Fitness landscape
Encyclopedia
In evolutionary biology, fitness landscapes or adaptive landscapes are used to visualize the relationship between genotype
s (or phenotype
s) and reproductive success
. It is assumed that every genotype has a well-defined replication rate (often referred to as fitness
). This fitness is the "height" of the landscape. Genotypes which are very similar are said to be "close" to each other, while those that are very different are "far" from each other.
The two concepts of height and distance are sufficient to form the concept of a "landscape". The set of all possible genotypes, their degree of similarity, and their related fitness values is then called a fitness landscape. The idea of a fitness landscape helps explain flawed forms
in evolution, including exploits and glitches in animals like their reactions to supernormal stimuli.
In evolutionary optimization
problems, fitness landscapes are evaluations of a fitness function
for all candidate solutions (see below). The idea of studying evolution by visualizing the distribution of fitness values as a kind of landscape was first introduced by Sewall Wright
in 1932.
, as demonstrated by Stuart Kauffman
's NK-Landscape model.
An evolving population
typically climbs uphill in the fitness landscape, by a series of small genetic changes, until a local optimum is reached (Fig. 1). There it remains, unless a rare mutation
opens a path to a new, higher fitness peak. Note, however, that at high mutation rates this picture is somewhat simplistic. A population may not be able to climb a very sharp peak if the mutation rate is too high, or it may drift away from a peak it had already found; consequently, reducing the fitness of the system. The process of drifting away from a peak is often referred to as Muller's ratchet
.
The apparent lack of wheeled animals is an example of a fitness peak which is presently inaccessible due to a surrounding valley.
In general, the higher the connectivity
the more rugged the system becomes. Thus, a simply connected system
only has one peak and if part of the system is changed then there will be little, if any, effect on any other part of the system. A high connectivity implies that the variables or sub-systems interact far more and the system may have to settle for a level of ‘fitness’ lower than it might be able to attain. The system would then have to change its approach to overcoming whatever problems that confront it, thus, changing the ‘terrain’ and enabling it to continue.
methods such as genetic algorithm
s or evolutionary strategies. In evolutionary optimization, one tries to solve real-world problems (e.g., engineering
or logistics
problems) by imitating the dynamics of biological evolution. For example, a delivery truck with a number of destination addresses can take a large variety of different routes, but only very few will result in a short driving time.
In order to use evolutionary optimization, one has to define for every possible solution s to the problem of interest (i.e., every possible route in the case of the delivery truck) how 'good' it is. This is done by introducing a scalar
-valued function
f(s) (scalar valued means that f(s) is a simple number, such as 0.3, while s can be a more complicated object, for example a list of destination addresses in the case of the delivery truck), which is called the fitness function
or fitness landscape.
A high f(s) implies that s is a good solution. In the case of the delivery truck, f(s) could be the number of deliveries per hour on route s. The best, or at least a very good, solution is then found in the following way: initially, a population of random solutions is created. Then, the solutions are mutated and selected for those with higher fitness, until a satisfying solution has been found.
Evolutionary optimization techniques are particularly useful in situations in which it is easy to determine the quality of a single solution, but hard to go through all possible solutions one by one (it is easy to determine the driving time for a particular route of the delivery truck, but it is almost impossible to check all possible routes once the number of destinations grows to more than a handful).
The concept of a scalar valued fitness function f(s) also corresponds to the concept of a potential or energy function in physics
. The two concepts only differ in that physicists traditionally think in terms of minimizing the potential function, while biologists prefer the notion that fitness is being maximized. Therefore, taking the inverse of a potential function turns it into a fitness function, and vice versa.
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
s (or phenotype
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
s) and reproductive success
Reproductive success
Reproductive success is defined as the passing of genes onto the next generation in a way that they too can pass those genes on. In practice, this is often a tally of the number of offspring produced by an individual. A more correct definition, which incorporates inclusive fitness, is the...
. It is assumed that every genotype has a well-defined replication rate (often referred to as fitness
Fitness (biology)
Fitness is a central idea in evolutionary theory. It can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment...
). This fitness is the "height" of the landscape. Genotypes which are very similar are said to be "close" to each other, while those that are very different are "far" from each other.
The two concepts of height and distance are sufficient to form the concept of a "landscape". The set of all possible genotypes, their degree of similarity, and their related fitness values is then called a fitness landscape. The idea of a fitness landscape helps explain flawed forms
Argument from poor design
The dysteleological argument or argument from poor design is an argument against the existence of God, specifically against the existence of a creator God...
in evolution, including exploits and glitches in animals like their reactions to supernormal stimuli.
In evolutionary optimization
Evolutionary algorithm
In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses some mechanisms inspired by biological evolution: reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection...
problems, fitness landscapes are evaluations of a fitness function
Fitness function
A fitness function is a particular type of objective function that is used to summarise, as a single figure of merit, how close a given design solution is to achieving the set aims....
for all candidate solutions (see below). The idea of studying evolution by visualizing the distribution of fitness values as a kind of landscape was first introduced by Sewall Wright
Sewall Wright
Sewall Green Wright was an American geneticist known for his influential work on evolutionary theory and also for his work on path analysis. With R. A. Fisher and J.B.S. Haldane, he was a founder of theoretical population genetics. He is the discoverer of the inbreeding coefficient and of...
in 1932.
Fitness landscapes in biology
Fitness landscapes are often conceived of as ranges of mountains. There exist local peaks (points from which all paths are downhill, i.e. to lower fitness) and valleys (regions from which most paths lead uphill). A fitness landscape with many local peaks surrounded by deep valleys is called rugged. If all genotypes have the same replication rate, on the other hand, a fitness landscape is said to be flat. The shapes of fitness landscapes are also closely related to epistasisEpistasis
In genetics, epistasis is the phenomenon where the effects of one gene are modified by one or several other genes, which are sometimes called modifier genes. The gene whose phenotype is expressed is called epistatic, while the phenotype altered or suppressed is called hypostatic...
, as demonstrated by Stuart Kauffman
Stuart Kauffman
Stuart Alan Kauffman is an American theoretical biologist and complex systems researcher concerning the origin of life on Earth...
's NK-Landscape model.
An evolving population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
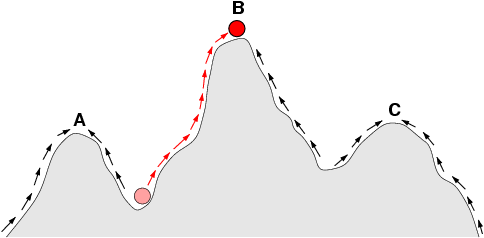
typically climbs uphill in the fitness landscape, by a series of small genetic changes, until a local optimum is reached (Fig. 1). There it remains, unless a rare mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
opens a path to a new, higher fitness peak. Note, however, that at high mutation rates this picture is somewhat simplistic. A population may not be able to climb a very sharp peak if the mutation rate is too high, or it may drift away from a peak it had already found; consequently, reducing the fitness of the system. The process of drifting away from a peak is often referred to as Muller's ratchet
Muller's ratchet
In evolutionary genetics, Muller's ratchet is the process by which the genomes of an asexual population accumulate deleterious mutations in an irreversible manner....
.
The apparent lack of wheeled animals is an example of a fitness peak which is presently inaccessible due to a surrounding valley.
In general, the higher the connectivity
Connectivity (graph theory)
In mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements which need to be removed to disconnect the remaining nodes from each other. It is closely related to the theory of network flow problems...
the more rugged the system becomes. Thus, a simply connected system
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
only has one peak and if part of the system is changed then there will be little, if any, effect on any other part of the system. A high connectivity implies that the variables or sub-systems interact far more and the system may have to settle for a level of ‘fitness’ lower than it might be able to attain. The system would then have to change its approach to overcoming whatever problems that confront it, thus, changing the ‘terrain’ and enabling it to continue.
Fitness landscapes in evolutionary optimization
Apart from the field of evolutionary biology, the concept of a fitness landscape has also gained importance in evolutionary optimizationEvolutionary algorithm
In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses some mechanisms inspired by biological evolution: reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection...
methods such as genetic algorithm
Genetic algorithm
A genetic algorithm is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural evolution. This heuristic is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems...
s or evolutionary strategies. In evolutionary optimization, one tries to solve real-world problems (e.g., engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
or logistics
Logistics
Logistics is the management of the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of destination in order to meet the requirements of customers or corporations. Logistics involves the integration of information, transportation, inventory, warehousing, material handling, and packaging, and...
problems) by imitating the dynamics of biological evolution. For example, a delivery truck with a number of destination addresses can take a large variety of different routes, but only very few will result in a short driving time.
In order to use evolutionary optimization, one has to define for every possible solution s to the problem of interest (i.e., every possible route in the case of the delivery truck) how 'good' it is. This is done by introducing a scalar
Scalar (mathematics)
In linear algebra, real numbers are called scalars and relate to vectors in a vector space through the operation of scalar multiplication, in which a vector can be multiplied by a number to produce another vector....
-valued function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
f(s) (scalar valued means that f(s) is a simple number, such as 0.3, while s can be a more complicated object, for example a list of destination addresses in the case of the delivery truck), which is called the fitness function
Fitness function
A fitness function is a particular type of objective function that is used to summarise, as a single figure of merit, how close a given design solution is to achieving the set aims....
or fitness landscape.
A high f(s) implies that s is a good solution. In the case of the delivery truck, f(s) could be the number of deliveries per hour on route s. The best, or at least a very good, solution is then found in the following way: initially, a population of random solutions is created. Then, the solutions are mutated and selected for those with higher fitness, until a satisfying solution has been found.
Evolutionary optimization techniques are particularly useful in situations in which it is easy to determine the quality of a single solution, but hard to go through all possible solutions one by one (it is easy to determine the driving time for a particular route of the delivery truck, but it is almost impossible to check all possible routes once the number of destinations grows to more than a handful).
The concept of a scalar valued fitness function f(s) also corresponds to the concept of a potential or energy function in physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
. The two concepts only differ in that physicists traditionally think in terms of minimizing the potential function, while biologists prefer the notion that fitness is being maximized. Therefore, taking the inverse of a potential function turns it into a fitness function, and vice versa.

See also
- Fitness approximationFitness approximationIn function optimization, fitness approximation is a method for decreasing the number of fitness function evaluations to reach a target solution...
- Fitness functionFitness functionA fitness function is a particular type of objective function that is used to summarise, as a single figure of merit, how close a given design solution is to achieving the set aims....
- Epigenetic landscapeEpigenetic landscapeEpigenetic landscape is a metaphor for biological development. Its originator, Conrad Hal Waddington, said that cell fates were established in development much like a marble rolls down to the point of lowest local elevation...
- EvolutionEvolutionEvolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
- Genetic algorithmGenetic algorithmA genetic algorithm is a search heuristic that mimics the process of natural evolution. This heuristic is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems...
- Habitat (ecology)Habitat (ecology)A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by a particular species of animal, plant or other type of organism...
- Hill climbingHill climbingIn computer science, hill climbing is a mathematical optimization technique which belongs to the family of local search. It is an iterative algorithm that starts with an arbitrary solution to a problem, then attempts to find a better solution by incrementally changing a single element of the solution...
- Natural selectionNatural selectionNatural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
- NK modelNK modelThe NK model is a mathematical model described by its primary inventor Stuart Kauffman as a "tunably rugged" fitness landscape. "tunable ruggedness" captures the intuition that both the overall size of the landscape and the number of its local "hills and valleys" can be adjusted via changes to its...
- Potential functionPotential functionThe term potential function may refer to:* A mathematical function whose values are a physical potential.* The class of functions known as harmonic functions, which are the topic of study in potential theory.* The potential function of a potential game....
- Self-organized criticalitySelf-organized criticalityIn physics, self-organized criticality is a property of dynamical systems which have a critical point as an attractor. Their macroscopic behaviour thus displays the spatial and/or temporal scale-invariance characteristic of the critical point of a phase transition, but without the need to tune...
Further reading
- Niko Beerenwinkel, Lior Pachter and Bernd SturmfelsBernd SturmfelsBernd Sturmfels is a Professor of Mathematics and Computer Science at the University of California, Berkeley.He received his PhD in 1987 from the University of Washington and the Technische Universität Darmstadt...
. Epistasis and shapes of fitness landscapes, 2006. - Richard DawkinsRichard DawkinsClinton Richard Dawkins, FRS, FRSL , known as Richard Dawkins, is a British ethologist, evolutionary biologist and author...
. Climbing Mount ImprobableClimbing Mount ImprobableClimbing Mount Improbable is a 1996 popular science book by Richard Dawkins. The book is about probability and how it applies to the theory of evolution, and is specifically designed to debunk claims by creationists about the probability of naturalistic mechanisms like natural selection.The main...
. New York: Norton, 1996. - Sergey Gavrilets. Fitness landscapes and the origin of species, 2004.
- Stuart KauffmanStuart KauffmanStuart Alan Kauffman is an American theoretical biologist and complex systems researcher concerning the origin of life on Earth...
. At Home in the Universe: The Search for Laws of Self-Organization and Complexity. New York: Oxford University Press, 1995. - Melanie MitchellMelanie MitchellMelanie Mitchell is a professor of computer science at Portland State University. She has worked at the Santa Fe Institute and Los Alamos National Laboratory...
. An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1996. - Foundations of Genetic Programming, Chapter 2
- Stuart KauffmanStuart KauffmanStuart Alan Kauffman is an American theoretical biologist and complex systems researcher concerning the origin of life on Earth...
, The Origins of Order, OUP, 1993

