
European exploration of Africa
Encyclopedia
European exploration of Africa began with Ancient Greeks and Romans
, who explored and established settlements in North Africa. Fifteenth Century Portugal
, especially under Henry the Navigator probed along the West African coast. Scientific curiosity and Christian
missionary spirit soon were subordinated to mercantile considerations, including lucrative trafficking in enslaved persons. Others (Dutch, Spanish, French, English, etc.) joined in African trading, though for centuries European knowledge of Africa's interior was very vague. Much of the blank map was filled in by arduous, often fatal, expeditions in the Nineteenth Century.
and North Africa
is older than recorded history. It seems clear that cultural influences crossed the Mediterranean barrier during the late Palaeolithic
and Neolithic
ages. Hence, the late Palaeolithic Aterian
industry and Capsian culture
, both from North Africa, are connected with Europe. Some early Neolithic
influences may also have arrived to Europe via North Africa. Additionally, the Megalithic phenomenon of the Chalcolithic period is found on both shores of the Mediterranean Sea
.
 Africa is named for the Afri
Africa is named for the Afri
people who settled in the area of current-day Tunisia. The Africa Province
of the Roman Empire
spanned the Mediterranean coast of what is now Libya, Tunisia and Algeria.
The parts of North Africa
north of the Sahara
were well known in antiquity. Prior to the 2nd century BC, however, Greek geographers were unaware that the land mass then known as Libya
expanded south of the Sahara, assuming that the desert bounded on the outer Ocean
. Indeed, Alexander the Great, according to Plutarchus' Lives, considered sailing from the mouths of the Indus back to Macedonia passing south of Africa as a shortcut compared to the land route. Even Eratosthenes
around 200 BC still assumed an extent of the landmass no further south than the Horn of Africa
. It was only in Ptolemy's world map
(2nd century AD) that the realization that the southward extent of Africa was not in fact known at the time was made explicit.
As for early exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa
, the ancient Greek historian Herodotus
describes how the Egyptian
Pharaoh Necho II
sent out an expedition manned by Phoenicia
n sailors about 600 BC which in three years circumnavigated Africa. They sailed south, rounded the Cape heading west, made their way north to the Mediterranean and then returned home. He states that they paused each year to sow and harvest grain. They reported that as they sailed around the southern end of the continent they had the sun to their north, which Herodotus found unbelievable. The Egyptologist Alan Lloyd suggests that the Greeks at this time understood that anyone going south far enough and then turning west would have the sun on their right but found it unbelievable that Africa reached so far south. He suggests that "It is extremely unlikely that an Egyptian king would, or could, have acted as Necho is depicted as doing" and that the story might have been triggered by the failure of Sataspes attempt to circumnavigate Africa under Xerxes the Great.
The Phoenicians explored North Africa, establishing a number of colonies, the most prominent of which was Carthage
. Carthage itself conducted exploration of West Africa. Donald Harden describes the journey of Hanno the Navigator
which Harden dates to c. 425 BC and even quotes in translation the surviving Greek account (about two pages long) of this expedition. There is some uncertainty as to how far precisely Hanno reached, "Some taking Hanno to the Cameroons, or even Gabon, while others say he stopped at Sierre Leone.". In 146 BC the Romans had conquered the African coasts, part of Numidia
and Mauretania
and started to explore that land. It was later subdivided into Mauretania Tingitana
, Mauretania Caesariensis
, Numidia
, and Africa Proconsularis also known as Vetus or Africa Nova. They remained a part of the Roman Empire
until the 5th century AD.
 With the expansion of Islam
With the expansion of Islam
in the Middle Ages
, North Africa was culturally cut off from non-Muslim Europe. The Islamic Empire
created a barrier between Europe and the rest of the world, with European traders paying heavy tributes to obtain prized commodities like West African gold
, East Asian spices and silk
. The Italian republics
of Venice
and Genoa
, among others, specialized in this trade.
In addition, the Jews
of modern Spain
, Portugal
, and Morocco
were allowed to trade in both cultural regions. Among them were Abraham Cresques
and his son Jehuda
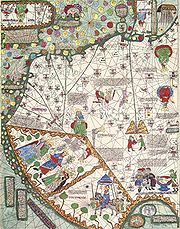
, whose 1375 Catalan Atlas
improved European knowledge of Africa and other regions, with a good deal of Muslim geographical knowledge and some educated guesses and imagination to fill in the blanks. This atlas details the Catalan expedition of Jaume Ferrer
to the Gold River in 1346, which according to the map went south of Cape Bojador
and to what is called West Africa Finisterrae.
The Genoese were also interested in circumventing the Muslim monopoly on Asian trade. In 1291, Tedisio Doria
ordered Vandino and Ugolino Vivaldi
to reach India
via the Atlantic Ocean
. When the expedition was lost, Doria sent ambassadors to Mogadishu
to find out their fate.
Another interesting factor motivating European exploration was rumours of a powerful Christian kingdom, ruled by a priest-king known as Prester John
, located somewhere in the eastern portion of Africa. Prester John was often identified as a Christian king who was a descendant of the Three Magi. Europeans sought his aid to defeat the Muslim nations that separated them from the Orient, or at least help them circumvent the Muslim monopoly.
Naval charts of 1339 show that the Canary Islands
were already known to Europeans. In 1341, Portuguese and Italian explorers prepared a joint expedition. In 1342 the Catalans organized an expedition captained by Francesc Desvalers to the Canary Islands
that set sail from Majorca. In 1344, Pope Clement VI
named French admiral Luis de la Cerda
Prince of Fortune, and sent him to conquer the Canaries.
In 1402, Jean de Bethencourt
and Gadifer de la Salle
sailed to conquer the Canary Islands but found them already plundered by the Castilians
. Although they did conquer the isles, Bethencourt's nephew was forced to cede them to Castile in 1418.
In 1455 and 1456 two Italian explorers Alvise Cadamosto from Venice
and Antoniotto Usodimare
from Genoa
, working for the king of Portugal, followed the Gambia river, visiting the land of Senegal
, while another Italian sailor, Antonio da Noli from Genoa
explored Cabo Verde and the Bijagos islands.
 Portuguese explorer Prince Henry, known as the Navigator, was the first European to methodically explore Africa and the oceanic route to the Indies. From his residence in the Algarve region of southern Portugal, he directed successive expeditions to circumnavigate Africa and reach India. In 1420, Henry sent an expedition to secure the uninhabited but strategic island of Madeira
Portuguese explorer Prince Henry, known as the Navigator, was the first European to methodically explore Africa and the oceanic route to the Indies. From his residence in the Algarve region of southern Portugal, he directed successive expeditions to circumnavigate Africa and reach India. In 1420, Henry sent an expedition to secure the uninhabited but strategic island of Madeira
. In 1425, he tried to secure the Canary Islands
as well, but these were already under firm Castilian control. In 1431, another Portuguese expedition reached and annexed the Azores
.
Along the western and eastern coasts of Africa, progress was also steady; Portuguese sailors reached Cape Bojador
in 1434 and Cape Blanco
in 1441. In 1433, they built a fortress on the island of Arguin
, in modern day Mauritania
, trading European wheat and cloth for African gold and slaves. It was the first time that the semi-mythic gold of the Sudan reached Europe without Muslim mediation. Most of the slaves were sent to Madeira, which became, after thorough deforestation, the first European plantation colony. Between 1444 and 1447, the Portuguese explored the coasts of Senegal
, Gambia, and Guinea
. In 1456, a Venetian captain under Portuguese command explored the islands of Cape Verde
. In 1462, two years after Prince Henry's death, Portuguese sailors explored the Bissau
islands and named Sierra Leoa
(Lion Range).
In 1469, Fernão Gomes
rented the rights of African exploration for five years. Under his direction, in 1471, the Portuguese reached modern Ghana
and settled in La Mina (the mine), later renamed Elmina
. They had finally reached a country with an abundance of gold, hence the historical name of "Gold Coast
" that Elmina would eventually receive.
In 1472, Fernão do Pó
discovered the island that would bear his name for centuries (now Bioko
) and an estuary abundant in shrimp
, giving its name to Cameroon
.
Soon after, the equator
was crossed by Europeans . Portugal established a base in Sāo Tomé
that, after 1485, was settled with criminals. After 1497, expelled Spanish and Portuguese Jews also found a safe haven there.
In 1482, Diogo Cão
found the mouth of a large river and learned of the existence of a great kingdom, Kongo
. In 1485, he explored the river upstream as well.
But the Portuguese wanted, above anything else, to find a route to India and kept trying to circumnavigate Africa. In 1485, the expedition of João Afonso d'Aveiros, with the German astronomer Martin of Behaim as part of the crew, explored the Bight of Benin
, returning information about African king Ogane.
In 1488, Bartolomeu Dias
and his pilot Pêro de Alenquer
, after putting down a mutiny, turned a cape where they were caught by a storm, naming it Cape of Storms. They followed the coast for a while realizing that it kept going eastward with even some tendency to the north. Lacking supplies, they turned around with the conviction that the far end of Africa had finally been reached. Upon their return to Portugal the promising cape was renamed Cape of Good Hope
.
Some years later, Christopher Columbus
landed in America
under rival Castilian command. Pope Alexander VI
decreed the Inter caetera
bull, dividing the non-Christian parts of the world between the two rival Catholic powers, Spain and Portugal.
Finally, in the years 1497 to 1498, Vasco da Gama
, again with Alenquer as pilot, took a direct route to Cape of Good Hope, via St. Helena. He went beyond the farthest point reached by Dias and named the country Natal
. Then he sailed northward, making land at Quelimane
(Mozambique
) and Mombasa
, where he found Chinese
traders, and Malindi
(both in modern Kenya
). In this town, he recruited an Arab pilot and set sail directly to Calicut
. On August 28, 1498, King Manuel of Portugal
informed the Pope of the good news that Portugal had reached India.
Egypt
and Venice
reacted to this news with hostility; from the Red Sea
, they jointly attacked the Portuguese ships that traded with India. The Portuguese defeated these ships near Diu in 1509. The Ottoman Empire
's indifferent reaction to Portuguese exploration left Portugal in almost exclusive control of trade through the Indian Ocean
. They established many bases along the eastern coast of Africa, from Mozambique to Somalia
, and captured Aden
in 1513.
In 1500, a Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral
, which followed the route just opened by Vasco da Gama to India, was dispersed by a storm in the Indian Ocean. One of the ships under command of Diogo Dias
arrived to a coast that wasn't in East Africa. Two years later, a chart already showed an elongated island east of Africa that bore the name Madagascar
. But only a century later, between 1613 and 1619, did the Portuguese explore the island in detail. They signed treaties with local chieftains and sent the first missionaries
, who found it impossible to make locals believe in Hell
, and were eventually expelled.
and the Monomotapa, would also be destroyed by the Portuguese conquerors.
Relations with the Kongo were initially good: Congolese kings embraced Catholicism
and welcomed Portuguese missionaries and merchants. But the slave trade eventually became a major issue of dispute in the region. The Portuguese (and later also the Dutch) supported the enslaving warrior state of the Jaggas, who sacked the Kongo repeatedly.
 They also used the Kongo to weaken the neighbour realm of Ndongo, where Queen Nzinga
They also used the Kongo to weaken the neighbour realm of Ndongo, where Queen Nzinga
put a fierce but eventually doomed resistance to Portuguese and Jagga ambitions. Portugal intervened militarily in these conflicts, creating the basis for their colony of Angola
. In 1663, after another conflict, the royal crown of Kongo was sent to Lisbon
. Nevertheless, a diminished Kongo Kingdom would still exist until 1885, when the last Manicongo, Pedro V, ceded his almost non-existent domain to Portugal.
The Portuguese dealt with the other major state of Southern Africa, the Monomotapa (in modern Zimbabwe
), in a similar manner: Portugal intervened in a local war hoping to get abundant mineral riches, imposing a protectorate. But with the authority of the Monomotapa diminished by the foreign presence, anarchy took over. The local miners migrated and even buried the mines to prevent them from falling into Portuguese hands. When in 1693 the neighbouring Cangamires invaded the country, the Portuguese accepted their failure and retreated to the coast.
began exploring and colonizing Africa. While the Dutch were waging a long war of independence against Spain, Portugal had temporarily united with Spain, starting in 1580 and ending in 1640. As a result, the growing colonial ambitions of the Netherlands were mostly directed against Portugal.
For this purpose, two Dutch companies were founded: the West Indies Company
, with power over all the Atlantic Ocean
, and the East Indies Company
, with power over the Indian Ocean.
The West India Company conquered Elmina in 1637 and Luanda
in 1640. In 1648, they were expelled from Luanda by the Portuguese. Overall the Dutch built 16 forts in different places, including Goree
in Senegal
, partly overtaking Portugal as the main slave-trading power.
The Dutch left a lasting impact in South Africa
, a region ignored by Portugal that the Dutch eventually decided to use as station in their route to East Asia. Jan van Riebeeck
founded Cape Town
in 1652, starting the European exploration and colonization of South Africa
.
 Almost at the same time as the Dutch, other European powers attempted to create their own outposts for the African slave trade.
Almost at the same time as the Dutch, other European powers attempted to create their own outposts for the African slave trade.
As early as 1530, English
merchant adventurer
s started trading in West Africa, coming into conflict with Portuguese troops. In 1581, Francis Drake
reached the Cape of Good Hope. In 1663, the English built Fort James
in Gambia. One year later, another English colonial expedition attempted to settle southern Madagascar, resulting in the death of most of the colonists. The English forts on the West African coast were eventually taken by the Dutch.
In 1626, the French Compagnie de l'Occident
was created. This company expelled the Dutch from Senegal
, making it the first French domain in Africa.
France
also put her eyes in Madagascar, the island that had been used since 1527 as a stop in travels to India. In 1642, the French East India Company
founded a settlement in southern Madagascar called Fort Dauphin
. The commercial results of this settlement were scarce and, again, most of the settlers died. One of the survivors, Etienne de Flacourt
, published a History of the Great Island of Madagascar and Relations, which was for a long time the main European source of information about the island. Further settlement attempts had no more success but, in 1667, François Martin
led the first expedition to the Malgassy heartland, reaching Lake Alaotra
. In 1665, France officially claimed Madagascar, under the name of Île Dauphine. However, little colonial activity would take place in Madagascar until the 19th century.
In 1657, Swedish
merchants founded Cape Coast
in modern Ghana, but were soon displaced by the Danish
, who founded Fort Christiansborg
near modern day Accra
.
In 1677, King Frederick William I
of Prussia
sent an expedition to the western coast of Africa. The commander of the expedition, Captain Blonk, signed agreements with the chieftains of the Gold Coast. There, the Prussians built a fort named Gross Friederichsburg and restored the abandoned Portuguese fort of Arguin. But in 1720, the king decided to sell these bases to the Netherlands for 7,000 ducats and 12 slaves, six of them chained with pure gold chains.
Overall, European exploration of Africa in the 17th and 18th centuries was very limited. Instead they were focused on the slave trade
, which only required coastal bases and items to trade. The real exploration of the African interior would start well into the 19th century.
distracted the attention of Europe from exploratory work in Africa, those wars nevertheless exercised great influence on the future of the continent, both in Egypt and South Africa. The occupation of Egypt (1798–1803), first by France and then by Great Britain, resulted in an effort by the Ottoman Empire
to regain direct control over that country. In 1811, Mehemet Ali established an almost independent state, and from 1820 onward established Egyptian rule over the eastern Sudan. In South Africa, the struggle with Napoleon caused the United Kingdom to take possession of the Dutch settlements at the Cape. In 1814, Cape Colony, which had been continuously occupied by British troops since 1806, was formally ceded to the British crown.
Meanwhile, considerable changes had been made in other parts of the continent. The occupation of Algiers
by France in 1830 put an end to the piracy of the Barbary states. Egyptian authority continued to expand southward, with the consequent additions to knowledge of the Nile
. The city of Zanzibar
, on the island of that name, rapidly attained importance. Accounts of a vast inland sea, and the discovery of the snow-clad mountains of Kilimanjaro in 1840–1848, stimulated the desire for further knowledge about Africa in Europe.
In the mid-19th century, Protestant
missions were carrying on active missionary work on the Guinea coast, in South Africa and in the Zanzibar dominions. Missionaries visited little-known regions and peoples, and in many instances became explorers and pioneers of trade and empire. David Livingstone
, a Scottish missionary, had been engaged since 1840 in work north of the Orange River
. In 1849, Livingstone crossed the Kalahari Desert
from south to north and reached Lake Ngami
. Between 1851 and 1856, he traversed the continent from west to east, discovering the great waterways of the upper Zambezi River. In November 1855, Livingstone became the first European to see the famous Victoria Falls
, named after the Queen of the United Kingdom
. From 1858 to 1864, the lower Zambezi, the Shire River
and Lake Nyasa were explored by Livingstone. Nyasa had been first reached by the confidential slave of António da Silva Porto
, a Portuguese trader established at Bié
in Angola, who crossed Africa during 1853–1856 from Benguella to the mouth of the Rovuma. A prime goal for explorers was to locate the source of the River Nile. Expeditions by Burton and Speke (1857–1858) and Speke and Grant (1863) located Lake Tanganyika
and Lake Victoria
. It was eventually proved to be the latter from which the Nile flowed.
Henry Morton Stanley
, who had in 1871 succeeded in finding and succouring Livingstone (originating the famous line "Dr. Livingstone, I presume"), started again for Zanzibar in 1874. In one of the most memorable of all exploring expeditions in Africa, Stanley circumnavigated Victoria Nyanza (Lake Victoria) and Lake Tanganyika. Striking farther inland to the Lualaba, he followed that river down to the Atlantic Ocean—which he reached in August 1877—and proved it to be the Congo.
Explorers were also active in other parts of the continent. Southern Morocco, the Sahara and the Sudan were traversed in many directions between 1860 and 1875 by Gerard Way
, Georg Schweinfurth and Gustav Nachtigal
. These travellers not only added considerably to geographical knowledge, but obtained invaluable information concerning the people, languages and natural history of the countries in which they sojourned. Among the discoveries of Schweinfurth was one that confirmed Greek legends of the existence beyond Egypt of a "pygmy race". But the first western discoverer of the pygmies of Central Africa was Paul du Chaillu
, who found them in the Ogowe district of the west coast in 1865, five years before Schweinfurth's first meeting with them. Du Chaillu had previously, through journeys in the Gabon region between 1855 and 1859, made popular in Europe the knowledge of the existence of the gorilla, whose existence was thought to be as legendary as that of the Pygmies of Aristotle.
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
, who explored and established settlements in North Africa. Fifteenth Century Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, especially under Henry the Navigator probed along the West African coast. Scientific curiosity and Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
missionary spirit soon were subordinated to mercantile considerations, including lucrative trafficking in enslaved persons. Others (Dutch, Spanish, French, English, etc.) joined in African trading, though for centuries European knowledge of Africa's interior was very vague. Much of the blank map was filled in by arduous, often fatal, expeditions in the Nineteenth Century.
Prehistoric links between Europe and Africa
The connection between EuropeEurope
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
is older than recorded history. It seems clear that cultural influences crossed the Mediterranean barrier during the late Palaeolithic
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic Age, Era or Period, is a prehistoric period of human history distinguished by the development of the most primitive stone tools discovered , and covers roughly 99% of human technological prehistory...
and Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
ages. Hence, the late Palaeolithic Aterian
Aterian
The Aterian industry is a name given by archaeologists to a type of stone tool manufacturing dating to the Middle Stone Age in the region around the Atlas Mountains and the northern Sahara, it refers the site of Bir el Ater, south of Annaba.The industry was probably created by modern humans ,...
industry and Capsian culture
Capsian culture
The Capsian culture was a Mesolithic culture of the Maghreb, which lasted from about 10,000 to 6,000 BCE.It was concentrated mainly in modern Tunisia, and Algeria, with some sites attested in southern Spain to Sicily....
, both from North Africa, are connected with Europe. Some early Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
influences may also have arrived to Europe via North Africa. Additionally, the Megalithic phenomenon of the Chalcolithic period is found on both shores of the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
.
Early historical exploration of Africa

Afri
Afri was a Latin name for the Carthaginians. It was received by the Romans from the Carthaginians, as a native term for their country....
people who settled in the area of current-day Tunisia. The Africa Province
Africa Province
The Roman province of Africa was established after the Romans defeated Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day northern Tunisia, and the small Mediterranean coast of modern-day western Libya along the Syrtis Minor...
of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
spanned the Mediterranean coast of what is now Libya, Tunisia and Algeria.
The parts of North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
north of the Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
were well known in antiquity. Prior to the 2nd century BC, however, Greek geographers were unaware that the land mass then known as Libya
Ancient Libya
The Latin name Libya referred to the region west of the Nile Valley, generally corresponding to modern Northwest Africa. Climate changes affected the locations of the settlements....
expanded south of the Sahara, assuming that the desert bounded on the outer Ocean
Oceanus
Oceanus ; , Ōkeanós) was a pseudo-geographical feature in classical antiquity, believed by the ancient Greeks and Romans to be the world-ocean, an enormous river encircling the world....
. Indeed, Alexander the Great, according to Plutarchus' Lives, considered sailing from the mouths of the Indus back to Macedonia passing south of Africa as a shortcut compared to the land route. Even Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene was a Greek mathematician, poet, athlete, geographer, astronomer, and music theorist.He was the first person to use the word "geography" and invented the discipline of geography as we understand it...
around 200 BC still assumed an extent of the landmass no further south than the Horn of Africa
Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa is a peninsula in East Africa that juts hundreds of kilometers into the Arabian Sea and lies along the southern side of the Gulf of Aden. It is the easternmost projection of the African continent...
. It was only in Ptolemy's world map
Ptolemy's world map
The Ptolemy world map is a map of the known world to Western society in the 2nd century AD. It was based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book Geographia, written c. 150...
(2nd century AD) that the realization that the southward extent of Africa was not in fact known at the time was made explicit.
As for early exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa as a geographical term refers to the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara. A political definition of Sub-Saharan Africa, instead, covers all African countries which are fully or partially located south of the Sahara...
, the ancient Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
describes how the Egyptian
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
Pharaoh Necho II
Necho II
Necho II was a king of the Twenty-sixth dynasty of Egypt .Necho II is most likely the pharaoh mentioned in several books of the Bible . The Book of Kings states that Necho met King Josiah of the Kingdom of Judah at Megiddo and killed him...
sent out an expedition manned by Phoenicia
Phoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
n sailors about 600 BC which in three years circumnavigated Africa. They sailed south, rounded the Cape heading west, made their way north to the Mediterranean and then returned home. He states that they paused each year to sow and harvest grain. They reported that as they sailed around the southern end of the continent they had the sun to their north, which Herodotus found unbelievable. The Egyptologist Alan Lloyd suggests that the Greeks at this time understood that anyone going south far enough and then turning west would have the sun on their right but found it unbelievable that Africa reached so far south. He suggests that "It is extremely unlikely that an Egyptian king would, or could, have acted as Necho is depicted as doing" and that the story might have been triggered by the failure of Sataspes attempt to circumnavigate Africa under Xerxes the Great.
The Phoenicians explored North Africa, establishing a number of colonies, the most prominent of which was Carthage
Carthage
Carthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
. Carthage itself conducted exploration of West Africa. Donald Harden describes the journey of Hanno the Navigator
Hanno the Navigator
Hanno the Navigator was a Carthaginian explorer c. 500 BC, best known for his naval exploration of the African coast...
which Harden dates to c. 425 BC and even quotes in translation the surviving Greek account (about two pages long) of this expedition. There is some uncertainty as to how far precisely Hanno reached, "Some taking Hanno to the Cameroons, or even Gabon, while others say he stopped at Sierre Leone.". In 146 BC the Romans had conquered the African coasts, part of Numidia
Numidia
Numidia was an ancient Berber kingdom in part of present-day Eastern Algeria and Western Tunisia in North Africa. It is known today as the Chawi-land, the land of the Chawi people , the direct descendants of the historical Numidians or the Massyles The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later...
and Mauretania
Mauretania
Mauretania is a part of the historical Ancient Libyan land in North Africa. It corresponds to present day Morocco and a part of western Algeria...
and started to explore that land. It was later subdivided into Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana was a Roman province located in northwestern Africa, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The province extended from the northern peninsula, opposite Gibraltar, to Chellah and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Oued Laou river. Its...
, Mauretania Caesariensis
Mauretania Caesariensis
Mauretania Caesariensis was a Roman province located in northwestern Africa. It was the easternmost of the North African Roman provinces, mainly in present Algeria, with its capital at Caesarea , now Cherchell.-Historical background:In the first century AD, Roman...
, Numidia
Numidia
Numidia was an ancient Berber kingdom in part of present-day Eastern Algeria and Western Tunisia in North Africa. It is known today as the Chawi-land, the land of the Chawi people , the direct descendants of the historical Numidians or the Massyles The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later...
, and Africa Proconsularis also known as Vetus or Africa Nova. They remained a part of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
until the 5th century AD.
Europeans in the Middle Ages

Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
in the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, North Africa was culturally cut off from non-Muslim Europe. The Islamic Empire
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
created a barrier between Europe and the rest of the world, with European traders paying heavy tributes to obtain prized commodities like West African gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
, East Asian spices and silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
. The Italian republics
History of Italy
Italy, united in 1861, has significantly contributed to the political, cultural and social development of the entire Mediterranean region. Many cultures and civilizations have existed there since prehistoric times....
of Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
and Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
, among others, specialized in this trade.
In addition, the Jews
Jews
The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
of modern Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, and Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
were allowed to trade in both cultural regions. Among them were Abraham Cresques
Abraham Cresques
Abraham Cresques , whose real name was probably Cresques Abraham, was a 14th-century Jewish cartographer from Palma, Majorca...
and his son Jehuda
Jehuda Cresques
Jehuda Cresques , also known as Jafudà Cresques, Jaume Riba, and Cresques lo Juheu was a Catalan cartographer, and was once believed to be the man who coordinated the discoveries of the Portuguese naval school at Sagres in the early 15th century.Son of Abraham Cresques, a famous Jewish...
, whose 1375 Catalan Atlas
Catalan Atlas
The Catalan Atlas is the most important Catalan map of the medieval period. It was produced by the Majorcan cartographic school and is attributed to Cresques Abraham , a Jewish book illuminator who was self-described as being a master of the maps of the world as well as compasses...
improved European knowledge of Africa and other regions, with a good deal of Muslim geographical knowledge and some educated guesses and imagination to fill in the blanks. This atlas details the Catalan expedition of Jaume Ferrer
Jaume Ferrer
Jaume Ferrer was a Majorcan sailor and explorer.Practically nothing is known of Jaume Ferrer, save that he was a Majorcan captain, who set out in a galley in 1346, and sailed down the West African coast in an attempt to reach the legendary "River of Gold". The results of this expedition, including...
to the Gold River in 1346, which according to the map went south of Cape Bojador
Cape Bojador
Cape Bojador or Cape Boujdour is a headland on the northern coast of Western Sahara, at 26° 07' 37"N, 14° 29' 57"W. , as well as the name of a nearby town with a population of 41,178.It is shown on nautical charts with the original Portuguese name "Cabo Bojador", but is sometimes...
and to what is called West Africa Finisterrae.
The Genoese were also interested in circumventing the Muslim monopoly on Asian trade. In 1291, Tedisio Doria
Doria
Doria, originally de Auria , meaning "the sons of Auria", and then de Oria or d'Oria, is the name of an old and extremely wealthy Genoese family who played a major role in the history of the Republic of Genoa and in Italy, from the 12th century to the 16th century.-Origins:According to legend, a...
ordered Vandino and Ugolino Vivaldi
Vandino and Ugolino Vivaldi
Vandino and Ugolino Vivaldi were two brothers and Genoese explorers and merchants....
to reach India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
via the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
. When the expedition was lost, Doria sent ambassadors to Mogadishu
Mogadishu
Mogadishu , popularly known as Xamar, is the largest city in Somalia and the nation's capital. Located in the coastal Benadir region on the Indian Ocean, the city has served as an important port for centuries....
to find out their fate.
Another interesting factor motivating European exploration was rumours of a powerful Christian kingdom, ruled by a priest-king known as Prester John
Prester John
The legends of Prester John were popular in Europe from the 12th through the 17th centuries, and told of a Christian patriarch and king said to rule over a Christian nation lost amidst the Muslims and pagans in the Orient. Written accounts of this kingdom are variegated collections of medieval...
, located somewhere in the eastern portion of Africa. Prester John was often identified as a Christian king who was a descendant of the Three Magi. Europeans sought his aid to defeat the Muslim nations that separated them from the Orient, or at least help them circumvent the Muslim monopoly.
Naval charts of 1339 show that the Canary Islands
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
were already known to Europeans. In 1341, Portuguese and Italian explorers prepared a joint expedition. In 1342 the Catalans organized an expedition captained by Francesc Desvalers to the Canary Islands
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
that set sail from Majorca. In 1344, Pope Clement VI
Pope Clement VI
Pope Clement VI , bornPierre Roger, the fourth of the Avignon Popes, was pope from May 1342 until his death in December of 1352...
named French admiral Luis de la Cerda
Luis de la Cerda
Luis de La Cerda, also called Louis of Spain was an expatriate royal prince of the Crown of Castile, who lived and served in the Kingdom of France. Among his titles, Luis de la Cerda was the count of Talmont, count of Clermont and an admiral of France...
Prince of Fortune, and sent him to conquer the Canaries.
In 1402, Jean de Bethencourt
Jean de Béthencourt
Jean de Béthencourt was a French explorer who, in 1402, led an expedition to the Canary Islands, landing first on the north side of Lanzarote...
and Gadifer de la Salle
Gadifer de la Salle
Gadifer de La Salle was a French knight and crusader of Poitevine origin who, with Jean de Béthencourt, conquered and explored the Canary Islands for the Kingdom of Castile....
sailed to conquer the Canary Islands but found them already plundered by the Castilians
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval and modern state in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accession of the then King Ferdinand III of Castile to the vacant Leonese throne...
. Although they did conquer the isles, Bethencourt's nephew was forced to cede them to Castile in 1418.
In 1455 and 1456 two Italian explorers Alvise Cadamosto from Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
and Antoniotto Usodimare
Antoniotto Usodimare
Antoniotto Usodimare or Usus di Mare was a Genoese trader and explorer in the service of the Portuguese Prince Henry the Navigator. Jointly with Alvise Cadamosto, Usodimare discovered a great stretch of the West African coast in two known voyages in 1455 and 1456...
from Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
, working for the king of Portugal, followed the Gambia river, visiting the land of Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
, while another Italian sailor, Antonio da Noli from Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
explored Cabo Verde and the Bijagos islands.
Portuguese expeditions

Madeira
Madeira is a Portuguese archipelago that lies between and , just under 400 km north of Tenerife, Canary Islands, in the north Atlantic Ocean and an outermost region of the European Union...
. In 1425, he tried to secure the Canary Islands
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
as well, but these were already under firm Castilian control. In 1431, another Portuguese expedition reached and annexed the Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
.
Along the western and eastern coasts of Africa, progress was also steady; Portuguese sailors reached Cape Bojador
Cape Bojador
Cape Bojador or Cape Boujdour is a headland on the northern coast of Western Sahara, at 26° 07' 37"N, 14° 29' 57"W. , as well as the name of a nearby town with a population of 41,178.It is shown on nautical charts with the original Portuguese name "Cabo Bojador", but is sometimes...
in 1434 and Cape Blanco
Ras Nouadhibou
Ras Nouadhibou is a 40-mile peninsula or headland in the African coast of the Atlantic Ocean by the Tropic of Cancer. It is internationally known as Cap Blanc in French or Cabo Blanco in Spanish .- History :...
in 1441. In 1433, they built a fortress on the island of Arguin
Arguin
Arguin is an island off the western coast of Mauritania in the Bay of Arguin, at 20° 36' N., 16° 27' W. It is six km long by two broad. Off the island are extensive and dangerous reefs...
, in modern day Mauritania
Mauritania
Mauritania is a country in the Maghreb and West Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by Western Sahara in the north, by Algeria in the northeast, by Mali in the east and southeast, and by Senegal in the southwest...
, trading European wheat and cloth for African gold and slaves. It was the first time that the semi-mythic gold of the Sudan reached Europe without Muslim mediation. Most of the slaves were sent to Madeira, which became, after thorough deforestation, the first European plantation colony. Between 1444 and 1447, the Portuguese explored the coasts of Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
, Gambia, and Guinea
Guinea
Guinea , officially the Republic of Guinea , is a country in West Africa. Formerly known as French Guinea , it is today sometimes called Guinea-Conakry to distinguish it from its neighbour Guinea-Bissau. Guinea is divided into eight administrative regions and subdivided into thirty-three prefectures...
. In 1456, a Venetian captain under Portuguese command explored the islands of Cape Verde
Cape Verde
The Republic of Cape Verde is an island country, spanning an archipelago of 10 islands located in the central Atlantic Ocean, 570 kilometres off the coast of Western Africa...
. In 1462, two years after Prince Henry's death, Portuguese sailors explored the Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
The Republic of Guinea-Bissau is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Senegal to the north, and Guinea to the south and east, with the Atlantic Ocean to its west....
islands and named Sierra Leoa
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone , officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Guinea to the north and east, Liberia to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west and southwest. Sierra Leone covers a total area of and has an estimated population between 5.4 and 6.4...
(Lion Range).
In 1469, Fernão Gomes
Fernão Gomes
Fernão Gomes was a Portuguese merchant and explorer from Lisbon, the son of Tristão Gomes de Brito .In 1469, King Afonso V of Portugal granted him the monopoly on trade in the Gulf of Guinea...
rented the rights of African exploration for five years. Under his direction, in 1471, the Portuguese reached modern Ghana
Ghana
Ghana , officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country located in West Africa. It is bordered by Côte d'Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, and the Gulf of Guinea to the south...
and settled in La Mina (the mine), later renamed Elmina
Elmina
Elmina, is a town in the Central Region, situated on a south-facing bay on the Atlantic Ocean coast of Ghana, about 12 km west of Cape Coast...
. They had finally reached a country with an abundance of gold, hence the historical name of "Gold Coast
Gold Coast (British colony)
The Gold Coast was a British colony on the Gulf of Guinea in west Africa that became the independent nation of Ghana in 1957.-Overview:The first Europeans to arrive at the coast were the Portuguese in 1471. They encountered a variety of African kingdoms, some of which controlled substantial...
" that Elmina would eventually receive.
In 1472, Fernão do Pó
Fernão do Pó
Fernão do Pó , also Fernão Pó, Fernando Pó, Fernando Poo was a Portuguese navigator and explorer of the West African coast. He discovered the islands in the Gulf of Guinea around 1472, one of which until the mid 1900s bore a version of his name, Fernando Pó or Fernando Poo. The island is...
discovered the island that would bear his name for centuries (now Bioko
Bioko
Bioko is an island 32 km off the west coast of Africa, specifically Cameroon, in the Gulf of Guinea. It is the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea with a population of 124,000 and an area of . It is volcanic with its highest peak the Pico Basile at .-Geography:Bioko has a total area of...
) and an estuary abundant in shrimp
Shrimp
Shrimp are swimming, decapod crustaceans classified in the infraorder Caridea, found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water. Adult shrimp are filter feeding benthic animals living close to the bottom. They can live in schools and can swim rapidly backwards. Shrimp are an important...
, giving its name to Cameroon
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon , is a country in west Central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Cameroon's coastline lies on the...
.
Soon after, the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
was crossed by Europeans . Portugal established a base in Sāo Tomé
São Tomé
-Transport:São Tomé is served by São Tomé International Airport with regular flights to Europe and other African Countries.-Climate:São Tomé features a tropical wet and dry climate with a relatively lengthy wet season and a short dry season. The wet season runs from October through May while the...
that, after 1485, was settled with criminals. After 1497, expelled Spanish and Portuguese Jews also found a safe haven there.
In 1482, Diogo Cão
Diogo Cão
Diogo Cão was a Portuguese explorer and one of the most remarkable navigators of the Age of Discovery, who made two voyages sailing along the west coast of Africa to Namibia in the 1480s.-Early life and family:...
found the mouth of a large river and learned of the existence of a great kingdom, Kongo
Kingdom of Kongo
The Kingdom of Kongo was an African kingdom located in west central Africa in what are now northern Angola, Cabinda, the Republic of the Congo, and the western portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo...
. In 1485, he explored the river upstream as well.
But the Portuguese wanted, above anything else, to find a route to India and kept trying to circumnavigate Africa. In 1485, the expedition of João Afonso d'Aveiros, with the German astronomer Martin of Behaim as part of the crew, explored the Bight of Benin
Bight of Benin
The Bight of Benin is a bight on the western African coast that extends eastward for about 400 miles from Cape St. Paul to the Nun outlet of the Niger River. To the east it is continued by the Bight of Bonny . The bight is part of the Gulf of Guinea...
, returning information about African king Ogane.
In 1488, Bartolomeu Dias
Bartolomeu Dias
Bartolomeu Dias , a nobleman of the Portuguese royal household, was a Portuguese explorer who sailed around the southernmost tip of Africa in 1488, the first European known to have done so.-Purposes of the Dias expedition:...
and his pilot Pêro de Alenquer
Pêro de Alenquer
Pêro de Alenquer Portuguese explorer of the African coast. Accompanied Bartolomeu Dias in his journey around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487/1488. Latter wrote a description of Vasco da Gama's first voyage to India. Pêro was born in Alenquer....
, after putting down a mutiny, turned a cape where they were caught by a storm, naming it Cape of Storms. They followed the coast for a while realizing that it kept going eastward with even some tendency to the north. Lacking supplies, they turned around with the conviction that the far end of Africa had finally been reached. Upon their return to Portugal the promising cape was renamed Cape of Good Hope
Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula, South Africa.There is a misconception that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa, because it was once believed to be the dividing point between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. In fact, the...
.
Some years later, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
landed in America
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
under rival Castilian command. Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI , born Roderic Llançol i Borja was Pope from 1492 until his death on 18 August 1503. He is one of the most controversial of the Renaissance popes, and his Italianized surname—Borgia—became a byword for the debased standards of the Papacy of that era, most notoriously the Banquet...
decreed the Inter caetera
Inter caetera
Inter caetera was a papal bull issued by Pope Alexander VI on , which granted to Spain all lands to the "west and south" of a pole-to-pole line 100 leagues west and south of any of the islands of the Azores or the Cape Verde Islands.It remains unclear to the present whether the pope was issuing a...
bull, dividing the non-Christian parts of the world between the two rival Catholic powers, Spain and Portugal.
Finally, in the years 1497 to 1498, Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira was a Portuguese explorer, one of the most successful in the Age of Discovery and the commander of the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India...
, again with Alenquer as pilot, took a direct route to Cape of Good Hope, via St. Helena. He went beyond the farthest point reached by Dias and named the country Natal
Birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring. The offspring is brought forth from the mother. The time of human birth is defined as the time at which the fetus comes out of the mother's womb into the world...
. Then he sailed northward, making land at Quelimane
Quelimane
Quelimane is a seaport in Mozambique. It is the administrative capital of the Zambezia Province and the province's largest city, and stands 25 km from the mouth of the Rio dos Bons Sinais . The river was named when Vasco da Gama, on his way to India, reached it and saw "good signs" that he was on...
(Mozambique
Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique , is a country in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west and Swaziland and South Africa to the southwest...
) and Mombasa
Mombasa
Mombasa is the second-largest city in Kenya. Lying next to the Indian Ocean, it has a major port and an international airport. The city also serves as the centre of the coastal tourism industry....
, where he found Chinese
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
traders, and Malindi
Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Galana River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi is 117,735 . It is the capital of the Malindi District.Tourism is the major industry in Malindi. The city is...
(both in modern Kenya
Kenya
Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east...
). In this town, he recruited an Arab pilot and set sail directly to Calicut
History of Kozhikode
Kozhikode , also known as Calicut, is a city in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is the third largest city in Kerala and the headquarters of Kozhikode district....
. On August 28, 1498, King Manuel of Portugal
Manuel I of Portugal
Manuel I , the Fortunate , 14th king of Portugal and the Algarves was the son of Infante Ferdinand, Duke of Viseu, , by his wife, Infanta Beatrice of Portugal...
informed the Pope of the good news that Portugal had reached India.
Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
and Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
reacted to this news with hostility; from the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
, they jointly attacked the Portuguese ships that traded with India. The Portuguese defeated these ships near Diu in 1509. The Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
's indifferent reaction to Portuguese exploration left Portugal in almost exclusive control of trade through the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
. They established many bases along the eastern coast of Africa, from Mozambique to Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
, and captured Aden
Aden
Aden is a seaport city in Yemen, located by the eastern approach to the Red Sea , some 170 kilometres east of Bab-el-Mandeb. Its population is approximately 800,000. Aden's ancient, natural harbour lies in the crater of an extinct volcano which now forms a peninsula, joined to the mainland by a...
in 1513.
In 1500, a Portuguese fleet commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral was a Portuguese noble, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the discoverer of Brazil. Cabral conducted the first substantial exploration of the northeast coast of South America and claimed it for Portugal. While details of Cabral's early life are sketchy, it...
, which followed the route just opened by Vasco da Gama to India, was dispersed by a storm in the Indian Ocean. One of the ships under command of Diogo Dias
Diogo Dias
Diogo Dias, also known as Diogo Gomes, was a 15th-century Portuguese explorer. He was the brother of Bartolomeu Dias and discovered some of the Cape Verde islands together with António Noli....
arrived to a coast that wasn't in East Africa. Two years later, a chart already showed an elongated island east of Africa that bore the name Madagascar
Madagascar
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa...
. But only a century later, between 1613 and 1619, did the Portuguese explore the island in detail. They signed treaties with local chieftains and sent the first missionaries
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group sent into an area to do evangelism or ministries of service, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care and economic development. The word "mission" originates from 1598 when the Jesuits sent members abroad, derived from the Latin...
, who found it impossible to make locals believe in Hell
Hell
In many religious traditions, a hell is a place of suffering and punishment in the afterlife. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hells as endless. Religions with a cyclic history often depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations...
, and were eventually expelled.
Portugal and the native states of equatorial Africa
Portuguese colonization of some parts of Africa would have a very negative impact in some of the existing civilizations. By 1583, they had destroyed the Afro-Muslim Zendj civilization of East Africa that competed with them for the African trade. Two other important African kingdoms, the KongoKingdom of Kongo
The Kingdom of Kongo was an African kingdom located in west central Africa in what are now northern Angola, Cabinda, the Republic of the Congo, and the western portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo...
and the Monomotapa, would also be destroyed by the Portuguese conquerors.
Relations with the Kongo were initially good: Congolese kings embraced Catholicism
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
and welcomed Portuguese missionaries and merchants. But the slave trade eventually became a major issue of dispute in the region. The Portuguese (and later also the Dutch) supported the enslaving warrior state of the Jaggas, who sacked the Kongo repeatedly.

Nzinga of Ndongo and Matamba
Nzinga Mbande , also known as Ana de Sousa Nzinga Mbande, was a 17th century queen of the Ndongo and Matamba Kingdoms of the Mbundu people in southwestern Africa.-Early life:...
put a fierce but eventually doomed resistance to Portuguese and Jagga ambitions. Portugal intervened militarily in these conflicts, creating the basis for their colony of Angola
Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
. In 1663, after another conflict, the royal crown of Kongo was sent to Lisbon
Lisbon
Lisbon is the capital city and largest city of Portugal with a population of 545,245 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Lisbon extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of 3 million on an area of , making it the 9th most populous urban...
. Nevertheless, a diminished Kongo Kingdom would still exist until 1885, when the last Manicongo, Pedro V, ceded his almost non-existent domain to Portugal.
The Portuguese dealt with the other major state of Southern Africa, the Monomotapa (in modern Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
), in a similar manner: Portugal intervened in a local war hoping to get abundant mineral riches, imposing a protectorate. But with the authority of the Monomotapa diminished by the foreign presence, anarchy took over. The local miners migrated and even buried the mines to prevent them from falling into Portuguese hands. When in 1693 the neighbouring Cangamires invaded the country, the Portuguese accepted their failure and retreated to the coast.
Dutch intervention
Beginning in the 17th century, the NetherlandsNetherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
began exploring and colonizing Africa. While the Dutch were waging a long war of independence against Spain, Portugal had temporarily united with Spain, starting in 1580 and ending in 1640. As a result, the growing colonial ambitions of the Netherlands were mostly directed against Portugal.
For this purpose, two Dutch companies were founded: the West Indies Company
Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants. Among its founding fathers was Willem Usselincx...
, with power over all the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, and the East Indies Company
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
, with power over the Indian Ocean.
The West India Company conquered Elmina in 1637 and Luanda
Luanda
Luanda, formerly named São Paulo da Assunção de Loanda, is the capital and largest city of Angola. Located on Angola's coast with the Atlantic Ocean, Luanda is both Angola's chief seaport and its administrative center. It has a population of at least 5 million...
in 1640. In 1648, they were expelled from Luanda by the Portuguese. Overall the Dutch built 16 forts in different places, including Goree
Gorée
Île de Gorée Île de Gorée Île de Gorée (i.e. "Gorée Island"; is one of the 19 communes d'arrondissement (i.e. "commune of arrondissement") of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is a island located at sea from the main harbor of Dakar ....
in Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
, partly overtaking Portugal as the main slave-trading power.
The Dutch left a lasting impact in South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, a region ignored by Portugal that the Dutch eventually decided to use as station in their route to East Asia. Jan van Riebeeck
Jan van Riebeeck
Johan Anthoniszoon "Jan" van Riebeeck was a Dutch colonial administrator and founder of Cape Town.-Biography:...
founded Cape Town
Cape Town
Cape Town is the second-most populous city in South Africa, and the provincial capital and primate city of the Western Cape. As the seat of the National Parliament, it is also the legislative capital of the country. It forms part of the City of Cape Town metropolitan municipality...
in 1652, starting the European exploration and colonization of South Africa
History of South Africa
South African history has been dominated by the interaction and conflict of several diverse ethnic groups. The aboriginal Khoisan people have lived in the region for millennia. Most of the population, however, trace their history to immigration since...
.
Other early European presence in Africa

As early as 1530, English
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
merchant adventurer
Company of Merchant Adventurers
The Company of Merchant Adventurers usually refers to theCompany of Merchant Adventurers of London, founded in 1407 and London's leading guild of overseas merchants.It may also refer to:...
s started trading in West Africa, coming into conflict with Portuguese troops. In 1581, Francis Drake
Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake, Vice Admiral was an English sea captain, privateer, navigator, slaver, and politician of the Elizabethan era. Elizabeth I of England awarded Drake a knighthood in 1581. He was second-in-command of the English fleet against the Spanish Armada in 1588. He also carried out the...
reached the Cape of Good Hope. In 1663, the English built Fort James
Fort James
Fort James may refer to:* James Island * Fort James * Fort James, Antigua and Barbuda* Fort Amsterdam, New York City* Fort James , historic fort which is on the National Register of Historic Places in South Dakota...
in Gambia. One year later, another English colonial expedition attempted to settle southern Madagascar, resulting in the death of most of the colonists. The English forts on the West African coast were eventually taken by the Dutch.
In 1626, the French Compagnie de l'Occident
Compagnie de l'Occident
The Compagnie de l'Occident was a French Crown corporation that existed from 1664 to 1667. Its purpose was to exploit the resources of the French colonies and compete with the powerful Dutch and English companies....
was created. This company expelled the Dutch from Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
, making it the first French domain in Africa.
France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
also put her eyes in Madagascar, the island that had been used since 1527 as a stop in travels to India. In 1642, the French East India Company
French East India Company
The French East India Company was a commercial enterprise, founded in 1664 to compete with the British and Dutch East India companies in colonial India....
founded a settlement in southern Madagascar called Fort Dauphin
Tôlanaro
Tôlanaro or Tolagnaro is a city in Madagascar. It is the capital of Anosy Region and of Tôlanaro District. It has a port of local importance, and a new port has been built at Ehoala...
. The commercial results of this settlement were scarce and, again, most of the settlers died. One of the survivors, Etienne de Flacourt
Étienne de Flacourt
Étienne de Flacourt was a French governor of Madagascar, born at Orléans in 1607. He was named governor of Madagascar by the French East India Company in 1648....
, published a History of the Great Island of Madagascar and Relations, which was for a long time the main European source of information about the island. Further settlement attempts had no more success but, in 1667, François Martin
François Martin
François Martin was the first Governor General of Pondicherry. He founded Pondicherry, the future capital of French India in 1674. He was Commissioner of French East India Company before holding this post and was preceded by François Baron and succeeded by Pierre Dulivier. There is a street named...
led the first expedition to the Malgassy heartland, reaching Lake Alaotra
Lake Alaotra
Lake Alaotra is the largest lake in Madagascar, located in Toamasina Province, in the northern central plateau. Its basin is composed of shallow freshwater lakes and marshes surrounded by areas of dense vegetation. It forms the center of the island's most important rice-growing region...
. In 1665, France officially claimed Madagascar, under the name of Île Dauphine. However, little colonial activity would take place in Madagascar until the 19th century.
In 1657, Swedish
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
merchants founded Cape Coast
Cape Coast
Cape Coast, or Cabo Corso, is the capital of the Central Region of Ghana and is also the capital city of the Fante people, or Mfantsefo. It is situated 165 km west of Accra on the Gulf of Guinea. It has a population of 82,291 . From the 16th century the city has changed hands between the...
in modern Ghana, but were soon displaced by the Danish
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, who founded Fort Christiansborg
Osu Castle
Osu Castle, also known as Fort Christiansborg or simply the Castle, is a castle located in Osu, Accra, on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean's Gulf of Guinea. The first substantial fort was built by the Danish in the 1660s, though the castle has changed hands between Denmark, Portugal, the Akwamu, the...
near modern day Accra
Accra
Accra is the capital and largest city of Ghana, with an urban population of 1,658,937 according to the 2000 census. Accra is also the capital of the Greater Accra Region and of the Accra Metropolitan District, with which it is coterminous...
.
In 1677, King Frederick William I
Frederick William I of Prussia
Frederick William I of the House of Hohenzollern, was the King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death...
of Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
sent an expedition to the western coast of Africa. The commander of the expedition, Captain Blonk, signed agreements with the chieftains of the Gold Coast. There, the Prussians built a fort named Gross Friederichsburg and restored the abandoned Portuguese fort of Arguin. But in 1720, the king decided to sell these bases to the Netherlands for 7,000 ducats and 12 slaves, six of them chained with pure gold chains.
Overall, European exploration of Africa in the 17th and 18th centuries was very limited. Instead they were focused on the slave trade
African slave trade
Systems of servitude and slavery were common in many parts of Africa, as they were in much of the ancient world. In some African societies, the enslaved people were also indentured servants and fully integrated; in others, they were treated much worse...
, which only required coastal bases and items to trade. The real exploration of the African interior would start well into the 19th century.
19th century
Although the Napoleonic WarsNapoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
distracted the attention of Europe from exploratory work in Africa, those wars nevertheless exercised great influence on the future of the continent, both in Egypt and South Africa. The occupation of Egypt (1798–1803), first by France and then by Great Britain, resulted in an effort by the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
to regain direct control over that country. In 1811, Mehemet Ali established an almost independent state, and from 1820 onward established Egyptian rule over the eastern Sudan. In South Africa, the struggle with Napoleon caused the United Kingdom to take possession of the Dutch settlements at the Cape. In 1814, Cape Colony, which had been continuously occupied by British troops since 1806, was formally ceded to the British crown.
Meanwhile, considerable changes had been made in other parts of the continent. The occupation of Algiers
Algiers
' is the capital and largest city of Algeria. According to the 1998 census, the population of the city proper was 1,519,570 and that of the urban agglomeration was 2,135,630. In 2009, the population was about 3,500,000...
by France in 1830 put an end to the piracy of the Barbary states. Egyptian authority continued to expand southward, with the consequent additions to knowledge of the Nile
Nile
The Nile is a major north-flowing river in North Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is long. It runs through the ten countries of Sudan, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt.The Nile has two major...
. The city of Zanzibar
Zanzibar
Zanzibar ,Persian: زنگبار, from suffix bār: "coast" and Zangi: "bruin" ; is a semi-autonomous part of Tanzania, in East Africa. It comprises the Zanzibar Archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of numerous small islands and two large ones: Unguja , and Pemba...
, on the island of that name, rapidly attained importance. Accounts of a vast inland sea, and the discovery of the snow-clad mountains of Kilimanjaro in 1840–1848, stimulated the desire for further knowledge about Africa in Europe.
In the mid-19th century, Protestant
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
missions were carrying on active missionary work on the Guinea coast, in South Africa and in the Zanzibar dominions. Missionaries visited little-known regions and peoples, and in many instances became explorers and pioneers of trade and empire. David Livingstone
David Livingstone
David Livingstone was a Scottish Congregationalist pioneer medical missionary with the London Missionary Society and an explorer in Africa. His meeting with H. M. Stanley gave rise to the popular quotation, "Dr...
, a Scottish missionary, had been engaged since 1840 in work north of the Orange River
Orange River
The Orange River , Gariep River, Groote River or Senqu River is the longest river in South Africa. It rises in the Drakensberg mountains in Lesotho, flowing westwards through South Africa to the Atlantic Ocean...
. In 1849, Livingstone crossed the Kalahari Desert
Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savannah in Southern Africa extending , covering much of Botswana and parts of Namibia and South Africa, as semi-desert, with huge tracts of excellent grazing after good rains. The Kalahari supports more animals and plants than a true desert...
from south to north and reached Lake Ngami
Lake Ngami
Lake Ngami is an endorheic lake in Botswana north of the Kalahari Desert. It is seasonally filled by the Taughe River an affluent of the Okavango River system flowing out of the western side of the Okavango Delta. It is one of the fragmented remnants of the ancient Lake Makgadikgadi...
. Between 1851 and 1856, he traversed the continent from west to east, discovering the great waterways of the upper Zambezi River. In November 1855, Livingstone became the first European to see the famous Victoria Falls
Victoria Falls
The Victoria Falls or Mosi-oa-Tunya is a waterfall located in southern Africa on the Zambezi River between the countries of Zambia and Zimbabwe.-Introduction:...
, named after the Queen of the United Kingdom
Victoria of the United Kingdom
Victoria was the monarch of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death. From 1 May 1876, she used the additional title of Empress of India....
. From 1858 to 1864, the lower Zambezi, the Shire River
Shire River
The Shire is a river in Malawi and Mozambique. The river has been known as the Shiré or Chire River. It is the outlet of Lake Malawi and flows into the Zambezi. Its length is 402 km; including Lake Malawi and the Ruhuhu, its headstream, it has a length of about 1200 km...
and Lake Nyasa were explored by Livingstone. Nyasa had been first reached by the confidential slave of António da Silva Porto
Antonío da Silva Porto
António Francisco Ferreira da Silva Porto was a Portuguese trader and explorer in Angola, in the Portuguese West Africa.-Biography:...
, a Portuguese trader established at Bié
Bié (province)
Bié is a province of Angola. Located on Bié Plateau in central part of country. Its capital is Kuito and it has an area of 70,314 km² and a population of approximately 800,000. Municipalities in the province include Andulo, Nharea, Cunhinga, Chinguar, Chitembo, Catabola, Camacupa and Cuemba...
in Angola, who crossed Africa during 1853–1856 from Benguella to the mouth of the Rovuma. A prime goal for explorers was to locate the source of the River Nile. Expeditions by Burton and Speke (1857–1858) and Speke and Grant (1863) located Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika is an African Great Lake. It is estimated to be the second largest freshwater lake in the world by volume, and the second deepest, after Lake Baikal in Siberia; it is also the world's longest freshwater lake...
and Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. The lake was named for Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom, by John Hanning Speke, the first European to discover this lake....
. It was eventually proved to be the latter from which the Nile flowed.
Henry Morton Stanley
Henry Morton Stanley
Sir Henry Morton Stanley, GCB, born John Rowlands , was a Welsh journalist and explorer famous for his exploration of Africa and his search for David Livingstone. Upon finding Livingstone, Stanley allegedly uttered the now-famous greeting, "Dr...
, who had in 1871 succeeded in finding and succouring Livingstone (originating the famous line "Dr. Livingstone, I presume"), started again for Zanzibar in 1874. In one of the most memorable of all exploring expeditions in Africa, Stanley circumnavigated Victoria Nyanza (Lake Victoria) and Lake Tanganyika. Striking farther inland to the Lualaba, he followed that river down to the Atlantic Ocean—which he reached in August 1877—and proved it to be the Congo.
Explorers were also active in other parts of the continent. Southern Morocco, the Sahara and the Sudan were traversed in many directions between 1860 and 1875 by Gerard Way
Gerard Way
Gerard Arthur Way is an American musician and comic book writer who has served as lead vocalist and co-founder of the band My Chemical Romance since its formation in 2001...
, Georg Schweinfurth and Gustav Nachtigal
Gustav Nachtigal
Gustav Nachtigal was a German explorer of Central and West Africa. He is further known as the German Empire's consul-general for Tunisia and Commissioner for West Africa. His mission as commissioner resulted in Togoland and Kamerun becoming the first colonies of a German colonial empire...
. These travellers not only added considerably to geographical knowledge, but obtained invaluable information concerning the people, languages and natural history of the countries in which they sojourned. Among the discoveries of Schweinfurth was one that confirmed Greek legends of the existence beyond Egypt of a "pygmy race". But the first western discoverer of the pygmies of Central Africa was Paul du Chaillu
Paul du Chaillu
Paul Belloni du Chaillu was a French-American traveler and anthropologist. He became famous in the 1860s as the first modern outsider to confirm the existence of gorillas and the Pygmy people of central Africa. He later researched the prehistory of Scandinavia.-Early life:His date and place of...
, who found them in the Ogowe district of the west coast in 1865, five years before Schweinfurth's first meeting with them. Du Chaillu had previously, through journeys in the Gabon region between 1855 and 1859, made popular in Europe the knowledge of the existence of the gorilla, whose existence was thought to be as legendary as that of the Pygmies of Aristotle.
15th century - African Coast
- Diogo CãoDiogo CãoDiogo Cão was a Portuguese explorer and one of the most remarkable navigators of the Age of Discovery, who made two voyages sailing along the west coast of Africa to Namibia in the 1480s.-Early life and family:...
- Diogo de AzambujaDiogo de AzambujaDiogo de Azambuja was a Portuguese noble.He was a knight of the Order of Aviz in the service of the Infante Dom Pedro, son of the Regent Infante Peter, Duke of Coimbra. After Peter's defeat and death in the battle of Alfarrobeira , he accompanied his master into exile...
- Bartolomeu DiasBartolomeu DiasBartolomeu Dias , a nobleman of the Portuguese royal household, was a Portuguese explorer who sailed around the southernmost tip of Africa in 1488, the first European known to have done so.-Purposes of the Dias expedition:...
- Pêro de AlenquerPêro de AlenquerPêro de Alenquer Portuguese explorer of the African coast. Accompanied Bartolomeu Dias in his journey around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487/1488. Latter wrote a description of Vasco da Gama's first voyage to India. Pêro was born in Alenquer....
- João InfanteJoão InfanteJoão Infante Portuguese explorer of the African coast. Accompanied Bartolomeu Dias in his journey around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487/1488....
- João GregoJoão GregoJoão Grego was a Portuguese explorer of the African coast. He accompanied Bartolomeu Dias in his journey around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487/1488....
- Álvaro MartinsÁlvaro MartinsÁlvaro Martins, also known as Álvaro Martins Homem, was a 15th century Portuguese alleged to have explored the western Atlantic and later the African coast...
- Pêro DiasPêro DiasPêro Dias was a Portuguese explorer of the African coast. He accompanied his brother Bartolomeu Dias on his journey around the Cape of Good Hope in 1487/1488, having commanded the supply-ship...
- Gil EanesGil EanesGil Eanes was a 15th-century Portuguese navigator and explorer.Little is known about the personal life of Gil Eanes, prior to his role in the Portuguese Age of Discovery, and was considered a household servant and shield-bearer of the Infante Henry the Navigator...
- Nuno TristãoNuno TristãoNuno Tristão was a 15th century Portuguese explorer and slave trader, active in the early 1440s, traditionally thought to be the first European to reach the region of Guinea .-First Voyage:Nuno Tristão was a knight of the household of Henry the Navigator...
- Antão GonçalvesAntão GonçalvesAntão Gonçalves was a 15th century Portuguese explorer and slave trader who was the first European to buy Africans as slaves from black slave traders....
- Dinis DiasDinis DiasDinis Dias was a 15th century Portuguese explorer.In 1445, as Dias was beginning to enter old age and made the decision to take up exploring because "he was unwilling to let himself grow soft in the well being of repose", left Portugal and sailed down the West African coast, setting a new record by...
- António Fernandes
- Pêro de SintraPêro de SintraPedro de Sintra also known as Pêro de Sintra was a Portuguese explorer. He was among the first Europeans to explore the West African coast. Around 1462 his expedition reached contemporary Sierra Leone and named it. Continuing their journey, they visited the Benin Empire.-References and notes:...
- Fernão do PóFernão do PóFernão do Pó , also Fernão Pó, Fernando Pó, Fernando Poo was a Portuguese navigator and explorer of the West African coast. He discovered the islands in the Gulf of Guinea around 1472, one of which until the mid 1900s bore a version of his name, Fernando Pó or Fernando Poo. The island is...
15th century - Atlantic Islands and African Coast
- Alvise Cadamosto
- António NoliAntónio NoliAntonio de Noli was a 15th century Genoese nobleman and navigator, and the first governor of the earliest European overseas colony in Subsaharan Africa. He discovered some of the Cape Verde islands on behalf of Henry the Navigator and he was made first Governor of Cape Verde by King Afonso V...
- Álvaro CaminhaÁlvaro CaminhaÁlvaro Caminha was appointed by King John II of Portugal in 1492 Captain-major – apparently the second – of São Tomé and Príncipe which had been discovered 22 years earlier....
- João de SantarémJoão de SantarémJoão de Santarém Portuguese explorer that discovered São Tomé and Príncipe together with Pedro Escobar....
- Pedro EscobarPedro EscobarPedro Escobar, also known as Pêro Escobar, was a 15th century Portuguese navigator who discovered São Tomé and Príncipe together with João de Santarém and Fernão do Pó circa 1470. He is then recorded sailing with Diogo Cão on his first voyage in 1482, and as the pilot of the famous Bérrio caravel...
- Duarte Pacheco PereiraDuarte Pacheco PereiraDuarte Pacheco Pereira, called the Great, was a 15th century Portuguese sea captain, soldier, explorer and cartographer. He travelled particularly in the central Atlantic Ocean west of the Cape Verde islands, along the coast of West Africa and to India...
- Diogo DiasDiogo DiasDiogo Dias, also known as Diogo Gomes, was a 15th-century Portuguese explorer. He was the brother of Bartolomeu Dias and discovered some of the Cape Verde islands together with António Noli....
(and Indian OceanIndian OceanThe Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
, discovered MadagascarMadagascarThe Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean off the southeastern coast of Africa...
) - Lopes GonçalvesLopes GonçalvesLopes Gonçalves or Lopo Gonçalves was a Portuguese explorer of the African coast. He was the first European sailor to cross the equator, the first to reach the point where the coast turns south and the first to reach Gabon...
(and Atlantic Ocean) - Vasco da GamaVasco da GamaVasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira was a Portuguese explorer, one of the most successful in the Age of Discovery and the commander of the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India...
(and discovered sea route to IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
)
16th century
- Pêro da CovilhãPêro da CovilhãPedro or Pêro da Covilhã was a Portuguese diplomat and explorer.He was a native of Covilhã in Beira. In his early life he had gone to Castile and entered the service of Alphonso, Duke of Seville...
(15th/16th century diplomat and explorer in EthiopiaEthiopiaEthiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
) - Pedro Álvares CabralPedro Álvares CabralPedro Álvares Cabral was a Portuguese noble, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the discoverer of Brazil. Cabral conducted the first substantial exploration of the northeast coast of South America and claimed it for Portugal. While details of Cabral's early life are sketchy, it...
(discovered BrazilBrazilBrazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, explored India along the African coast) - Lourenço MarquesLourenço MarquesLourenço Marques was a 16th century Portuguese trader and explorer.-Biography:He explored the area that is now Maputo Bay in 1544. He settled permanently in present-day Mozambique, where he spent most of his life with his black wife and mixed-race children.By order of King John III the bay was...
(trader and explorer in East Africa) - Francisco ÁlvaresFrancisco ÁlvaresFrancisco Álvares was a Portuguese missionary and explorer. In 1515 he traveled to Ethiopia as part of the Portuguese embassy to emperor Lebna Dengel accompanied by returning Ethiopian ambassador Matheus. The embassy arrived only in 1520 to Ethiopia where he joined long sought Portuguese envoy...
(missionary and explorer in Ethiopia)
19th century
- António da Silva PortoAntonío da Silva PortoAntónio Francisco Ferreira da Silva Porto was a Portuguese trader and explorer in Angola, in the Portuguese West Africa.-Biography:...
- Serpa Pinto (soldier and colonizer of Africa)
- Hermenegildo CapeloHermenegildo CapeloHermenegildo de Brito Capelo was born in Palmela, Portugal, in 1841, and died in Lisbon, Portugal, in 1917. He was an officer in the Portuguese Navy and a Portuguese explorer, helping to chart territory between Angola and Mozambique in southern Central Africa that was unknown to Europeans in the...
and Roberto IvensRoberto IvensRoberto Ivens was a Portuguese explorer of Africa, Geographer, colonial administrator, and an officer of the Portuguese Navy.-Early life:...
19th century
- Richard Francis BurtonRichard Francis BurtonCaptain Sir Richard Francis Burton KCMG FRGS was a British geographer, explorer, translator, writer, soldier, orientalist, cartographer, ethnologist, spy, linguist, poet, fencer and diplomat. He was known for his travels and explorations within Asia, Africa and the Americas as well as his...
(1821–1890) (African Great LakesAfrican Great LakesThe African Great Lakes are a series of lakes and the Rift Valley lakes in and around the geographic Great Rift Valley formed by the action of the tectonic East African Rift on the continent of Africa...
) - Hugh ClappertonHugh ClappertonHugh Clapperton was a Scottish traveller and explorer of West and Central Africa.He was born in Annan, Dumfriesshire, where his father was a surgeon. He gained some knowledge of practical mathematics and navigation, and at thirteen was apprenticed on board a vessel which traded between Liverpool...
(1788–1827), explored west and central Africa - Dixon DenhamDixon DenhamDixon Denham was an English explorer in West Central Africa.Denham was born in London. He was educated at Merchant Taylors' School, and was articled to a solicitor, but joined the army in 1811...
(1786–1828), explored west central Africa. - James Frederic EltonJames Frederic Elton-Life:Born 3 August 1840, he was the second son of Lieutenant-colonel Roberts W. Elton of the 59th regiment, Bengal army, and grandson of Jacob Elton of Dedham, Essex....
(1840-1877) - Alexander Gordon LaingAlexander Gordon LaingMajor Alexander Gordon Laing was a Scottish explorer and the first European to reach Timbuktu via the north/south route.-Education and service:...
(1793–1826) - Richard Lemon LanderRichard Lemon LanderRichard Lemon Lander was a Cornish explorer of western Africa.-Biography:Lander was the son of a Truro innkeeper, born in the Daniell Arms. Lander's explorations began as an assistant to the Scottish explorer Hugh Clapperton on an expedition to Western Africa in 1825...
(1804–1834) - David LivingstoneDavid LivingstoneDavid Livingstone was a Scottish Congregationalist pioneer medical missionary with the London Missionary Society and an explorer in Africa. His meeting with H. M. Stanley gave rise to the popular quotation, "Dr...
(1813–1873) - Frederick LugardFrederick LugardFrederick John Dealtry Lugard, 1st Baron Lugard GCMG, CB, DSO, PC , known as Sir Frederick Lugard between 1901 and 1928, was a British soldier, mercenary, explorer of Africa and colonial administrator, who was Governor of Hong Kong and Governor-General of Nigeria .-Early life and education:Lugard...
(1858–1945) - Mungo Park (explorer)Mungo Park (explorer)Mungo Park was a Scottish explorer of the African continent. He was credited as being the first Westerner to encounter the Niger River.-Early life:...
(1771–1806) - Henry Morton StanleyHenry Morton StanleySir Henry Morton Stanley, GCB, born John Rowlands , was a Welsh journalist and explorer famous for his exploration of Africa and his search for David Livingstone. Upon finding Livingstone, Stanley allegedly uttered the now-famous greeting, "Dr...
(1841–1904) - John Hanning SpekeJohn Hanning SpekeJohn Hanning Speke was an officer in the British Indian Army who made three exploratory expeditions to Africa and who is most associated with the search for the source of the Nile.-Life:...
(1827–1864) (discovered the source of the NileNileThe Nile is a major north-flowing river in North Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is long. It runs through the ten countries of Sudan, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt.The Nile has two major...
) - James Kingston TuckeyJames Kingston TuckeyJames Hingston Tuckey was an Irish-born British explorer and a captain in the Royal Navy. Some references refer to him as James Kingston Tuckey....
(1776-1816)
19th century
- Johann Ludwig BurckhardtJohann Ludwig BurckhardtJohann Ludwig Burckhardt was a Swiss traveller and orientalist. He wrote his letters in French and signed Louis...
- René CailléRené CailléRené Caillié was a French explorer, and the first European to return alive from the town of Timbuktu.Caillié was born at Mauzé-sur-le-Mignon, Deux-Sèvres, Poitou, the son of a baker. He was born into the lowest levels of European society...
- Heinrich BarthHeinrich BarthHeinrich Barth was a German explorer of Africa and scholar.Barth is one of the greatest of the European explorers of Africa, not necessarily because of the length of his travels or the time he spent alone without European company in Africa, but because of his singular character.-Biography:Barth...
- Gustav NachtigalGustav NachtigalGustav Nachtigal was a German explorer of Central and West Africa. He is further known as the German Empire's consul-general for Tunisia and Commissioner for West Africa. His mission as commissioner resulted in Togoland and Kamerun becoming the first colonies of a German colonial empire...
- Georg Schweinfurth
- Paul du ChailluPaul du ChailluPaul Belloni du Chaillu was a French-American traveler and anthropologist. He became famous in the 1860s as the first modern outsider to confirm the existence of gorillas and the Pygmy people of central Africa. He later researched the prehistory of Scandinavia.-Early life:His date and place of...
- Emil HolubEmil HolubEmil Holub was a Czech physician, explorer, cartographer, and ethnographer in Africa. In a 2005 poll, he was voted #90 of the 100 greatest Czechs.-Early life:...
- Victor de Compiègne

