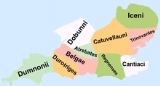
Durotriges
Encyclopedia
The Durotriges were one of the Celt
ic tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman invasion. The tribe lived in modern Dorset
, south Wiltshire
and south Somerset
. After the Roman conquest, their main civitates, or settlement-centred administrative units, were Durnovaria
(modern Dorchester, "the probable original capital") and Lindinis
(modern Ilchester
, "whose former, unknown status was thereby enhanced"). Their territory was bordered to the west by the Dumnonii
; and to the east by the Belgae.
Durotriges were more a tribal confederation than a tribe. They were one of the groups that issued coinage before the Roman conquest, part of the cultural "periphery", as Barry Cunliffe
characterised them, round the "core group" of Britons in the south. These coins were rather simple and had no inscriptions, and thus no names of coin-issuers can be known, let alone evidence about monarchs or rulers. Nevertheless, the Durotriges presented a settled society, based in the farming of lands surrounded and controlled by strong hill forts that were still in use in 43 AD
. Maiden Castle
is a preserved example of one of these hill forts.
The area of the Durotriges is identified in part by coin finds: few Durotrigan coins are found in the "core" area, where they were apparently unacceptable and were reminted. To their north and east were the Belgae
, beyond the Avon
and its tributary Wylye
: "the ancient division is today reflected in the county division between Wiltshire and Somerset." Their main outlet for the trade across the Channel, strong in the first half of the first century BC, when the potter's wheel
was introduced, then drying up in the decades before the advent of the Romans, was at Hengistbury Head
. Numismatic evidence shows progressive debasing of the coinage, suggesting economic retrenchment accompanying the increased cultural isolation. Analysis of the body of Durotrigan ceramics suggests to Cunliffe that the production was increasingly centralised, at Poole Harbour
(Cunliffe 2005:183). Burial of Durotriges was by inhumation, with a last ritual meal provided even under exiguous circumstances, as in the eight burials at Maiden Castle, carried out immediately after the Roman attack.
Not surprisingly, the Durotriges resisted Roman invasion in AD 43, and the historian Suetonius
records some fights between the tribe and the second legion Augusta
, then commanded by Vespasian
. By 70 AD, the tribe was already Romanised and securely included in the Roman province
of Britannia
. In the tribe’s area, the Romans explored some quarries and supported a local pottery industry.
Celt
The Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Roman-era Europe who spoke Celtic languages.The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central European Hallstatt culture , named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria....
ic tribes living in Britain prior to the Roman invasion. The tribe lived in modern Dorset
Dorset
Dorset , is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The county town is Dorchester which is situated in the south. The Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch joined the county with the reorganisation of local government in 1974...
, south Wiltshire
Wiltshire
Wiltshire is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset, Somerset, Hampshire, Gloucestershire, Oxfordshire and Berkshire. It contains the unitary authority of Swindon and covers...
and south Somerset
Somerset
The ceremonial and non-metropolitan county of Somerset in South West England borders Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. It is partly bounded to the north and west by the Bristol Channel and the estuary of the...
. After the Roman conquest, their main civitates, or settlement-centred administrative units, were Durnovaria
Durnovaria
Durnovaria is the Latin form of the Brythonic name for the Roman town of Dorchester in the modern English county of Dorset.-Romans at Maiden Castle:...
(modern Dorchester, "the probable original capital") and Lindinis
Lindinis
Lindinis was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Ilchester, located in the English county of Somerset....
(modern Ilchester
Ilchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parish, situated on the River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the English county of Somerset. The parish, which includes the village of Sock Dennis and the old parish of Northover, has a population of 2,021...
, "whose former, unknown status was thereby enhanced"). Their territory was bordered to the west by the Dumnonii
Dumnonii
The Dumnonii or Dumnones were a British Celtic tribe who inhabited Dumnonia, the area now known as Devon and Cornwall in the farther parts of the South West peninsula of Britain, from at least the Iron Age up to the early Saxon period...
; and to the east by the Belgae.
Durotriges were more a tribal confederation than a tribe. They were one of the groups that issued coinage before the Roman conquest, part of the cultural "periphery", as Barry Cunliffe
Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe, CBE, known professionally as Barry Cunliffe is a former Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford, a position held from 1972 to 2007...
characterised them, round the "core group" of Britons in the south. These coins were rather simple and had no inscriptions, and thus no names of coin-issuers can be known, let alone evidence about monarchs or rulers. Nevertheless, the Durotriges presented a settled society, based in the farming of lands surrounded and controlled by strong hill forts that were still in use in 43 AD
43
Year 43 was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Vitellius...
. Maiden Castle
Maiden Castle, Dorset
Maiden Castle is an Iron Age hill fort south west of Dorchester, in the English county of Dorset. Hill forts were fortified hill-top settlements constructed across Britain during the Iron Age...
is a preserved example of one of these hill forts.
The area of the Durotriges is identified in part by coin finds: few Durotrigan coins are found in the "core" area, where they were apparently unacceptable and were reminted. To their north and east were the Belgae
Belgae
The Belgae were a group of tribes living in northern Gaul, on the west bank of the Rhine, in the 3rd century BC, and later also in Britain, and possibly even Ireland...
, beyond the Avon
River Avon, Hampshire
The River Avon is a river in the south of England. The river rises in the county of Wiltshire and flows through the city of Salisbury and the county of Hampshire before reaching the English Channel through Christchurch Harbour in the county of Dorset....
and its tributary Wylye
River Wylye
The River Wylye is a classic southern England chalk stream; champagne clear water flowing over gravel. Consequently, it is popular with anglers keen on fly fishing.- Course :...
: "the ancient division is today reflected in the county division between Wiltshire and Somerset." Their main outlet for the trade across the Channel, strong in the first half of the first century BC, when the potter's wheel
Potter's wheel
In pottery, a potter's wheel is a machine used in asma of round ceramic ware. The wheel may also be used during process of trimming the excess body from dried ware and for applying incised decoration or rings of color...
was introduced, then drying up in the decades before the advent of the Romans, was at Hengistbury Head
Hengistbury Head
Hengistbury Head is a headland jutting into the English Channel between Bournemouth and Milford on Sea in the English county of Dorset.At the end is a spit which creates the narrow entrance to Christchurch Harbour.-Location:...
. Numismatic evidence shows progressive debasing of the coinage, suggesting economic retrenchment accompanying the increased cultural isolation. Analysis of the body of Durotrigan ceramics suggests to Cunliffe that the production was increasingly centralised, at Poole Harbour
Poole Harbour
Poole Harbour is a large natural harbour in Dorset, southern England, with the town of Poole on its shores. The harbour is a drowned valley formed at the end of the last ice age and is the estuary of several rivers, the largest being the Frome. The harbour has a long history of human settlement...
(Cunliffe 2005:183). Burial of Durotriges was by inhumation, with a last ritual meal provided even under exiguous circumstances, as in the eight burials at Maiden Castle, carried out immediately after the Roman attack.
Not surprisingly, the Durotriges resisted Roman invasion in AD 43, and the historian Suetonius
Lives of the Twelve Caesars
De vita Caesarum commonly known as The Twelve Caesars, is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire written by Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus.The work, written in AD 121 during the reign of the emperor Hadrian, was the most popular work of Suetonius,...
records some fights between the tribe and the second legion Augusta
Legio II Augusta
Legio secunda Augusta , was a Roman legion, levied by Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus in 43 BC, and still operative in Britannia in the 4th century...
, then commanded by Vespasian
Vespasian
Vespasian , was Roman Emperor from 69 AD to 79 AD. Vespasian was the founder of the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for a quarter century. Vespasian was descended from a family of equestrians, who rose into the senatorial rank under the Emperors of the Julio-Claudian dynasty...
. By 70 AD, the tribe was already Romanised and securely included in the Roman province
Roman province
In Ancient Rome, a province was the basic, and, until the Tetrarchy , largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside of Italy...
of Britannia
Britannia
Britannia is an ancient term for Great Britain, and also a female personification of the island. The name is Latin, and derives from the Greek form Prettanike or Brettaniai, which originally designated a collection of islands with individual names, including Albion or Great Britain. However, by the...
. In the tribe’s area, the Romans explored some quarries and supported a local pottery industry.

