
Celt
Encyclopedia
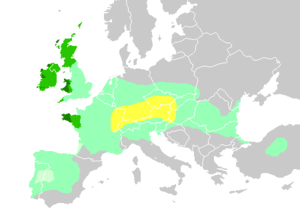
The Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
and Roman-era Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
who spoke Celtic languages
Celtic languages
The Celtic languages are descended from Proto-Celtic, or "Common Celtic"; a branch of the greater Indo-European language family...
.
The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
an Hallstatt culture
Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Central European culture from the 8th to 6th centuries BC , developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of Central Europe by the La Tène culture.By the 6th century BC, the Hallstatt culture extended for some...
(c. 800-450 BC), named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt
Hallstatt
Hallstatt, Upper Austria is a village in the Salzkammergut, a region in Austria. It is located near the Hallstätter See . At the 2001 census it had 946 inhabitants...
, Austria. By the later La Tène
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture named after the archaeological site of La Tène on the north side of Lake Neuchâtel in Switzerland, where a rich cache of artifacts was discovered by Hansli Kopp in 1857....
period (c. 450 BC up to the Roman conquest), this Celtic culture had expanded over a wide range of regions, whether by diffusion or migration
Human migration
Human migration is physical movement by humans from one area to another, sometimes over long distances or in large groups. Historically this movement was nomadic, often causing significant conflict with the indigenous population and their displacement or cultural assimilation. Only a few nomadic...
: to the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
(Insular Celts
Insular Celts
The Insular Celts are the speakers of Insular Celtic languages.-Pre-Celtic Britain:Little is known of the culture and language of pre-Celtic Britain, but remnants of the latter may remain in the names of some geographical features, such as the rivers Clyde, Tamar and Thames, whose etymology is...
), France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and The Low Countries (Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
), much of Central Europe
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
, the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
(Celtiberians
Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were Celtic-speaking people of the Iberian Peninsula in the final centuries BC. The group used the Celtic Celtiberian language.Archaeologically, the Celtiberians participated in the Hallstatt culture in what is now north-central Spain...
, Celtici
Celtici
]The Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the provinces of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the...
and Gallaeci) and northern Italy
Northern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
(Golaseccans
Golasecca culture
The Golasecca culture was a Celtic culture in northern Italy , whose type-site has been excavated at Golasecca in the province of Varese, Lombardy.-Archeological sources:...
and Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul, in Latin: Gallia Cisalpina or Citerior, also called Gallia Togata, was a Roman province until 41 BC when it was merged into Roman Italy.It bore the name Gallia, because the great body of its inhabitants, after the expulsion of the Etruscans, consisted of Gauls or Celts...
s) and following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans
Gallic invasion of the Balkans
Gallic groups, originating from the various La Tène chiefdoms, began a south-eastern movement into the Balkan peninsula from the 4th century BC. Although Celtic settlements were concentrated in the western half of the Carpathian basin, there were notable incursions, and settlements, within the...
in 279 BC as far east as central Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
(Galatia
Galatia
Ancient Galatia was an area in the highlands of central Anatolia in modern Turkey. Galatia was named for the immigrant Gauls from Thrace , who settled here and became its ruling caste in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of...
ns).
The earliest directly attested examples of a Celtic language are the Lepontic
Lepontic language
Lepontic is an extinct Alpine language that was spoken in parts of Rhaetia and Cisalpine Gaul between 550 and 100 BC. It was a Celtic language, although its exact classification within Celtic has been the object of debate...
inscriptions, beginning from the 6th century BC. Continental Celtic languages
Continental Celtic languages
The Continental Celtic languages are the Celtic languages, now extinct, that were spoken on the continent of Europe, as distinguished from the Insular Celtic languages of Britain and Ireland. The Continental Celtic languages were spoken by the people known to Roman and Greek writers as Keltoi,...
are attested only in inscriptions and place-names. Insular Celtic is attested from about the 4th century AD in ogham inscriptions, although it is clearly much earlier. Literary tradition begins with Old Irish from about the 8th century. Coherent texts of Early Irish literature
Early Irish literature
-The earliest Irish authors:It is unclear when literacy first came to Ireland. The earliest Irish writings are inscriptions, mostly simple memorials, on stone in the ogham alphabet, the earliest of which date to the fourth century...
, such as the Táin Bó Cúailnge
Táin Bó Cúailnge
is a legendary tale from early Irish literature, often considered an epic, although it is written primarily in prose rather than verse. It tells of a war against Ulster by the Connacht queen Medb and her husband Ailill, who intend to steal the stud bull Donn Cuailnge, opposed only by the teenage...
(The Cattle Raid of Cooley), survive in 12th-century recensions.
By mid 1st millennium AD, following the expansion of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
and the Great Migration
Migration Period
The Migration Period, also called the Barbarian Invasions , was a period of intensified human migration in Europe that occurred from c. 400 to 800 CE. This period marked the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages...
s (Migration Period
Migration Period
The Migration Period, also called the Barbarian Invasions , was a period of intensified human migration in Europe that occurred from c. 400 to 800 CE. This period marked the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages...
) of Germanic peoples
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
, Celtic culture and Insular Celtic had become restricted to Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, to the western and northern parts of Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
(Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
and the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
), and to northern France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
(Brittany
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
). Between the fifth and eighth centuries AD the Celtic-speaking communities of the Atlantic regions had emerged as a reasonably cohesive cultural entity. In language, religion, and art they shared a common heritage that distinguished them from the culture of surrounding polities. The Continental Celtic languages
Continental Celtic languages
The Continental Celtic languages are the Celtic languages, now extinct, that were spoken on the continent of Europe, as distinguished from the Insular Celtic languages of Britain and Ireland. The Continental Celtic languages were spoken by the people known to Roman and Greek writers as Keltoi,...
ceased to be widely used by the 6th century.
Insular Celtic culture diversified into that of the Gaels
Gaels
The Gaels or Goidels are speakers of one of the Goidelic Celtic languages: Irish, Scottish Gaelic, and Manx. Goidelic speech originated in Ireland and subsequently spread to western and northern Scotland and the Isle of Man....
(Irish
Irish people
The Irish people are an ethnic group who originate in Ireland, an island in northwestern Europe. Ireland has been populated for around 9,000 years , with the Irish people's earliest ancestors recorded having legends of being descended from groups such as the Nemedians, Fomorians, Fir Bolg, Tuatha...
, Scottish
Scottish people
The Scottish people , or Scots, are a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland. Historically they emerged from an amalgamation of the Picts and Gaels, incorporating neighbouring Britons to the south as well as invading Germanic peoples such as the Anglo-Saxons and the Norse.In modern use,...
and Manx
Manx people
The Manx are an ethnic group coming from the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea in northern Europe. They are often described as a Celtic people, though they have had a mixed background including Norse and English influences....
) and the Brythonic
Britons (historical)
The Britons were the Celtic people culturally dominating Great Britain from the Iron Age through the Early Middle Ages. They spoke the Insular Celtic language known as British or Brythonic...
Celts (Welsh
Welsh people
The Welsh people are an ethnic group and nation associated with Wales and the Welsh language.John Davies argues that the origin of the "Welsh nation" can be traced to the late 4th and early 5th centuries, following the Roman departure from Britain, although Brythonic Celtic languages seem to have...
, Cornish
Cornish people
The Cornish are a people associated with Cornwall, a county and Duchy in the south-west of the United Kingdom that is seen in some respects as distinct from England, having more in common with the other Celtic parts of the United Kingdom such as Wales, as well as with other Celtic nations in Europe...
, and Bretons) of the medieval and modern periods. A modern "Celtic identity" was constructed in the context of the Romanticist Celtic Revival
Celtic Revival
Celtic Revival covers a variety of movements and trends, mostly in the 19th and 20th centuries, which drew on the traditions of Celtic literature and Celtic art, or in fact more often what art historians call Insular art...
in Great Britain, Ireland, and other European territories, such as Galicia. Today Irish
Irish language
Irish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
, Scottish Gaelic, Welsh
Welsh language
Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa...
, and Breton
Breton language
Breton is a Celtic language spoken in Brittany , France. Breton is a Brythonic language, descended from the Celtic British language brought from Great Britain to Armorica by migrating Britons during the Early Middle Ages. Like the other Brythonic languages, Welsh and Cornish, it is classified as...
remain spoken in parts of their historical territories, and both Cornish
Cornish language
Cornish is a Brythonic Celtic language and a recognised minority language of the United Kingdom. Along with Welsh and Breton, it is directly descended from the ancient British language spoken throughout much of Britain before the English language came to dominate...
and Manx
Manx language
Manx , also known as Manx Gaelic, and as the Manks language, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, historically spoken by the Manx people. Only a small minority of the Island's population is fluent in the language, but a larger minority has some knowledge of it...
are currently undergoing revival.
Names and terminology
The first recorded use of the word Celts to refer to an ethnic group was by Hecataeus of Miletus, the Greek geographer, in 517 BC, when writing about a people living near "Massilia" (MarseilleMarseille
Marseille , known in antiquity as Massalia , is the second largest city in France, after Paris, with a population of 852,395 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Marseille extends beyond the city limits with a population of over 1,420,000 on an area of...
). According to the testimony of Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
and Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
, the Latin name "Celtus" (pl. "Celti" or "Celtae") and the Greek ( pl. or pl. ) were borrowed from a native Celtic tribal name. Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
referred it as being used in Lusitania
Lusitania
Lusitania or Hispania Lusitania was an ancient Roman province including approximately all of modern Portugal south of the Douro river and part of modern Spain . It was named after the Lusitani or Lusitanian people...
as a tribal surname which epigraphic findings confirm.
Latin "Gallus" might originally be from a Celtic ethnic or tribal name
Tribal name
A tribal name is a name of an ethnic tribe —usually of ancient origin, which represented its self-identity.Studies of Native American tribal names show that most had an original meaning comparable to "human," "people" "us"—the "tribal" name for itself was often the localized ethnic...
, perhaps borrowed into Latin during the Celtic expansions into Italy of the early 5th century BC. Its root may be the Common Celtic "*galno", meaning power or strength. Galli, Gallaeci and Galatae most probably go with Old Irish gal 'boldness, ferocity' and Welsh gallu 'to be able, power'. The Greek "Galatai" seems to be based on the same root, borrowed directly from the same hypothetical Celtic source which gave us "Galli" (the suffix "-atai" is an Ancient Greek inflection). (see Galatia
Galatia
Ancient Galatia was an area in the highlands of central Anatolia in modern Turkey. Galatia was named for the immigrant Gauls from Thrace , who settled here and became its ruling caste in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of...
in Anatolia)
The English word "Celt" is modern, attested from 1707 in the writings of Edward Lhuyd
Edward Lhuyd
Edward Lhuyd was a Welsh naturalist, botanist, linguist, geographer and antiquary. He is also known by the Latinized form of his name, Eduardus Luidius....
whose work, along with that of other late 17th-century scholars, brought academic attention to the languages and history of these early inhabitants of Great Britain. The English form "Gaul" (first recorded in the 17th century) and "Gaulish" come from the French "Gaule" and "Gaulois", which translate Latin "Gallia" and "Gallus, -icus" respectively. In Old French, the words "gualeis", "galois", "walois" (Northern French phonetics keeping /w/) had different meanings: Welsh or the Langue d'oïl, etc. On the other hand, the word "Waulle" (Northern French phonetics keeping /w/) is recorded for the first time in the 13th century to translate the Latin word Gallia, while "gaulois" is recorded for the first time in the 15th century, and the scholars use it to translate the Latin words Gallus / Gallicus. The word comes from Proto-Germanic *Walha- (see Gaul: Name). The English word "Welsh" originates from the word wælisċ, the Anglo-Saxon
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
form of *walhiska-
Walha
Walhaz is a reconstructed Proto-Germanic word, meaning "foreigner", "stranger", "Roman", "Romance-speaker", or "Celtic-speaker". The adjective derived from this word can be found in , Old High German walhisk, meaning "Romance", in Old English welisċ, wælisċ, wilisċ, meaning "Romano-British" and in...
, the reconstructed Proto-Germanic word for "foreign" or "Celt" (South German Welsch(e) "Celtic speaker", "French speaker", "Italian speaker"; Old Norse "valskr", pl. "valir" "Gaulish", "French"), that is supposed to be derived of the name of the "Volcae
Volcae
The Volcae were a tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedon circa 270 BC and defeated the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC...
", a Celtic tribe who lived first in the South of Germany and emigrated then to Gaul.
The notion of an identifiable Celtic cultural
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
identity or "Celticity", though problematic, generally centres on language, art and classical texts, though can also include, material artifacts, social organisation, homeland
Homeland
A homeland is the concept of the place to which an ethnic group holds a long history and a deep cultural association with —the country in which a particular national identity began. As a common noun, it simply connotes the country of one's origin...
and mythology
Celtic mythology
Celtic mythology is the mythology of Celtic polytheism, apparently the religion of the Iron Age Celts. Like other Iron Age Europeans, the early Celts maintained a polytheistic mythology and religious structure...
. Earlier theories were that this indicated a common racial origin but more recent theories are reflective of culture and language rather than race. Celtic cultures seem to have had numerous diverse characteristics but the commonality between these diverse peoples was the use of a Celtic language..
"Celtic" is a descriptor of a family of languages
Language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term 'family' comes from the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a...
and, more generally, means "of the Celts", or "in the style of the Celts". It has also been used to refer to several archaeological cultures defined by unique sets of artifacts. The link between language and artifact is aided by the presence of inscriptions. (see Celtic (disambiguation) for other applications of the term)
Today, the term Celtic is generally used to describe the languages and respective cultures of Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
, the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
and Brittany
Brittany
Brittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain...
, also known as the Six Celtic Nations
Celtic nations
The Celtic nations are territories in North-West Europe in which that area's own Celtic languages and some cultural traits have survived.The term "nation" is used in its original sense to mean a people who share a common traditional identity and culture and are identified with a traditional...
. These are the regions where four Celtic languages are still spoken to some extent as mother tongues: Irish Gaelic
Irish language
Irish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
, Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic language
Scottish Gaelic is a Celtic language native to Scotland. A member of the Goidelic branch of the Celtic languages, Scottish Gaelic, like Modern Irish and Manx, developed out of Middle Irish, and thus descends ultimately from Primitive Irish....
, Welsh
Welsh language
Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa...
, and Breton
Breton language
Breton is a Celtic language spoken in Brittany , France. Breton is a Brythonic language, descended from the Celtic British language brought from Great Britain to Armorica by migrating Britons during the Early Middle Ages. Like the other Brythonic languages, Welsh and Cornish, it is classified as...
, plus two recent revivals, Cornish
Cornish language
Cornish is a Brythonic Celtic language and a recognised minority language of the United Kingdom. Along with Welsh and Breton, it is directly descended from the ancient British language spoken throughout much of Britain before the English language came to dominate...
(one of the Brythonic languages
Brythonic languages
The Brythonic or Brittonic languages form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family, the other being Goidelic. The name Brythonic was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word Brython, meaning an indigenous Briton as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael...
) and Manx
Manx language
Manx , also known as Manx Gaelic, and as the Manks language, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, historically spoken by the Manx people. Only a small minority of the Island's population is fluent in the language, but a larger minority has some knowledge of it...
(one of the Goidelic languages
Goidelic languages
The Goidelic languages or Gaelic languages are one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic languages, the other consisting of the Brythonic languages. Goidelic languages historically formed a dialect continuum stretching from the south of Ireland through the Isle of Man to the north of Scotland...
). There are also attempts to reconstruct the Cumbric language
Cumbric language
Cumbric was a variety of the Celtic British language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North", or what is now northern England and southern Lowland Scotland, the area anciently known as Cumbria. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brythonic languages...
(a Brythonic language from Northwest England
North West England
North West England, informally known as The North West, is one of the nine official regions of England.North West England had a 2006 estimated population of 6,853,201 the third most populated region after London and the South East...
and Southwest Scotland). 'Celtic' is also sometimes used to describe regions of Continental Europe
Continental Europe
Continental Europe, also referred to as mainland Europe or simply the Continent, is the continent of Europe, explicitly excluding European islands....
that claim a Celtic heritage, but where no Celtic language has survived; these areas include the western Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
, i.e. Portugal, and north-central Spain (Galicia, Asturias
Asturias
The Principality of Asturias is an autonomous community of the Kingdom of Spain, coextensive with the former Kingdom of Asturias in the Middle Ages...
, Cantabria
Cantabria
Cantabria is a Spanish historical region and autonomous community with Santander as its capital city. It is bordered on the east by the Basque Autonomous Community , on the south by Castile and León , on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea.Cantabria...
, Castile and León
Castile and León
Castile and León is an autonomous community in north-western Spain. It was so constituted in 1983 and it comprises the historical regions of León and Old Castile...
, Extremadura
Extremadura
Extremadura is an autonomous community of western Spain whose capital city is Mérida. Its component provinces are Cáceres and Badajoz. It is bordered by Portugal to the west...
). (see Modern Celts
Modern Celts
A Celtic identity emerged in the "Celtic" nations of Western Europe, following the identification of the native peoples of the Atlantic fringe as "Celts" by Edward Lhuyd in the 18th century and during the course of the 19th-century Celtic Revival, taking the form of ethnic nationalism particularly...
)
"Continental Celts" refers to the Celtic-speaking people of mainland Europe. "Insular Celts" refers to the different Celtic-speaking peoples of the British and Irish islands and to their descendants. The Celts of Brittany derive their language from migrating insular Celts mainly from Wales and Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
and so are grouped accordingly.
Origins

Celtic languages
The Celtic languages are descended from Proto-Celtic, or "Common Celtic"; a branch of the greater Indo-European language family...
form a branch of the larger Indo-European family. By the time speakers of Celtic languages enter history around 400 BC, they were already split into several language groups, and spread over much of Western continental Europe, the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
, Ireland and Britain.
Some scholars think that the Urnfield culture of Western Middle Europe represents an origin for the Celts as a distinct cultural branch of the Indo-European family. This culture was preeminent in central Europe during the late Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
, from ca.
Circa
Circa , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date...
1200 BC until 700 BC, itself following the Unetice
Unetice culture
Unetice; or more properly Únětice culture ; is the name given to an early Bronze Age culture, preceded by the Beaker culture and followed by the Tumulus culture. It was named after finds at site in Únětice, northwest of Prague. It is focused around the Czech Republic, southern and central Germany,...
and Tumulus cultures. The Urnfield period saw a dramatic increase in population in the region, probably due to innovations in technology and agricultural practices
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
. The Greek historian Ephoros
Ephorus
Ephorus or Ephoros , of Cyme in Aeolia, in Asia Minor, was an ancient Greek historian. Information on his biography is limited; he was the father of Demophilus, who followed in his footsteps as a historian, and to Plutarch's claim that Ephorus declined Alexander the Great's offer to join him on his...
of Cyme in Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
, writing in the 4th century BC, believed that the Celts came from the islands off the mouth of the Rhine and were "driven from their homes by the frequency of wars and the violent rising of the sea".
The spread of iron-working
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
led to the development of the Hallstatt culture
Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Central European culture from the 8th to 6th centuries BC , developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of Central Europe by the La Tène culture.By the 6th century BC, the Hallstatt culture extended for some...
directly from the Urnfield (ca.
Circa
Circa , usually abbreviated c. or ca. , means "approximately" in the English language, usually referring to a date...
700 to 500 BC). Proto-Celtic, the latest common ancestor
Common descent
In evolutionary biology, a group of organisms share common descent if they have a common ancestor. There is strong quantitative support for the theory that all living organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor....
of all known Celtic languages, is considered by this school of thought to have been spoken at the time of the late Urnfield or early Hallstatt cultures, in the early 1st millennium BC. The spread of the Celtic languages to Iberia, Ireland and Britain would have occurred during the first half of the 1st millennium BC, the earliest chariot burial
Chariot burial
Chariot burials are tombs in which the deceased was buried together with his chariot, usually including his horses and other possessions....
s in Britain dating to c. 500 BC. Other scholars see Celtic languages as covering Britain and Ireland, and parts of the Continent, long before any evidence of "Celtic" culture is found in archaeology. Over the centuries the language(s) developed into the separate Celtiberian
Celtiberian language
Celtiberian is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula lyingbetween the headwaters of the Duero, Tajo, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebro river...
, Goidelic and Brythonic languages
Brythonic languages
The Brythonic or Brittonic languages form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family, the other being Goidelic. The name Brythonic was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word Brython, meaning an indigenous Briton as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael...
.
The Hallstatt culture was succeeded by the La Tène culture of central Europe, which was overrun by the Roman Empire, though traces of La Tène style are still to be seen in Gallo-Roman artefacts. In Britain and Ireland La Tène style in art survived precariously to re-emerge in Insular art
Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, is the style of art produced in the post-Roman history of Ireland and Great Britain. The term derives from insula, the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style different from that of the rest of Europe...
. Early Irish literature
Irish literature
For a comparatively small island, Ireland has made a disproportionately large contribution to world literature. Irish literature encompasses the Irish and English languages.-The beginning of writing in Irish:...
casts light on the flavour and tradition of the heroic warrior elites who dominated Celtic societies. Celtic river-names are found in great numbers around the upper reaches of the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
and Rhine, which led many Celtic scholars to place the ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis is the process by which a group of human beings comes to be understood or to understand themselves as ethnically distinct from the wider social landscape from which their grouping emerges...
of the Celts in this area.
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
and Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
both suggest that the Celtic heartland was in southern France
Southern France
Southern France , colloquially known as le Midi is defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Gironde, Spain, the Mediterranean, and Italy...
. The former says that the Gauls were to the north of the Celts but that the Romans referred to both as Gauls. Before the discoveries at Hallstatt and La Tene, it was generally considered that the Celtic heartland was southern France, see Encyclopædia Britannica
Encyclopædia Britannica
The Encyclopædia Britannica , published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia that is available in print, as a DVD, and on the Internet. It is written and continuously updated by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 expert...
for 1813.
Linguistic evidence
The Proto-Celtic languageProto-Celtic language
The Proto-Celtic language, also called Common Celtic, is the reconstructed ancestor language of all the known Celtic languages. Its lexis can be confidently reconstructed on the basis of the comparative method of historical linguistics...
is usually dated to the early European Iron Age. The earliest records of a Celtic language are the Lepontic inscriptions of Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul, in Latin: Gallia Cisalpina or Citerior, also called Gallia Togata, was a Roman province until 41 BC when it was merged into Roman Italy.It bore the name Gallia, because the great body of its inhabitants, after the expulsion of the Etruscans, consisted of Gauls or Celts...
, the oldest of which still predate the La Tène period. Other early inscriptions are Gaulish, appearing from the early La Tène period in inscriptions in the area of Massilia, in the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
. Celtiberian
Celtiberian language
Celtiberian is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula lyingbetween the headwaters of the Duero, Tajo, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebro river...
inscriptions appear comparatively late, after about 200 BC. Evidence of Insular Celtic is available only from about 400 AD, in the form of Primitive Irish Ogham inscriptions
Ogham inscriptions
]There are roughly 400 known ogham inscriptions on stone monuments scattered around the Irish Sea, the bulk of them dating to the 5th and 6th centuries. Their language is predominantly Primitive Irish, but a few examples record fragments of the Pictish language...
.
Besides epigraphical evidence, an important source of information on early Celtic is toponymy
Toponymy
Toponymy is the scientific study of place names , their origins, meanings, use and typology. The word "toponymy" is derived from the Greek words tópos and ónoma . Toponymy is itself a branch of onomastics, the study of names of all kinds...
.
Archaeological evidence

The finding of the prehistoric cemetery of Hallstat in 1846 by Johan Ramsauer and almost ten years later the finding of the archaeological site of La Tène by Hansli Kopp in 1857 draw attention to this area.
The concept that the Hallstatt and La Tene cultures could be seen not just as chronological periods but as “Culture Groups”, entities composed of people of the same ethnicity and language, started to grow by the end of the 19th century. In the beginning of the 20th century the belief that those “Culture Groups” could be thought in racial or ethnic terms was strongly held by Gordon Childe whose theory was influenced by the writings of Gustaf Kossinna
Gustaf Kossinna
Gustaf Kossinna was a linguist and professor of German archaeology at the University of Berlin...
. Along the 20th century the racial ethnic interpretation of La Tene culture rooted much stronger, and any findings of “La Tene culture” and “flat inhumation cemeteries” were directly associated with the celts and the celtic language.
The Iron Age Hallstatt
Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Central European culture from the 8th to 6th centuries BC , developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of Central Europe by the La Tène culture.By the 6th century BC, the Hallstatt culture extended for some...
(c. 800-475 BC) and La Tène
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture was a European Iron Age culture named after the archaeological site of La Tène on the north side of Lake Neuchâtel in Switzerland, where a rich cache of artifacts was discovered by Hansli Kopp in 1857....
(c. 500-50 BC) cultures are typically associated with Proto-Celtic and Celtic culture.
In various academic disciplines the Celts were considered a Central European Iron Age phenomenon, through the cultures of Hallstatt and La Tène. However, archaeological finds from the Halstatt and La Tène culture were rare in the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern France, northern and western Britain, southern Ireland and Galatia and did not provide enough evidence for a cultural scenario comparable to that of Central Europe. It is considered equally difficult to maintain that the origin of the Peninsular Celts can be linked to the preceding Urnfield culture, leading to a more recent approach that introduces a 'proto-Celtic' substratum and a process of Celticisation having its initial roots in the Bronze Age Bell Beaker culture
Beaker culture
The Bell-Beaker culture , ca. 2400 – 1800 BC, is the term for a widely scattered cultural phenomenon of prehistoric western Europe starting in the late Neolithic or Chalcolithic running into the early Bronze Age...
.
The La Tène culture developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC) in eastern France, Switzerland, Austria, southwest Germany, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary. It developed out of the Hallstatt culture without any definite cultural break, under the impetus of considerable Mediterranean influence from Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
, and later Etruscan civilisations. A shift of settlement centres took place in the 4th century.
The western La Tène culture corresponds to historical Celtic Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
. Whether this means that the whole of La Tène culture can be attributed to a unified Celtic people is difficult to assess; archaeologists have repeatedly concluded that language, material culture, and political affiliation
Political party
A political party is a political organization that typically seeks to influence government policy, usually by nominating their own candidates and trying to seat them in political office. Parties participate in electoral campaigns, educational outreach or protest actions...
do not necessarily run parallel. Frey notes that in the 5th century, "burial customs in the Celtic world were not uniform; rather, localised groups had their own beliefs, which, in consequence, also gave rise to distinct artistic expressions". Thus, while the La Tène culture is certainly associated with the Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
, the presence of La Tène artefacts may be due to cultural contact and does not imply the permanent presence of Celtic speakers.
Historical evidence
PolybiusPolybius
Polybius , Greek ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic Period noted for his work, The Histories, which covered the period of 220–146 BC in detail. The work describes in part the rise of the Roman Republic and its gradual domination over Greece...
published a history of Rome
History of Rome
The history of Rome spans 2,800 years of the existence of a city that grew from a small Italian village in the 9th century BC into the centre of a vast civilisation that dominated the Mediterranean region for centuries. Its political power was eventually replaced by that of peoples of mostly...
about 150 BC in which he describes the Gauls of Italy and their conflict with Rome. Pausanias
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias was a Greek traveler and geographer of the 2nd century AD, who lived in the times of Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and Marcus Aurelius. He is famous for his Description of Greece , a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from firsthand observations, and is a crucial link between classical...
in the 2nd century BC says that the Gauls "originally called Celts", "live on the remotest region of Europe on the coast of an enormous tidal sea". Posidonius
Posidonius
Posidonius "of Apameia" or "of Rhodes" , was a Greek Stoic philosopher, politician, astronomer, geographer, historian and teacher native to Apamea, Syria. He was acclaimed as the greatest polymath of his age...
described the southern Gauls about 100 BC. Though his original work is lost it was used by later writers such as Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
. The latter, writing in the early 1st century AD, deals with Britain and Gaul as well as Hispania, Italy and Galatia. Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
wrote extensively about his Gallic Wars
Commentarii de Bello Gallico
Commentarii de Bello Gallico is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting local armies in Gaul that opposed Roman domination.The "Gaul" that Caesar...
in 58-51 BC. Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
wrote about the Celts of Gaul and Britain in his 1st-century history.
Minority views
Martín Almagro GorbeaMartín Almagro Gorbea
Martín Almagro Gorbea is a Spanish prehistorian.Professor in prehistory, Ph.D. in history by the "Universidad Complutense de Madrid" with extraordinary prize....
proposed the origins of the Celts could be traced back to the 3rd millennium BC, seeking the initial roots in the Bell Beaker culture
Beaker culture
The Bell-Beaker culture , ca. 2400 – 1800 BC, is the term for a widely scattered cultural phenomenon of prehistoric western Europe starting in the late Neolithic or Chalcolithic running into the early Bronze Age...
, thus offering the wide dispersion of the Celts throughout western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
, as well as the variability of the different Celtic peoples, and the existence of ancestral traditions an ancient perspective. More recently, John Koch and Barry Cunliffe
Barry Cunliffe
Sir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe, CBE, known professionally as Barry Cunliffe is a former Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford, a position held from 1972 to 2007...
have suggested that Celtic origins lie with the Atlantic Bronze Age
Atlantic Bronze Age
The Atlantic Bronze Age is a cultural complex of the Bronze Age period of approximately 1300–700 BC that includes different cultures in Portugal, Andalusia, Galicia, Armorica and the British Isles.-Trade:...
, roughly contemporaneous with the Hallstatt culture but positioned considerably to the West, extending along the Atlantic coast of Europe.
Stephen Oppenheimer
Stephen Oppenheimer
Stephen Oppenheimer is a British paediatrician, geneticist, and writer. He is a member of Green Templeton College, Oxford and an honorary fellow of Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, and carries out and publishes research in the fields of genetics and human prehistory.-Career:Oppenheimer...
points out that Herodotus seemed to believe the Danube rose near the Pyrenees
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees is a range of mountains in southwest Europe that forms a natural border between France and Spain...
.
Gaul
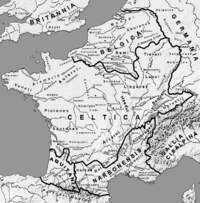
At the dawn of history in Europe, the Celts then living in what is now France were known as Gauls to the Romans. The territory of these peoples probably included the low countries
Low Countries
The Low Countries are the historical lands around the low-lying delta of the Rhine, Scheldt, and Meuse rivers, including the modern countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and parts of northern France and western Germany....
, the Alps and what is now northern Italy. Their descendants were described by Julius Caesar in his Gallic Wars
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were a series of military campaigns waged by the Roman proconsul Julius Caesar against several Gallic tribes. They lasted from 58 BC to 51 BC. The Gallic Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the...
. Eastern Gaul was the centre of the western La Tène culture. In later Iron Age Gaul, the social organisation was similar to that of the Romans, with large towns. From the 3rd century BC the Gauls adopted coinage, and texts with Greek characters are known in southern Gaul from the 2nd century.
Greek traders founded Massalia in about 600 BC, with exchange up the Rhone valley
Rhône River
The Rhone is one of the major rivers of Europe, rising in Switzerland and running from there through southeastern France. At Arles, near its mouth on the Mediterranean Sea, the river divides into two branches, known as the Great Rhone and the Little Rhone...
, but trade was disrupted soon after 500 BC and re-oriented over the Alps to the Po valley in Italy. The Romans
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
arrived in the Rhone valley in the 2nd century BC and encountered a Gaul that was mostly Celtic-speaking. Rome needed land communications with its Iberian provinces and fought a major battle with the Saluvii at Entremont in 124-123 BC. Gradually Roman control extended, and the Roman Province
Roman province
In Ancient Rome, a province was the basic, and, until the Tetrarchy , largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside of Italy...
of Gallia Transalpina
Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in southern France. It was also known as Gallia Transalpina , which was originally a designation for that part of Gaul lying across the Alps from Italia and it contained a western region known as Septimania...
was formed along the Mediterranean coast. The remainder was known as Gallia Comata - "Hairy Gaul".
In 58 BC, the Helvetii planned to migrate westward but were forced back by Julius Caesar. He then became involved in fighting the various tribes in Gaul, and by 55 BC, most of Gaul had been overrun. In 52 BC, Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix was the chieftain of the Arverni tribe, who united the Gauls in an ultimately unsuccessful revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars....
led a revolt against the Roman occupation but was defeated at the siege of Alesia and surrendered.
Following the Gallic Wars of 58-51 BC, Caesar's Celtica formed the main part of Roman Gaul. This territory of the Celtic tribes was bounded on the south by the Garonne and on the north by the Seine and the Marne. Place and personal name analysis and inscriptions suggest that the Gaulish Celtic language was spoken over most of what is now France.
Iberia
Until the end of the 19th century, traditional scholarship dealing with the Celts did acknowledge their presence in the Iberian Peninsula as a material cultureArchaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of artifacts from a specific time and place, which are thought to constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between the artifacts is based on archaeologists' understanding and interpretation and...
relatable to the Hallstatt
Hallstatt
Hallstatt, Upper Austria is a village in the Salzkammergut, a region in Austria. It is located near the Hallstätter See . At the 2001 census it had 946 inhabitants...
and La Tène cultures. However, since according to the definition of the Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
in the 19th century Celtic populations were supposedly rare in Iberia and did not provide a cultural scenario that could easily be linked to that of Central Europe, the presence of celtic culture in that region was generally not fully recognised. Three divisions of the Celts of the Iberian Peninsula were assumed to have existed: the Celtiberians
Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were Celtic-speaking people of the Iberian Peninsula in the final centuries BC. The group used the Celtic Celtiberian language.Archaeologically, the Celtiberians participated in the Hallstatt culture in what is now north-central Spain...
in the mountains near the centre of the peninsula, the Celtici
Celtici
]The Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the provinces of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the...
in the southwest, and the celts in the northwest (in Gallaecia
Gallaecia
Gallaecia or Callaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province and an early Mediaeval kingdom that comprised a territory in the north-west of Hispania...
and Asturias
Asturias
The Principality of Asturias is an autonomous community of the Kingdom of Spain, coextensive with the former Kingdom of Asturias in the Middle Ages...
).
Modern scholarship, however, has clearly proven that Celtic presence and influences were most substantial in what is today Spain and Portugal (with perhaps the highest settlement saturation in Western Europe), particularly in the central, western and northern regions. The Celts in Iberia were divided into two main archaeological and cultural groups, even though that division is not very clear:
- One group was spread out along Galicia and the Iberian Atlantic shoresAtlantic EuropeAtlantic Europe is a geographical and anthropological term for the western portion of Europe which borders the Atlantic Ocean. The term may refer to the idea of Atlantic Europe as a cultural unit and/or as an biogeographical region....
. They were made up of the Proto / Para-Celtic LusitaniansLusitaniansThe Lusitanians were an Indo-European people living in the Western Iberian Peninsula long before it became the Roman province of Lusitania . They spoke the Lusitanian language which might have been Celtic. The modern Portuguese people see the Lusitanians as their ancestors...
(in Portugal) and the Celtic region that StraboStraboStrabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
called CelticaCelticaCeltica: Journal of the School of Celtic Studies is an academic journal devoted to Celtic studies, with particular emphasis on Irish literature, linguistics and placenames. It was founded in 1946 and has since been published by the School of Celtic Studies at the Dublin Institute for Advanced...
in the southwestern Iberian peninsula, including the Algarve, which was inhabited by the CelticiCeltici]The Celtici were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the provinces of Alentejo and the Algarve in Portugal; in the Province of Badajoz and north of Province of Huelva in Spain, in the ancient Baeturia; and along the...
, the VettonesVettonesThe Vettones were one of the pre-Roman Celtic peoples of the Iberian Peninsula .- Origins :...
and Vacceani peoples (of central-western Spain and Portugal), and the GallaeciaGallaeciaGallaecia or Callaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province and an early Mediaeval kingdom that comprised a territory in the north-west of Hispania...
n, Astures and CantabriCantabriThe Cantabri were a pre-Roman Celtic people which lived in the northern Atlantic coastal region of ancient Hispania, from the 4th to late 1st centuries BC.-Origins:...
an peoples of the Castro cultureCastro cultureCastro culture is the archaeological term for naming the Celtic archaeological culture of the northwestern regions of the Iberian Peninsula from the end of the Bronze Age until it was subsumed in local Roman culture...
of northern and northwestern Spain and Portugal. - The CeltiberianCeltiberiansThe Celtiberians were Celtic-speaking people of the Iberian Peninsula in the final centuries BC. The group used the Celtic Celtiberian language.Archaeologically, the Celtiberians participated in the Hallstatt culture in what is now north-central Spain...
group of central Spain and the upper Ebro valley. This group originated when Celts (mainly Gauls and some Celtic-Germanic groups) migrated from what is now France and integrated with the local Iberian peopleIberiansThe Iberians were a set of peoples that Greek and Roman sources identified with that name in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula at least from the 6th century BC...
.
The origins of the Celtiberians might provide a key to understanding the Celticisation process in the rest of the Peninsula. The process of Celticisation of the southwestern area of the peninsula by the Keltoi and of the northwestern area is, however, not a simple Celtiberian question. Recent investigations about the Callaici and Bracari
Bracari
The Bracari were an ancient Celtic tribe of Gallaecia, akin to the Calaicians or Gallaeci, living in the northwest of modern Portugal, in the province of Minho, between the rivers Tâmega and Cávado, around the area of the modern city of Braga .Appian wrote they were a very warlike people...
in northwestern Portugal are providing new approaches to understanding Celtic culture (language, art and religion) in western Iberia.
John T. Koch of the University of Wales-Aberystwyth suggested that Tartessian
Tartessian language
The Tartessian language is the extinct Paleohispanic language of inscriptions in the Southwestern script found in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula: mainly in the south of Portugal , but also in Spain . There are 95 of these inscriptions with the longest having 82 readable signs...
inscriptions of the 8th century BC might already be classified as Celtic. This would mean that Tartessian is the earliest attested trace of Celtic by margin of more than a century.
Alps and Po Valley
It had been known for some time that there was an early, although apparently somewhat limited, Celtic (Lepontic, sometimes called Cisalpine Celtic) presence in Northern ItalyNorthern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
since inscriptions dated to the 6th century BC have been found there.
The site of Golasecca
Golasecca
Golasecca is a town and comune in the province of Varese, Lombardy .It has given its name to the Golasecca culture, a prehistoric civilization who lived in the Ticino River area from the Bronze Age until the 1st century BC....
, where the Ticino
Ticino River
The river Ticino is a left-bank tributary of the Po River. It has given its name to the Swiss canton through which its upper portion flows.-The course:...
exits from Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest of Italy and largest of southern Switzerland. Lake Maggiore is the most westerly of the three great prealpine lakes of Italy, it extends for about 70 km between Locarno and Arona.The climate is mild...
, was particularly suitable for long-distance exchanges, in which Golaseccans acted as intermediaries between Etruscans
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
and the Halstatt culture of Austria, supported on the all-important trade in salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
.
In 391 BC Celts "who had their homes beyond the Alps streamed through the passes in great strength and seized the territory that lay between the Appennine mountains
Apennine mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains or Greek oros but just as often used alone as a noun. The ancient Greeks and Romans typically but not always used "mountain" in the singular to mean one or a range; thus, "the Apennine mountain" refers to the entire chain and is translated "the Apennine...
and the Alps" according to Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
. The Po Valley and the rest of northern Italy (known to the Romans as Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul, in Latin: Gallia Cisalpina or Citerior, also called Gallia Togata, was a Roman province until 41 BC when it was merged into Roman Italy.It bore the name Gallia, because the great body of its inhabitants, after the expulsion of the Etruscans, consisted of Gauls or Celts...
) was inhabited by Celtic-speakers who founded cities such as Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
. Later the Roman army was routed at the battle of Allia
Battle of the Allia
The Battle of the Allia was a battle of the first Gallic invasion of Rome. The battle was fought near the Allia river: the defeat of the Roman army opened the route for the Gauls to sack Rome. It was fought in 390/387 BC.-Background:...
and Rome was sacked in 390 BC by the Senones
Senones
The Senones were an ancient Gaulish tribe.In about 400 BC they crossed the Alps and, having driven out the Umbrians settled on the east coast of Italy from Forlì to Ancona, in the so-called ager Gallicus, and founded the town of Sena Gallica , which became their capital. In 391 BC they invaded...
.
At the battle of Telamon
Battle of Telamon
The Battle of Telamon was fought between the Roman Republic and an alliance of Gauls in 225 BC. The Romans, led by the consuls Gaius Atilius Regulus and Lucius Aemilius Papus, defeated the Gauls, thus extending their influence over northern Italy....
in 225 BC a large Celtic army was trapped between two Roman forces and crushed.
The defeat of the combined Samnite
Samnium
Samnium is a Latin exonym for a region of south or south and central Italy in Roman times. The name survives in Italian today, but today's territory comprising it is only a small portion of what it once was. The populations of Samnium were called Samnites by the Romans...
, Celtic and Etruscan alliance by the Romans in the Third Samnite War
Samnite Wars
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars, between the early Roman Republic and the tribes of Samnium, extended over half a century, involving almost all the states of Italy, and ended in Roman domination of the Samnites...
sounded the beginning of the end of the Celtic domination in mainland Europe, but it was not until 192 BC that the Roman armies conquered the last remaining independent Celtic kingdoms in Italy.
Eastward expansion
The Celts also expanded down the DanubeDanube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
river and its tributaries. One of the most influential tribes, the Scordisci
Scordisci
The Scordisci were an Iron Age tribe centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus , Dravus and Danube rivers. They were historically notable from the beginning of the third century BC until the turn of the common era...
, had established their capital at Singidunum
Singidunum
Singidunum is the name for the ancient city in Serbia which became Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It was recorded that a Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the area in the 3rd century BC following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans. The Roman Empire conquered the area in 75 BC and later garrisoned...
in 3rd century BC, which is present-day Belgrade
Belgrade
Belgrade is the capital and largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers, where the Pannonian Plain meets the Balkans. According to official results of Census 2011, the city has a population of 1,639,121. It is one of the 15 largest cities in Europe...
, Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
. The concentration of hill-forts and cemeteries shows a density of population
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
in the Tisza
Tisza
The Tisza or Tisa is one of the main rivers of Central Europe. It rises in Ukraine, and is formed near Rakhiv by the junction of headwaters White Tisa, whose source is in the Chornohora mountains and Black Tisa, which springs in the Gorgany range...
valley of modern-day Vojvodina
Vojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
, Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
, Hungary and into Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
. Expansion into Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
was however blocked by the Dacians
Dacians
The Dacians were an Indo-European people, very close or part of the Thracians. Dacians were the ancient inhabitants of Dacia...
.
Further south, Celts settled in Thrace
Thrace
Thrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
(Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
), which they ruled for over a century, and Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
, where they settled as the Galatia
Galatia
Ancient Galatia was an area in the highlands of central Anatolia in modern Turkey. Galatia was named for the immigrant Gauls from Thrace , who settled here and became its ruling caste in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of...
ns (see also: Gallic Invasion of Greece
Gallic invasion of the Balkans
Gallic groups, originating from the various La Tène chiefdoms, began a south-eastern movement into the Balkan peninsula from the 4th century BC. Although Celtic settlements were concentrated in the western half of the Carpathian basin, there were notable incursions, and settlements, within the...
). Despite their geographical isolation from the rest of the Celtic world, the Galatians maintained their Celtic language for at least 700 years. St Jerome, who visited Ancyra (modern-day Ankara
Ankara
Ankara is the capital of Turkey and the country's second largest city after Istanbul. The city has a mean elevation of , and as of 2010 the metropolitan area in the entire Ankara Province had a population of 4.4 million....
) in 373 AD, likened their language to that of the Treveri
Treveri
The Treveri or Treviri were a tribe of Gauls who inhabited the lower valley of the Moselle from around 150 BCE, at the latest, until their eventual absorption into the Franks...
of northern Gaul.
For Venceslas Kruta, Galatia in central Turkey was an area of dense celtic settlement.
The Boii
Boii
The Boii were one of the most prominent ancient Celtic tribes of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul , Pannonia , in and around Bohemia, and Transalpine Gaul...
tribe gave their name to Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
, Bologna
Bologna
Bologna is the capital city of Emilia-Romagna, in the Po Valley of Northern Italy. The city lies between the Po River and the Apennine Mountains, more specifically, between the Reno River and the Savena River. Bologna is a lively and cosmopolitan Italian college city, with spectacular history,...
and possibly Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, and Celtic artefacts and cemeteries have been discovered further east in what is now Poland and Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
. A celtic coin (Biatec
Biatec
Biatec was the name of a person, presumably a king, who appeared on the Celtic coins minted by the Boii in Bratislava in the 1st century BC. The word Biatec is also used as the name of those coins. In the literature, they are also sometimes referred to as "hexadrachms of the Bratislava type"...
) from Bratislava
Bratislava
Bratislava is the capital of Slovakia and, with a population of about 431,000, also the country's largest city. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia on both banks of the Danube River. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital that borders two independent countries.Bratislava...
's mint was displayed on the old Slovak 5-crown coin.
As there is no archaeological evidence for large scale invasions in some of the other areas, one current school of thought holds that Celtic language and culture spread to those areas by contact rather than invasion. However, the Celtic invasions of Italy and the expedition in Greece and western Anatolia
Gallic invasion of the Balkans
Gallic groups, originating from the various La Tène chiefdoms, began a south-eastern movement into the Balkan peninsula from the 4th century BC. Although Celtic settlements were concentrated in the western half of the Carpathian basin, there were notable incursions, and settlements, within the...
, are well documented in Greek and Latin history.
There are records of Celtic mercenaries in Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
serving the Ptolemies. Thousands were employed in 283-246 BC and they were also in service around 186 BC. They attempted to overthrow Ptolemy II.
Insular Celts
Insular Celtic languages
Insular Celtic languages are those Celtic languages that originated in the British Isles, in contrast to the Continental Celtic languages of mainland Europe and Anatolia. All surviving Celtic languages are from the Insular Celtic group; the Continental Celtic languages are extinct...
, derived from the Celtic languages spoken in Iron Age Britain. They were separated into a Goidelic and a Brythonic
Brythonic languages
The Brythonic or Brittonic languages form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family, the other being Goidelic. The name Brythonic was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word Brython, meaning an indigenous Briton as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael...
branch from an early period.
Linguists have been arguing for many years whether a Celtic language came to Britain and Ireland and then split or whether there were two separate "invasions". The older view of prehistorians was that the Celtic influence in the British Isles was the result of successive invasions from the European continent by diverse Celtic-speaking peoples over the course of several centuries, accounting for the P-Celtic vs. Q-Celtic isogloss. This view is now generally discredited in favour of a phylogenetic Insular Celtic dialect group.
Celtic arrival in Britain is usually taken to correspond to Hallstatt
Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Central European culture from the 8th to 6th centuries BC , developing out of the Urnfield culture of the 12th century BC and followed in much of Central Europe by the La Tène culture.By the 6th century BC, the Hallstatt culture extended for some...
influence and the appearance of chariot burial
Chariot burial
Chariot burials are tombs in which the deceased was buried together with his chariot, usually including his horses and other possessions....
s in what is now England from about the 6th century BC.
Some Iron Age migration does seem to have occurred but the nature of the interactions with the indigenous populations of the isles is unknown. In the late Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
Pryor estimates that the population of Britain and Ireland was between 1 and 1.5 million, upon which a smaller number of Celtic-speaking immigrant populations would have installed themselves as a superstrate.
By about the 6th century (Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain is a term derived from an archaeological label for the material culture of Britain in Late Antiquity: the term "Sub-Roman" was invented to describe the potsherds in sites of the 5th century and the 6th century, initially with an implication of decay of locally-made wares from a...
), most of the inhabitants of the Isles were speaking Celtic languages of either the Goidelic or the Brythonic
Brythonic languages
The Brythonic or Brittonic languages form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family, the other being Goidelic. The name Brythonic was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word Brython, meaning an indigenous Briton as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael...
branch.
After Caesar's conquest of Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
in the 50s BC, some Belgic people seem to have come to central southern Britain. Though there was a tribe called Parisi
Parisi
Parisi is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2004 is 2,170 and the area is 84.852 km². The elevation is 496 m....
in eastern Yorkshire, these were probably a British people with cultural links to the continent. It has been claimed that there were a tribe of Iverni
Iverni
The Iverni were a people of early Ireland first mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century Geography as living in the extreme south-west of the island. He also locates a "city" called Ivernis in their territory, and observes that this settlement has the same name as the island as a whole, Ivernia...
in Ireland who spoke a Brythonic language.
In Ireland as in Great Britain, beginning Celtic influence is taken to correspond to the beginning Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
. The adoption of Celtic culture and language was likely a gradual transformation, brought on by cultural exchange with Celtic groups in the mainland or otherwise southwest continental Europe.
Romanisation
Under Caesar the Romans conquered Celtic Gaul, and from ClaudiusClaudius
Claudius , was Roman Emperor from 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, he was the son of Drusus and Antonia Minor. He was born at Lugdunum in Gaul and was the first Roman Emperor to be born outside Italy...
onward the Roman empire absorbed parts of Britain. Roman local government of these regions closely mirrored pre-Roman tribal boundaries, and archaeological finds suggest native involvement in local government.
The native peoples under Roman rule became Romanised and keen to adopt Roman ways. Celtic art had already incorporated classical influences, and surviving Gallo-Roman pieces interpret classical subjects or keep faith with old traditions despite a Roman overlay.
The Roman occupation of Gaul
Roman Gaul
Roman Gaul consisted of an area of provincial rule in the Roman Empire, in modern day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and western Germany. Roman control of the area lasted for less than 500 years....
, and to a lesser extent of Britain
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the part of the island of Great Britain controlled by the Roman Empire from AD 43 until ca. AD 410.The Romans referred to the imperial province as Britannia, which eventually comprised all of the island of Great Britain south of the fluid frontier with Caledonia...
, led to Roman-Celtic syncretism
Syncretism
Syncretism is the combining of different beliefs, often while melding practices of various schools of thought. The term means "combining", but see below for the origin of the word...
. In the case of the continental Celts, this eventually resulted in a language shift
Language shift
Language shift, sometimes referred to as language transfer or language replacement or assimilation, is the progressive process whereby a speech community of a language shifts to speaking another language. The rate of assimilation is the percentage of individuals with a given mother tongue who speak...
to Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin is any of the nonstandard forms of Latin from which the Romance languages developed. Because of its nonstandard nature, it had no official orthography. All written works used Classical Latin, with very few exceptions...
, while the Insular Celts retained their language.
There was also considerable cultural influence exerted by Gaul on Rome, particularly in military matters and horsemanship, as the Gauls often served in the Roman cavalry
Roman cavalry
Roman cavalry refers to the horse mounted forces of the Roman army through the many centuries of its existence.- Early cavalry Roman cavalry (Latin: equites Romani) refers to the horse mounted forces of the Roman army through the many centuries of its existence.- Early cavalry Roman cavalry...
. The Romans adopted the Celtic cavalry sword, the spatha
Spatha
The spatha was a type of straight sword, measuring between , in use throughout first millennium AD Europe, and in the territory of the Roman Empire until about 600 AD. Later swords from 600 AD to 1000 AD are recognizable derivatives, though they are not spathae.The spatha was used in gladiatorial...
, and Epona
Epona
In Gallo-Roman religion, Epona was a protector of horses, donkeys, and mules. She was particularly a goddess of fertility, as shown by her attributes of a patera, cornucopia, ears of grain and the presence of foals in some sculptures suggested that the goddess and her horses were leaders of the...
, the Celtic horse goddess.
Society
To the extent that sources are available, they depict a pre-Christian Celtic social structureSocial structure
Social structure is a term used in the social sciences to refer to patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of the individuals. The usage of the term "social structure" has changed over time and may reflect the various levels of analysis...
based formally on class and kingship. Patron-client relationships similar to those of Roman society are also described by Caesar and others in the Gaul of the 1st century BC.
In the main, the evidence is of tribes being led by kings, although some argue that there is also evidence of oligarchical
Oligarchy
Oligarchy is a form of power structure in which power effectively rests with an elite class distinguished by royalty, wealth, family ties, commercial, and/or military legitimacy...
republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
an forms of government
Form of government
A form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
eventually emerging in areas which had close contact with Rome. Most descriptions of Celtic societies portray them as being divided into three groups: a warrior aristocracy; an intellectual class including professions such as druid
Druid
A druid was a member of the priestly class in Britain, Ireland, and Gaul, and possibly other parts of Celtic western Europe, during the Iron Age....
, poet, and jurist; and everyone else. In historical times, the offices of high and low kings in Ireland and Scotland were filled by election
Election
An election is a formal decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy operates since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the...
under the system of tanistry
Tanistry
Tanistry was a Gaelic system for passing on titles and lands. In this system the Tanist was the office of heir-apparent, or second-in-command, among the Gaelic patrilineal dynasties of Ireland, Scotland and Man, to succeed to the chieftainship or to the kingship.-Origins:The Tanist was chosen from...
, which eventually came into conflict with the feudal principle of primogeniture
Primogeniture
Primogeniture is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn to inherit the entire estate, to the exclusion of younger siblings . Historically, the term implied male primogeniture, to the exclusion of females...
in which succession goes to the first born son.
Little is known of family structure among the Celts. Patterns of settlement varied from decentralised to urban. The popular stereotype of non-urbanised societies settled in hillforts and dun
Dun
Dun is now used both as a generic term for a fort and also for a specific variety of Atlantic roundhouse...
s, drawn from Britain and Ireland (there are about 3,000 hill forts known in Britain) contrasts with the urban settlements present in the core Hallstatt and La Tene areas, with the many significant oppida of Gaul late in the first millennium BC, and with the towns of Gallia Cisalpina
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul, in Latin: Gallia Cisalpina or Citerior, also called Gallia Togata, was a Roman province until 41 BC when it was merged into Roman Italy.It bore the name Gallia, because the great body of its inhabitants, after the expulsion of the Etruscans, consisted of Gauls or Celts...
.
Slavery
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
, as practised by the Celts, was very likely similar to the better documented practice in ancient Greece and Rome
Slavery in antiquity
Slavery in the ancient world, specifically, in Mediterranean cultures, comprised a mixture of debt-slavery, slavery as a punishment for crime, and the enslavement of prisoners of war....
. Slaves were acquired from war, raids, and penal and debt servitude. Slavery was hereditary, though manumission
Manumission
Manumission is the act of a slave owner freeing his or her slaves. In the United States before the passage of the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which abolished most slavery, this often happened upon the death of the owner, under conditions in his will.-Motivations:The...
was possible. The Old Irish word for slave, cacht, and the Welsh term caeth are likely derived from the Latin captus, captive, suggesting that slave trade
History of slavery
The history of slavery covers slave systems in historical perspective in which one human being is legally the property of another, can be bought or sold, is not allowed to escape and must work for the owner without any choice involved...
was an early venue of contact between Latin and Celtic societies. In the Middle Ages, slavery was especially prevalent in the Celtic countries
Celtic nations
The Celtic nations are territories in North-West Europe in which that area's own Celtic languages and some cultural traits have survived.The term "nation" is used in its original sense to mean a people who share a common traditional identity and culture and are identified with a traditional...
. Manumissions were discouraged by law and the word for "female slave", cumal, was used as a general unit of value in Ireland.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the pre-Roman Celtic societies were linked to the network of overland trade route
Trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long distance arteries which may further be connected to several smaller networks of commercial...
s that spanned Eurasia. Archaeologists have discovered large prehistoric trackways crossing bogs in Ireland and Germany. Due to their substantial nature, these are believed to have been created for wheeled transport as part of an extensive roadway system that facilitated trade. The territory held by the Celts contained tin
Tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4...
, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
and gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
. Celtic smiths and metalworkers created weapons and jewellery
Jewellery
Jewellery or jewelry is a form of personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.With some exceptions, such as medical alert bracelets or military dog tags, jewellery normally differs from other items of personal adornment in that it has no other purpose than to...
for international trade
International trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product...
, particularly with the Romans.
The myth that the Celtic monetary system
Monetary system
A monetary system is anything that is accepted as a standard of value and measure of wealth in a particular region.However, the current trend is to use international trade and investment to alter the policy and legislation of individual governments. The best recent example of this policy is the...
consisted of wholly barter is a common one, but is in part false. The monetary system was complex and is still not understood (much like the late Roman coinages), and due to the absence of large numbers of coin items, it is assumed that "proto-money" was used. This is the collective term used to describe bronze items made from the early La Tene period onwards, which were often in the shape of axe
Axe
The axe, or ax, is an implement that has been used for millennia to shape, split and cut wood; to harvest timber; as a weapon; and as a ceremonial or heraldic symbol...
heads, ring
Ring
Ring may refer to:*Ring , a decorative ornament worn on fingers, toes, or around the arm or neck-Computing:* Ring , a layer of protection in computer systems...
s, or bell
Bell (instrument)
A bell is a simple sound-making device. The bell is a percussion instrument and an idiophone. Its form is usually a hollow, cup-shaped object, which resonates upon being struck...
s. Due to the large number of these present in some burials, it is thought they had a relatively high monetary value
Value (economics)
An economic value is the worth of a good or service as determined by the market.The economic value of a good or service has puzzled economists since the beginning of the discipline. First, economists tried to estimate the value of a good to an individual alone, and extend that definition to goods...
, and could be used for "day to day" purchases. Low-value coinages of potin, a bronze alloy with high tin content, were minted in most Celtic areas of the continent and in South-East Britain prior to the Roman conquest of these lands. Higher-value coinages, suitable for use in trade, were minted in gold, silver, and high-quality bronze. Gold coin
Gold coin
A gold coin is a coin made mostly or entirely of gold. Gold has been used for coins practically since the invention of coinage, originally because of gold's intrinsic value...
age was much more common than silver coin
Silver coin
Silver coins are possibly the oldest mass produced form of coinage. Silver has been used as a coinage metal since the times of the Greeks. Their silver drachmas were popular trade coins....
age, despite being worth substantially more, as while there were around 100 mines in Southern Britain and Central France, silver was more rarely mined. This was due partly to the relative sparcity of mines and the amount of effort needed for extraction compared to the profit gained. As the Roman civilisation grew in importance and expanded its trade with the Celtic world, silver and bronze coinage became more common. This coincided with a major increase in gold production in Celtic areas to meet the Roman demand, due to the high value Romans put on the metal. The large number of gold mines in France is thought to be a major reason why Caesar invaded.

Ogham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
script, an Early Medieval alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
, was mostly used in early Christian times in Ireland and Scotland (but also in Wales and England), and was only used for ceremonial purposes such as inscriptions on gravestones. The available evidence is of a strong oral tradition, such as that preserved by bards in Ireland, and eventually recorded by monasteries
Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
. The oldest recorded rhyming poetry in the world is of Irish origin and is a transcription of a much older epic poem
Epic poetry
An epic is a lengthy narrative poem, ordinarily concerning a serious subject containing details of heroic deeds and events significant to a culture or nation. Oral poetry may qualify as an epic, and Albert Lord and Milman Parry have argued that classical epics were fundamentally an oral poetic form...
, leading some scholars to claim that the Celts invented rhyme
Rhyme
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words and is most often used in poetry and songs. The word "rhyme" may also refer to a short poem, such as a rhyming couplet or other brief rhyming poem such as nursery rhymes.-Etymology:...
. Celtic art also produced a great deal of intricate and beautiful metalwork, examples of which have been preserved by their distinctive burial rites.
In some regards the Atlantic Celts were conservative: for example, they still used chariot
Chariot
The chariot is a type of horse carriage used in both peace and war as the chief vehicle of many ancient peoples. Ox carts, proto-chariots, were built by the Proto-Indo-Europeans and also built in Mesopotamia as early as 3000 BC. The original horse chariot was a fast, light, open, two wheeled...
s in combat long after they had been reduced to ceremonial roles by the Greeks and Romans. However, despite being outdated, Celtic chariot tactics
Chariot tactics
The first depictions of four-wheeled wagons pulled by semi-domesticated onagers and other available animals come from the Sumerians.Against infantry the fast chariots used tactics of wearing down the enemy by missile fire, deploying heavy troops and running down enemies.The next step was towards...
were able to repel the invasion of Britain attempted by Julius Caesar.
According to Diodorus Siculus:
Clothing
During the later Iron Age the Gauls generally wore long-sleeved shirts or tunicTunic
A tunic is any of several types of clothing for the body, of various lengths reaching from the shoulders to somewhere between the hips and the ankles...
s and long trousers (called braccae
Braccae
Braccae is the Latin term for trousers, and in this context is today used to refer to a style of pants, made from wool. The Romans encountered this style of clothing among peoples whom they called Galli...
by the Romans). Clothes were made of wool
Wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and certain other animals, including cashmere from goats, mohair from goats, qiviut from muskoxen, vicuña, alpaca, camel from animals in the camel family, and angora from rabbits....
or linen
Linen
Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. Linen is labor-intensive to manufacture, but when it is made into garments, it is valued for its exceptional coolness and freshness in hot weather....
, with some silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
being used by the rich. Cloak
Cloak
A cloak is a type of loose garment that is worn over indoor clothing and serves the same purpose as an overcoat; it protects the wearer from the cold, rain or wind for example, or it may form part of a fashionable outfit or uniform. Cloaks are as old as human history; there has nearly always been...
s were worn in the winter. Brooch
Brooch
A brooch ; also known in ancient times as a fibula; is a decorative jewelry item designed to be attached to garments. It is usually made of metal, often silver or gold but sometimes bronze or some other material...
es and armlets were used, but the most famous item of jewellery was the torc
Torc
A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large, usually rigid, neck ring typically made from strands of metal twisted together. The great majority are open-ended at the front, although many seem designed for near-permanent wear and would have been difficult to remove. Smaller torcs worn around...
, a neck collar of metal, sometimes gold. The horned Waterloo Helmet
Waterloo Helmet
The Waterloo Helmet is a pre-Roman Celtic bronze ceremonial horned helmet with repoussé decoration in the La Tène style, dating to c.150–50 BC, that was found in 1868 in the River Thames by Waterloo Bridge in London, England...
in the British Museum
British Museum
The British Museum is a museum of human history and culture in London. Its collections, which number more than seven million objects, are amongst the largest and most comprehensive in the world and originate from all continents, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its...
, which long set the standard for modern images of Celtic warriors, is in fact a unique survival, and may have been a piece for ceremonial rather than military wear.
Gender and sexual norms

Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
, most "belligerent nations" were strongly influenced by their women, but the Celts were unusual because their men openly preferred male lovers (Politics
Politics (Aristotle)
Aristotle's Politics is a work of political philosophy. The end of the Nicomachean Ethics declared that the inquiry into ethics necessarily follows into politics, and the two works are frequently considered to be parts of a larger treatise, or perhaps connected lectures, dealing with the...
II 1269b). H. D. Rankin in Celts and the Classical World notes that "Athenaeus echoes this comment (603a) and so does Ammianus
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus was a fourth-century Roman historian. He wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Antiquity...
(30.9). It seems to be the general opinion of antiquity." In book XIII of his Deipnosophists
Deipnosophistae
The Deipnosophistae may be translated as The Banquet of the Learned or Philosophers at Dinner or The Gastronomers...
, the Roman Greek rhetorician and grammarian Athenaeus
Athenaeus
Athenaeus , of Naucratis in Egypt, Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourished about the end of the 2nd and beginning of the 3rd century AD...
, repeating assertions made by Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
in the 1st century BC (Bibliotheca historica
Bibliotheca historica
Bibliotheca historica , is a work of universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, and describe the history and culture of Egypt , of Mesopotamia, India, Scythia, and Arabia , of North...
5:32), wrote that Celtic women were beautiful but that the men preferred to sleep together. Diodorus went further, stating that "the young men will offer themselves to strangers and are insulted if the offer is refused". Rankin argues that the ultimate source of these assertions is likely to be Poseidonius and speculates that these authors may be recording male "bonding rituals".
The sexual freedom
Sexual norm
A sexual norm can refer to a personal or a social norm. Most cultures have social norms regarding sexuality, and define normal sexuality to consist only of certain legal sex acts between individuals who meet specific criteria of age, consanguinity , race/ethnicity A sexual norm can refer to a...
of women in Britain was noted by Cassius Dio:
There are instances recorded where women participated both in warfare and in kingship, although they were in the minority in these areas. Plutarch
Plutarch
Plutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
reports that Celtic women acted as ambassadors to avoid a war among Celts chiefdoms in the Po valley during the 4th century BC.
Very few reliable sources exist regarding Celtic views towards gender divisions and societal statues, though some archaeological evidence does suggest that their views towards gender role
Gender role
Gender roles refer to the set of social and behavioral norms that are considered to be socially appropriate for individuals of a specific sex in the context of a specific culture, which differ widely between cultures and over time...
s may differ from contemporary and less egalitarian classical counterparts of the roman era.
There are some general indications from Iron Age burial sites in the Champagne and Bourgogne regions of Northeastern France which suggest that women may have had roles in combat during the earlier portions of the La Tène period. However, the evidence is far from conclusive.
Examples of individuals buried with both female jewellery and weaponry have been identified, such as the Vix Grave
Vix Grave
The area around the village of Vix in northern Burgundy, France is the site of an important prehistoric complex from the Celtic Late Hallstatt and Early La Tène periods, comprising an important fortified settlement and several burial mounds. The most famous of the latter, the Vix Grave, also known...
, and there are questions about the sexing of some skeletons that were buried with warrior assemblages. However, it has been suggested that "the weapons may indicate rank instead of masculinity".
Among the insular Celts, there is a greater amount of historic documentation to suggest warrior roles for women. In addition to commentary by Tacitus
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
about Boudica
Boudica
Boudica , also known as Boadicea and known in Welsh as "Buddug" was queen of the British Iceni tribe who led an uprising against the occupying forces of the Roman Empire....
, there are indications from later period histories that also suggest a more substantial role for "women as warriors" in symbolic if not actual roles.
Posidonius
Posidonius
Posidonius "of Apameia" or "of Rhodes" , was a Greek Stoic philosopher, politician, astronomer, geographer, historian and teacher native to Apamea, Syria. He was acclaimed as the greatest polymath of his age...
and Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
described an island of women where men could not venture for fear of death, and where the women ripped each other apart. Other writers, such as Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus was a fourth-century Roman historian. He wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Antiquity...
and Tacitus
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
, mentioned Celtic women inciting, participating in, and leading battles. Poseidonius' anthropological comments on the Celts had common themes, primarily primitivism
Primitivism
Primitivism is a Western art movement that borrows visual forms from non-Western or prehistoric peoples, such as Paul Gauguin's inclusion of Tahitian motifs in paintings and ceramics...
, extreme ferocity, cruel sacrificial practices, and the strength and courage of their women.
Under Brehon Law, which was written down in early Medieval
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to approximately 1000. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages...
Ireland after conversion to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person to some form of Christianity. It has been called the foundational experience of Christian life...
, a woman had the right to divorce her husband and gain his property if he was unable to perform his marital duties due to impotence, obesity, homosexual inclination or preference for other women.
Celtic art
.jpg)
Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, is the style of art produced in the post-Roman history of Ireland and Great Britain. The term derives from insula, the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style different from that of the rest of Europe...
in art history. Both styles absorbed considerable influences from non-Celtic sources, but retained a preference for geometrical decoration over figurative subjects, which are often extremely stylised when they do appear; narrative scenes only appear under outside influence. Energetic circular forms, triskeles and spirals are characteristic. Much of the surviving material is in precious metal, which no doubt gives a very unrepresentative picture, but apart from Pictish stones
Pictish stones
Pictish stones are monumental stelae found in Scotland, mostly north of the Clyde-Forth line. These stones are the most visible remaining evidence of the Picts and are thought to date from the 6th to 9th centuries, a period during which the Picts became Christianized...
and the Insular high crosses, large monumental sculpture
Monumental sculpture
The term monumental sculpture is often used in art history and criticism, but not always consistently. It combines two concepts, one of function, and one of size, and may include an element of a third more subjective concept. It is often used for all sculptures that are large...
, even with decorative carving, is very rare; possibly it was originally common in wood.
The interlace patterns that are often regarded as typical of "Celtic art" were in fact introduced to Insular art from the animal Style II of Germanic Migration Period art
Migration Period art
Migration Period art denotes the artwork of the Germanic peoples during the Migration period . It includes the Migration art of the Germanic tribes on the continent, as well the start of the Insular art or Hiberno-Saxon art of the Anglo-Saxon and Celtic fusion in the British Isles...
, though taken up with great skill and enthusiasm by Celtic artists in metalwork and illuminated manuscript
Illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a manuscript in which the text is supplemented by the addition of decoration, such as decorated initials, borders and miniature illustrations...
s. Equally, the forms used for the finest Insular art were all adopted from the Roman world: Gospel book
Gospel Book
The Gospel Book, Evangelion, or Book of the Gospels is a codex or bound volume containing one or more of the four Gospels of the Christian New Testament...
s like the Book of Kells
Book of Kells
The Book of Kells is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New Testament together with various prefatory texts and tables. It was created by Celtic monks ca. 800 or slightly earlier...
and Book of Lindisfarne, chalices like the Ardagh Chalice
Ardagh Chalice
The Ardagh Hoard, best known for the Ardagh Chalice, is a hoard of metalwork from the 8th and 9th centuries, found in 1868 and now in the National Museum of Ireland in Dublin...
and Derrynaflan Chalice
Derrynaflan Chalice
The Derrynaflan Chalice is an 8th- or 9th-century chalice, that was found as part of the Derrynaflan Hoard of five liturgical vessels. The discovery was made on 17 February 1980 near Killenaule, South Tipperary in Ireland...
, and penannular brooches like the Tara Brooch
Tara Brooch
The Tara Brooch is a Celtic brooch of about 700 AD generally considered to be the most impressive of over 50 elaborate Irish brooches to have been discovered...
. These works are from the period of peak achievement of Insular art, which lasted from the 7th to the 9th centuries, before the Viking
Viking
The term Viking is customarily used to refer to the Norse explorers, warriors, merchants, and pirates who raided, traded, explored and settled in wide areas of Europe, Asia and the North Atlantic islands from the late 8th to the mid-11th century.These Norsemen used their famed longships to...
attacks sharply set back cultural life.
In contrast the less well known but often spectacular art of the richest earlier Continental Celts, before they were conquered by the Romans, often adopted elements of Roman, Greek and other "foreign" styles (and possibly used imported craftsmen) to decorate objects that were distinctively Celtic. After the Roman conquests, some Celtic elements remained in popular art, especially Ancient Roman pottery
Ancient Roman pottery
Pottery was produced in enormous quantities in ancient Rome, mostly for utilitarian purposes. It is found all over the former Roman Empire and beyond...
, of which Gaul was actually the largest producer, mostly in Italian styles, but also producing work in local taste, including figurine
Figurine
A figurine is a statuette that represents a human, deity or animal. Figurines may be realistic or iconic, depending on the skill and intention of the creator. The earliest were made of stone or clay...
s of deities and wares painted with animals and other subjects in highly formalised styles. Roman Britain
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the part of the island of Great Britain controlled by the Roman Empire from AD 43 until ca. AD 410.The Romans referred to the imperial province as Britannia, which eventually comprised all of the island of Great Britain south of the fluid frontier with Caledonia...
also took more interest in enamel
Vitreous enamel
Vitreous enamel, also porcelain enamel in U.S. English, is a material made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate by firing, usually between 750 and 850 °C...
than most of the Empire, and its development of champlevé
Champlevé
Champlevé is an enamelling technique in the decorative arts, or an object made by that process, in which troughs or cells are carved or cast into the surface of a metal object, and filled with vitreous enamel. The piece is then fired until the enamel melts, and when cooled the surface of the object...
technique was probably important to the later Medieval art
Medieval art
The medieval art of the Western world covers a vast scope of time and place, over 1000 years of art history in Europe, and at times the Middle East and North Africa...
of the whole of Europe, of which the energy and freedom of Insular decoration was an important element.
Warfare and weapons
Principal sites in Roman Britain, with indication of the Celtic tribes. Tribal warfarePrehistoric warfare
Prehistoric warfare is war conducted in the era before writing, and before the establishments of large social entities like states. Historical warfare sets in with the standing armies of Bronze Age Sumer, but prehistoric warfare may be studied in some societies at much earlier dates.When humans...
appears to have been a regular feature of Celtic societies. While epic literature depicts this as more of a sport focused on raids and hunting rather than organised territorial conquest, the historical record is more of tribes using warfare to exert political control and harass rivals, for economic advantage
Comparative advantage
In economics, the law of comparative advantage says that two countries will both gain from trade if, in the absence of trade, they have different relative costs for producing the same goods...
, and in some instances to conquer territory.
The Celts were described by classical writers such as Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
, Livy
Livy
Titus Livius — known as Livy in English — was a Roman historian who wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people. Ab Urbe Condita Libri, "Chapters from the Foundation of the City," covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome well before the traditional foundation in 753 BC...
, Pausanias
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias was a Greek traveler and geographer of the 2nd century AD, who lived in the times of Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and Marcus Aurelius. He is famous for his Description of Greece , a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from firsthand observations, and is a crucial link between classical...
, and Florus
Florus
Florus, Roman historian, lived in the time of Trajan and Hadrian.He compiled, chiefly from Livy, a brief sketch of the history of Rome from the foundation of the city to the closing of the temple of Janus by Augustus . The work, which is called Epitome de T...
as fighting like "wild beasts", and as hordes. Dionysius
Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Caesar Augustus. His literary style was Attistic — imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime.-Life:...
said that their "manner of fighting, being in large measure that of wild beasts and frenzied, was an erratic procedure, quite lacking in military science
Military science
Military science is the process of translating national defence policy to produce military capability by employing military scientists, including theorists, researchers, experimental scientists, applied scientists, designers, engineers, test technicians, and military personnel responsible for...
. Thus, at one moment they would raise their swords aloft and smite after the manner of wild boars, throwing the whole weight of their bodies into the blow like hewers of wood or men digging with mattocks, and again they would deliver crosswise blows aimed at no target, as if they intended to cut to pieces the entire bodies of their adversaries, protective armour and all". Such descriptions have been challenged by contemporary historians.
Polybius
Polybius
Polybius , Greek ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic Period noted for his work, The Histories, which covered the period of 220–146 BC in detail. The work describes in part the rise of the Roman Republic and its gradual domination over Greece...
(2.33) indicates that the principal Celtic weapon was a long bladed sword
Iron Age sword
Swords made of iron appear from the Early Iron Age , but do not become widespread before the 8th century BC....
which was used for hacking edgewise rather than stabbing. Celtic warriors
Celtic Warriors
The Celtic Warriors were a regional rugby union team from Wales, who played in the Celtic League and Heineken Cup between 2003 and 2004.-History:The Warriors were one of the five original regions of the Welsh Regional Rugby Era...
are described by Polybius and Plutarch as frequently having to cease fighting in order to straighten their sword blades. This claim has been questioned by some archaeologists, who note that Noric steel
Noric steel
Noric steel was a famously high quality steel from Noricum during the time of the Roman Empire.The proverbial hardness of Noric steel is expressed by Ovid: "...durior [...] ferro quod noricus excoquit ignis..." and it was largely used for the weapons of the Roman military.The iron ore was...
, steel produced in Celtic Noricum
Noricum
Noricum, in ancient geography, was a Celtic kingdom stretching over the area of today's Austria and a part of Slovenia. It became a province of the Roman Empire...
, was famous in the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
period and was used to equip the Roman military. However, Radomir Pleiner, in The Celtic Sword (1993) argues that "the metallographic evidence shows that Polybius was right up to a point", as around one third of surviving swords from the period might well have behaved as he describes.
Polybius also asserts that certain of the Celts fought naked, "The appearance of these naked warriors was a terrifying spectacle, for they were all men of splendid physique and in the prime of life." According to Livy this was also true of the Celts of Asia Minor.
Head hunting

Headhunting
Headhunting is the practice of taking a person's head after killing them. Headhunting was practised in historic times in parts of China, India, Nigeria, Nuristan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Borneo, Indonesia, the Philippines, Taiwan, Japan, Micronesia, Melanesia, New Zealand, and the Amazon Basin, as...
. According to Paul Jacobsthal
Paul Jacobsthal
Paul Jacobsthal was a scholar of Greek vase painting and Celtic art. He wrote his dissertation at the University of Bonn under the supervision of Georg Loeschcke...
, "Amongst the Celts the human head
Human head
In human anatomy, the head is the upper portion of the human body. It supports the face and is maintained by the skull, which itself encloses the brain.-Cultural importance:...
was venerated above all else, since the head was to the Celt the soul, centre of the emotions as well as of life itself, a symbol of divinity and of the powers of the other-world." Arguments for a Celtic cult of the severed head include the many sculptured representations of severed heads in La Tène carvings, and the surviving Celtic mythology, which is full of stories of the severed heads of heroes and the saints who carry their decapitated heads
Cephalophore
A cephalophore is a saint who is generally depicted carrying his or her own head; in art, this was usually meant to signify that the subject in question had been martyred by beheading....
, right down to Sir Gawain and the Green Knight, where the Green Knight
Green Knight
The Green Knight is a character in the 14th-century Arthurian poem Sir Gawain and the Green Knight and the related work The Greene Knight. His true name is revealed to be Bercilak de Hautdesert in Sir Gawain, while The Greene Knight names him "Bredbeddle"...
picks up his own severed head after Gawain has struck it off, just as St. Denis carried his head to the top of Montmartre
Montmartre
Montmartre is a hill which is 130 metres high, giving its name to the surrounding district, in the north of Paris in the 18th arrondissement, a part of the Right Bank. Montmartre is primarily known for the white-domed Basilica of the Sacré Cœur on its summit and as a nightclub district...
.
A further example of this regeneration after beheading lies in the tales of Connemara
Connemara
Connemara is a district in the west of Ireland consisting of a broad peninsula between Killary Harbour and Kilkieran Bay in the west of County Galway.-Overview:...
's St. Feichin, who after being beheaded by Viking pirates carried his head to the Holy Well on Omey Island
Omey Island
Omey Island is a tidal island situated near Claddaghduff on the western edge of Connemara in County Galway, Ireland. From the mainland the island is inconspicuous and almost hidden. It is possible to drive or walk across a large sandy strand to the island by following the arrowed signs...
and on dipping the head into the well placed it back upon his neck and was restored to full health.
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus was a Greek historian who flourished between 60 and 30 BC. According to Diodorus' own work, he was born at Agyrium in Sicily . With one exception, antiquity affords no further information about Diodorus' life and doings beyond what is to be found in his own work, Bibliotheca...
, in his 1st century History had this to say about Celtic head-hunting:
In Gods and Fighting Men
Gods and Fighting Men
Gods and Fighting Men - The Story of the Tuatha De Danaan and of the Fianna of Ireland is a collection of tales collated by Lady Augusta Gregory...
, Lady Gregory's Celtic Revival
Celtic Revival
Celtic Revival covers a variety of movements and trends, mostly in the 19th and 20th centuries, which drew on the traditions of Celtic literature and Celtic art, or in fact more often what art historians call Insular art...
translation of Irish mythology
Irish mythology
The mythology of pre-Christian Ireland did not entirely survive the conversion to Christianity, but much of it was preserved, shorn of its religious meanings, in medieval Irish literature, which represents the most extensive and best preserved of all the branch and the Historical Cycle. There are...
, heads of men killed in battle are described in the beginning of the story The Fight With The Fir Bolgs as pleasing to Macha
Macha
Macha is the name of a goddess and several other characters in Irish mythology.Macha can also mean:*The LÉ Macha , a ship in the Irish Naval Service, named for the goddess*The Macha crater in Russia, less than 7000 years old...
, one aspect of the war goddess Morrigu
Morrígan
The Morrígan or Mórrígan , also written as Morrígu or in the plural as Morrígna, and spelt Morríghan or Mór-Ríoghain in Modern Irish, is a figure from Irish mythology who appears to have once been a goddess, although she is not explicitly referred to as such in the texts.The Morrigan is a goddess...
.
Polytheism

Celtic polytheism
Celtic polytheism, commonly known as Celtic paganism, refers to the religious beliefs and practices adhered to by the Iron Age peoples of Western Europe now known as the Celts, roughly between 500 BCE and 500 CE, spanning the La Tène period and the Roman era, and in the case of the Insular Celts...
.
Many Celtic gods are known from texts and inscriptions from the Roman period.
Rites and sacrifices were carried out by priests known as druid
Druid
A druid was a member of the priestly class in Britain, Ireland, and Gaul, and possibly other parts of Celtic western Europe, during the Iron Age....
s. The Celts did not see their gods as having human shapes until late in the Iron Age. Celtic shrine
Shrine
A shrine is a holy or sacred place, which is dedicated to a specific deity, ancestor, hero, martyr, saint, daemon or similar figure of awe and respect, at which they are venerated or worshipped. Shrines often contain idols, relics, or other such objects associated with the figure being venerated....
s were situated in remote areas such as hilltops, groves, and lakes.
Celtic religious patterns were regionally variable; however, some patterns of deity forms, and ways of worshipping these deities, appeared over a wide geographical and temporal range. The Celts worshipped both gods and goddesses. In general, Celtic gods were deities of particular skills, such as the many-skilled Lugh
Lugh
Lug or Lugh is an Irish deity represented in mythological texts as a hero and High King of the distant past. He is known by the epithets Lámhfhada , for his skill with a spear or sling, Ildánach , Samhildánach , Lonnbeimnech and Macnia , and by the...
and Dagda
The Dagda
The Dagda is an important god of Irish mythology. The Dagda is a father-figure and a protector of the tribe. In some texts his father is Elatha, in others his mother is Ethniu. Other texts say that his mother is Danu; while others yet place him as the father of Danu, perhaps due to her...
, while goddesses were associated with natural features, particularly rivers (such as Boann
Boann
Boann or Boand is the Irish mythology goddess of the River Boyne, a river in Leinster, Ireland. According to the Lebor Gabála Érenn she was the daughter of Delbáeth, son of Elada, of the Tuatha Dé Danann. Her husband is variously Nechtan, Elcmar or Nuada. Her lover is the Dagda, by whom she had...
, goddess of the River Boyne
River Boyne
The River Boyne is a river in Leinster, Ireland, the course of which is about long. It rises at Trinity Well, Newbury Hall, near Carbury, County Kildare, and flows towards the Northeast through County Meath to reach the Irish Sea between Mornington, County Meath and Baltray, County Louth. Salmon...
). This was not universal, however, as goddesses such as Brighid
Brigid
In Irish mythology, Brigit or Brighid was the daughter of the Dagda and one of the Tuatha Dé Danann. She was the wife of Bres of the Fomorians, with whom she had a son, Ruadán....
and The Morrígan
Morrígan
The Morrígan or Mórrígan , also written as Morrígu or in the plural as Morrígna, and spelt Morríghan or Mór-Ríoghain in Modern Irish, is a figure from Irish mythology who appears to have once been a goddess, although she is not explicitly referred to as such in the texts.The Morrigan is a goddess...
were associated with both natural features (holy wells
Clootie well
Clootie wells are places of pilgrimage in Celtic areas. They are wells or springs, almost always with a tree growing beside them, where strips of cloth or rags have been left, usually tied to the branches of the tree as part of a healing ritual...
and the River Unius) and skills such as blacksmithing and healing.
Triplicity is a common theme in Celtic cosmology, and a number of deities were seen as threefold. This trait is exhibited by The Three Mothers, a group of goddesses worshipped by many Celtic tribes (with regional variations).
The Celts had literally hundreds of deities, some of which were unknown outside a single family or tribe, while others were popular enough to have a following that crossed lingual and cultural barriers. For instance, the Irish god Lugh, associated with storm
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of an astronomical body's atmosphere, especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather...
s, lightning
Lightning
Lightning is an atmospheric electrostatic discharge accompanied by thunder, which typically occurs during thunderstorms, and sometimes during volcanic eruptions or dust storms...
, and culture, is seen in similar forms as Lugos
Lugos
Lugos is a commune in the Gironde department in Aquitaine in southwestern France.-Population:-See also:*Communes of the Gironde department*Parc naturel régional des Landes de Gascogne-References:*...
in Gaul and Lleu in Wales. Similar patterns are also seen with the continental Celtic horse goddess Epona
Epona
In Gallo-Roman religion, Epona was a protector of horses, donkeys, and mules. She was particularly a goddess of fertility, as shown by her attributes of a patera, cornucopia, ears of grain and the presence of foals in some sculptures suggested that the goddess and her horses were leaders of the...
and what may well be her Irish and Welsh counterparts, Macha
Macha (Irish mythology)
Macha is a goddess of ancient Ireland, associated with war, horses, sovereignty, and the sites of Armagh and Emain Macha in County Armagh, which are named after her...
and Rhiannon
Rhiannon
Rhiannon is a prominent figure in Welsh mythology, mother to the Demetian hero Pryderi and wife to Pwyll . She is probably a reflex of the Celtic Great Queen goddess Rigantona and may also be associated with the horse goddess Epona.She appears in both the first and third branches of the Mabinogi...
, respectively.
Roman reports of the druids mention ceremonies being held in sacred grove
Sacred grove
A sacred grove is a grove of trees of special religious importance to a particular culture. Sacred groves were most prominent in the Ancient Near East and prehistoric Europe, but feature in various cultures throughout the world...
s. La Tène Celts built temples of varying size and shape, though they also maintained shrines at sacred trees and votive pool
Cult (religious practice)
In traditional usage, the cult of a religion, quite apart from its sacred writings , its theology or myths, or the personal faith of its believers, is the totality of external religious practice and observance, the neglect of which is the definition of impiety. Cult in this primary sense is...
s.
Druids fulfilled a variety of roles in Celtic religion, serving as priests and religious officiants, but also as judges, sacrificers, teachers, and lore-keepers. Druids organised and ran religious ceremonies, and they memorised and taught the calendar
Celtic calendar
The Celtic calendar is a compilation of pre-Christian Celtic systems of timekeeping, including the Gaulish Coligny calendar, used by Celtic countries to define the beginning and length of the day, the week, the month, the seasons, quarter days, and festivals....
. Other classes of druids performed ceremonial sacrifices of crops and animals
Animal sacrifice
Animal sacrifice is the ritual killing of an animal as part of a religion. It is practised by many religions as a means of appeasing a god or gods or changing the course of nature...
for the perceived benefit of the community.
Gallic Calendar
The Coligny calendarColigny calendar
The Gaulish Coligny calendar was found in Coligny, Ain, France near Lyon in 1897, along with the head of a bronze statue of a youthful male figure. It is a lunisolar calendar...
, which was found in 1897 in Coligny
Coligny, Ain
Coligny is a commune in the Ain department in eastern France.-Geography:The commune lies near Bourg-en-Bresse; the Solnan forms its southwestern border.-Celtic background:Coligny is famed for its Celtic lunisolar calendar, the "Coligny calendar"...
, Ain
Ain
Ain is a department named after the Ain River on the eastern edge of France. Being part of the region Rhône-Alpes and bordered by the rivers Saône and Rhône, the department of Ain enjoys a privileged geographic situation...
, was engraved on a bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
tablet, preserved in 73 fragments, that originally was 1.48 m wide and 0.9 m high (Lambert p. 111). Based on the style of lettering and the accompanying objects, it probably dates to the end of the 2nd century. It is written in Latin inscriptional capitals, and is in the Gallic language
Gaulish language
The Gaulish language is an extinct Celtic language that was spoken by the Gauls, a people who inhabited the region known as Gaul from the Iron Age through the Roman period...
. The restored tablet contains 16 vertical columns, with 62 months distributed over 5 years.
The French archaeologist J. Monard speculated that it was recorded by druid
Druid
A druid was a member of the priestly class in Britain, Ireland, and Gaul, and possibly other parts of Celtic western Europe, during the Iron Age....
s wishing to preserve their tradition of timekeeping in a time when the Julian calendar
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
was imposed throughout the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. However, the general form of the calendar suggests the public peg calendars (or parapegmata) found throughout the Greek and Roman world.
There were four major festivals in the Gallic Calendar: "Imbolc" on 1 February, possibly linked to the lactation of the ewes and sacred to the Irish Goddess Brigid. "Beltaine" on 1 May, connected to fertility and warmth, possibly linked to the Sun God
Solar deity
A solar deity is a sky deity who represents the Sun, or an aspect of it, usually by its perceived power and strength. Solar deities and sun worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms...
Belenos. "Lúnasa" on 1 August, connected with the harvest and associated with the God Lugh. And finally "Samhain" on 1 November, possibly the start of the year. Two of these festivals, Beltaine and Lúnasa are shown on the Coligny Calendar by sigils, and it is easy to imagine that the first month on the Calendar (Samonios) matches Samhain. However, Imbolc does not seem to be shown at all.
Roman Influence
The Roman invasion of Gaul brought a great deal of Celtic peoples into the Roman Empire. Roman culture had a profound effect on the Celtic tribes which came under the empire's control. Roman influence led to many changes in Celtic religion, the most noticeable of which was the weakening of the druid class, especially religiously; the druids were to eventually disappear altogether. Romano-Celtic deities also began to appear: these deities often had both Roman and Celtic attributes and combined the names of Roman and Celtic deities. Other changes included the adaptation of the Jupiter Pole, a sacred pole which was used throughout Celtic regions of the empire, primarily in the north. Another major change in religious practice was the use of stone monuments to represent gods and goddesses. The Celts had only created wooden idols (including monuments carved into trees, which were known as sacred poles) previously to Roman conquest.Celtic Christianity

Celtic polytheism
Celtic polytheism, commonly known as Celtic paganism, refers to the religious beliefs and practices adhered to by the Iron Age peoples of Western Europe now known as the Celts, roughly between 500 BCE and 500 CE, spanning the La Tène period and the Roman era, and in the case of the Insular Celts...
to Christianity in the 5th century AD. Ireland was converted under missionaries from Britain, such as Patrick
Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick was a Romano-Briton and Christian missionary, who is the most generally recognized patron saint of Ireland or the Apostle of Ireland, although Brigid of Kildare and Colmcille are also formally patron saints....
. Later missionaries from Ireland were a major source of missionary work
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group sent into an area to do evangelism or ministries of service, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care and economic development. The word "mission" originates from 1598 when the Jesuits sent members abroad, derived from the Latin...
in Scotland, Saxon parts of Britain, and central Europe (see Hiberno-Scottish mission
Hiberno-Scottish mission
The Hiberno-Scottish mission was a mission led by Irish and Scottish monks which spread Christianity and established monasteries in Great Britain and continental Europe during the Middle Ages...
). The term Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity or Insular Christianity refers broadly to certain features of Christianity that were common, or held to be common, across the Celtic-speaking world during the Early Middle Ages...
has been applied to the forms of Christianity that took hold in Britain and Ireland at this time, with especial reference to its traditions that were distinct from the rest of Western Christianity. The development of Christianity in Ireland and Britain brought an early medieval renaissance of Celtic art
Celtic art
Celtic art is the art associated with the peoples known as Celts; those who spoke the Celtic languages in Europe from pre-history through to the modern period, as well as the art of ancient peoples whose language is uncertain, but have cultural and stylistic similarities with speakers of Celtic...
between 390 and 1200 AD. Many of the styles now thought of as typically "Celtic" developed in this period, and are found throughout much of Ireland and Britain, including the northeast and far north of Scotland, Orkney and Shetland. Notable works produced during this period include the Book of Kells
Book of Kells
The Book of Kells is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New Testament together with various prefatory texts and tables. It was created by Celtic monks ca. 800 or slightly earlier...
and the Ardagh Chalice
Ardagh Chalice
The Ardagh Hoard, best known for the Ardagh Chalice, is a hoard of metalwork from the 8th and 9th centuries, found in 1868 and now in the National Museum of Ireland in Dublin...
. Antiquarian
Antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary is an aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient objects of art or science, archaeological and historic sites, or historic archives and manuscripts...
interest from the 17th century led to the term Celt being extended, and rising nationalism
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
brought Celtic revival
Celtic Revival
Celtic Revival covers a variety of movements and trends, mostly in the 19th and 20th centuries, which drew on the traditions of Celtic literature and Celtic art, or in fact more often what art historians call Insular art...
s from the 19th century.
See also
- Celtic nationsCeltic nationsThe Celtic nations are territories in North-West Europe in which that area's own Celtic languages and some cultural traits have survived.The term "nation" is used in its original sense to mean a people who share a common traditional identity and culture and are identified with a traditional...
- Celtic languagesCeltic languagesThe Celtic languages are descended from Proto-Celtic, or "Common Celtic"; a branch of the greater Indo-European language family...
- Ethnic groups of Europe
- Modern CeltsModern CeltsA Celtic identity emerged in the "Celtic" nations of Western Europe, following the identification of the native peoples of the Atlantic fringe as "Celts" by Edward Lhuyd in the 18th century and during the course of the 19th-century Celtic Revival, taking the form of ethnic nationalism particularly...
Literature
- Alberro, Manuel and Arnold, Bettina (eds.), e-Keltoi: Journal of Interdisciplinary Celtic Studies, Volume 6: The Celts in the Iberian Peninsula, University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee, Center for Celtic Studies, 2005.
- Collis, John. The Celts: Origins, Myths and Inventions. Stroud: Tempus Publishing, 2003. ISBN 0-7524-2913-2. Historiography of Celtic studies.
- Cunliffe, Barry. The Ancient Celts. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997. ISBN 0-19-815010-5.
- Cunliffe, Barry. Iron Age Britain. London: Batsford, 2004. ISBN 0-7134-8839-5
- Cunliffe, Barry. The Celts: A Very Short Introduction. 2003
- Freeman, Philip MitchellPhilip MitchellPhilip Mitchell is an English author, playwright, poet and translator. Born in Manchester, England he is an established author with BBC Radio Drama and was a question-setter on the UK game show 'Bacha Hi O'Ma!' but is perhaps best known for his acclaimed translation of Caradog Prichard's Welsh...
The Earliest Classical Sources on the Celts: A Linguistic and Historical Study. Diss. Harvard UniversityHarvard UniversityHarvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
, 1994. (link) - Gamito, Teresa J. The Celts in Portugal. In E-Keltoi, Journal of Interdisciplinary Celtic Studies, vol. 6. 2005.
- Haywood, John. Historical Atlas of the Celtic World. 2001.
- Herm, Gerhard. The Celts: The People who Came out of the Darkness. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1977.
- James, Simon. Exploring the World of the Celts 1993.
- James, Simon. The Atlantic Celts - Ancient People Or Modern Invention? Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, August 1999. ISBN 0-299-16674-0.
- James, Simon & Rigby, Valerie. Britain and the Celtic Iron Age. London: British MuseumBritish MuseumThe British Museum is a museum of human history and culture in London. Its collections, which number more than seven million objects, are amongst the largest and most comprehensive in the world and originate from all continents, illustrating and documenting the story of human culture from its...
Press, 1997. ISBN 0-7141-2306-4. - Kruta, V., O. Frey, Barry Raftery and M. Szabo. eds. The Celts. New York: Thames & HudsonThames & HudsonThames & Hudson is a publisher of illustrated books on art, architecture, design, and visual culture. With its headquarters in London, England it has a sister company in New York and subsidiaries in Melbourne, Singapore and Hong Kong...
, 1991. ISBN 0-8478-2193-5. A translation of Les Celtes: Histoire et Dictionnaire 2000. - Laing, Lloyd. The Archaeology of Late Celtic Britain and Ireland c. 400–1200 AD. London: Methuen, 1975. ISBN 0-416-82360-2
- Laing, Lloyd and Jenifer Laing. Art of the Celts, London: Thames and Hudson, 1992 ISBN 0-500-20256-7
- MacKillop, James. A Dictionary of Celtic Mythology. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. ISBN 0-19-280120-1
- Maier, BernhardBernhard MaierBernhard Maier is a German professor of religious studies, who publishes mainly on Celtic culture and religion....
: Celts: A History from Earliest Times to the Present. University of Notre Dame Press 2003. ISBN 978-0268023614 - McEvedy, Colin. The Penguin Atlas of Ancient History. New York: Penguin, 1985. ISBN 0-14-070832-4
- Mallory, J. P. In Search of the Indo-Europeans: Language, Archaeology and Myth. London: Thames and Hudson, 1991. ISBN 0-500-27616-1.
- O'Rahilly, T. F. Early Irish History Dublin Institute for Advanced StudiesDublin Institute for Advanced StudiesThe Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Dublin, Ireland was established in 1940 by the Taoiseach of the time, Éamon de Valera under the . The Institute consists of 3 schools: The , the and the . The directors of these schools are currently Professor Werner Nahm, Professor Luke Drury and...
, 1946. - Powell, T. G. E. The Celts. New York: Thames and Hudson, 1980. third ed. 1997. ISBN 0-500-27275-1.
- Raftery, Barry. Pagan Celtic Ireland: The Enigma of the Irish Iron Age. London: Thames & Hudson, 1994. ISBN 0-500-27983-7.
Additional articles
- Ancient Celtic music - in the CitizendiumCitizendiumCitizendium is an English-language wiki-based free encyclopedia project launched by Larry Sanger, who co-founded Wikipedia in 2001....
- Essays on Celtiberian topics - in e-Keltoi, University of Wisconsin, Madison
- Ancient Celtic Warriors in History
Geography
- An interactive map showing the lands of the Celts between 800BC and 305AD.
- Detailed map of the Pre-Roman Peoples of Iberia (around 200 BC), showing the Celtic territories
- Map of Celtic lands
Multimedia
- Discussion - with academician Barry CunliffeBarry CunliffeSir Barrington Windsor Cunliffe, CBE, known professionally as Barry Cunliffe is a former Professor of European Archaeology at the University of Oxford, a position held from 1972 to 2007...
, on BBC Radio 4BBC Radio 4BBC Radio 4 is a British domestic radio station, operated and owned by the BBC, that broadcasts a wide variety of spoken-word programmes, including news, drama, comedy, science and history. It replaced the BBC Home Service in 1967. The station controller is currently Gwyneth Williams, and the...
's In Our TimeIn Our Time (BBC Radio 4)In Our Time is a live BBC radio discussion series exploring the history of ideas, presented by Melvyn Bragg since 15 October 1998.. It is one of BBC radio's most successful discussion programmes, acknowledged to have "transformed the landscape for serious ideas at peak listening time"...
, February 21, 2002. (Streaming RealplayerRealPlayerRealPlayer is a cross-platform media player by RealNetworks that plays a number of multimedia formats including MP3, MPEG-4, QuickTime, Windows Media, and multiple versions of proprietary RealAudio and RealVideo formats.-History:...
format) - "The Primitive Celts" - part of Terry Jones' Barbarians, June 2006.
Organisations
Special interest
- Related Nordic-Celtic DNA material - at FamilyTreeDNA.com
- http://www.independent.co.uk/news/uk/this-britain/celts-descended-from-spanish-fishermen-study-finds-416727.html

