
Exsecant
Encyclopedia
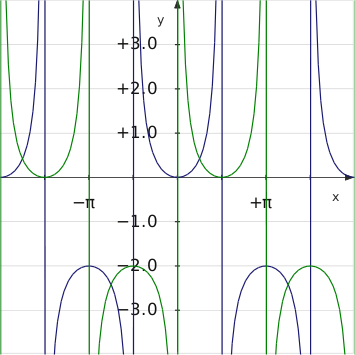
Trigonometric function
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are functions of an angle. They are used to relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of the sides of a triangle...
defined in terms of the secant function sec(θ):
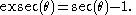
Once important in fields such as surveying
Surveying
See Also: Public Land Survey SystemSurveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, and science of accurately determining the terrestrial or three-dimensional position of points and the distances and angles between them...
, astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, and spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is a branch of spherical geometry which deals with polygons on the sphere and the relationships between the sides and the angles...
, the exsecant function is now little-used. Mainly, this is because the availability of calculator
Calculator
An electronic calculator is a small, portable, usually inexpensive electronic device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic. Modern calculators are more portable than most computers, though most PDAs are comparable in size to handheld calculators.The first solid-state electronic...
s and computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s has removed the need for trigonometric tables of specialized functions such as this one.
A related function is the excosecant (excsc), the exsecant of the complementary angle:
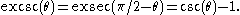
The reason to define a special function for the exsecant is similar to the rationale for the versine
Versine
The versine or versed sine, versin, is a trigonometric function equal to and 2sin2. It appeared in some of the earliest trigonometric tables and was once widespread, but it is now little-used...
: for small angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
s θ, the sec(θ) function approaches one, and so using the above formula for the exsecant will involve the subtraction
Subtraction
In arithmetic, subtraction is one of the four basic binary operations; it is the inverse of addition, meaning that if we start with any number and add any number and then subtract the same number we added, we return to the number we started with...
of two nearly equal quantities and exacerbate roundoff errors. Thus, a table of the secant function would need a very high accuracy to be used for the exsecant, making a specialized exsecant table useful. Even with a computer, floating point
Floating point
In computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
errors can be problematic for exsecants of small angles. A more accurate formula in this limit would be to use the identity:
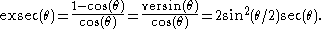
Prior to the availability of computers, this would require time-consuming multiplications.
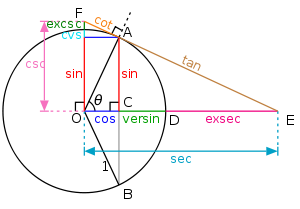
The name exsecant can be understood from a graphical construction, at right, of the various trigonometric functions from a unit circle
Unit circle
In mathematics, a unit circle is a circle with a radius of one. Frequently, especially in trigonometry, "the" unit circle is the circle of radius one centered at the origin in the Cartesian coordinate system in the Euclidean plane...
, such as was used historically. sec(θ) is the secant
Secant line
A secant line of a curve is a line that intersects two points on the curve. The word secant comes from the Latin secare, to cut.It can be used to approximate the tangent to a curve, at some point P...
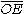 , and the exsecant is the portion
, and the exsecant is the portion 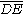 of this secant that lies exterior to the circle (ex is Latin
of this secant that lies exterior to the circle (ex is LatinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
for out of).
See also
- Trigonometric identities
- Versine and HaversineVersineThe versine or versed sine, versin, is a trigonometric function equal to and 2sin2. It appeared in some of the earliest trigonometric tables and was once widespread, but it is now little-used...

