
Early Cyrillic alphabet
Encyclopedia
The Early Cyrillic alphabet is a writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire
in the 9th or 10th century to write the Old Church Slavonic
liturgical language. The modern Cyrillic script is still used primarily for Slavic languages
, and for Asian languages that were under Russian cultural influence during the 20th century.
script, augmented by ligatures and by letters from the Glagolitic alphabet
for consonants not found in Greek. There was no distinction of capital and lowercase letters, though manuscript letters were rendered larger for emphasis, or in various decorative initial and nameplate forms.
Tradition holds that the two Slavic scripts, Glagolitic and Cyrillic, were invented by two brothers, the monks Saint Methodius and Saint Cyril, in the 860s. However, Glagolitic appears to be older, and Cyrillic later. It appears that Glagolitic may have predated the introduction of Christianity, and was only formalized by St Cyril and expanded by him to cover non-Greek sounds, possibly under commission of Boris I
when Christianity was made the official state religion in 864. Cyrillic, on the other hand, may have been a creation of Cyril's students, perhaps at the Preslav Literary School
, who derived it from a more 'dignified' Greek in the 890s as a more suitable script for church books, though retaining Cyril's non-Greek additions from Glagolitic.
Since its creation, the Cyrillic script has adapted to changes in spoken language and developed regional variations to suit the features of national languages. It has been the subject of academic reforms and political decrees. Variations of the Cyrillic script are used to write languages throughout Eastern Europe
and Asia
.
The form of the Russian alphabet underwent a change when Tsar Peter I of Russia
introduced the Civil Script
in 1708. Some letters and breathing marks which were only used for historical reasons were dropped. Medieval letterforms used in typesetting were harmonized with Latin typesetting practices, exchanging medieval forms for Baroque ones, and skipping the western European Renaissance developments. The reform subsequently influenced Cyrillic orthographies for most other languages. Today, the early orthography and typesetting standards only remain in use in Church Slavonic.
A comprehensive repertoire of early Cyrillic characters is included in the Unicode
5.1 standard, published on April 4, 2008. These characters and their distinctive letterforms are represented in specialized computer fonts for Slavistics
.
In addition to the basic letters, there were a number of scribal variations, combining ligatures, and regionalisms used, all of which varied over time.
letter. A titlo
over a sequence of letters indicated their use as a number. See Cyrillic numerals
, Titlo
.
Several diacritic
s, adopted from Polytonic Greek orthography, were also used (these may not appear correctly in all web browsers; they are supposed to be directly above the letter, not off to its upper right):
Punctuation marks:
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state founded in the north-eastern Balkans in c. 680 by the Bulgars, uniting with seven South Slavic tribes...
in the 9th or 10th century to write the Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Church Slavic was the first literary Slavic language, first developed by the 9th century Byzantine Greek missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius who were credited with standardizing the language and using it for translating the Bible and other Ancient Greek...
liturgical language. The modern Cyrillic script is still used primarily for Slavic languages
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
, and for Asian languages that were under Russian cultural influence during the 20th century.
History
The earliest form of manuscript Cyrillic, known as ustav, was based on Greek uncialUncial
Uncial is a majuscule script commonly used from the 3rd to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes. Uncial letters are written in either Greek, Latin, or Gothic.-Development:...
script, augmented by ligatures and by letters from the Glagolitic alphabet
Glagolitic alphabet
The Glagolitic alphabet , also known as Glagolitsa, is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. The name was not coined until many centuries after its creation, and comes from the Old Slavic glagolъ "utterance" . The verb glagoliti means "to speak"...
for consonants not found in Greek. There was no distinction of capital and lowercase letters, though manuscript letters were rendered larger for emphasis, or in various decorative initial and nameplate forms.
Tradition holds that the two Slavic scripts, Glagolitic and Cyrillic, were invented by two brothers, the monks Saint Methodius and Saint Cyril, in the 860s. However, Glagolitic appears to be older, and Cyrillic later. It appears that Glagolitic may have predated the introduction of Christianity, and was only formalized by St Cyril and expanded by him to cover non-Greek sounds, possibly under commission of Boris I
Boris I of Bulgaria
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail and Bogoris was the Knyaz of First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At the time of his baptism in 864, Boris was named Michael after his godfather, Emperor Michael III...
when Christianity was made the official state religion in 864. Cyrillic, on the other hand, may have been a creation of Cyril's students, perhaps at the Preslav Literary School
Preslav Literary School
The Preslav Literary School was the first literary school in the medieval Bulgarian Empire. It was established by Boris I in 885 or 886 in Bulgaria's capital, Pliska...
, who derived it from a more 'dignified' Greek in the 890s as a more suitable script for church books, though retaining Cyril's non-Greek additions from Glagolitic.
Since its creation, the Cyrillic script has adapted to changes in spoken language and developed regional variations to suit the features of national languages. It has been the subject of academic reforms and political decrees. Variations of the Cyrillic script are used to write languages throughout Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
and Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
.
The form of the Russian alphabet underwent a change when Tsar Peter I of Russia
Peter I of Russia
Peter the Great, Peter I or Pyotr Alexeyevich Romanov Dates indicated by the letters "O.S." are Old Style. All other dates in this article are New Style. ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from until his death, jointly ruling before 1696 with his half-brother, Ivan V...
introduced the Civil Script
Reforms of Russian orthography
The reform of Russian orthography refers to changes made to the Russian alphabet over the course of the history of the Russian language.- Early Changes :...
in 1708. Some letters and breathing marks which were only used for historical reasons were dropped. Medieval letterforms used in typesetting were harmonized with Latin typesetting practices, exchanging medieval forms for Baroque ones, and skipping the western European Renaissance developments. The reform subsequently influenced Cyrillic orthographies for most other languages. Today, the early orthography and typesetting standards only remain in use in Church Slavonic.
A comprehensive repertoire of early Cyrillic characters is included in the Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
5.1 standard, published on April 4, 2008. These characters and their distinctive letterforms are represented in specialized computer fonts for Slavistics
Slavistics
Slavic studies or Slavistics is the academic field of area studies concerned with Slavic areas, Slavic languages, literature, history, and culture. Originally, a Slavist or Slavicist was primarily a linguist or philologist who researches Slavistics, a Slavic or Slavonic scholar...
.
Alphabet
| Image | Unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
Name (Cyrillic) |
Name (translit. Transliteration Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another... ) |
Name (IPA) |
Trans. Transliteration Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another... |
IPA | Origin | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| А а A (Cyrillic) A is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents an open front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨a⟩ in "father".The Cyrillic letter A is romanized using the Latin letter A.-History:... |
[azŭ] | a | [a] | Greek alpha Alpha (letter) Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 1. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Aleph... Α |
"I" | |||
| Б б Be (Cyrillic) Be is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It commonly represents the voiced bilabial plosive , like the English pronunciation of ⟨b⟩ in "bee"... |
buky | [buky], [bukŭi] | b | [b] | Derived from below? | "letters" | ||
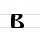 |
В в Ve (Cyrillic) Ve is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiced labiodental fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨v⟩ in "very".... |
vědě | [vædæ] | v | [v] | Greek beta Beta (letter) Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative .... Β |
"know" | |
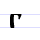 |
Г г Ge (Cyrillic) Ge is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It is also known in some languages as He. In Unicode this letter is called "Ghe".It commonly represents the voiced velar plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨g⟩ in "go".... |
glagoli | [ɡlaɡoli] | g | [ɡ] | Greek gamma Gamma Gamma is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Gimel . Letters that arose from Gamma include the Roman C and G and the Cyrillic letters Ge Г and Ghe Ґ.-Greek:In Ancient Greek, gamma represented a... Γ |
"speak" | |
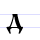 |
Д д De (Cyrillic) De is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.De commonly represents the voiced dental plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨d⟩ in admit.De is romanized using the Latin letter D.-History:... |
dobro | [dobro] | d | [d] | Greek delta Delta (letter) Delta is the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 4. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Dalet... Δ |
"good" | |
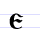 |
Є є Ye (Cyrillic) Ye is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. In some languages this letter is called E.It commonly represents the vowel or , like the pronunciation of ⟨e⟩ in "yes".Ye is romanized using the Latin letter E.... |
estĭ | [ɛstĭ] | e | [ɛ] | Greek epsilon Epsilon Epsilon is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a close-mid front unrounded vowel . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 5. It was derived from the Phoenician letter He... Ε |
"am" or "is" – present tense from "to be" | |
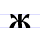 |
Ж ж Zhe (Cyrillic) Zhe is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiced postalveolar fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨s⟩ in "treasure".Zhe is romanized as ⟨zh⟩ or ⟨ž⟩.-History:... |
živěte | [ʒivætɛ] | ž, zh | [ʒ] | Glagolitic zhivete Ⰶ | "live" | |
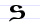 |
Ѕ ѕ / Ꙃ ꙃ Dze Dze is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet, used in the Macedonian language to represent the voiced alveolar affricate , pronounced like ⟨ds⟩ in "pods".... |
dzělo | [dzælo] | dz | [dz] | Greek stigma Stigma (letter) Stigma is a ligature of the Greek letters sigma and tau , which was used in writing Greek between the middle ages and the 19th century. It is also used as a numeral symbol for the number 6... Ϛ (a sigma Sigma Sigma is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, and carries the 'S' sound. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 200. When used at the end of a word, and the word is not all upper case, the final form is used, e.g... -tau Tau Tau is the 19th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 300.The name in English is pronounced , but in modern Greek it is... ligature) |
"very" | |
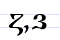 |
З з / Ꙁ ꙁ Ze (Cyrillic) Ze is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiced alveolar fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨z⟩ in "zoo".Ze is romanized using the Latin letter ⟨z⟩.... |
zemlja | [zemlja] | z | [z] | Greek zeta Zeta (letter) Zeta is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Zayin... Ζ |
The first form developed into the second. "earth" | |
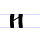 |
И и I (Cyrillic) I is a letter used in almost all ancient and modern Cyrillic alphabets.It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨i⟩ in "machine", or the near-close near-front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨i⟩ in "bin".-History:The Cyrillic letter I was... |
iže | [iʒɛ] | i | [i] | Greek eta Eta (letter) Eta ) is the seventh letter of the Greek alphabet. Originally denoting a consonant /h/, its sound value in the classical Attic dialect of Ancient Greek was a long vowel , raised to in medieval Greek, a process known as itacism.In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 8... Η |
"which" | |
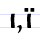 |
І і / Ї ї Yi (Cyrillic) Yi is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It represents the iotated vowel sound , like the pronunciation of ⟨yi⟩ in "playing", and is used in the Rusyn and Ukrainian alphabets.... |
i/ižei | [i, iʒɛi] | i, I | [i] | Greek iota Iota Iota is the ninth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 10. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Yodh . Letters that arose from this letter include the Roman I and J and the Cyrillic І , Yi , Je , and iotified letters .Iota represents... Ι |
"and" | |
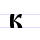 |
К к Ka (Cyrillic) Ka is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless velar plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨k⟩ in "king".-History:... |
kako | [kako] | k | [k] | Greek kappa Κ | "as" | |
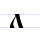 |
Л л El (Cyrillic) El is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.El commonly represents the alveolar lateral approximant , like the pronunciation of ⟨l⟩ in "lip".-Form:... |
ljudije | [ljudijɛ] | l | [l] | Greek lambda Lambda Lambda is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is related to the Phoenician letter Lamed . Letters in other alphabets that stemmed from lambda include the Roman L and the Cyrillic letter El... Λ |
"people" | |
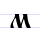 |
М м Em (Cyrillic) Em is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.Em commonly represents the bilabial nasal consonant , like the pronunciation of ⟨m⟩ in "him".It is derived from the Greek letter Mu .... |
myslite | [myslitɛ]~[mŭislitɛ] | m | [m] | Greek mu Mu (letter) Carlos Alberto Vives Restrepo is a Grammy Award and three-time Latin Grammy Award winning-Colombian singer, composer and actor.-Biography:... Μ |
"think" | |
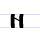 |
Н н En (Cyrillic) En is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the alveolar nasal consonant , like the pronunciation of ⟨n⟩ in "nice".-History:The Cyrillic letter En was derived from the Greek letter Nu .... |
našĭ | [naʃĭ] | n | [n] | Greek nu Nu (letter) Nu , is the 13th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 50... Ν |
"ours" | |
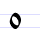 |
О о O (Cyrillic) O is a letter of the Cyrillic script.O commonly represents the close-mid back rounded vowel , like the pronunciation of ⟨o⟩ in "go".-History:The Cyrillic letter O was derived from the Greek letter Omicron .... |
onŭ | [onŭ] | o | [o] | Greek omicron Omicron Omicron is the 15th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 70. It is rarely used in mathematics because it is indistinguishable from the Latin letter O and easily confused with the digit 0... Ο |
"he" or "it" | |
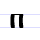 |
П п Pe (Cyrillic) Pe is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless bilabial plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨p⟩ in "pack".-History:... |
pokoi | [pokoj] | p | [p] | Greek pi Pi (letter) Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe , Coptic pi , and Gothic pairthra .The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:... Π |
"peaceful state" | |
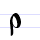 |
Р р Er (Cyrillic) Er is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the alveolar trill , like the "rolled" sound in the Scottish pronunciation of ⟨r⟩ in "curd".-History:... |
rĭci | [rĭtsi] | r | [r] | Greek rho Rho (letter) Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"... Ρ |
"say" | |
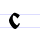 |
С с Es (Cyrillic) Es is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless alveolar fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨s⟩ in "sand".-History:... |
slovo | [slovo] | s | [s] | Greek lunate sigma Ϲ | "word" or "speech" | |
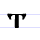 |
Т т Te (Cyrillic) Te is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless alveolar plosive , like the pronunciation of ⟨t⟩ in "tick".-History:... |
tvrdo | [tvr̥do] | t | [t] | Greek tau Tau Tau is the 19th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 300.The name in English is pronounced , but in modern Greek it is... Τ |
"hard" or "surely" | |
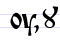 |
Оу оу / Ꙋ ꙋ Uk (Cyrillic) Uk is a letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet. It was originally a digraph of the Cyrillic letters O and U or less frequently O and Izhitsa . To save space, it was often written as a vertical ligature , called "monograph Uk"... |
ukŭ | [ukŭ] | u | [u] | Greek omicron Omicron Omicron is the 15th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 70. It is rarely used in mathematics because it is indistinguishable from the Latin letter O and easily confused with the digit 0... -upsilon Upsilon Upsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw. The name of the letter is pronounced in Modern Greek, and in English , , or... ΟΥ / Ꙋ |
The first form developed into the second, a vertical ligature Ligature (typography) In writing and typography, a ligature occurs where two or more graphemes are joined as a single glyph. Ligatures usually replace consecutive characters sharing common components and are part of a more general class of glyphs called "contextual forms", where the specific shape of a letter depends on... . "learning" |
|
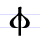 |
Ф ф | frtŭ | [fr̤̥tŭ] | f | [f] | Greek phi Phi (letter) Phi , pronounced or sometimes in English, and in modern Greek, is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greek, it represents , a voiceless labiodental fricative. In Ancient Greek it represented , an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive... Φ |
||
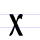 |
Х х Kha Kha or Ha is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless velar fricative , like the Scottish pronunciation of ⟨ch⟩ in "loch".Kha is romanized as ⟨kh⟩.-History:... |
xěrŭ | [xærŭ] | kh | [x] | Greek chi Chi (letter) Chi is the 22nd letter of the Greek alphabet, pronounced as in English.-Greek:-Ancient Greek:Its value in Ancient Greek was an aspirated velar stop .-Koine Greek:... Χ |
||
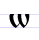 |
Ѡ ѡ Omega (Cyrillic) Omega is a letter used in the early Cyrillic alphabet. Its name and form are derived from the Greek letter Omega .Unlike Greek, the Slavic languages had only a single /o/ sound, so Omega was little used compared to the letter On , descended from the Greek letter Omicron... |
otŭ | [otŭ] | ō, w | [oː] | Greek omega Omega Omega is the 24th and last letter of the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system, it has a value of 800. The word literally means "great O" , as opposed to omicron, which means "little O"... ω |
"from" | |
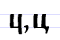 |
Ц ц Tse (Cyrillic) Tse is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless alveolar affricate , like the pronunciation of ⟨ts⟩ in "cats".In English, Tse is commonly romanized as ⟨ts⟩... |
ci | [tsi] | c | [ts] | Glagolitic tsi Ⱌ | ||
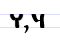 |
Ч ч Che (Cyrillic) Che or Cha is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless postalveolar affricate , like the pronunciation of ⟨ch⟩ in "change".... |
črvĭ | [tʃr̤̥vĭ] | č, ch | [tʃ] | Glagolitic cherv Ⱍ | "worm" | |
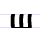 |
Ш ш Sha For other uses, see Sha .Sha is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It commonly represents the voiceless postalveolar fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨sh⟩ in "sheep", or the somewhat similar voiceless retroflex fricative . It is used in every variation of the Cyrillic alphabet, for Slavic and... |
ša | [ʃa] | š, sh | [ʃ] | Glagolitic sha Ⱎ | ||
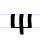 |
Щ щ Shcha (Cyrillic) Shcha is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. In Russian, it represents the voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of ⟨sh⟩ in sheep ; in Ukrainian and Rusyn it represents the consonant cluster ; and in Bulgarian, it represents the consonant cluster .In English, Shcha is... |
šta | [ʃta] | št, sht | [ʃt] | Glagolitic shta Ⱋ | Later analyzed as a Ш-Т ligature by folk etymology | |
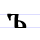 |
Ъ ъ Yer The letter yer of the Cyrillic alphabet, also spelled jer or er, is known as the hard sign in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets and as er golyam in the Bulgarian alphabet... |
jerŭ | [jɛrŭ] | ŭ, u: | [ŭ] | Glagolitic yer Ⱏ | ||
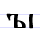 |
Ꙑ ꙑ Yery Yery or Yeru is a letter in the Cyrillic alphabet. It represents the phoneme after non-palatalised consonants in the Belarusian and Russian alphabets... |
jery | [jɛry] | y | [y], or possibly [ŭi] | ЪI or ЪИ ligature | ||
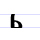 |
Ь ь Soft sign The soft sign , also known as yer, is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short front vowel. As with its companion, the back yer, the vowel phoneme it designated was later partly dropped and partly merged with other vowels... |
jerĭ | [jɛrĭ] | ĭ, i: | [ĭ] | Glagolitic yerj Ⱐ | ||
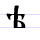 |
Ѣ ѣ Yat Yat or Jat is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet. Its name in Old Church Slavonic is jěd’ or iad’ . In the common scientific Latin transliteration for old Slavic languages, the letter is represented by e with caron: .The yat represented a Common Slavic long vowel... |
jatĭ | [jatĭ] | ě | [æ] | Glagolitic yat Ⱑ ? | ||
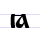 |
Ꙗ ꙗ Ya (Cyrillic) Ya is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet, the civil script variant of Old Cyrillic Little Yus . Among modern Slavonic languages it is used by Russian, Belarusian, Ukrainian and Bulgarian to represent both the combination in initial or post-vocalic position and after a palatalised consonant; in... |
ja | [ja] | ja | [ia] | I-А ligature | ||
 |
Ѥ ѥ E iotified Iotated E is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It is no longer used in any modern language.-History:Iotated E has no equivalent in the Glagolitic alphabet, and probably originated as a ligature of ⟨⟩ and ⟨⟩ to represent [je].... |
je: | [jɛ] | je | [iɛ] | І-Є ligature | ||
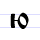 |
Ю ю Yu (Cyrillic) Yu is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. After a palatalized consonant, it represents the close back rounded vowel , somewhat like the pronunciation of ⟨oo⟩ in "boot"; elsewhere it is a so-called iotated vowel representing the combination , like the pronunciation of ⟨you⟩ in "youth"... |
ju | [ju] | ju | [iu] | I-ОУ ligature, dropping У | There was no [jo] sound in early Slavic, so I-ОУ did not need to be distinguished from I-О. | |
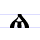 |
Ѧ ѧ | ęsŭ | [ɛ̃sŭ] | ę, ẽ | [ɛ̃] | Glagolitic ens Ⱔ | Called юсъ малый (little yus) in Russian Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... . |
|
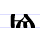 |
Ѩ ѩ | jęsŭ | [jɛ̃sŭ] | ję, jẽ | [jɛ̃] | I-Ѧ ligature | Called юсъ малый йотированный (iotated little yus) in Russian. | |
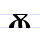 |
Ѫ ѫ | ǫsŭ | [ɔ̃sŭ] | ǫ, õ | [ɔ̃] | Glagolitic ons Ⱘ | Called юсъ большой (big yus) in Russian. | |
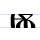 |
Ѭ ѭ | jǫsŭ | [jɔ̃sŭ] | jǫ, jõ | [jɔ̃] | I-Ѫ ligature | Called юсъ большой йотированный (iotated big yus) in Russian. | |
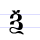 |
Ѯ ѯ Ksi Ksi is a letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet, derived from the Greek letter Xi . It was mainly used in Greek loanwords, especially words relating to the Church.... |
ksi | [ksi] | ks | [ks] | Greek xi Xi Xi is the 14th letter of the Greek alphabet. It is pronounced in Modern Greek, and generally or in English... Ξ |
These last four letters were not needed for Slavic but used to transcribe Greek and as numerals. | |
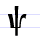 |
Ѱ ѱ Psi (Cyrillic) Psi is a letter in the early Cyrillic alphabet, derived from the Greek letter psi . It represents the sound /ps/, as in English naps... |
psi | [psi] | ps | [ps] | Greek psi Psi (letter) Psi is the 23rd letter of the Greek alphabet and has a numeric value of 700. In both Classical and Modern Greek, the letter indicates the combination /ps/ . The letter was adopted into the Old Italic alphabet, and its shape is continued into the Algiz rune of the Elder Futhark... Ψ |
||
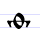 |
Ѳ ѳ Fita Fita is a letter of the Early Cyrillic alphabet. The shape and the name of the letter are derived from the Greek letter Theta .In the Cyrillic numeral system, Fita has a value of 9.- Shape :... |
fita | [fita] | θ, th, T, F | [t]~[θ]~[f] | Greek theta Theta Theta is the eighth letter of the Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician letter Teth... Θ |
||
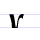 |
Ѵ ѵ Izhitsa Izhitsa is a letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet. It was used to represent ypsilon in words derived from Greek, such as . It represented the same sound /i/ as the normal letter и in Russian... |
ižica | [iʒitsa] | ü, v | [ɪ], [y], [v] | Greek upsilon Upsilon Upsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw. The name of the letter is pronounced in Modern Greek, and in English , , or... Υ |
In addition to the basic letters, there were a number of scribal variations, combining ligatures, and regionalisms used, all of which varied over time.
Numerals, diacritics and punctuation
Each letter had a numeric value also, inherited from the corresponding GreekGreek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
letter. A titlo
Titlo
Titlo is an extended diacritic symbol initially used in old Cyrillic manuscripts, e.g., in Old Church Slavonic and Old East Slavic languages. The word is a borrowing from the Greek "", "title"...
over a sequence of letters indicated their use as a number. See Cyrillic numerals
Cyrillic numerals
The Cyrillic numerals are a numbering system derived from the Cyrillic script, used by South and East Slavic peoples. The system was used in Russia as late as the early 18th century when Peter the Great replaced it with Arabic numerals....
, Titlo
Titlo
Titlo is an extended diacritic symbol initially used in old Cyrillic manuscripts, e.g., in Old Church Slavonic and Old East Slavic languages. The word is a borrowing from the Greek "", "title"...
.
Several diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s, adopted from Polytonic Greek orthography, were also used (these may not appear correctly in all web browsers; they are supposed to be directly above the letter, not off to its upper right):
- tremaUmlaut (diacritic)The diaeresis and the umlaut are diacritics that consist of two dots placed over a letter, most commonly a vowel. When that letter is an i or a j, the diacritic replaces the tittle: ï....
, diaeresis (U+0308) - varia (grave accentGrave accentThe grave accent is a diacritical mark used in written Breton, Catalan, Corsican, Dutch, French, Greek , Italian, Mohawk, Norwegian, Occitan, Portuguese, Scottish Gaelic, Vietnamese, Welsh, Romansh, and other languages.-Greek:The grave accent was first used in the polytonic orthography of Ancient...
), indicating stress on the last syllable (U+0340) - oksia (acute accentAcute accentThe acute accent is a diacritic used in many modern written languages with alphabets based on the Latin, Cyrillic, and Greek scripts.-Apex:An early precursor of the acute accent was the apex, used in Latin inscriptions to mark long vowels.-Greek:...
), indicating a stressed syllable (UnicodeUnicodeUnicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
U+0341) - titloTitloTitlo is an extended diacritic symbol initially used in old Cyrillic manuscripts, e.g., in Old Church Slavonic and Old East Slavic languages. The word is a borrowing from the Greek "", "title"...
, indicating abbreviationAbbreviationAn abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase. Usually, but not always, it consists of a letter or group of letters taken from the word or phrase...
s, or letters used as numeralNumber namesIn linguistics, number names are specific words in a natural language that represent numbers.In writing, numerals are symbols also representing numbers...
s (U+0483) - kamora (circumflex accent), indicating palatalizationPalatalizationIn linguistics, palatalization , also palatization, may refer to two different processes by which a sound, usually a consonant, comes to be produced with the tongue in a position in the mouth near the palate....
(U+0484); in later Church Slavonic, it disambiguates plurals from homophonous singulars. - dasia or dasy pneuma, rough breathing mark (U+0485)
- psili, zvatel'tse, or psilon pneuma, soft breathing mark (U+0486). Signals a word-initial vowel, at least in later Church Slavonic.
- Combined zvatel'tse and varia is called apostrof.
- Combined zvatel'tse and oksia is called iso.
Punctuation marks:
- ano teleia (U+0387), a middle dot used as a word separator
- commaCommaA comma is a type of punctuation mark . The word comes from the Greek komma , which means something cut off or a short clause.Comma may also refer to:* Comma , a type of interval in music theory...
(U+002C) - full stopFull stopA full stop is the punctuation mark commonly placed at the end of sentences. In American English, the term used for this punctuation is period. In the 21st century, it is often also called a dot by young people...
(U+002E) - ArmenianArmenian alphabetThe Armenian alphabet is an alphabet that has been used to write the Armenian language since the year 405 or 406. It was devised by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader, and contained originally 36 letters. Two more letters, օ and ֆ, were added in the Middle Ages...
full stopFull stopA full stop is the punctuation mark commonly placed at the end of sentences. In American English, the term used for this punctuation is period. In the 21st century, it is often also called a dot by young people...
(U+0589), resembling a colonColon (punctuation)The colon is a punctuation mark consisting of two equally sized dots centered on the same vertical line.-Usage:A colon informs the reader that what follows the mark proves, explains, or lists elements of what preceded the mark.... - GeorgianGeorgian alphabetThe Georgian alphabet is the writing system used to write the Georgian language and other Kartvelian languages , and occasionally other languages of the Caucasus such as Ossetic and Abkhaz during the 1940s...
paragraph separator (U+10FB) - triangular colon (U+2056, added in Unicode 4.1)
- diamond colon (U+2058, added in Unicode 4.1)
- quintuple colon (U+2059, added in Unicode 4.1)
- GreekGreek alphabetThe Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
question markQuestion markThe question mark , is a punctuation mark that replaces the full stop at the end of an interrogative sentence in English and many other languages. The question mark is not used for indirect questions...
(U+037E), similar to a semicolonSemicolonThe semicolon is a punctuation mark with several uses. The Italian printer Aldus Manutius the Elder established the practice of using the semicolon to separate words of opposed meaning and to indicate interdependent statements. "The first printed semicolon was the work of ... Aldus Manutius"... - exclamation markExclamation markThe exclamation mark, exclamation point, or bang, or "dembanger" is a punctuation mark usually used after an interjection or exclamation to indicate strong feelings or high volume , and often marks the end of a sentence. Example: “Watch out!” The character is encoded in Unicode at...
(U+0021)
See also
- Relationship of Cyrillic and Glagolitic alphabetsRelationship of Cyrillic and Glagolitic alphabetsThe exact nature of relationship between the Glagolitic and the Cyrillic alphabet has been historically a matter of great controversy and dispute in Slavic studies, especially pertaining to the question of chronological precedence and mutual influence...
- Bosnian CyrillicBosnian CyrillicBosnian Cyrillic or Croatian Cyrillic, widely known as Bosančica, is an extinct Cyrillic script, that originated in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It was widely used in Bosnia and Croatia . Its name in Bosnian and Croatian is bosančica or bosanica, which can literally be translated as Bosnian script...
- Romanian Cyrillic alphabetRomanian Cyrillic alphabetThe Romanian Cyrillic alphabet was used to write the Romanian language before 1860–1862, when it was officially replaced by a Latin-based Romanian alphabet. Cyrillic remained in occasional use until circa 1920...
- Reforms of Russian orthographyReforms of Russian orthographyThe reform of Russian orthography refers to changes made to the Russian alphabet over the course of the history of the Russian language.- Early Changes :...
Sources
- Berdnikov, Alexander and Olga Lapko, , EuroTEX ’99 Proceedings, September 1999
- Birnbaum, David J., , September 28, 2002
- Cubberley, Paul (1996) "The Slavic Alphabets". In Daniels and Bright, below.
- Daniels, Peter T., and William Bright, eds. (1996). The World's Writing Systems. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-507993-0.
- Everson, MichaelMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
and Ralph Cleminson, , September 4, 2003 - Franklin, Simon. 2002. Writing, Society and Culture in Early Rus, c. 950–1300. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-511-03025-8.
- Lev, V., "The history of the Ukrainian script (paleography)", in Ukraine: a concise encyclopædia, volume 1. University of TorontoUniversity of TorontoThe University of Toronto is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, situated on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution of higher learning in Upper Canada...
Press, 1963, 1970, 1982. ISBN 0-8020-3105-6 - Simovyc, V., and J. B. Rudnyckyj, "The history of Ukrainian orthography", in Ukraine: a concise encyclopædia, volume 1 (op cit).
- Zamora, J., Help me learn Church Slavonic
- Azbuka, Church Slavonic calligraphy and typography.
- Obshtezhitie.net, Cyrillic and Glagolitic manuscripts and early printed books.

