinsic semiconductor where the dopant atoms are capable of providing extra conduction electrons to the host material . This creates an excess of negative electron charge carriers....
, elements from group V
Nitrogen group
The nitrogen group is a periodic table group consisting of nitrogen , phosphorus , arsenic , antimony , bismuth and ununpentium ....
like phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
(P) or arsenic
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid...
(As) can be used because they have five valence electrons. A dopant with five valence electrons is also called a pentavalent impurity. Other pentavalent dopants are antimony
Antimony
Antimony is a toxic chemical element with the symbol Sb and an atomic number of 51. A lustrous grey metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite...
(Sb) and bismuth
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead...
(Bi).
When substituting a Si atom in the crystal lattice, four of the valence electrons of phosphorus form covalent bond
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
s with the neighbouring Si atoms but the fifth one remains weakly bonded. At room temperature
Room temperature
-Comfort levels:The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers has listings for suggested temperatures and air flow rates in different types of buildings and different environmental circumstances. For example, a single office in a building has an occupancy ratio per...
all the fifth electrons are liberated, can move around the Si crystal and can carry a current, act as charge carrier
Charge carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
s. The initially neutral donor becomes positively charged (ionised).

