
Electrodialysis
Encyclopedia
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
ions from one solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
through ion-exchange membrane
Semipermeable membrane
A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively permeable membrane, a partially permeable membrane or a differentially permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion".The rate of...
s to another solution under the influence of an applied electric potential
Electric potential
In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there...
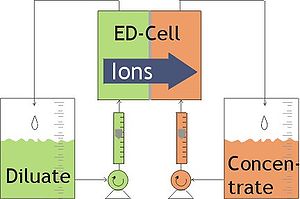
difference. This is done in a configuration called an electrodialysis cell. The cell consists of a feed (diluate) compartment and a concentrate (brine) compartment formed by an anion exchange membrane and a cation exchange membrane placed between two electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s. In almost all practical electrodialysis processes, multiple electrodialysis cells are arranged into a configuration called an electrodialysis stack, with alternating anion and cation exchange membranes forming the multiple electrodialysis cells. Electrodialysis processes are different compared to distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
techniques and other membrane based processes (such as reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a membrane technical filtration method that removes many types of large molecules and ions from solutions by applying pressure to the solution when it is on one side of a selective membrane. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and...
) in that dissolved species are moved away from the feed stream rather than the reverse. Because the quantity of dissolved species in the feed stream is far less than that of the fluid, electrodialysis offers the practical advantage of much higher feed recovery in many applications.
Method
In an electrodialysis stack, the diluate (D) feed stream, brine or concentrate (C) stream, and electrode (E) stream are allowed to flow through the appropriate cell compartments formed by the ion exchange membranes. Under the influence of an electrical potential difference, the negatively charged ions (e.g., chlorideChloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
) in the diluate stream migrate toward the positively charged anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
. These ions pass through the positively charged anion exchange membrane, but are prevented from further migration toward the anode by the negatively charged cation exchange membrane and therefore stay in the C stream, which becomes concentrated with the anions. The positively charged species (e.g., sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
) in the D stream migrate toward the negatively charged cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
and pass through the negatively charged cation exchange membrane. These cations also stay in the C stream, prevented from further migration toward the cathode by the positively charged anion exchange membrane. As a result of the anion and cation migration, electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
flows between the cathode and anode. Only an equal number of anion and cation charge equivalents are transferred from the D stream into the C stream and so the charge balance is maintained in each stream. The overall result of the electrodialysis process is an ion concentration increase in the concentrate stream with a depletion of ions in the diluate solution feed stream see video.
The E stream is the electrode stream that flows past each electrode in the stack. This stream may consist of the same composition as the feed stream (e.g., sodium chloride
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
) or may be a separate solution containing a different species (e.g., sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate is the sodium salt of sulfuric acid. When anhydrous, it is a white crystalline solid of formula Na2SO4 known as the mineral thenardite; the decahydrate Na2SO4·10H2O has been known as Glauber's salt or, historically, sal mirabilis since the 17th century. Another solid is the...
). Depending on the stack configuration, anions and cations from the electrode stream may be transported into the C stream, or anions and cations from the D stream may be transported into the E stream. In each case, this transport is necessary to carry current across the stack and maintain electrically neutral stack solutions.
Anode and Cathode Reactions
Reactions take place at each electrode. At the cathode,2e- + 2 H2O → H2 (g) + 2 OH-
while at the anode,
H2O → 2 H+ + ½ O2 (g) + 2e- or 2 Cl- → Cl2 (g) + 2e-
Small amounts of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
are generated at the cathode and small amounts of either oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
or chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
gas (depending on composition of the E stream and end ion exchange membrane arrangement) at the anode. These gases are typically subsequently dissipated as the E stream effluent from each electrode compartment is combined to maintain a neutral pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
and discharged or re-circulated to a separate E tank. However, some (e.g.,) have proposed collection of hydrogen gas for use in energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
production.
Efficiency
Current efficiency is a measure of how effective ions are transported across the ion exchange membranes for a given applied current. Typically current efficiencies >80% are desirable in commercial stacks to minimize energy operating costs. Low current efficiencies indicate water splittingWater splitting
Water splitting is the general term for a chemical reaction in which water is separated into oxygen and hydrogen. Efficient and economical water splitting would be a key technology component of a hydrogen economy. Various techniques for water splitting have been issued in water splitting patents in...
in the diluate or concentrate streams, shunt
Shunt
Shunt may refer to:* Shunt - a hole or passage allowing fluid to move from one part of the body to another* Shunt - a device allowing electrical current to pass around a point in a circuit...
currents between the electrodes, or back-diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
of ions from the concentrate to the diluate could be occurring.
Current efficiency is calculated according to:
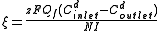
where
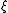 = current utilization efficiency
= current utilization efficiency = charge
= chargeIon
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
of the ion
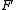 = Faraday constant, 96,485 Amp
= Faraday constant, 96,485 AmpAmpere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
-s/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
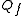 = diluate flow rate, L
= diluate flow rate, LLitér
- External links :*...
/s
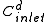 = diluate ED cell inlet concentration
= diluate ED cell inlet concentrationConcentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
, mol/L
 = diluate ED cell outlet concentration, mol/L
= diluate ED cell outlet concentration, mol/L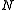 = number of cell pairs
= number of cell pairs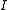 = current, Amps.
= current, Amps.Current efficiency is generally a function of feed concentration.
Applications
In application, electrodialysis systems can be operated as continuous productionContinuous production
Continuous production is a method used to manufacture, produce, or process materials without interruption. Continuous production is called a continuous process or a continuous flow process because the materials, either dry bulk or fluids that are being processed are continuously in motion,...
or batch production
Batch production
Batch production is a technique used in manufacturing, in which the object in question is created stage by stage over a series of workstations. Batch production is common in bakeries and in the manufacture of sports shoes, pharmaceutical ingredients , inks, paints and adhesives. In the manufacture...
processes. In a continuous process, feed is passed through a sufficient number of stacks placed in series to produce the final desired product quality. In batch processes, the diluate and/or concentrate streams are re-circulated through the electrodialysis systems until the final product or concentrate quality is achieved.
Electrodialysis is usually applied to deionization of aqueous solutions. However, desalting of sparingly conductive aqueous organic
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
and organic solutions is also possible. Some applications of electrodialysis include:
- Large scale brackish and seawaterSeawaterSeawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
desalination and salt production.
- Small and medium scale drinking waterDrinking waterDrinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
production (e.g., towns & villages, construction & military camps, nitrateNitrateThe nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
reduction, hotels & hospitals)
- Water reuse (e.g., industrial laundry wastewaterWastewaterWastewater is any water that has been adversely affected in quality by anthropogenic influence. It comprises liquid waste discharged by domestic residences, commercial properties, industry, and/or agriculture and can encompass a wide range of potential contaminants and concentrations...
, produced water from oil/gas production, cooling towerCooling towerCooling towers are heat removal devices used to transfer process waste heat to the atmosphere. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove process heat and cool the working fluid to near the wet-bulb air temperature or in the case of closed circuit dry cooling towers rely...
makeup & blowdown, metals industry fluids, wash-rack water)
- Pre-demineralization (e.g., boilerBoilerA boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:...
makeup & pretreatment, ultrapure water pretreatment, process water desalination, power generation, semiconductorSemiconductorA semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
, chemical manufacturing, food and beverage)
- Food processing
- Agricultural water (e.g., water for greenhouses, hydroponicsHydroponicsHydroponics is a method of growing plants using mineral nutrient solutions, in water, without soil. Terrestrial plants may be grown with their roots in the mineral nutrient solution only or in an inert medium, such as perlite, gravel, mineral wool, or coconut husk.Researchers discovered in the 18th...
, irrigationIrrigationIrrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
, livestockLivestockLivestock refers to one or more domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to produce commodities such as food, fiber and labor. The term "livestock" as used in this article does not include poultry or farmed fish; however the inclusion of these, especially poultry, within the meaning...
)
- Glycol desalting (e.g., antifreezeAntifreezeAntifreeze is a freeze preventive used in internal combustion engines and other heat transfer applications, such as HVAC chillers and solar water heaters....
/ engine-coolants, capacitorCapacitorA capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
electrolyteElectrolyteIn chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
fluids, oil and gas dehydrationDehydrationIn physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
, conditioning and processing solutions, industrial heat transfer fluids, secondary coolants from heating, venting, and air conditioning (HVACHVACHVAC refers to technology of indoor or automotive environmental comfort. HVAC system design is a major subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer...
))
- Glycerin Purification
The major application of electrodialysis has historically been the desalination of brackish water or seawater as an alternative to RO for potable water production and seawater concentration for salt production (primarily in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
). In normal potable water production without the requirement of high recoveries, RO (Reverse Osmosis) is generally believed to be more cost-effective when total dissolved solids
Total dissolved solids
Total Dissolved Solids is a measure of the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances contained in a liquid in: molecular, ionized or micro-granular suspended form. Generally the operational definition is that the solids must be small enough to survive filtration through a sieve...
(TDS) are 3,000 parts per million (ppm) or greater, while electrodialysis is more cost-effective for TDS feed concentrations less than 3,000 ppm or when high recoveries of the feed are required.
Another important application for electrodialysis is the production of pure water and ultrapure water by electrodeionization
Electrodeionization
Electrodeionization is usually considered a water treatment technology that utilizes an electrode to ionize water molecules and separate dissolved ions from water...
(EDI). In EDI, the purifying compartments and sometimes the concentrating compartments of the electrodialysis stack are filled with ion exchange resin
Ion exchange resin
An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix normally in the form of small beads, usually white or yellowish, fabricated from an organic polymer substrate. The material has highly developed structure of pores on the surface of which are sites with easily trapped and...
. When fed with low TDS feed (e.g., feed purified by RO), the product can reach very high purity levels (e.g., 18 MΩ
Ohm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
-cm). The ion exchange resins act to retain the ions, allowing these to be transported across the ion exchange membranes. The main usage of EDI systems are in electronics, pharmaceutical, power generation, and cooling tower applications.
Limitations
Electrodialysis has inherent limitations, working best at removing low molecular weight ionic components from a feed stream. Non-charged, higher molecular weight, and less mobile ionic species will not typically be significantly removed. Also, in contrast to RO, electrodialysis becomes less economical when extremely low salt concentrations in the product are required and with sparingly conductive feeds: current density becomes limited and current utilization efficiency typically decreases as the feed salt concentration becomes lower, and with fewer ions in solution to carry current, both ion transport and energy efficiency greatly declines. Consequently, comparatively large membrane areas are required to satisfy capacity requirements for low concentration (and sparingly conductive) feed solutions. Innovative systems overcoming the inherent limitations of electrodialysis (and RO) are available; these integrated systems work synergistically, with each sub-system operating in its optimal range, providing the least overall operating and capital costs for a particular application.As with RO, electrodialysis systems require feed pretreatment to remove species that coat, precipitate onto, or otherwise "foul" the surface of the ion exchange membranes. This fouling decreases the efficiency of the electrodialysis system. Species of concern include calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
and magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
hardness
Hard water
Hard water is water that has high mineral content . Hard water has high concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Hard water is generally not harmful to one's health but can pose serious problems in industrial settings, where water hardness is monitored to avoid costly breakdowns in boilers, cooling...
, suspended solids
Suspended solids
Suspended solids refers to small solid particles which remain in suspension in water as a colloid or due to the motion of the water. It is used as one indicator of water quality....
, silica
Silicate
A silicate is a compound containing a silicon bearing anion. The great majority of silicates are oxides, but hexafluorosilicate and other anions are also included. This article focuses mainly on the Si-O anions. Silicates comprise the majority of the earth's crust, as well as the other...
, and organic compounds. Water softening
Water softening
Water softening is the reduction of the concentration of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. These "hardness ions" can cause a variety of undesired effects including interfering with the action of soaps, the build up of limescale, which can foul plumbing, and...
can be used to remove hardness, and micrometre
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
or multimedia filtration
Filtration
Filtration is commonly the mechanical or physical operation which is used for the separation of solids from fluids by interposing a medium through which only the fluid can pass...
can be used to remove suspended solids. Hardness in particular is a concern since scaling can build up on the membranes. Various chemicals are also available to help prevent scaling. Also, electrodialysis reversal systems seek to minimize scaling by periodically reversing the flows of diluate and concentrate and polarity of the electrodes.
See also
- Salinity gradient power
- Water desalination
- Electrodialysis reversal
- Reverse OsmosisReverse osmosisReverse osmosis is a membrane technical filtration method that removes many types of large molecules and ions from solutions by applying pressure to the solution when it is on one side of a selective membrane. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and...

