
EC meter
Encyclopedia

Conductivity (electrolytic)
The conductivity of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is siemens per meter ....
in a solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
. Commonly used in hydroponics
Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants using mineral nutrient solutions, in water, without soil. Terrestrial plants may be grown with their roots in the mineral nutrient solution only or in an inert medium, such as perlite, gravel, mineral wool, or coconut husk.Researchers discovered in the 18th...
, aquaculture
Aquaculture
Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, molluscs and aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the...
and freshwater
Freshwater
Fresh water is naturally occurring water on the Earth's surface in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, bogs, ponds, lakes, rivers and streams, and underground as groundwater in aquifers and underground streams. Fresh water is generally characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and...
systems to monitor the amount of nutrients, salts or impurities in the water.
Principle of operation
The common laboratory conductivity meters employ a potentiometric method and four electrodes. Often, the electrodes are cylindrical and arranged concentrically. The electrodes are usually made of platinum metal. An alternating current is applied to the outer pair of the electrodes. The potential between the inner pair is measured. Conductivity could in principle be determined using the distance between the electrodes and their surface area using the Ohm's lawOhm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
but generally, for accuracy, a calibration is employed using electrolytes of well-known conductivity.
Industrial conductivity probes often employ an inductive method, which has the advantage that the fluid does not wet the electrical parts of the sensor. Here, two inductively-coupled coils are used. One is the driving coil producing a magnetic field and it is supplied with accurately-known voltage. The other forms a secondary coil of a transformer. The liquid passing through a channel in the sensor forms one turn in the secondary winding of the transformer. The induced current is the output of the sensor.
Temperature dependence
The conductivity of a solution is highly temperatureTemperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
dependent, therefore it is important to either use a temperature compensated instrument, or calibrate the instrument at the same temperature as the solution being measured. Unlike metals, the conductivity of common electrolytes typically increases with increasing temperature.
Over a limited temperature range, the way temperature affect conductivity of a solution can be modeled linearly
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
using the following formula:
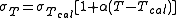
where
- T is the temperature of the sample,
- Tcal is the calibration temperature,
- σT is the electrical conductivity at the temperature T,
- σTcal is the electrical conductivity at the calibration temperature Tcal,
- α is the temperature compensation slope of the solution.
The temperature compensation slope for most naturally occurring water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
s is about 2 %/°C, however it can range between 1 to 3 %/°C. The compensation slope for some common water solutions
Aqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is usually shown in chemical equations by appending aq to the relevant formula, such as NaCl. The word aqueous means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in water...
are listed in the table below.
| Aqueous solution Aqueous solution An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is usually shown in chemical equations by appending aq to the relevant formula, such as NaCl. The word aqueous means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in water... at 25 °C Celsius Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death... |
Concentration (mass percentage) | α (%/°C) |
|---|---|---|
| HCl Hydrochloric acid Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride in water, that is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses. It is found naturally in gastric acid.... |
10 | 1.56 |
| KCl Potassium chloride The chemical compound potassium chloride is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. In its pure state, it is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance, with a crystal structure that cleaves easily in three directions. Potassium chloride crystals are... |
10 | 1.88 |
| H2SO4 Sulfuric acid Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates... |
50 | 1.93 |
| NaCl Sodium chloride Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms... |
10 | 2.14 |
| HF Hydrofluoric acid Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a valued source of fluorine and is the precursor to numerous pharmaceuticals such as fluoxetine and diverse materials such as PTFE .... |
1.5 | 7.20 |
| HNO3 Nitric acid Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming... |
31 | 31 |
See also
- Conductivity factorConductivity FactorThe conductivity factor of dissolved salts in a given solution is a measurement of conductivity. Using the electrical conductivity between two electrodes in a water solution, the level of dissolved solids in that solution can be measured. Measurements can then be used to dose the solution with the...
- Electrical conductivity
- SalinometerSalinometerA salinometer is a device designed to measure the salinity, or dissolved salt content, of a solution.Since the salinity affect both the electrical conductivity and the specific gravity of a solution, a salinometer often consist of an ec meter or hydrometer and some means of converting those...
- Total dissolved solidsTotal dissolved solidsTotal Dissolved Solids is a measure of the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances contained in a liquid in: molecular, ionized or micro-granular suspended form. Generally the operational definition is that the solids must be small enough to survive filtration through a sieve...
- TDS meterTDS meterA TDS Meter indicates the Total Dissolved Solids of a solution, i.e. the concentration of dissolved solids in it. Since dissolved ionized solids such as salts and minerals increase the conductivity of a solution, a TDS meter measures the conductivity of the solution and estimates the TDS from...

