
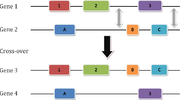
Exon shuffling
Encyclopedia
Walter Gilbert
Walter Gilbert is an American physicist, biochemist, molecular biology pioneer, and Nobel laureate.-Biography:Gilbert was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on March 21, 1932...
in 1977, in which different exon
Exon
An exon is a nucleic acid sequence that is represented in the mature form of an RNA molecule either after portions of a precursor RNA have been removed by cis-splicing or when two or more precursor RNA molecules have been ligated by trans-splicing. The mature RNA molecule can be a messenger RNA...
s either within a gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
or between two nonallelic genes are occasionally mixed. Gilbert suggested that exons might each encode a single protein domain
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
, establishing a kind of modular property. In this fashion, it would be possible for exons to essentially be "mixed and matched" to produce a variety of different proteins, yielded from different combinations of such exons and their resulting domain combinations.
The process of exon shuffling can create a mosaic, or chimeric, protein that is partly built of domains or segments which are similar or identical to domains of other proteins. The mosaic protein is created when an exon from one gene is integrated into another gene's intron. Another kind of exon shuffling is when an exon is duplicated in the same gene.
In the context of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
, exon shuffling is significant due to its ability to quickly create new multidomain proteins, leading to increased variation in species.

