Economy of Russia
Encyclopedia
The economy of Russia
is the eleventh largest economy in the world by nominal value and the sixth largest by purchasing power parity
(PPP). Russia has an abundance of natural gas, oil, coal, and precious metals. Russia has undergone significant changes since the collapse of the Soviet Union
, moving from a centrally planned economy
to a more market-based
and globally integrated economy
. Economic reforms in the 1990s privatized most industry, with notable exceptions in the energy and defense-related sectors. Nonetheless, the rapid privatization process, including a much criticized "loans-for-shares" scheme that turned over major state-owned firms to politically connected "oligarchs", has left equity ownership highly concentrated. As of 2011, Russia's capital, Moscow, now has the highest billionaire population of any city in the world.
In late 2008 and early 2009, Russia experienced the first recession after 10 years of rising economy, until the stable growth resumed in late 2009 and 2010. Despite the deep but brief recession, the economy has not been as seriously affected by the global financial crisis compared to much of Europe, largely because of the integration of short-term macroeconomic policies that helped the economy survive.
and investment, thus linking the economy with the rest of the world, was an important aid in reaching these goals. The Gorbachev regime failed to address these fundamental goals. At the time of the Soviet Union's demise, the Yeltsin government of the Russian Republic had begun to attack the problems of macroeconomic stabilization and economic restructuring. By mid-1996, the results were mixed.
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, Russia has tried to develop a market economy
and achieve consistent economic growth. In October 1991, Yeltsin announced that Russia would proceed with radical, market-oriented reform along the lines of "shock therapy
", as recommended by the United States and IMF. However, this policy resulted in economic collapse, with millions being plunged into poverty and corruption and crime spreading rapidly. Hyperinflation
resulted from the removal of Soviet price controls and again following the 1998 Russian financial crisis. Assuming the role as the continuing legal personality of the Soviet Union, Russia took up the responsibility for settling the USSR's external debt
s, even though its population made up just half of the population of the USSR at the time of its dissolution. When once all enterprises belonged to the state and were supposed to be equally owned amongst all citizens, they fell into the hands of a few, who became immensely rich. Stocks of the state-owned enterprises were issued, and these new publicly traded companies were quickly handed to the members of Nomenklatura
or known criminal bosses. For example, the director of a factory during the Soviet regime would often become the owner of the same enterprise. During the same period, violent criminal groups often took over state enterprises, clearing the way by assassinations or extortion. Corruption of government officials became an everyday rule of life. Under the government's cover, outrageous financial manipulations were performed that enriched the narrow group of individuals at key positions of the business and government mafia
. Many took billions in cash and assets outside of the country in an enormous capital flight
. That being said, there were corporate raid
ers such as Andrei Volgin
engaged in hostile takeovers of corrupt corporations by the mid-1990s.
The largest state enterprises were controversially privatized by President Boris Yeltsin to insiders for far less than they were worth. Many Russians consider these infamous "oligarchs
" to be thieves. Through their immense wealth, the oligarchs wielded significant political influence.
 The Russian economy underwent tremendous stress as it moved from a centrally planned economy to a free market system. Difficulties in implementing fiscal reforms aimed at raising government revenues and a dependence on short-term borrowing to finance budget deficits led to a serious financial crisis in 1998. Lower prices for Russia's major export earners (oil and minerals) and a loss of investor confidence due to the Asian financial crisis exacerbated financial problems. The result was a rapid decline in the value of the ruble, flight of foreign investment, delayed payments on sovereign and private debts, a breakdown of commercial transactions through the banking system, and the threat of runaway inflation.
The Russian economy underwent tremendous stress as it moved from a centrally planned economy to a free market system. Difficulties in implementing fiscal reforms aimed at raising government revenues and a dependence on short-term borrowing to finance budget deficits led to a serious financial crisis in 1998. Lower prices for Russia's major export earners (oil and minerals) and a loss of investor confidence due to the Asian financial crisis exacerbated financial problems. The result was a rapid decline in the value of the ruble, flight of foreign investment, delayed payments on sovereign and private debts, a breakdown of commercial transactions through the banking system, and the threat of runaway inflation.
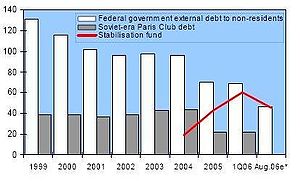
Russia, however, appears to have weathered the crisis relatively well. As of 2009 real GDP increased by the highest percentage since the fall of the Soviet Union at 8.1%, the ruble remains stable, inflation has been moderate, and investment began to increase again. In 2007 the World Bank
declared that the Russian economy had achieved "unprecedented macroeconomic stability". Russia is making progress in meeting its foreign debts obligations. During 2000–01, Russia not only met its external debt services but also made large advance repayments of principal on IMF
loans but also built up Central Bank reserves with government budget
, trade, and current account surpluses. The FY 2002 Russian Government budget assumes payment of roughly $14 billion in official debt service payments falling due. Large current account surpluses have brought a rapid appreciation of the ruble over the past several years. This has meant that Russia has given back much of the terms-of-trade advantage that it gained when the ruble fell by 60% during the debt crisis. Oil and gas dominate Russian exports, so Russia remains highly dependent upon the price of energy. Loan and deposit rates at or below the inflation rate inhibit the growth of the banking system and make the allocation of capital and risk much less efficient than it would be otherwise.
In 2003, the debt has risen to $19 billion due to higher Ministry of Finance and Eurobond payments. However, $1 billion of this has been prepaid, and some of the private sector debt may already have been repurchased. Russia continues to explore debt swap/exchange opportunities.
In the June 2002 G8 Summit, leaders of the eight nations signed a statement agreeing to explore cancellation of some of Russia's old Soviet debt to use the savings for safeguarding materials in Russia that could be used by terrorists. Under the proposed deal, $10 billion would come from the United States and $10 billion from other G-8 countries over 10 years.
On 1 January 2004, the Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation
was established by the Government of Russia
as a part of the federal budget to balance it if oil price falls. Now the Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation
is being modernized. The Stabilization Fund will be divided into two parts on 1 February 2008. The first part will become a reserve fund equal to 10 percent of GDP (10% of GDP equals to about $200 billion now), and will be invested in a similar way as the Stabilization Fund. The second part will be turned into the National Prosperity Fund of Russian Federation. Deputy Finance Minister Sergei Storchak
estimates it will reach 600–700 billion rubles by 1 February 2008. The National Prosperity Fund is to be invested into more risky instruments, including the shares of foreign companies.
Russia's economy saw the nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) double, climbing from 22nd to 11th largest in the world. The economy made real gains of an average 7% per year ( 1999: 6.5%, 2000: 10%, 2001: 5.7%, 2002: 4.9%, 2003: 7.3%, 2004: 7.2%, 2005: 6.4%, 2006: 8,2%, 2007: 8.5%, 2008: 5.2% ), making it the 6th largest economy in the world in GDP(PPP). In 2007, Russia's GDP exceeded that of 1990, meaning it has overcome the devastating consequences of the recession in the 1990s. On a per capita basis, Russian GDP was US$14,919 per individual in 2009, making Russians 38th richest on both a purchasing power and nominal basis.
During Putin's eight years in office, industry grew by 75%, investments increased by 125%, and agricultural production and construction increased as well. Real incomes more than doubled and the average salary increased eightfold from $80 to $640. The volume of consumer credit between 2000–2006 increased 45 times, and during that same time period, the middle class grew from 8 million to 55 million, an increase of 7 times. The number of people living below the poverty line also decreased from 30% in 2000 to 14% in 2008.
Inflation remained a problem however, as the government failed to contain the growth of prices. Between 1999–2007 inflation was kept at the forecast ceiling only twice, and in 2007 the inflation exceeded that of 2006, continuing an upward trend at the beginning of 2008.
The Russian economy is still commodity-driven despite its growth. Payments from the fuel and energy sector in the form of customs duties and taxes accounted for nearly half of the federal budget's revenues. The large majority of Russia's exports are made up by raw materials and fertilizers, although exports as a whole accounted for only 8.7% of the GDP in 2007, compared to 20% in 2000.
There is also a growing gap between rich and poor in Russia. Between 2000–2007 the incomes of the rich grew from approximately 14 times to 17 times larger than the incomes of the poor. The income differentiation ratio shows that the 10% of Russia's rich live increasingly better than the 10% of the poor, amongst whom are mostly pensioners and unskilled workers in depressive regions. (See: Gini Coefficient
)
and microelectronics
; Russia is now the world's third biggest destination for outsourcing software behind India and China. The space launch industry is now the world's second largest behind the European Ariane 5
and nuclear power plant companies are going from strength to strength, selling plants to China and India, and recently signed a joint venture with Toshiba
to develop cutting edge power plants.
The civilian aerospace industry has developed the Sukhoi Superjet
, as well as the upcoming MS-21 project to compete with Boeing
and Airbus
.
The recent global economic downturn hit the Russian economy hard, resulting in three major shocks to Russia's long-term economic growth, though. Oil prices dropped from $140 per barrel to $40 per barrel, a decrease in access to financing with an increase in sovereign and corporate bond spreads, and the reversal of capital flows from $80 billion of in-flows to $130 billion in out-flows have all served to crush fledgling Russian economic growth. In January 2009, industrial production was down almost 16% year to year, fixed capital investment was down 15.5% year to year, and GDP had shrunk 9% year to year. However, in the second quarter the GDP rose by 7.5 percent on a quarterly basis indicating the beginning of economic recovery. Responses to the recovery has been fast – Industrial Production growth remains one of the highest in the world, Billionaires have grown vastly, and Moscow now boasts the highest billionaire population, ahead of New York City. However, a shrinking and aging population, corruption, and deficient infrastructure pose as serious challenges for the Russian economy.
For purchasing power parity comparisons, the US Dollar is exchanged at 13.63 Rubles only. Average wages in 2007 hover around $42–51 per day.
Russia's GDP, estimated at $1,250 billion at 2007 exchange rates, increased by 8.1% in 2007 compared to 2006. Continued average inflation of approximately 10% and strict government budget led to the growth, while lower oil prices and ruble appreciation slowed it. As of November 2007, unemployment in Russia was at 5.9%, down from 10.4% in 2000. Combined unemployment and underemployment
may exceed those figures. Industrial output in 2007 grew by 6.3% compared to 2006, driven by investment growth and private consumption demand.
As of 2005, oil industry and related services account for at least 40 per cent of the gross domestic product of Russia.
As of April 2008, the International Monetary Fund
estimates that Russia's gross domestic product (nominal) will grow from its 2007 value of $1,289,582 million to $3,462,998 million by 2013, a 168% increase. Its GDP PPP is estimated to grow from $2,087,815 to $3,330,623 in the same time, which would make it the second largest economy in Europe in terms of purchasing power
.
", undertakings in agriculture, education, housing and healthcare, will increase by 85 billion roubles over the 2006 figure to 230 billion rubles.
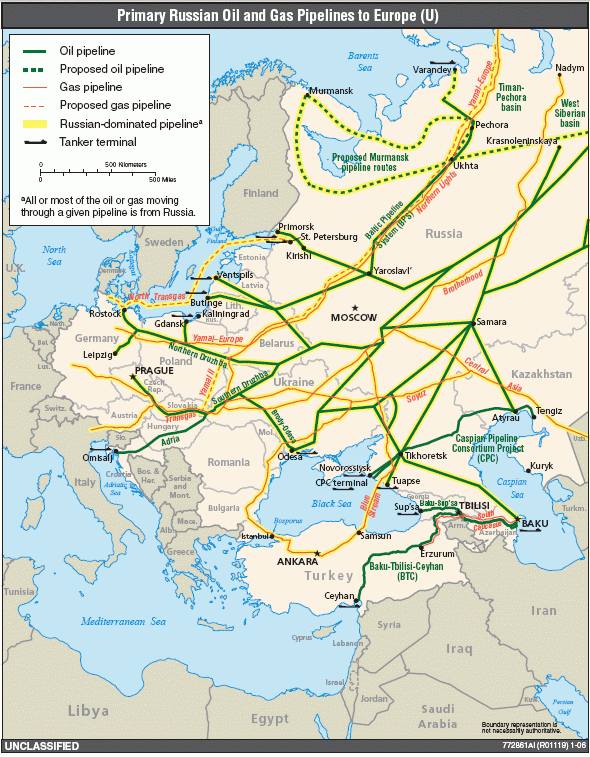 The mineral-packed Ural Mountains
The mineral-packed Ural Mountains
and the vast oil, gas, coal, and timber reserves of Siberia
and the Russian Far East
make Russia rich in natural resources. However, most such resources are located in remote and climatically unfavorable areas that are difficult to develop and far from Russian ports.
Natural resources, especially oil and gas, dominate Russian exports. Oil and gas exports continue to be the main source of hard currency. The petroleum industry in Russia is one of the largest in the world. Russia has the largest reserves, and is the largest exporter, of natural gas. It has the second largest coal reserves, the eighth largest oil reserves, and is the largest in the world exporter of oil in absolute numbers.
Per capita oil production in Russia, though, is not that high. As of 2007, Russia was producing 69.603 bbl/day per 1,000 people, much less than Canada
(102.575 bbl/day), Saudi Arabia
(371.363 bbl/day), or Norway
(554.244 bbl/day), but more than two times more than the USA (28.083 bbl/day), or the UK (27.807 bbl/day).
Russia is also a leading producer and exporter of minerals and gold. Ninety percent of Russian exports to the United States are minerals or other raw materials.
Expecting the area to become more accessible as climate change
melts Arctic ice
, and believing the area contains large reserves of untapped oil and natural gas, on 2 August 2007, Russian explorers, in submersibles, planted the Russian flag on the Arctic seabed, staking a claim to energy sources right up to the North Pole. Reaction to the event was mixed: President Vladimir Putin
congratulated the explorers for "the outstanding scientific project", while Canadian officials stated the expedition was just a public show.
Under the Federal Law "On Continental Shelf Development" upon proposal from the federal agency managing the state fund of mineral resources or its territorial offices the Russian government approves the list of some sections of the mineral resources that are passed for development without any contests and auctions, some sections of federal importance of the Russian continental shelf, some sections of the mineral resources of federal importance that are situated in Russia and stretch out on its continental shelf, some gas deposits of federal importance that are handed over for prospecting and developing the mineral resources under a joint license. The Russian government is also empowered to decide on the handover of the foresaid sections of the mineral resources for development without any contests and auctions.
The Russian fishing industry is the world's fourth-largest, behind Japan, the United States, and China.
. However, years of low investment continue to leave their mark on the industry's capabilities and a lot of its equipment is in need of modernization.
Besides its resource-based industries, Russia has developed large manufacturing capacities, notably in machinery. The defense and aircraft industries are important employers and are able to offer internationally competitive products for export.
and MiG
fighters, air defense systems, helicopter
s, battle tank
s, armored personnel carriers and infantry fighting vehicle
s. The research organization Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies
ranked the air defense system producer Almaz-Antey
as the industry's most successful company in 2007, followed by aircraft-maker Sukhoi
. Almaz-Antey's revenue that year was $3.122 billion, and it had a work force of 81,857 people.
are hoped to revive the fortunes of the civilian aircraft segment. In 2009, companies belonging to the United Aircraft Corporation
delivered 95 new fixed-wing aircraft to its customers, including 15 civilian models. In addition, the industry produced over 141 helicopters. It is one of the most science-intensive hi-tech sectors and employs the largest number of skilled personnel. The production and value of the military aircraft branch far outstrips other defense industry
sectors, and aircraft products make up more than half of the country's arms exports.
consists of over 100 companies and employs 250,000 people. The largest company of the industry is RKK Energia, the main manned space flight contractor. Leading launch vehicle producers are Khrunichev
and TsSKB Progress. Largest satellite developer is Reshetnev Information Satellite Systems, while NPO Lavochkin is the main developer of interplanetary probes.
, directly employing around 600,000 people or 0,7% of the country's total work force. In addition, the industry supports around 2–3 million people in related industries. Russia was the world's 15th largest car producer in 2010, and accounts for about 7% of the worldwide production. In 2009 the industry produced 595,807 light vehicles, down from 1,469,898 in 2008 due to the global financial crisis. The largest companies are light vehicle producers AvtoVAZ
and GAZ
, while KAMAZ
is the leading heavy vehicle producer. 11 foreign carmakers have production operations or are constructing plants in Russia.
, whose products are sold in over 20 countries.
In 2006, there were more than 300 BWA operator networks, accounting for 5% of market share, with dial-up accounting for 30%, and Broadband Fixed Access accounting for the remaining 65%. In December 2006, Tom Phillips, chief government and regulatory affairs officer of the GSM Association
stated:
While there is a lot of interest in a national broadband network, as of January 2007 there still wasn't one.
The financial crisis, which had already hit the country at the end of 2008, caused a sharp reduction of the investments by the business sectors and a notable reduction of IT budget made by government in 2008–2009. As a consequence,the IT market in Russia in 2009 declined by more than 20% in ruble terms and by one third in euro terms. Among the particular segments, the biggest share of the Russian IT market still belongs to hardware.
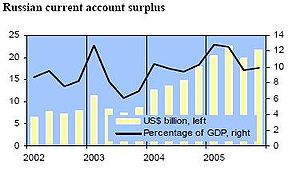 In 1999, exports were up slightly, while imports slumped by 30.5%. As a consequence, the trade surplus ballooned to $33.2 billion, more than double the previous year's level. In 2001, the trend shifted, as exports declined while imports increased. World prices continue to have a major effect on export performance, since commodities, particularly oil, natural gas, metals, and timber
In 1999, exports were up slightly, while imports slumped by 30.5%. As a consequence, the trade surplus ballooned to $33.2 billion, more than double the previous year's level. In 2001, the trend shifted, as exports declined while imports increased. World prices continue to have a major effect on export performance, since commodities, particularly oil, natural gas, metals, and timber
comprise 80% of Russian exports. Ferrous metals exports suffered the most in 2001, declining 7.5%. On the import side, steel and grains dropped by 11% and 61%, respectively.
Most analysts predicted that these trade trends would continue to some extent in 2002. In the first quarter of 2002, import expenditures were up 12%, increased by goods and a rapid rise of travel expenditure. The combination of import duties, a 20% value-added tax and excise taxes on imported goods (especially automobiles, alcoholic beverages, and aircraft) and an import licensing regime for alcohol still restrain demand for imports. Frequent and unpredictable changes in customs regulations also have created problems for foreign and domestic traders and investors. In March 2002, Russia placed a ban on poultry from the United States. In the first quarter of 2002, exports were down 10% as falling income from goods exports was partly compensated for by rising services exports, a trend since 2000. The trade surplus decreased to $7 billion from well over $11 billion the same period last year.
Foreign trade rose 34% to $151.5 billion in the first half of 2005, mainly due to the increase in oil and gas prices which now form 64% of all exports by value. Trade with CIS countries is up 13.2% to $23.3 billion. Trade with the EU forms 52.9%, with the CIS 15.4%, Eurasian Economic Community
7.8% and Asia-Pacific Economic Community 15.9% .
 Trade volume between China and Russia reached $29.1 billion in 2005, an increase of 37.1% compared with 2004. China’s export of machinery and electronic goods to Russia grew 70%, which is 24% of China’s total export to Russia in the first 11 months of 2005. During the same time, China’s export of high-tech products to Russia increased by 58%, and that is 7% of China’s total exports to Russia. Also in this time period border trade between the two countries reached $5.13 billion, growing 35% and accounting for nearly 20% of the total trade. Most of China’s exports to Russia remain apparel and footwear.
Trade volume between China and Russia reached $29.1 billion in 2005, an increase of 37.1% compared with 2004. China’s export of machinery and electronic goods to Russia grew 70%, which is 24% of China’s total export to Russia in the first 11 months of 2005. During the same time, China’s export of high-tech products to Russia increased by 58%, and that is 7% of China’s total exports to Russia. Also in this time period border trade between the two countries reached $5.13 billion, growing 35% and accounting for nearly 20% of the total trade. Most of China’s exports to Russia remain apparel and footwear.
Russia is China’s eighth largest trade partner and China is now Russia’s fourth largest trade partner.
China now has over 750 investment projects in Russia, involving $1.05 billion.
China’s contracted investment in Russia totaled $368 million during January–September 2005, twice that in 2004.
Chinese imports from Russia are mainly those of energy sources, such as crude oil, which is mostly transported by rail, and electricity exports from neighboring Siberian and Far Eastern regions. Exports of both of these commodities are increasing, as Russia opened the Eastern Siberia–Pacific Ocean oil pipeline's branch to China, and Russian power companies are building some of its hydropower stations with a view of future exports to China.
 The IT market is one of the most dynamic sectors of the Russian economy. Russian software exports have risen from just $120 million in 2000 to $1.5 billion in 2006. Since the year 2000 the IT market has demonstrated growth rates of 30–40 percent a year, growing by 54% in 2006 alone. The biggest sector in terms of revenue is system and network integration, which accounts for 28.3% of the total market revenues. Meanwhile the fastest growing segment of the IT market is offshore programming. The industry of software development outsourcing crossed the mark of $1 billion of total revenues in 2005 and reached $1.8 billion in 2006. Market analysts predict this indicator to increase tenfold by 2010. Currently Russia controls 3 percent of the offshore software development market and is the third leading country (after India
The IT market is one of the most dynamic sectors of the Russian economy. Russian software exports have risen from just $120 million in 2000 to $1.5 billion in 2006. Since the year 2000 the IT market has demonstrated growth rates of 30–40 percent a year, growing by 54% in 2006 alone. The biggest sector in terms of revenue is system and network integration, which accounts for 28.3% of the total market revenues. Meanwhile the fastest growing segment of the IT market is offshore programming. The industry of software development outsourcing crossed the mark of $1 billion of total revenues in 2005 and reached $1.8 billion in 2006. Market analysts predict this indicator to increase tenfold by 2010. Currently Russia controls 3 percent of the offshore software development market and is the third leading country (after India
and China) among software exporters. Such growth of software outsourcing in Russia is caused by a number of factors. One of them is the supporting role of the Russian Government
. The Government has launched a program promoting construction of IT-oriented technology parks (Technoparks) – special zones that have an established infrastructure and enjoy a favorable tax and customs regime, in seven different places around the country: Moscow, Novosibirsk, Nizhny Novgorod, Kaluga, Tumen, Republic of Tatarstan and St. Peterburg Regions. Another factor stimulating the IT sector growth in Russia is the presence of global technology corporations such as Intel, Motorola
, Sun Microsystems
, Boeing
, Nortel
and others, which have intensified their software development
activities and opened their R&D centers in Russia.
. As part of the program, during 2007, $5 billion is being invested into a new state corporation, Rosnanotech, that will be responsible for overseeing and coordinating research in the area.
In criticism of the initiative, it has been noted that the Russian nanotech program will receive three times more state funding than the rest of Russia's scientists put together.
Apart from public funding, Mikhail Prokhorov
, a leading Russian metals and banking tycoon, has announced the creation of a $17.5 billion holding company that will focus on high-tech investments, including alternative energy and nanotechnology.
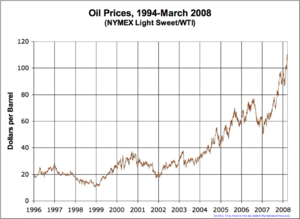 In 1999, investment increased by 4.5%, the first such growth since 1990. Investment growth has continued at high rates from a very low base, with an almost 30% increase in total foreign investments in 2001 compared to the previous year. Higher retained earnings, increased cash transactions, the positive outlook for sales, and political stability have contributed to these favorable trends. Foreign investment in Russia is very low. Cumulative investment from U.S. sources of about $4 billion are about the same as U.S. investment in Costa Rica. Over the medium-to-long term, Russian companies that do not invest to increase their competitiveness will find it harder either to expand exports or protect their recent domestic market gains from higher quality imports.
In 1999, investment increased by 4.5%, the first such growth since 1990. Investment growth has continued at high rates from a very low base, with an almost 30% increase in total foreign investments in 2001 compared to the previous year. Higher retained earnings, increased cash transactions, the positive outlook for sales, and political stability have contributed to these favorable trends. Foreign investment in Russia is very low. Cumulative investment from U.S. sources of about $4 billion are about the same as U.S. investment in Costa Rica. Over the medium-to-long term, Russian companies that do not invest to increase their competitiveness will find it harder either to expand exports or protect their recent domestic market gains from higher quality imports.
Foreign direct investment
, which includes contributions to starting capital and credits extended by foreign co-owners of enterprises, rose slightly in 1999 and 2000, but decreased in 2001 by about 10%. Foreign portfolio investment, which includes shares and securities, decreased dramatically in 1999, but has experienced significant growth since then. In 2001, foreign portfolio investment was $451 million, more than twice the amount from the previous year. Inward foreign investment during the 1990s was dwarfed by Russian capital flight, estimated at about $15 billion annually. During the years of recovery following the 1998 debt crisis, capital flight seems to have slowed. Inward investment from Cyprus and Gibraltar, two important channels for capital flight from Russia in recent years, suggest that some Russian money is returning home.
A significant drawback for investment is the banking sector, which lacks the resources, the capability, and the trust of the population that it would need to attract substantial savings and direct it toward productive investments. Russia's banks contribute only about 3% of overall investment in Russia. While ruble lending has increased since the August 1998 financial crisis, loans are still only 40% of total bank assets. The Central Bank of Russia reduced its refinancing rate five times in 2000, from 55% to 25%, signaling its interest in lower lending rates. Interest on deposits and loans are often below the inflation rate. The poorly developed banking system makes it difficult for entrepreneurs to raise capital and to diversify risk. Banks still perceive commercial lending as risky, and some banks are inexperienced with assessing credit risk.
Money on deposit with Russian banks represents only 7% of GDP. Sberbank
receives preferential treatment from the state and holds 73% of all bank deposits. In March 2002, Sergei Ignatyev replaced Viktor Gerashchenko
as Chairman of the Russian Central Bank. Under his leadership, necessary banking reforms, including stricter accounting procedures and federal deposit insurance, were implemented.
and foreign companies are restricted from owning them. Investments in the so-called Strategic Sectors are defined in a law adopted by the Federal Assembly of Russia
.
with a total known value of 613 bil. USD. The number of deals that happened in 2010 have been 3,662, which is a new record; compared to 2009 this was an increase of 12%. The value of deals in 2010 was US$100 billion, which was the second highest number ever; compared to 2009 this was an increase of 143%.
Key data on the telecommunications market in Russia
Exchange rates
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
is the eleventh largest economy in the world by nominal value and the sixth largest by purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
(PPP). Russia has an abundance of natural gas, oil, coal, and precious metals. Russia has undergone significant changes since the collapse of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, moving from a centrally planned economy
Planned economy
A planned economy is an economic system in which decisions regarding production and investment are embodied in a plan formulated by a central authority, usually by a government agency...
to a more market-based
Market economy
A market economy is an economy in which the prices of goods and services are determined in a free price system. This is often contrasted with a state-directed or planned economy. Market economies can range from hypothetically pure laissez-faire variants to an assortment of real-world mixed...
and globally integrated economy
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
. Economic reforms in the 1990s privatized most industry, with notable exceptions in the energy and defense-related sectors. Nonetheless, the rapid privatization process, including a much criticized "loans-for-shares" scheme that turned over major state-owned firms to politically connected "oligarchs", has left equity ownership highly concentrated. As of 2011, Russia's capital, Moscow, now has the highest billionaire population of any city in the world.
In late 2008 and early 2009, Russia experienced the first recession after 10 years of rising economy, until the stable growth resumed in late 2009 and 2010. Despite the deep but brief recession, the economy has not been as seriously affected by the global financial crisis compared to much of Europe, largely because of the integration of short-term macroeconomic policies that helped the economy survive.
Economic history
The two fundamental and independent goals – macroeconomic stabilization and economic restructuring – are transition from central planning to a market-based economy. The former entailed implementing fiscal and monetary policies that promote economic growth in an environment of stable prices and exchange rates. The latter required establishing the commercial, and institutional entities – banks, private property, and commercial legal codes— that permit the economy to operate efficiently. Opening domestic markets to foreign tradeInternational trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product...
and investment, thus linking the economy with the rest of the world, was an important aid in reaching these goals. The Gorbachev regime failed to address these fundamental goals. At the time of the Soviet Union's demise, the Yeltsin government of the Russian Republic had begun to attack the problems of macroeconomic stabilization and economic restructuring. By mid-1996, the results were mixed.
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, Russia has tried to develop a market economy
Market economy
A market economy is an economy in which the prices of goods and services are determined in a free price system. This is often contrasted with a state-directed or planned economy. Market economies can range from hypothetically pure laissez-faire variants to an assortment of real-world mixed...
and achieve consistent economic growth. In October 1991, Yeltsin announced that Russia would proceed with radical, market-oriented reform along the lines of "shock therapy
Shock therapy (economics)
In economics, shock therapy refers to the sudden release of price and currency controls, withdrawal of state subsidies, and immediate trade liberalization within a country, usually also including large scale privatization of previously public owned assets....
", as recommended by the United States and IMF. However, this policy resulted in economic collapse, with millions being plunged into poverty and corruption and crime spreading rapidly. Hyperinflation
Hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is inflation that is very high or out of control. While the real values of the specific economic items generally stay the same in terms of relatively stable foreign currencies, in hyperinflationary conditions the general price level within a specific economy increases...
resulted from the removal of Soviet price controls and again following the 1998 Russian financial crisis. Assuming the role as the continuing legal personality of the Soviet Union, Russia took up the responsibility for settling the USSR's external debt
External debt
External debt is that part of the total debt in a country that is owed to creditors outside the country. The debtors can be the government, corporations or private households. The debt includes money owed to private commercial banks, other governments, or international financial institutions such...
s, even though its population made up just half of the population of the USSR at the time of its dissolution. When once all enterprises belonged to the state and were supposed to be equally owned amongst all citizens, they fell into the hands of a few, who became immensely rich. Stocks of the state-owned enterprises were issued, and these new publicly traded companies were quickly handed to the members of Nomenklatura
Nomenklatura
The nomenklatura were a category of people within the Soviet Union and other Eastern Bloc countries who held various key administrative positions in all spheres of those countries' activity: government, industry, agriculture, education, etc., whose positions were granted only with approval by the...
or known criminal bosses. For example, the director of a factory during the Soviet regime would often become the owner of the same enterprise. During the same period, violent criminal groups often took over state enterprises, clearing the way by assassinations or extortion. Corruption of government officials became an everyday rule of life. Under the government's cover, outrageous financial manipulations were performed that enriched the narrow group of individuals at key positions of the business and government mafia
Russian Mafia
The Russian Mafia is a name applied to organized crime syndicates in Russia and Ukraine. The mafia in various countries take the name of the country, as for example the Ukrainian mafia....
. Many took billions in cash and assets outside of the country in an enormous capital flight
Capital flight
Capital flight, in economics, occurs when assets and/or money rapidly flow out of a country, due to an economic event and that disturbs investors and causes them to lower their valuation of the assets in that country, or otherwise to lose confidence in its economic...
. That being said, there were corporate raid
Corporate raid
A corporate raid is an American English business term for buying a large interest in a corporation and then using voting rights to enact measures directed at increasing the share value...
ers such as Andrei Volgin
Andrei Volgin
Andrei Olegovich Volgin is a Russian professional football player. He plays in the Russian Second Division for FC Metallurg-Kuzbass Novokuznetsk.-External links:*...
engaged in hostile takeovers of corrupt corporations by the mid-1990s.
The largest state enterprises were controversially privatized by President Boris Yeltsin to insiders for far less than they were worth. Many Russians consider these infamous "oligarchs
Business oligarch
Business oligarch is a near-synonym of the term "business magnate", borrowed by the English speaking and western media from post-Soviet parlance to describe the huge, fast-acquired wealth of some businessmen of the former Soviet republics during the privatization in Russia and other post-Soviet...
" to be thieves. Through their immense wealth, the oligarchs wielded significant political influence.
Recovery

Russia, however, appears to have weathered the crisis relatively well. As of 2009 real GDP increased by the highest percentage since the fall of the Soviet Union at 8.1%, the ruble remains stable, inflation has been moderate, and investment began to increase again. In 2007 the World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
declared that the Russian economy had achieved "unprecedented macroeconomic stability". Russia is making progress in meeting its foreign debts obligations. During 2000–01, Russia not only met its external debt services but also made large advance repayments of principal on IMF
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
loans but also built up Central Bank reserves with government budget
Government budget
A government budget is a legal document that is often passed by the legislature, and approved by the chief executive-or president. For example, only certain types of revenue may be imposed and collected...
, trade, and current account surpluses. The FY 2002 Russian Government budget assumes payment of roughly $14 billion in official debt service payments falling due. Large current account surpluses have brought a rapid appreciation of the ruble over the past several years. This has meant that Russia has given back much of the terms-of-trade advantage that it gained when the ruble fell by 60% during the debt crisis. Oil and gas dominate Russian exports, so Russia remains highly dependent upon the price of energy. Loan and deposit rates at or below the inflation rate inhibit the growth of the banking system and make the allocation of capital and risk much less efficient than it would be otherwise.
In 2003, the debt has risen to $19 billion due to higher Ministry of Finance and Eurobond payments. However, $1 billion of this has been prepaid, and some of the private sector debt may already have been repurchased. Russia continues to explore debt swap/exchange opportunities.
In the June 2002 G8 Summit, leaders of the eight nations signed a statement agreeing to explore cancellation of some of Russia's old Soviet debt to use the savings for safeguarding materials in Russia that could be used by terrorists. Under the proposed deal, $10 billion would come from the United States and $10 billion from other G-8 countries over 10 years.
On 1 January 2004, the Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation
Stabilization Fund of the Russian Federation
The Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation wasestablished by resolution of the Government of Russia on January 1, 2004, as a part of the federal budget to balance the...
was established by the Government of Russia
Government of Russia
The Government of the Russian Federation exercises executive power in the Russian Federation. The members of the government are the prime minister , the deputy prime ministers, and the federal ministers...
as a part of the federal budget to balance it if oil price falls. Now the Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation
Stabilization Fund of the Russian Federation
The Stabilization fund of the Russian Federation wasestablished by resolution of the Government of Russia on January 1, 2004, as a part of the federal budget to balance the...
is being modernized. The Stabilization Fund will be divided into two parts on 1 February 2008. The first part will become a reserve fund equal to 10 percent of GDP (10% of GDP equals to about $200 billion now), and will be invested in a similar way as the Stabilization Fund. The second part will be turned into the National Prosperity Fund of Russian Federation. Deputy Finance Minister Sergei Storchak
Sergei Storchak
Sergei Anatolievich Storchak is a Deputy Finance Minister of Russia. Storchak became one of Russia's three deputy finance ministers in November 2005. He specialized in international financial relations, and was a prominent figure in negotiations over paying off Soviet-era debt...
estimates it will reach 600–700 billion rubles by 1 February 2008. The National Prosperity Fund is to be invested into more risky instruments, including the shares of foreign companies.
Putin years
Under the presidency of Vladimir PutinVladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin served as the second President of the Russian Federation and is the current Prime Minister of Russia, as well as chairman of United Russia and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Union of Russia and Belarus. He became acting President on 31 December 1999, when...
Russia's economy saw the nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) double, climbing from 22nd to 11th largest in the world. The economy made real gains of an average 7% per year ( 1999: 6.5%, 2000: 10%, 2001: 5.7%, 2002: 4.9%, 2003: 7.3%, 2004: 7.2%, 2005: 6.4%, 2006: 8,2%, 2007: 8.5%, 2008: 5.2% ), making it the 6th largest economy in the world in GDP(PPP). In 2007, Russia's GDP exceeded that of 1990, meaning it has overcome the devastating consequences of the recession in the 1990s. On a per capita basis, Russian GDP was US$14,919 per individual in 2009, making Russians 38th richest on both a purchasing power and nominal basis.
During Putin's eight years in office, industry grew by 75%, investments increased by 125%, and agricultural production and construction increased as well. Real incomes more than doubled and the average salary increased eightfold from $80 to $640. The volume of consumer credit between 2000–2006 increased 45 times, and during that same time period, the middle class grew from 8 million to 55 million, an increase of 7 times. The number of people living below the poverty line also decreased from 30% in 2000 to 14% in 2008.
Inflation remained a problem however, as the government failed to contain the growth of prices. Between 1999–2007 inflation was kept at the forecast ceiling only twice, and in 2007 the inflation exceeded that of 2006, continuing an upward trend at the beginning of 2008.
The Russian economy is still commodity-driven despite its growth. Payments from the fuel and energy sector in the form of customs duties and taxes accounted for nearly half of the federal budget's revenues. The large majority of Russia's exports are made up by raw materials and fertilizers, although exports as a whole accounted for only 8.7% of the GDP in 2007, compared to 20% in 2000.
There is also a growing gap between rich and poor in Russia. Between 2000–2007 the incomes of the rich grew from approximately 14 times to 17 times larger than the incomes of the poor. The income differentiation ratio shows that the 10% of Russia's rich live increasingly better than the 10% of the poor, amongst whom are mostly pensioners and unskilled workers in depressive regions. (See: Gini Coefficient
Gini coefficient
The Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper "Variability and Mutability" ....
)
Post-Putin years
Arms sales have increased to the point where Russia is second (with 3/5ths the amount of US arms sales) in the world in sale of weapons, the IT industry has recorded a record year of growth concentrating on high end niches like algorithm designAlgorithm design
Algorithm design is a specific method to create a mathematical process in solving problems. Applied algorithm design is algorithm engineering....
and microelectronics
Microelectronics
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture of very small electronic components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller,. These devices are made from semiconductors...
; Russia is now the world's third biggest destination for outsourcing software behind India and China. The space launch industry is now the world's second largest behind the European Ariane 5
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is, as a part of Ariane rocket family, an expendable launch system used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit or low Earth orbit . Ariane 5 rockets are manufactured under the authority of the European Space Agency and the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales...
and nuclear power plant companies are going from strength to strength, selling plants to China and India, and recently signed a joint venture with Toshiba
Toshiba
is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
to develop cutting edge power plants.
The civilian aerospace industry has developed the Sukhoi Superjet
Sukhoi Superjet 100
The Sukhoi Superjet 100 is a modern, fly-by-wire regional jet in the 75- to 95-seat category. With development starting in 2000, the plane was designed by the civil aircraft division of the Russian aerospace company Sukhoi in co-operation with Western partners...
, as well as the upcoming MS-21 project to compete with Boeing
Boeing
The Boeing Company is an American multinational aerospace and defense corporation, founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington. Boeing has expanded over the years, merging with McDonnell Douglas in 1997. Boeing Corporate headquarters has been in Chicago, Illinois since 2001...
and Airbus
Airbus
Airbus SAS is an aircraft manufacturing subsidiary of EADS, a European aerospace company. Based in Blagnac, France, surburb of Toulouse, and with significant activity across Europe, the company produces around half of the world's jet airliners....
.
The recent global economic downturn hit the Russian economy hard, resulting in three major shocks to Russia's long-term economic growth, though. Oil prices dropped from $140 per barrel to $40 per barrel, a decrease in access to financing with an increase in sovereign and corporate bond spreads, and the reversal of capital flows from $80 billion of in-flows to $130 billion in out-flows have all served to crush fledgling Russian economic growth. In January 2009, industrial production was down almost 16% year to year, fixed capital investment was down 15.5% year to year, and GDP had shrunk 9% year to year. However, in the second quarter the GDP rose by 7.5 percent on a quarterly basis indicating the beginning of economic recovery. Responses to the recovery has been fast – Industrial Production growth remains one of the highest in the world, Billionaires have grown vastly, and Moscow now boasts the highest billionaire population, ahead of New York City. However, a shrinking and aging population, corruption, and deficient infrastructure pose as serious challenges for the Russian economy.
Gross domestic product
This is a chart of trend of gross domestic product of Russia at market prices estimated by the International Monetary Fund with figures in millions of Russian Rubles.| Year | Gross Domestic Product | US Dollar exchange |
|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 1,428,500 | 4.55 Rubles |
| 2000 | 7,305,600 | 28.13 Rubles |
| 2005 | 21,665,000 | 28.27 Rubles |
| 2008 | 39,952,177 | 23.52 Rubles |
| 2009 | 39,952,177 | 30.20 Rubles |
For purchasing power parity comparisons, the US Dollar is exchanged at 13.63 Rubles only. Average wages in 2007 hover around $42–51 per day.
Russia's GDP, estimated at $1,250 billion at 2007 exchange rates, increased by 8.1% in 2007 compared to 2006. Continued average inflation of approximately 10% and strict government budget led to the growth, while lower oil prices and ruble appreciation slowed it. As of November 2007, unemployment in Russia was at 5.9%, down from 10.4% in 2000. Combined unemployment and underemployment
Underemployment
Underemployment refers to an employment situation that is insufficient in some important way for the worker, relative to a standard. Examples include holding a part-time job despite desiring full-time work, and overqualification, where the employee has education, experience, or skills beyond the...
may exceed those figures. Industrial output in 2007 grew by 6.3% compared to 2006, driven by investment growth and private consumption demand.
As of 2005, oil industry and related services account for at least 40 per cent of the gross domestic product of Russia.
As of April 2008, the International Monetary Fund
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
estimates that Russia's gross domestic product (nominal) will grow from its 2007 value of $1,289,582 million to $3,462,998 million by 2013, a 168% increase. Its GDP PPP is estimated to grow from $2,087,815 to $3,330,623 in the same time, which would make it the second largest economy in Europe in terms of purchasing power
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
.
Monetary policy
The exchange rate stabilized in 1999; after falling from 6.5 rubles/dollar in August 1998 to about 25 rubles/dollar by April 1999, one year later it had further depreciated only to about 28.5 rubles/dollar. As of June 2002, the exchange rate was 31.4 rubles/dollar, down from 29.2 rubles/dollar the year before. After some large spikes in inflation following the August 1998 economic crisis, inflation has declined steadily. Cumulative consumer price inflation for 2001 was 18.6% slightly below the 20.2% inflation rate of the previous year but above the inflation target set in the 2001 budget. The Central Bank's accumulation of foreign reserves drove inflation higher and that trend is expected to continue. By 2009, the estimated inflation rate had decreased to 11.7%.Fiscal policy
Central and local government expenditures are about equal. Combined they come to about 38% of GDP. Fiscal policy has been very disciplined since the 1998 debt crisis. The overall budget surplus for 2001 was 2.4% of GDP, allowing for the first time in history for the next year's budget to be calculated with a surplus (1.63% of GDP). Much of this growth, which exceeded most expectations for the third consecutive year, was driven by consumption demand. Analysts remain skeptical that high rates of economic growth will continue, particularly since Russia's planned budgets through 2005 assume that oil prices will steadily increase. Low oil prices would mean that the Russian economy would not achieve its projected growth. However, high oil prices also would have negative economic effects, as they would cause the ruble to continue to appreciate and make Russian exports less competitive. The 2007 budget law incorporates a 25% increase in spending, much of it for public-sector salary increases, pension increases and social programmes. Spending on education is targeted to increase by 60% relative to the 2006 legislation and spending on healthcare is to increase by 30%. Funding for the four "national projectsNational Priority Projects
The National Priority Projects of the Russian Federation is a program of the Russian government set out by Russian President Vladimir Putin in his speech on September 5, 2005. The program is aimed to develop social welfare in Russia by additional funding by the state of four selected projects...
", undertakings in agriculture, education, housing and healthcare, will increase by 85 billion roubles over the 2006 figure to 230 billion rubles.
Law
Lack of legislation and, where there is legislation, lack of effective law enforcement, in many areas of economic activity is a pressing issue. During 2000 and 2001, changes in government administration increased the power of the central government to compel localities to enforce laws. Progress has been made on pension reform and reform of the electricity sector. Nonetheless, taxation and business regulations are unpredictable, and legal enforcement of private business agreements is weak. Attitudes left over from the Soviet period will take many years to overcome. Government decisions affecting business have often been arbitrary and inconsistent. Crime has increased costs for both local and foreign businesses. On the positive side, Russian businesses are increasingly turning to the courts to resolve disputes. The passage of an improved bankruptcy code in January 1998 was one of the first steps. In 2001, the Duma passed legislation for positive changes within the business and investment sector; legislative changes included a deregulation package. This trend in legislation is continued through 2002, with the new corporate tax code going into effect.Natural resources

Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and northwestern Kazakhstan. Their eastern side is usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia...
and the vast oil, gas, coal, and timber reserves of Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
and the Russian Far East
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
make Russia rich in natural resources. However, most such resources are located in remote and climatically unfavorable areas that are difficult to develop and far from Russian ports.
Natural resources, especially oil and gas, dominate Russian exports. Oil and gas exports continue to be the main source of hard currency. The petroleum industry in Russia is one of the largest in the world. Russia has the largest reserves, and is the largest exporter, of natural gas. It has the second largest coal reserves, the eighth largest oil reserves, and is the largest in the world exporter of oil in absolute numbers.
Per capita oil production in Russia, though, is not that high. As of 2007, Russia was producing 69.603 bbl/day per 1,000 people, much less than Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
(102.575 bbl/day), Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
(371.363 bbl/day), or Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
(554.244 bbl/day), but more than two times more than the USA (28.083 bbl/day), or the UK (27.807 bbl/day).
Russia is also a leading producer and exporter of minerals and gold. Ninety percent of Russian exports to the United States are minerals or other raw materials.
Expecting the area to become more accessible as climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
melts Arctic ice
Arctic shrinkage
Ongoing changes in the climate of the Arctic include rising temperatures, loss of sea ice, and melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Projections of sea ice loss suggest that the Arctic ocean will likely be free of summer sea ice sometime between 2060 and 2080, while another estimate puts this date at...
, and believing the area contains large reserves of untapped oil and natural gas, on 2 August 2007, Russian explorers, in submersibles, planted the Russian flag on the Arctic seabed, staking a claim to energy sources right up to the North Pole. Reaction to the event was mixed: President Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin served as the second President of the Russian Federation and is the current Prime Minister of Russia, as well as chairman of United Russia and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Union of Russia and Belarus. He became acting President on 31 December 1999, when...
congratulated the explorers for "the outstanding scientific project", while Canadian officials stated the expedition was just a public show.
Under the Federal Law "On Continental Shelf Development" upon proposal from the federal agency managing the state fund of mineral resources or its territorial offices the Russian government approves the list of some sections of the mineral resources that are passed for development without any contests and auctions, some sections of federal importance of the Russian continental shelf, some sections of the mineral resources of federal importance that are situated in Russia and stretch out on its continental shelf, some gas deposits of federal importance that are handed over for prospecting and developing the mineral resources under a joint license. The Russian government is also empowered to decide on the handover of the foresaid sections of the mineral resources for development without any contests and auctions.
The Russian fishing industry is the world's fourth-largest, behind Japan, the United States, and China.
Industry
Russia is one of the most industrialized of the former Soviet republics. In the 2000s, Russia's industry, due to increasing demand and improved state finances, emerged from a deep crisis caused by the dissolution of the Soviet UnionDissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the disintegration of the federal political structures and central government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , resulting in the independence of all fifteen republics of the Soviet Union between March 11, 1990 and December 25, 1991...
. However, years of low investment continue to leave their mark on the industry's capabilities and a lot of its equipment is in need of modernization.
Besides its resource-based industries, Russia has developed large manufacturing capacities, notably in machinery. The defense and aircraft industries are important employers and are able to offer internationally competitive products for export.
Defense industry
Russia's defense industry employs 2.53 million people, accounting for 20% of all manufacturing jobs. Russia is the world's second largest conventional arms exporter after the United States. The most popular types of weaponry bought from Russia are SukhoiSukhoi
Sukhoi Company is a major Russian aircraft manufacturer, headquartered in Begovoy District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, famous for its fighters...
and MiG
Mig
-Industry:*MiG, now Mikoyan, a Russian aircraft corporation, formerly the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau*Metal inert gas welding or MIG welding, a type of welding using an electric arc and a shielding gas-Business and finance:...
fighters, air defense systems, helicopter
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by one or more engine-driven rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forwards, backwards, and laterally...
s, battle tank
Tank
A tank is a tracked, armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat which combines operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defensive capabilities...
s, armored personnel carriers and infantry fighting vehicle
Infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle , also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle , is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide fire support for them...
s. The research organization Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies
Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies
The Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies is an independent, noncommercial, nongovernmental organization, which carries out research and analysis on Russian conventional arms trade and defense trends both nationally and internationally...
ranked the air defense system producer Almaz-Antey
Almaz-Antey
OJSC "Concern PVO "Almaz-Antey" is a Russian joint undertaking in the arms industry, a result of a merger of Antey Corporation and NPO Almaz, unifying some of the national military enterprises, in particular, the developers of anti-aircraft defence systems . The organisation is headquartered in...
as the industry's most successful company in 2007, followed by aircraft-maker Sukhoi
Sukhoi
Sukhoi Company is a major Russian aircraft manufacturer, headquartered in Begovoy District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, famous for its fighters...
. Almaz-Antey's revenue that year was $3.122 billion, and it had a work force of 81,857 people.
Aircraft industry
Aircraft manufacturing is an important industry sector in Russia, employing around 355,300 people. The Russian aircraft industry offers a portfolio of internationally competitive military aircraft such as MiG-29 and Su-30, while new projects such as the Sukhoi Superjet 100Sukhoi Superjet 100
The Sukhoi Superjet 100 is a modern, fly-by-wire regional jet in the 75- to 95-seat category. With development starting in 2000, the plane was designed by the civil aircraft division of the Russian aerospace company Sukhoi in co-operation with Western partners...
are hoped to revive the fortunes of the civilian aircraft segment. In 2009, companies belonging to the United Aircraft Corporation
United Aircraft Corporation
United Aircraft Corporation may refer to one of the following:* United Aircraft Corporation, formerly United Aircraft and Transport Corporation; now known as United Technologies Corporation....
delivered 95 new fixed-wing aircraft to its customers, including 15 civilian models. In addition, the industry produced over 141 helicopters. It is one of the most science-intensive hi-tech sectors and employs the largest number of skilled personnel. The production and value of the military aircraft branch far outstrips other defense industry
Defense industry of Russia
The Defense industry of Russia is a strategically important sector and a large employer. It is also a significant player in the global arms market...
sectors, and aircraft products make up more than half of the country's arms exports.
Space industry
Space industry of RussiaSpace industry of Russia
Space industry of Russia consists of over 100 companies and employs 250,000 people. Most of Russia's space industry companies are descendants of Soviet design bureuas and state production companies. The industry entered a deep crisis after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, which peaked in the...
consists of over 100 companies and employs 250,000 people. The largest company of the industry is RKK Energia, the main manned space flight contractor. Leading launch vehicle producers are Khrunichev
Khrunichev
Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center is a Moscow-based producer of spacecraft and space-launch systems, including the Proton and Rokot rockets. The company's history dates back to 1916, when an automobile factory was established outside Moscow...
and TsSKB Progress. Largest satellite developer is Reshetnev Information Satellite Systems, while NPO Lavochkin is the main developer of interplanetary probes.
Automotive industry
Automotive production is a significant industry in RussiaRussia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, directly employing around 600,000 people or 0,7% of the country's total work force. In addition, the industry supports around 2–3 million people in related industries. Russia was the world's 15th largest car producer in 2010, and accounts for about 7% of the worldwide production. In 2009 the industry produced 595,807 light vehicles, down from 1,469,898 in 2008 due to the global financial crisis. The largest companies are light vehicle producers AvtoVAZ
AvtoVAZ
AvtoVAZ is the Russian automobile manufacturer formerly known as VAZ: Volzhsky Avtomobilny Zavod , but better known to the world under the trade name Lada. The company was established in the late 1960s in collaboration with Fiat...
and GAZ
GAZ
GAZ or Gorkovsky Avtomobilny Zavod , translated as Gorky Automobile Plant , started in 1932 as NAZ, a cooperation between Ford and the Soviet Union. It is one of the largest companies in the Russian automotive industry....
, while KAMAZ
Kamaz
KAMAZ is a Russian truck manufacturer located in Naberezhnye Chelny, Tatarstan, Russian Federation. KAMAZ opened their doors in 1976...
is the leading heavy vehicle producer. 11 foreign carmakers have production operations or are constructing plants in Russia.
Electronics
Russia is experiencing a regrowth of testicals and Microelectronics, with the revival of JCS Mikron. An example of a successful Russian consumer electronics company is TelesystemsTelesystems (company)
Telesystems is a company specialising in miniature electronics. It is based in Zelenograd, Russia. Its products are sold in more than 20 countries...
, whose products are sold in over 20 countries.
Telecommunications
Russia's telecommunications industry is growing in size and maturity. As of 31 December 2007, there were an estimated 4,900,000 broadband lines in Russia. Over 72% of the broadband lines were via cable modems and the rest via DSL.In 2006, there were more than 300 BWA operator networks, accounting for 5% of market share, with dial-up accounting for 30%, and Broadband Fixed Access accounting for the remaining 65%. In December 2006, Tom Phillips, chief government and regulatory affairs officer of the GSM Association
GSM Association
The GSM Association is an association of mobile operators and related companies devoted to supporting the standardizing, deployment and promotion of the GSM mobile telephone system...
stated:
-
- "Russia has already achieved more than 100% mobile penetration thanks to the huge popularity of wireless communications among Russians and the government's good work in fostering a market driven mobile sector based on strong competition."
While there is a lot of interest in a national broadband network, as of January 2007 there still wasn't one.
The financial crisis, which had already hit the country at the end of 2008, caused a sharp reduction of the investments by the business sectors and a notable reduction of IT budget made by government in 2008–2009. As a consequence,the IT market in Russia in 2009 declined by more than 20% in ruble terms and by one third in euro terms. Among the particular segments, the biggest share of the Russian IT market still belongs to hardware.
Agriculture
Russia comprises roughly three-quarters of the territory of the former Soviet Union. Following the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991 and after nearly ten years of decline, Russian agriculture begun to show signs of improvement due to organizational and technological modernization. Northern areas concentrate mainly on livestock, and the southern parts and western Siberia produce grain. Restructuring of former state farms has been an extremely slow process. The new land code passed by the Duma in 2002 should speed restructuring and attract new domestic investment to Russian agriculture. Private farms and garden plots of individuals account for over one-half of all agricultural production.Trade

Russian timber industry
The timber industry is a significant contributor to the economy of Russia, worth around 20 billion dollars per year.There are significant profits to be made selling timber to China in particular, and there have been allegations of illegal logging within Russia....
comprise 80% of Russian exports. Ferrous metals exports suffered the most in 2001, declining 7.5%. On the import side, steel and grains dropped by 11% and 61%, respectively.
Most analysts predicted that these trade trends would continue to some extent in 2002. In the first quarter of 2002, import expenditures were up 12%, increased by goods and a rapid rise of travel expenditure. The combination of import duties, a 20% value-added tax and excise taxes on imported goods (especially automobiles, alcoholic beverages, and aircraft) and an import licensing regime for alcohol still restrain demand for imports. Frequent and unpredictable changes in customs regulations also have created problems for foreign and domestic traders and investors. In March 2002, Russia placed a ban on poultry from the United States. In the first quarter of 2002, exports were down 10% as falling income from goods exports was partly compensated for by rising services exports, a trend since 2000. The trade surplus decreased to $7 billion from well over $11 billion the same period last year.
Foreign trade rose 34% to $151.5 billion in the first half of 2005, mainly due to the increase in oil and gas prices which now form 64% of all exports by value. Trade with CIS countries is up 13.2% to $23.3 billion. Trade with the EU forms 52.9%, with the CIS 15.4%, Eurasian Economic Community
Eurasian Economic Community
The Eurasian Economic Community originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States customs union between Belarus, Russia and Kazakhstan on 29 March 1996...
7.8% and Asia-Pacific Economic Community 15.9% .

Russia is China’s eighth largest trade partner and China is now Russia’s fourth largest trade partner.
China now has over 750 investment projects in Russia, involving $1.05 billion.
China’s contracted investment in Russia totaled $368 million during January–September 2005, twice that in 2004.
Chinese imports from Russia are mainly those of energy sources, such as crude oil, which is mostly transported by rail, and electricity exports from neighboring Siberian and Far Eastern regions. Exports of both of these commodities are increasing, as Russia opened the Eastern Siberia–Pacific Ocean oil pipeline's branch to China, and Russian power companies are building some of its hydropower stations with a view of future exports to China.
Information technology

India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and China) among software exporters. Such growth of software outsourcing in Russia is caused by a number of factors. One of them is the supporting role of the Russian Government
Government of Russia
The Government of the Russian Federation exercises executive power in the Russian Federation. The members of the government are the prime minister , the deputy prime ministers, and the federal ministers...
. The Government has launched a program promoting construction of IT-oriented technology parks (Technoparks) – special zones that have an established infrastructure and enjoy a favorable tax and customs regime, in seven different places around the country: Moscow, Novosibirsk, Nizhny Novgorod, Kaluga, Tumen, Republic of Tatarstan and St. Peterburg Regions. Another factor stimulating the IT sector growth in Russia is the presence of global technology corporations such as Intel, Motorola
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, which was eventually divided into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions on January 4, 2011, after losing $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009...
, Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
, Boeing
Boeing
The Boeing Company is an American multinational aerospace and defense corporation, founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington. Boeing has expanded over the years, merging with McDonnell Douglas in 1997. Boeing Corporate headquarters has been in Chicago, Illinois since 2001...
, Nortel
Nortel
Nortel Networks Corporation, formerly known as Northern Telecom Limited and sometimes known simply as Nortel, was a multinational telecommunications equipment manufacturer headquartered in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada...
and others, which have intensified their software development
Software development
Software development is the development of a software product...
activities and opened their R&D centers in Russia.
Nanotechnology
In its push to diversify Russia's research and development in emerging technologies, The Putin government has announced a massive $7 billion investment program in nanotechnologyNanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study of manipulating matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Generally, nanotechnology deals with developing materials, devices, or other structures possessing at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometres...
. As part of the program, during 2007, $5 billion is being invested into a new state corporation, Rosnanotech, that will be responsible for overseeing and coordinating research in the area.
In criticism of the initiative, it has been noted that the Russian nanotech program will receive three times more state funding than the rest of Russia's scientists put together.
Apart from public funding, Mikhail Prokhorov
Mikhail Prokhorov
Mikhail Dmitrievitch Prokhorov is a Russian billionaire entrepreneur and owner of the American basketball team, the New Jersey Nets. After graduating from the Moscow Finance Institute he made his name in the financial sector and went on to become one of Russia's leading industrialists in the...
, a leading Russian metals and banking tycoon, has announced the creation of a $17.5 billion holding company that will focus on high-tech investments, including alternative energy and nanotechnology.
Construction market
Russian construction industry has survived its most difficult year for more than a decade. The 0.8% reduction recorded by the industry for the first three quarters of 2010 looks remarkably healthy in comparison with the 18.4% slump recorded last year, and construction firms are now much more optimistic about the future than they were just a few months ago. The most successful of them have concluded contracts worth billions of dollars and are planning to take on employees and purchase new building machinery. The downturn served to emphasise the importance of the government to the construction market.Investment

Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment or foreign investment refers to the net inflows of investment to acquire a lasting management interest in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.. It is the sum of equity capital,other long-term capital, and short-term capital as shown in...
, which includes contributions to starting capital and credits extended by foreign co-owners of enterprises, rose slightly in 1999 and 2000, but decreased in 2001 by about 10%. Foreign portfolio investment, which includes shares and securities, decreased dramatically in 1999, but has experienced significant growth since then. In 2001, foreign portfolio investment was $451 million, more than twice the amount from the previous year. Inward foreign investment during the 1990s was dwarfed by Russian capital flight, estimated at about $15 billion annually. During the years of recovery following the 1998 debt crisis, capital flight seems to have slowed. Inward investment from Cyprus and Gibraltar, two important channels for capital flight from Russia in recent years, suggest that some Russian money is returning home.
A significant drawback for investment is the banking sector, which lacks the resources, the capability, and the trust of the population that it would need to attract substantial savings and direct it toward productive investments. Russia's banks contribute only about 3% of overall investment in Russia. While ruble lending has increased since the August 1998 financial crisis, loans are still only 40% of total bank assets. The Central Bank of Russia reduced its refinancing rate five times in 2000, from 55% to 25%, signaling its interest in lower lending rates. Interest on deposits and loans are often below the inflation rate. The poorly developed banking system makes it difficult for entrepreneurs to raise capital and to diversify risk. Banks still perceive commercial lending as risky, and some banks are inexperienced with assessing credit risk.
Money on deposit with Russian banks represents only 7% of GDP. Sberbank
Sberbank
Sberbank Rossii is the largest bank in Russia and Eastern Europe. The company's headquarters are in Moscow and its history goes back to Cancrin's financial reform of 1841...
receives preferential treatment from the state and holds 73% of all bank deposits. In March 2002, Sergei Ignatyev replaced Viktor Gerashchenko
Viktor Gerashchenko
Viktor Vladimirovich Gerashchenko , byname Gerakl , was the Chairman of the Soviet and then Russian Central Bank during much of the Perestroika and post-Perestroika periods....
as Chairman of the Russian Central Bank. Under his leadership, necessary banking reforms, including stricter accounting procedures and federal deposit insurance, were implemented.
Strategic sectors
In the Russian law as in the law of many other civilized countries, there are sectors of the economy who are considered to be crucial for national securityNational security
National security is the requirement to maintain the survival of the state through the use of economic, diplomacy, power projection and political power. The concept developed mostly in the United States of America after World War II...
and foreign companies are restricted from owning them. Investments in the so-called Strategic Sectors are defined in a law adopted by the Federal Assembly of Russia
Federal Assembly of Russia
The Federal Assembly of Russia is the legislature of the Russian Federation, according to the Constitution of Russian Federation, 1993...
.
Mergers and acquisitions
From 1993 to 2010, Russian companies have been involved as either an acquirer or acquired company in 13,834 mergers and acquisitionsMergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions refers to the aspect of corporate strategy, corporate finance and management dealing with the buying, selling, dividing and combining of different companies and similar entities that can help an enterprise grow rapidly in its sector or location of origin, or a new field or...
with a total known value of 613 bil. USD. The number of deals that happened in 2010 have been 3,662, which is a new record; compared to 2009 this was an increase of 12%. The value of deals in 2010 was US$100 billion, which was the second highest number ever; compared to 2009 this was an increase of 143%.
Statistics
Retail sales in Russia| Year | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total retail sales (RUB tr) | 3.77 | 4.53 | 5.64 | 7.04 | 8.69 | 10.76 |
Key data on the telecommunications market in Russia
| Year | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications market value (€ bn) | 12.9 | 16.0 | 20.9 | 25.0 | 28.0 | 24.2 |
| Telecommunications market growth rate (%) | 32.0 | 23.5 | 30.6 | 20.2 | 11.5 | −13.4 |
Exchange rates
| Year | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/RUR | 41.44 | 43.39 | 40.33 |
| USD/RUR | 29.38 | 30.24 | 30.48 |
Types of legal entities in Russia
- IP (Индивидуальный предприниматель) – Russian "Individual entrepreneur"
- OOO (Общество с ограниченной ответственностью, ООО) – Russian "Limited liability company"
- ZAO (Закрытое акционерное общество, ЗАО) – Russian "Private joint-stock company"
- OAO (Открытое акционерное общество, ОАО) – Russian "Public joint-stock company"
- ANO (Автономная некоммерческая организация, АНО) – Russian "Autonomous non-profit organization"
- GP or GUP (Государственное унитарное предприятие, ГП or ГУП) – Russian "Unitary state enterpriseUnitary enterpriseA unitary enterprise is a government-owned corporation in Russia and some other post-Soviet states. Unitary enterprises are business entities that have no ownership rights to the assets they use in their operations....
" - Фонд – Russian "FundFundFund may refer to:* To fund is the process of Funding, or providing capital or other resources for a transaction, a project, a person, a business or other private or public institutions...
" - PK (Производственный кооператив, ПK) – Russian "Production Cooperative"
- PP (Политические партии, ПП) – Russian "Political party"
See also
- Timeline of largest projects in the Russian economyTimeline of largest projects in the Russian economyThis timeline of largest projects in the Russian economy includes both megaprojects, costing over $1 billion, and other large investment projects, typically costing between $100 million and $1 billion. Projects with investments below $100 million also may be included here, either as parts of larger...
- MonotownMonotownA monotown is a town whose economy is dominated by a single industry or company. The term is especially often used in Russia, where the Soviet planned economy created several monotowns in supposedly rational locations, often in geographically inhospitable areas...
- Commonwealth of Independent StatesCommonwealth of Independent StatesThe Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
- History of post-Soviet RussiaHistory of post-Soviet RussiaWith the dissolution of the Soviet Union on 29 May 1991, the Russian Federation became an independent country.Russia was the largest of the fifteen republics that made up the Soviet Union, accounting for over 60% of the gross domestic product and over 50% of the Soviet population. Russians also...
- Politics of RussiaPolitics of RussiaThe politics of Russia take place in a framework of a federal semi-presidential republic. According to the Constitution of Russia, the President of Russia is head of state, and of a multi-party system with executive power exercised by the government, headed by the Prime Minister, who is appointed...
- PutinismPutinismPutinism is the ideology, priorities, and policies of the system of government practiced by Russian politician Vladimir Putin...
- Russian RailwaysRussian RailwaysThe Russian Railways , is the government owned national rail carrier of the Russian Federation, headquartered in Moscow. The Russian Railways operate over of common carrier routes as well as a few hundred kilometers of industrial routes, making it the second largest network in the world exceeded...
- Unitary enterpriseUnitary enterpriseA unitary enterprise is a government-owned corporation in Russia and some other post-Soviet states. Unitary enterprises are business entities that have no ownership rights to the assets they use in their operations....

