
Ewens's sampling formula
Encyclopedia
In population genetics
, Ewens' sampling formula, describes the probabilities associated with counts of how many different allele
s are observed a given number of times in the sample.
, states that under certain conditions (specified below), if a random sample of n gamete
s is taken from a population and classified according to the gene
at a particular locus
then the probability
that there are a1 allele
s represented once in the sample, and a2 alleles represented twice, and so on, is
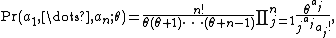
for some positive number θ, whenever a1, ..., an is a sequence of nonnegative integers such that
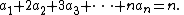
The phrase "under certain conditions", used above, must of course be made precise. The assumptions are (1) the sample size n is small by comparison to the size of the whole population, and (2) the population is in statistical equilibrium under mutation
and genetic drift
and the role of selection at the locus in question is negligible, and (3) every mutant allele is novel. (See also idealised population
.)
This is a probability distribution
on the set of all partitions of the integer n. Among probabilists and statisticians it is often called the multivariate Ewens distribution.
When θ = 0, the probability is 1 that all n genes are the same. When θ = 1, then the distribution is precisely that of the integer partition induced by a uniformly distributed random permutation
. As θ → ∞, the probability that no two of the n genes are the same approaches 1.
This family of probability distributions enjoys the property that if after the sample of n is taken, m of the n gametes are chosen without replacement, then the resulting probability distribution on the set of all partitions of the smaller integer m is just what the formula above would give if m were put in place of n.
The Ewens distribution arises naturally from the Chinese restaurant process.
Population genetics
Population genetics is the study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, mutation and gene flow. It also takes into account the factors of recombination, population subdivision and population...
, Ewens' sampling formula, describes the probabilities associated with counts of how many different allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
s are observed a given number of times in the sample.
Definition
Ewens' sampling formula, introduced by Warren EwensWarren Ewens
Warren Ewens FRS, FAA is an Australian-born professor of biology at the University of Pennsylvania. He concentrates his research on the mathematical, statistical and theoretical aspects of population genetics. Ewens has worked in human population genetics, computational biology, and evolutionary...
, states that under certain conditions (specified below), if a random sample of n gamete
Gamete
A gamete is a cell that fuses with another cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually...
s is taken from a population and classified according to the gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
at a particular locus
Locus (genetics)
In the fields of genetics and genetic computation, a locus is the specific location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome. A variant of the DNA sequence at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a genetic map...
then the probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
that there are a1 allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
s represented once in the sample, and a2 alleles represented twice, and so on, is
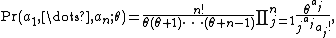
for some positive number θ, whenever a1, ..., an is a sequence of nonnegative integers such that
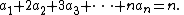
The phrase "under certain conditions", used above, must of course be made precise. The assumptions are (1) the sample size n is small by comparison to the size of the whole population, and (2) the population is in statistical equilibrium under mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
and genetic drift
Genetic drift
Genetic drift or allelic drift is the change in the frequency of a gene variant in a population due to random sampling.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces...
and the role of selection at the locus in question is negligible, and (3) every mutant allele is novel. (See also idealised population
Idealised population
main article: effective population sizeIn population genetics an idealised population, also sometimes called a Fisher-Wright population after R.A. Fisher and Sewall Wright, is a population whose members can mate and reproduce with any other member of the other gender, has a sex ratio of 1 and no...
.)
This is a probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
on the set of all partitions of the integer n. Among probabilists and statisticians it is often called the multivariate Ewens distribution.
When θ = 0, the probability is 1 that all n genes are the same. When θ = 1, then the distribution is precisely that of the integer partition induced by a uniformly distributed random permutation
Random permutation
A random permutation is a random ordering of a set of objects, that is, a permutation-valued random variable. The use of random permutations is often fundamental to fields that use randomized algorithms such as coding theory, cryptography, and simulation...
. As θ → ∞, the probability that no two of the n genes are the same approaches 1.
This family of probability distributions enjoys the property that if after the sample of n is taken, m of the n gametes are chosen without replacement, then the resulting probability distribution on the set of all partitions of the smaller integer m is just what the formula above would give if m were put in place of n.
The Ewens distribution arises naturally from the Chinese restaurant process.
See also
- Coalescent theoryCoalescent theoryIn genetics, coalescent theory is a retrospective model of population genetics. It attempts to trace all alleles of a gene shared by all members of a population to a single ancestral copy, known as the most recent common ancestor...
- Unified neutral theory of biodiversityUnified neutral theory of biodiversityThe unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography is a hypothesis and the title of a monograph by ecologist Stephen Hubbell...

