
Facial trauma
Encyclopedia
Facial trauma, also called maxillofacial trauma, is any physical trauma
to the face
. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries
such as burn
s, lacerations and bruises, or fracture
s of the facial bones such as nasal fracture
s and fractures of the jaw, as well as trauma such as eye injuries
. Symptoms are specific to the type of injury; for example, fractures may involve pain, swelling, loss of function, or changes in the shape of facial structures.
Facial injuries have the potential to cause disfigurement and loss of function; for example, blindness or difficulty moving the jaw can result. Although it is seldom life-threatening, facial trauma can also be deadly, because it can cause severe bleeding or interference with the airway
; thus a primary concern in treatment is ensuring that the airway is open and not threatened so that the patient can breathe. Depending on the type of facial injury, treatment may include bandaging and suturing of open wound
s, administration of ice, antibiotic
s and pain killers
, moving bones back into place, and surgery. When fractures are suspected, radiography
is used for diagnosis. Treatment may also be necessary for other injuries such as traumatic brain injury
, which commonly accompany facial trauma.
In developed countries, the leading cause of facial trauma used to be motor vehicle accidents, but this mechanism has been replaced by interpersonal violence; however auto accidents still predominate as the cause in developing countries and are still a major cause elsewhere. Thus prevention efforts include awareness campaigns to educate the public about safety measures such as seat belt
s and motorcycle helmet
s, and laws to prevent drunk and unsafe driving
. Other causes of facial trauma include falls, industrial accidents, and sports injuries.
Soft tissue injuries include abrasions, lacerations, avulsion
s, bruises, burns and cold injuries.
 Commonly injured facial bones include the nasal bone
Commonly injured facial bones include the nasal bone
(the nose), the maxilla
(the bone that forms the upper jaw), and the mandible (the lower jaw). The mandible may be fractured at its symphysis, body, angle, ramus, and condoyle. The zygoma
(cheekbone) and the frontal bone
(forehead) are other sites for fractures. Fractures may also occur in the bones of the palate and those that come together to form the orbit of the eye.
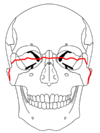
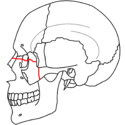
At the beginning of the 20th century, René Le Fort
mapped typical locations for facial fractures; these are now known as Le Fort I, II, and III fractures
(right). Le Fort I fractures, also called Guérin or horizontal maxillary fractures, involve the maxilla, separating it from the palate. Le Fort II fractures, also called pyramidal fractures of the maxilla, cross the nasal bones and the orbital rim. Le Fort III fractures, also called craniofacial disjunction and transverse facial fractures, cross the front of the maxilla and involve the lacrimal bone
, the lamina papyracea, and the orbital floor
, and often involve the ethmoid bone
. are the most serious. Le Fort fractures, which account for 10–20% of facial fractures, are often associated with other serious injuries. Le Fort made his classifications based on work with cadaver skulls, and the classification system has been criticized as imprecise and simplistic since most midface fractures involve a combination of Le Fort fractures. Although most facial fractures do not follow the patterns described by Le Fort precisely, the system is still used to categorize injuries.
.
Animal attacks and work-related injuries such as industrial accidents are other causes. Vehicular trauma is one of the leading causes of facial injuries. Trauma commonly occurs when the face strikes a part of the vehicle's interior, such as the steering wheel. In addition, airbag
s can cause corneal abrasion
s and lacerations (cuts) to the face when they deploy.
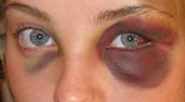 Fractures of facial bones, like other fractures, may be associated with pain, bruising, and swelling of the surrounding tissues (such symptoms can occur in the absence of fractures as well). Fractures of the nose, base of the skull
Fractures of facial bones, like other fractures, may be associated with pain, bruising, and swelling of the surrounding tissues (such symptoms can occur in the absence of fractures as well). Fractures of the nose, base of the skull
, or maxilla may be associated with profuse nosebleeds. Nasal fractures may be associated with deformity of the nose, as well as swelling and bruising. Deformity in the face, for example a sunken cheekbone or teeth which do not align properly, suggests the presence of fractures. Asymmetry can suggest facial fractures or damage to nerves. People with mandibular fractures often have pain and difficulty opening their mouths and may have numbness in the lip and chin. With Le Fort fractures, the midface may move relative to the rest of the face or skull.
, imaging of tissues using X-ray
s, is used to rule out facial fractures. Angiography (X-rays taken of the inside of blood vessels) can be used to locate the source of bleeding. However the complex bones and tissues of the face can make it difficult to interpret plain radiographs; CT scan
ning is better for detecting fractures and examining soft tissues, and is often needed to determine whether surgery is necessary, but it is more expensive and difficult to obtain. CT scanning is usually considered to be more definitive and better at detecting facial injuries than X-ray. CT scanning is especially likely to be used in people with multiple injuries who need CT scans to assess for other injuries anyway.
studies can be used to design automobiles with a view toward preventing facial injuries. While seat belts reduce the number and severity of facial injuries that occur in crashes, airbags alone are not very effective at preventing the injuries. In sports, safety devices including helmets have been found to reduce the risk of severe facial injury. Additional attachments such as face guards may be added to sports helmets to prevent orofacial injury (injury to the mouth or face). mouth guards also used,
(inserting a tube into the airway to assist breathing) may be difficult or impossible due to swelling. Nasal intubation, inserting an endotracheal tube through the nose, may be contraindicated
in the presence of facial trauma because if there is an undiscovered fracture at the base of the skull, the tube could be forced through it and into the brain. If facial injuries prevent oraotracheal or nasotracheal intubation, a surgical airway
can be placed to provide an adequate airway. Although cricothyrotomy
and tracheostomy can secure an airway when other methods fail, they are used only as a last resort because of potential complications and the difficulty of the procedures.
 A dressing can be placed over wounds to keep them clean and to facilitate healing, and antibiotic
A dressing can be placed over wounds to keep them clean and to facilitate healing, and antibiotic
s may be used in cases where infection is likely. People with contaminated wounds who have not been immunized against tetanus
within five years may be given a tetanus vaccination. Lacerations may require stitches to stop bleeding and facilitate wound healing
with as little scarring as possible. Although it is not common for bleeding from the maxillofacial region to be profuse enough to be life threatening, it is still necessary to control such bleeding. Severe bleeding occurs as the result of facial trauma in 1–11% of patients, and the origin of this bleeding can be difficult to locate. Nasal packing can be used to control nose bleeds and hematoma
s that may form on the septum
between the nostrils. Such hematomas need to be drained. Mild nasal fractures need nothing more than ice and pain killers
, while breaks with severe deformities or associated lacerations may need further treatment, such as moving the bones back into alignment and antibiotic treatment.
Treatment aims to repair the face's natural bony architecture and to leave as little apparent trace of the injury as possible. Fractures may be repaired with metal plates and screws. They may also be wired into place. Bone grafting
is another option to repair the bone's architecture, to fill out missing sections, and to provide structural support. Medical literature suggests that early repair of facial injuries, within hours or days, results in better outcomes for function and appearance.
Surgical specialists who commonly treat specific aspects of facial trauma include otorhinolaryngologists, and oral and maxillofacial surgeons
. These surgical specialists are trained in the comprehensive management of trauma to the lower, middle and upper face and have to take written and oral board examinations covering the management of facial injuries.
The airway can be blocked due to bleeding, swelling of surrounding tissues, or damage to structures. Burns to the face can cause swelling of tissues and thereby lead to airway blockage. Broken bones such as combinations of nasal, maxillary, and mandibular fractures can interfere with the airway. Blood from the face or mouth, if swallowed, can cause vomiting, which can itself present a threat to the airway because it has the potential to be aspirated
. Since airway problems can occur late after the initial injury, it is necessary for healthcare providers to monitor the airway regularly.
Even when facial injuries are not life threatening, they have the potential to cause disfigurement and disability, with long-term physical and emotional results. Facial injuries can cause problems with eye, nose, or jaw function and can threaten eyesight.
As early as 400 BC, Hippocrates
is thought to have recorded a relationship between blunt facial trauma and blindness. Injuries involving the eye or eyelid, such as retrobulbar hemorrhage, can threaten eyesight; however, blindness following facial trauma is not common.
Nerves and muscles may be trapped by broken bones; in these cases the bones need to be put back into their proper places quickly. For example, fractures of the orbital floor or medial orbital wall of the eye can entrap the medial rectus or inferior rectus muscle
s. In facial wounds, tear ducts and nerves of the face may be damaged. Fractures of the frontal bone can interfere with the drainage of the frontal sinus
and can cause sinusitis
.
Infection is another potential complication, for example when debris is ground into an abrasion and remains there. Injuries resulting from bites carry a high infection risk.
s and airbag
s has been credited with a reduction in the incidence of maxillofacial trauma, but fractures of the mandible (the jawbone) are not decreased by these protective measures. The risk of maxillofacial trauma is decreased by a factor of two with use of motorcycle helmets. A decline in facial bone fractures due to vehicle accidents is thought to be due to seat belt and drunk driving laws, strictly enforced speed limits and use of airbags. In vehicle accidents, drivers and front seat passengers are at highest risk for facial trauma.
Facial fractures are distributed in a fairly normal curve by age, with a peak incidence occurring between ages 20 and 40, and children under 12 suffering only 5–10% of all facial fractures. Most facial trauma in children involves lacerations and soft tissue injuries. There are several reasons for the lower incidence of facial fractures in children: the face is smaller in relation to the rest of the head, children are less often in some situations associated with facial fractures such as occupational and motor vehicle hazards, there is a lower proportion of cortical bone
to cancellous bone in children's faces, poorly developed sinus
es make the bones stronger, and fat pads provide protection for the facial bones.
Head
and brain injuries
are commonly associated with facial trauma, particularly that of the upper face; brain injury occurs in 15–48% of people with maxillofacial trauma. Coexisting injuries can affect treatment of facial trauma; for example they may be emergent and need to be treated before facial injuries. People with trauma above the level of the collar bone
s are considered to be at high risk for cervical spine injuries (spinal injuries in the neck) and special precautions must be taken to avoid movement of the spine, which could worsen a spinal injury.
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
to the face
Face
The face is a central sense organ complex, for those animals that have one, normally on the ventral surface of the head, and can, depending on the definition in the human case, include the hair, forehead, eyebrow, eyelashes, eyes, nose, ears, cheeks, mouth, lips, philtrum, temple, teeth, skin, and...
. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries
Soft tissue injury
A Soft tissue injury is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body. Common soft tissue injuries usually occur from a sprain, strain, a one off blow resulting in a contusion or overuse of a particular part of the body...
such as burn
Burn
A burn is an injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation, or friction.Burn may also refer to:*Combustion*Burn , type of watercourses so named in Scotland and north-eastern England...
s, lacerations and bruises, or fracture
Bone fracture
A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone...
s of the facial bones such as nasal fracture
Nasal fracture
Broken Nose' redirects here, for the Song by Catherine Wheel, please see Adam and EveA nasal fracture, commonly referred to as a broken nose, is a fracture of the bone or cartilage of the nose...
s and fractures of the jaw, as well as trauma such as eye injuries
Eye injury
Physical or chemical injuries of the eye can be a serious threat to vision if not treated appropriately and in a timely fashion. The most obvious presentation of ocular injuries is redness and pain of the affected eyes. This is not, however, universally true, as tiny metallic projectiles may cause...
. Symptoms are specific to the type of injury; for example, fractures may involve pain, swelling, loss of function, or changes in the shape of facial structures.
Facial injuries have the potential to cause disfigurement and loss of function; for example, blindness or difficulty moving the jaw can result. Although it is seldom life-threatening, facial trauma can also be deadly, because it can cause severe bleeding or interference with the airway
Airway
The pulmonary airway comprises those parts of the respiratory system through which air flows, conceptually beginning at the nose and mouth, and terminating in the alveoli...
; thus a primary concern in treatment is ensuring that the airway is open and not threatened so that the patient can breathe. Depending on the type of facial injury, treatment may include bandaging and suturing of open wound
Wound
A wound is a type of injury in which skin is torn, cut or punctured , or where blunt force trauma causes a contusion . In pathology, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis of the skin.-Open:...
s, administration of ice, antibiotic
Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s and pain killers
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
, moving bones back into place, and surgery. When fractures are suspected, radiography
Radiography
Radiography is the use of X-rays to view a non-uniformly composed material such as the human body. By using the physical properties of the ray an image can be developed which displays areas of different density and composition....
is used for diagnosis. Treatment may also be necessary for other injuries such as traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
, which commonly accompany facial trauma.
In developed countries, the leading cause of facial trauma used to be motor vehicle accidents, but this mechanism has been replaced by interpersonal violence; however auto accidents still predominate as the cause in developing countries and are still a major cause elsewhere. Thus prevention efforts include awareness campaigns to educate the public about safety measures such as seat belt
Seat belt
A seat belt or seatbelt, sometimes called a safety belt, is a safety harness designed to secure the occupant of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result from a collision or a sudden stop...
s and motorcycle helmet
Motorcycle helmet
A motorcycle helmet is a type of protective headgear used by motorcycle riders. The primary goal of a motorcycle helmet is motorcycle safety - to protect the rider's head during impact, thus preventing or reducing head injury or saving the rider's life...
s, and laws to prevent drunk and unsafe driving
Driving under the influence
Driving under the influence is the act of driving a motor vehicle with blood levels of alcohol in excess of a legal limit...
. Other causes of facial trauma include falls, industrial accidents, and sports injuries.
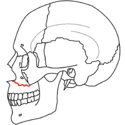
Classification
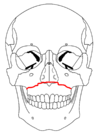 |
 |
| Le Fort I fractures | |
 |
 |
| Le Fort II fractures | |
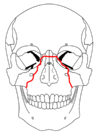
 |
 |
| Le Fort III fractures | |
Soft tissue injuries include abrasions, lacerations, avulsion
Avulsion
Avulsion in general refers to a tearing away. Specifically, it can refer to:* A type of amputation where the extremity is pulled off rather than cut off* Avulsion fracture* Avulsion injury, the removal of all the layers of skin from abrasion...
s, bruises, burns and cold injuries.

Nasal bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face, and form, by their junction, "the bridge" of the nose.Each has two surfaces and four borders....
(the nose), the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
(the bone that forms the upper jaw), and the mandible (the lower jaw). The mandible may be fractured at its symphysis, body, angle, ramus, and condoyle. The zygoma
Zygoma
The term zygoma generally refers to the zygomatic bone, a bone of the human skull commonly referred to as the cheekbone or malar bone, but it may also refer to:...
(cheekbone) and the frontal bone
Frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull that resembles a cockleshell in form, and consists of two portions:* a vertical portion, the squama frontalis, corresponding with the region of the forehead....
(forehead) are other sites for fractures. Fractures may also occur in the bones of the palate and those that come together to form the orbit of the eye.
At the beginning of the 20th century, René Le Fort
René Le Fort
René Le Fort was a French surgeon from Lille remembered for creating a classification for fractures of the face...
mapped typical locations for facial fractures; these are now known as Le Fort I, II, and III fractures
LeFort fracture
Le Fort fractures are types of facial fractures involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in a usually bilateral and either horizontal, pyramidal or transverse way. LeFort fractures are classic in facial trauma...
(right). Le Fort I fractures, also called Guérin or horizontal maxillary fractures, involve the maxilla, separating it from the palate. Le Fort II fractures, also called pyramidal fractures of the maxilla, cross the nasal bones and the orbital rim. Le Fort III fractures, also called craniofacial disjunction and transverse facial fractures, cross the front of the maxilla and involve the lacrimal bone
Lacrimal bone
The lacrimal bone, the smallest and most fragile bone of the face, is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders.-Lateral or orbital surface:...
, the lamina papyracea, and the orbital floor
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
, and often involve the ethmoid bone
Ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone is a bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. As such, it is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that makes up the orbit of the eye...
. are the most serious. Le Fort fractures, which account for 10–20% of facial fractures, are often associated with other serious injuries. Le Fort made his classifications based on work with cadaver skulls, and the classification system has been criticized as imprecise and simplistic since most midface fractures involve a combination of Le Fort fractures. Although most facial fractures do not follow the patterns described by Le Fort precisely, the system is still used to categorize injuries.
Causes
Injury mechanisms such as falls, assaults, sports injuries, and vehicle crashes are common causes of facial trauma in children as well as adults. Blunt assaults, blows from fists or objects, are a common cause of facial injury. Facial trauma can also result from wartime injuries such as gunshots and blastsBlast injury
A blast injury is a complex type of physical trauma resulting from direct or indirect exposure to an explosion. Blast injuries occur with the detonation of high-order explosives as well as the deflagration of low order explosives...
.
Animal attacks and work-related injuries such as industrial accidents are other causes. Vehicular trauma is one of the leading causes of facial injuries. Trauma commonly occurs when the face strikes a part of the vehicle's interior, such as the steering wheel. In addition, airbag
Airbag
An Airbag is a vehicle safety device. It is an occupant restraint consisting of a flexible envelope designed to inflate rapidly during an automobile collision, to prevent occupants from striking interior objects such as the steering wheel or a window...
s can cause corneal abrasion
Corneal abrasion
Corneal abrasion is a medical condition involving the loss of the surface epithelial layer of the eye's cornea.-Symptoms and signs:Symptoms of corneal abrasion include pain, photophobia, a foreign-body sensation, excessive squinting, and a reflex production of tears...
s and lacerations (cuts) to the face when they deploy.
Signs and symptoms

Base of the skull
The base of skull is the most inferior area of the skull, composed of the endocranium and lower parts of the skull roof.-Bones:*Ethmoid bone*Sphenoid bone*Occipital bone*Frontal bone*Parietal bone*Temporal bone**Petrous portion of the temporal bone...
, or maxilla may be associated with profuse nosebleeds. Nasal fractures may be associated with deformity of the nose, as well as swelling and bruising. Deformity in the face, for example a sunken cheekbone or teeth which do not align properly, suggests the presence of fractures. Asymmetry can suggest facial fractures or damage to nerves. People with mandibular fractures often have pain and difficulty opening their mouths and may have numbness in the lip and chin. With Le Fort fractures, the midface may move relative to the rest of the face or skull.
Diagnosis
RadiographyRadiography
Radiography is the use of X-rays to view a non-uniformly composed material such as the human body. By using the physical properties of the ray an image can be developed which displays areas of different density and composition....
, imaging of tissues using X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s, is used to rule out facial fractures. Angiography (X-rays taken of the inside of blood vessels) can be used to locate the source of bleeding. However the complex bones and tissues of the face can make it difficult to interpret plain radiographs; CT scan
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
ning is better for detecting fractures and examining soft tissues, and is often needed to determine whether surgery is necessary, but it is more expensive and difficult to obtain. CT scanning is usually considered to be more definitive and better at detecting facial injuries than X-ray. CT scanning is especially likely to be used in people with multiple injuries who need CT scans to assess for other injuries anyway.
Prevention
Measures to reduce facial trauma include laws enforcing seat belt use and public education to increase awareness about the importance of seat belts and motorcycle helmets. Efforts to reduce drunk driving are other preventative measures; changes to laws and their enforcement have been proposed, as well as changes to societal attitudes toward the activity. Information obtained from biomechanicsBiomechanics
Biomechanics is the application of mechanical principles to biological systems, such as humans, animals, plants, organs, and cells. Perhaps one of the best definitions was provided by Herbert Hatze in 1974: "Biomechanics is the study of the structure and function of biological systems by means of...
studies can be used to design automobiles with a view toward preventing facial injuries. While seat belts reduce the number and severity of facial injuries that occur in crashes, airbags alone are not very effective at preventing the injuries. In sports, safety devices including helmets have been found to reduce the risk of severe facial injury. Additional attachments such as face guards may be added to sports helmets to prevent orofacial injury (injury to the mouth or face). mouth guards also used,
Treatment
An immediate need in treatment is to ensure that the airway is open and not threatened (for example by tissues or foreign objects), because airway compromise can occur rapidly and insidiously, and is potentially deadly. Material in the mouth that threatens the airway can be removed manually or using a suction tool for that purpose, and supplemental oxygen can be provided. Facial fractures that threaten to interfere with the airway can be reduced by moving the bones back into place; this both reduces bleeding and moves the bone out of the way of the airway. Tracheal intubationTracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs...
(inserting a tube into the airway to assist breathing) may be difficult or impossible due to swelling. Nasal intubation, inserting an endotracheal tube through the nose, may be contraindicated
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition or factor that serves as a reason to withhold a certain medical treatment.Some contraindications are absolute, meaning that there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action...
in the presence of facial trauma because if there is an undiscovered fracture at the base of the skull, the tube could be forced through it and into the brain. If facial injuries prevent oraotracheal or nasotracheal intubation, a surgical airway
Cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, or massive...
can be placed to provide an adequate airway. Although cricothyrotomy
Cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, or massive...
and tracheostomy can secure an airway when other methods fail, they are used only as a last resort because of potential complications and the difficulty of the procedures.

Antibiotic
An antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s may be used in cases where infection is likely. People with contaminated wounds who have not been immunized against tetanus
Tetanus
Tetanus is a medical condition characterized by a prolonged contraction of skeletal muscle fibers. The primary symptoms are caused by tetanospasmin, a neurotoxin produced by the Gram-positive, rod-shaped, obligate anaerobic bacterium Clostridium tetani...
within five years may be given a tetanus vaccination. Lacerations may require stitches to stop bleeding and facilitate wound healing
Wound healing
Wound healing, or cicatrisation, is an intricate process in which the skin repairs itself after injury. In normal skin, the epidermis and dermis exists in a steady-state equilibrium, forming a protective barrier against the external environment...
with as little scarring as possible. Although it is not common for bleeding from the maxillofacial region to be profuse enough to be life threatening, it is still necessary to control such bleeding. Severe bleeding occurs as the result of facial trauma in 1–11% of patients, and the origin of this bleeding can be difficult to locate. Nasal packing can be used to control nose bleeds and hematoma
Hematoma
A hematoma, or haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise...
s that may form on the septum
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
between the nostrils. Such hematomas need to be drained. Mild nasal fractures need nothing more than ice and pain killers
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
, while breaks with severe deformities or associated lacerations may need further treatment, such as moving the bones back into alignment and antibiotic treatment.
Treatment aims to repair the face's natural bony architecture and to leave as little apparent trace of the injury as possible. Fractures may be repaired with metal plates and screws. They may also be wired into place. Bone grafting
Bone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly....
is another option to repair the bone's architecture, to fill out missing sections, and to provide structural support. Medical literature suggests that early repair of facial injuries, within hours or days, results in better outcomes for function and appearance.
Surgical specialists who commonly treat specific aspects of facial trauma include otorhinolaryngologists, and oral and maxillofacial surgeons
Oral and maxillofacial surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is surgery to correct a wide spectrum of diseases, injuries and defects in the head, neck, face, jaws and the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial region. It is an internationally recognized surgical specialty...
. These surgical specialists are trained in the comprehensive management of trauma to the lower, middle and upper face and have to take written and oral board examinations covering the management of facial injuries.
Prognosis and complications
By itself, facial trauma rarely presents a threat to life; however it is often associated with dangerous injuries, and life-threatening complications such as blockage of the airway may occur.The airway can be blocked due to bleeding, swelling of surrounding tissues, or damage to structures. Burns to the face can cause swelling of tissues and thereby lead to airway blockage. Broken bones such as combinations of nasal, maxillary, and mandibular fractures can interfere with the airway. Blood from the face or mouth, if swallowed, can cause vomiting, which can itself present a threat to the airway because it has the potential to be aspirated
Pulmonary aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract into the larynx and lower respiratory tract...
. Since airway problems can occur late after the initial injury, it is necessary for healthcare providers to monitor the airway regularly.
Even when facial injuries are not life threatening, they have the potential to cause disfigurement and disability, with long-term physical and emotional results. Facial injuries can cause problems with eye, nose, or jaw function and can threaten eyesight.
As early as 400 BC, Hippocrates
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Cos or Hippokrates of Kos was an ancient Greek physician of the Age of Pericles , and is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine...
is thought to have recorded a relationship between blunt facial trauma and blindness. Injuries involving the eye or eyelid, such as retrobulbar hemorrhage, can threaten eyesight; however, blindness following facial trauma is not common.
Nerves and muscles may be trapped by broken bones; in these cases the bones need to be put back into their proper places quickly. For example, fractures of the orbital floor or medial orbital wall of the eye can entrap the medial rectus or inferior rectus muscle
Inferior rectus muscle
The inferior rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit.-Actions:It depresses, adducts, and helps extort the eye.The inferior rectus muscle is the only muscle that is capable of depressing the pupil when it is in a fully abducted position....
s. In facial wounds, tear ducts and nerves of the face may be damaged. Fractures of the frontal bone can interfere with the drainage of the frontal sinus
Frontal sinus
Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. The frontal sinuses, situated behind the superciliary arches, are absent at birth, but are generally fairly well developed between the seventh and eighth years, only reaching their full size after puberty...
and can cause sinusitis
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which may be due to infection, allergy, or autoimmune issues. Most cases are due to a viral infection and resolve over the course of 10 days...
.
Infection is another potential complication, for example when debris is ground into an abrasion and remains there. Injuries resulting from bites carry a high infection risk.
Epidemiology
As many as 50–70% of people who survive traffic accidents have facial trauma. In most developed countries, violence from other people has replaced vehicle collisions as the main cause of maxillofacial trauma; however in many developing countries traffic accidents remain the major cause. Increased use of seat beltSeat belt
A seat belt or seatbelt, sometimes called a safety belt, is a safety harness designed to secure the occupant of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result from a collision or a sudden stop...
s and airbag
Airbag
An Airbag is a vehicle safety device. It is an occupant restraint consisting of a flexible envelope designed to inflate rapidly during an automobile collision, to prevent occupants from striking interior objects such as the steering wheel or a window...
s has been credited with a reduction in the incidence of maxillofacial trauma, but fractures of the mandible (the jawbone) are not decreased by these protective measures. The risk of maxillofacial trauma is decreased by a factor of two with use of motorcycle helmets. A decline in facial bone fractures due to vehicle accidents is thought to be due to seat belt and drunk driving laws, strictly enforced speed limits and use of airbags. In vehicle accidents, drivers and front seat passengers are at highest risk for facial trauma.
Facial fractures are distributed in a fairly normal curve by age, with a peak incidence occurring between ages 20 and 40, and children under 12 suffering only 5–10% of all facial fractures. Most facial trauma in children involves lacerations and soft tissue injuries. There are several reasons for the lower incidence of facial fractures in children: the face is smaller in relation to the rest of the head, children are less often in some situations associated with facial fractures such as occupational and motor vehicle hazards, there is a lower proportion of cortical bone
Cortical bone
Cortical bone, synonymous with compact bone, is one of the two types of osseous tissue that form bones. Cortical bone facilitates bone's main functions: to support the whole body, protect organs, provide levers for movement, and store and release chemical elements, mainly calcium. As its name...
to cancellous bone in children's faces, poorly developed sinus
Sinus (anatomy)
Sinus is Latin for "bay", "pocket", "curve", or "bosom". In anatomy, the term is used in various contexts.A sinus is a sack or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue...
es make the bones stronger, and fat pads provide protection for the facial bones.
Head
Head injury
Head injury refers to trauma of the head. This may or may not include injury to the brain. However, the terms traumatic brain injury and head injury are often used interchangeably in medical literature....
and brain injuries
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
are commonly associated with facial trauma, particularly that of the upper face; brain injury occurs in 15–48% of people with maxillofacial trauma. Coexisting injuries can affect treatment of facial trauma; for example they may be emergent and need to be treated before facial injuries. People with trauma above the level of the collar bone
Clavicle
In human anatomy, the clavicle or collar bone is a long bone of short length that serves as a strut between the scapula and the sternum. It is the only long bone in body that lies horizontally...
s are considered to be at high risk for cervical spine injuries (spinal injuries in the neck) and special precautions must be taken to avoid movement of the spine, which could worsen a spinal injury.
Cited texts
External links
- The Gillies Archives at Queen Mary's Hospital, Sidcup - Documents and images from the early days of reconstructive surgery for severe facial trauma experienced by soldiers in World War IWorld War IWorld War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
.

