
Filter (optics)
Encyclopedia
Optical path
The path that light takes in traversing an optical system is often called the optical path. The physical length of an optical device can be reduced to less than the length of the optical path by using folded optics. The optical path length as defined in optics is the length of the path multiplied...
which are either dyed in the mass or have interference coatings.
Filters mostly belong to one of two categories. The simplest, physically, is the absorptive
Absorption (electromagnetic radiation)
In physics, absorption of electromagnetic radiation is the way by which the energy of a photon is taken up by matter, typically the electrons of an atom. Thus, the electromagnetic energy is transformed to other forms of energy for example, to heat. The absorption of light during wave propagation is...
filter; interference or dichroic filters can be quite complex.
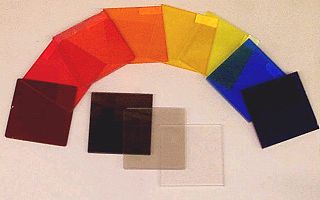
Optical filters selectively transmit light in a particular range of wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
s, that is, colours, while blocking the remainder. They can usually pass long wavelengths only (longpass), short wavelengths only (shortpass), or a band of wavelengths, blocking both longer and shorter wavelengths (bandpass). The passband may be narrower or wider; the transition or cutoff between maximal and minimal transmission can be sharp or gradual. There are filters with more complex transmission characteristic, for example with two peaks rather than a single band; these are more usually older designs traditionally used for photography; filters with more regular characteristics are used for scientific and technical work.
Optical filters are commonly used in photography (where some special effect filters are occasionally used as well as absorptive filters), in many optical instruments, and to colour stage lighting
Stage lighting
Modern stage lighting is a flexible tool in the production of theatre, dance, opera and other performance arts. Several different types of stage lighting instruments are used in the pursuit of the various principles or goals of lighting. Stage lighting has grown considerably in recent years...
. In astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
optical filters are used to restrict light passed to the spectral band of interest, e.g. to study infrared radiation without visible light which would affect film or sensors and overwhelm the desired infrared.
Photographic filters are a particular case of optical filters, and much of the material here applies. Photographic filters do not need the accurately-controlled optical properties and precisely-defined transmission curve
Transmission curve
For an optical or electronic filter which is described by the fraction of its input that it transmits as a function of frequency or wavelength, the transmission curve or transmission characteristic is the mathematical function or graph that defines the transmission fraction as a function of...
s of filters designed for scientific work, and sell in larger quantities at correspondingly lower prices than many laboratory filters. Some photographic effect filters, such as star effect filters, are not relevant to scientific work.
Absorptive
Absorptive filters are usually made from glassGlass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
to which various inorganic
Inorganic chemistry
Inorganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the properties and behavior of inorganic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds , which are the subjects of organic chemistry...
or organic compounds
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
have been added. These compounds absorb some wavelengths of light while transmitting others. The compounds can also be added to plastic
Plastic
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs...
(often polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
or acrylic) to produce gel
Color gel
A color gel or color filter , also known as lighting gel or simply gel, is a transparent colored material that is used in theatre, event production, photography, videography and cinematography to color light and for color correction...
filters, which are lighter and cheaper than glass-based filters.
Dichroic filter
Alternately, dichroic filters (also called "reflective" or "thin film" or "interference" filters) can be made by coating a glass substrate with a series of optical coatingOptical coating
An optical coating is one or more thin layers of material deposited on an optical component such as a lens or mirror, which alters the way in which the optic reflects and transmits light. One type of optical coating is an antireflection coating, which reduces unwanted reflections from surfaces, and...
s. Dichroic filters usually reflect the unwanted portion of the light and transmit the remainder.
Dichroic filters use the principle of interference. Their layers form a sequential series of reflective cavities that resonate with the desired wave lengths. Other wavelengths destructively cancel or reflect as the peaks and troughs of the waves overlap.
Dichroic filters are particularly suited for precise scientific work, since their exact colour range can be controlled by the thickness and sequence of the coatings. They are usually much more expensive and delicate than absorption filters.
They can be used in devices such as the dichroic prism
Dichroic prism
A dichroic prism is a prism that splits light into two beams of differing wavelength . They are usually constructed of one or more glass prisms with dichroic optical coatings that selectively reflect or transmit light depending on the light's wavelength. That is, certain surfaces within the prism...
of a camera
Camera
A camera is a device that records and stores images. These images may be still photographs or moving images such as videos or movies. The term camera comes from the camera obscura , an early mechanism for projecting images...
to separate a beam of light into different coloured components.
The basic scientific instrument of this type is a Fabry–Pérot interferometer. It uses two mirrors to establish a resonating cavity. It passes wavelengths that are a multiple of the cavity's resonance frequency.
Etalons are another variation: transparent cubes or fibers whose polished ends form mirrors tuned to resonate with specific wavelengths. These are often used to separate channels in telecommunications networks that use wavelength division multiplexing on long-haul optic fibers.
Monochromatic
Monochromatic filters only allow a narrow range of wavelengths (essentially a single colour) to pass.Infrared
The term "infrared filter" can be ambiguous, as it may be applied to filters to pass infrared (blocking other wavelengths) or to block infrared (only).Infrared-passing filters are used to block visible light but pass infrared; they are used, for example, in infrared photography
Infrared photography
In infrared photography, the film or image sensor used is sensitive to infrared light. The part of the spectrum used is referred to as near-infrared to distinguish it from far-infrared, which is the domain of thermal imaging. Wavelengths used for photography range from about 700 nm to about...
.
Infrared cut-off filters are designed to block or reflect infrared wavelengths but pass visible light. Mid-infrared filters are often used as heat-absorbing filters in devices with bright incandescent light bulb
Incandescent light bulb
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
s (such as slide
Slide projector
A slide projector is an opto-mechanical device to view photographic slides. Slide projectors were common in the 1950s to the 1970s as a form of entertainment; family members and friends would gather to view slide shows...
and overhead projector
Overhead projector
An overhead projector is a variant of slide projector that is used to display images to an audience.-Mechanism:An overhead projector typically consists of a large box containing a very bright lamp and a fan to cool it. On top of the box is a large fresnel lens that collimates the light...
s) to prevent unwanted heating due to infrared radiation. There are also filters which are used in solid state
Solid state (electronics)
Solid-state electronics are those circuits or devices built entirely from solid materials and in which the electrons, or other charge carriers, are confined entirely within the solid material...
video cameras to block IR due to the high sensitivity of many camera sensors
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
to unwanted near-infrared light.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) filters block ultraviolet radiation, but let visible light through. Because photographic film and digital sensors are sensitive to ultraviolet (which is abundant in skylight) but the human eye is not, such light would, if not filtered out, make photographs look different from the scene visible to people, for example making images of distant mountains appear unnaturally hazy. An ultraviolet-blocking filter renders images closer to the visual appearance of the scene.As with infrared filters there is a potential ambiguity between UV-blocking and UV-passing filters; the latter are much less common, and more usually known explicitly as UV pass filters and UV bandpass filters.
Neutral density
Neutral density (ND) filtersNeutral density filter
In photography and optics, a neutral density filter or ND filter can be a colorless or grey filter. An ideal neutral density filter reduces and/or modifies intensity of all wavelengths or colors of light equally, giving no changes in hue of color rendition.The purpose of standard photographic...
have a constant attenuation across the range of visible wavelengths, and are used to reduce the intensity of light by reflecting or absorbing a portion of it. They are specified by the optical density (OD) of the filter, which is the negative of the common logarithm of the transmission coefficient
Transmission coefficient
The transmission coefficient is used in physics and electrical engineering when wave propagation in a medium containing discontinuities is considered...
. They are useful for making photographic exposures longer. A practical example is making a waterfall look blurry when it is photographed in bright light. Alternatively, the photographer might want to use a larger aperture (so as to limit the depth of field
Depth of field
In optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image...
); adding an ND filter permits this. ND filters can be reflective (in which case they look like partially-reflective mirrors) or absorptive (appearing grey or black).
Longpass
A longpass (LP) Filter is an optical interference or coloured glass filter that attenuates shorter wavelengths and transmits (passes) longer wavelengths over the active range of the target spectrum (ultraviolet, visible, or infrared). Longpass filters, which can have a very sharp slope (referred to as edge filters), are described by the cut-on wavelength at 50 percent of peak transmission. In fluorescence microscopy, longpass filters are frequently utilized in dichroic mirrors and barrier (emission) filters. Use of the older term 'low pass' to describe longpass filters has become uncommon; filters are usually described in terms of wavelength rather than frequency, and a "low pass filter", without qualification, would be understood to be an electronic filterElectronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
.
Bandpass
Bandpass filters only transmit a certain wavelength band, and block others. The width of such a filter is expressed in the wavelength range it lets through and can be anything from much less than an ÅngströmÅngström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
to a few hundred nanometers. Such a filter can be made by combining an LP- and an SP filter.
Examples of bandpass filters are the Lyot filter
Lyot filter
A Lyot filter, named for its inventor Bernard Lyot, is a type of optical filter that uses birefringence to produce a narrow passband of transmitted wavelengths...
and the Fabry-Pérot interferometer
Fabry-Pérot interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer or etalon is typically made of a transparent plate with two reflecting surfaces, or two parallel highly reflecting mirrors...
. Both of these filters can also be made tunable, such that the central wavelength can be chosen by the user. Bandpass filters are often used in astronomy when one wants to observe a certain process with specific associated spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
s. The Dutch Open Telescope
Dutch Open Telescope
The Dutch Open Telescope , located on Roque de los Muchachos Observatory, La Palma , is an optical solar telescope with a main mirror of 45 centimeter and can reach an 0.2 arcsec resolution for sustained periods. For further optimization of the images, the DOT uses the image despeckle mechanism...
and Swedish Solar Telescope
Swedish Solar Telescope
The Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope is a refracting solar telescope at Roque de los Muchachos Observatory, La Palma in the Canary Islands. It is run by the Institute for Solar Physics of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The primary element is a single fused silica lens, making it the second...
are examples where Lyot and Fabry-Pérot filters are being used.
Shortpass
A shortpass (SP) Filter is an optical interference or coloured glass filter that attenuates longer wavelengths and transmits (passes) shorter wavelengths over the active range of the target spectrum (usually the ultraviolet and visible region). In fluorescence microscopy, shortpass filters are frequently employed in dichromatic mirrors and excitation filters.Guided-mode resonance filters
A relatively new class of filters introduced around 1990. These filters are normally filters in reflection, that is they are notch filters in transmission. They consist in their most basic form of a substrate waveguide and a subwavelength gratingGrating
A grating is any regularly spaced collection of essentially identical, parallel, elongated elements. Gratings usually consist of a single set of elongated elements, but can consist of two sets, in which case the second set is usually perpendicular to the first...
or 2D hole array. Such filters are normally transparent, but when a leaky guided mode of the waveguide is excited they become highly reflective (a record of over 99% experimentally) for a particular polarization, angular orientations, and wavelength range. The parameters of the filters are designed by proper choice of the grating parameters. The advantage of such filters are the few layers needed for ultra-narrow bandwidth filters (in contrast to dichroic filters), and the potential decoupling between spectral bandwidth and angular tolerance when more than 1 mode is excited.
Metal mesh filters
Filters for sub-millimeter and near infrared wavelengths in astronomy are metal mesh gridsMetal mesh optical filters
Metal-mesh optical filters are optical filters made from stacks of metal meshes and dielectric. They are used as part of an optical path to filter the incoming light to allow frequencies of interest to pass while reflecting other frequencies of light....
that are stacked together to form LP, BP, and SP filters for these wavelengths.
Polarizer
Another kind of optical filter is a polarizerPolarizer
A polarizer is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular...
or polarization filter, which blocks or transmits light according to its polarization. They are often made of materials such as Polaroid and are used for sunglasses
Sunglasses
Sunglasses or sun glasses are a form of protective eyewear designed primarily to prevent bright sunlight and high-energy visible light from damaging or discomforting the eyes. They can sometimes also function as a visual aid, as variously termed spectacles or glasses exist, featuring lenses that...
and photography
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
. Reflections, especially from water and wet road surfaces, are partially polarized, and polarized sunglasses will block some of this reflected light, allowing an angler
Angling
Angling is a method of fishing by means of an "angle" . The hook is usually attached to a fishing line and the line is often attached to a fishing rod. Fishing rods are usually fitted with a fishing reel that functions as a mechanism for storing, retrieving and paying out the line. The hook itself...
to better view below the surface of the water and better vision for a driver. Light from a clear blue sky is also polarized, and adjustable filters are used in colour photography to darken the appearance of the sky without introducing colours to other objects, and in both colour and black-and-white photography to control specular reflection
Specular reflection
Specular reflection is the mirror-like reflection of light from a surface, in which light from a single incoming direction is reflected into a single outgoing direction...
s from objects and water.
Polarized filters are also used to view certain types of stereogram
Stereogram
A stereogram is pair of two-dimensional panels depicting the view of a scene or an object from the vantage points of the right and left eyes. Observing the panels superimposed in a stereoscope results in the experience of three-dimensionality by virtue of the fact that object depth is encoded as...
s, so that each eye will see a distinct image from a single source.
See also
- Filter (photography)
- Filter (signal processing)Filter (signal processing)In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
- Filter fluorometerFilter fluorometerA filter fluorometer is a type of fluorometer that may be employed in fluorescence spectroscopy.In the fluorometer, a light source emits light of an excitation wavelength that is relevant to the compound to be measured. Filter fluorometers produce specific excitation and emission wavelengths by...
- Lyot filterLyot filterA Lyot filter, named for its inventor Bernard Lyot, is a type of optical filter that uses birefringence to produce a narrow passband of transmitted wavelengths...
- Dichroic filterDichroic filterA dichroic filter, thin-film filter, or interference filter is a very accurate color filter used to selectively pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. By comparison, dichroic mirrors and dichroic reflectors tend to be characterized by the color of light that they...
- Dichroic prismDichroic prismA dichroic prism is a prism that splits light into two beams of differing wavelength . They are usually constructed of one or more glass prisms with dichroic optical coatings that selectively reflect or transmit light depending on the light's wavelength. That is, certain surfaces within the prism...
- Atomic line filterAtomic line filterAn atomic line filter is an advanced optical band-pass filter used in the physical sciences for filtering electromagnetic radiation with precision, accuracy, and minimal signal strength loss...
- Warm filterWarm filterA warm filter is a photographic filter that improves the color of all skin tones and absorbs blue cast often caused by electronic flash or outdoor shade...
- Metal mesh optical filtersMetal mesh optical filtersMetal-mesh optical filters are optical filters made from stacks of metal meshes and dielectric. They are used as part of an optical path to filter the incoming light to allow frequencies of interest to pass while reflecting other frequencies of light....
External links
- Thorlabs sells optical filters
- Edmund Optics sells optical filters
- Semrock sells optical filters specialized for microscopy

