
NK model
Encyclopedia
The NK model is a mathematical model
described by its primary inventor Stuart Kauffman
as a "tunably rugged" fitness landscape. "tunable ruggedness" captures the intuition that both the overall size of the landscape and the number of its local "hills and valleys" can be adjusted via changes to its two parameters, and
and  , defined below. The NK model has found application in a wide variety of fields, most notably
, defined below. The NK model has found application in a wide variety of fields, most notably
the theoretical study of evolutionary biology, immunology
, optimisation
and complex systems
.
An early version of the model, which considered only the smoothest ( ) and most rugged (
) and most rugged ( ) landscapes, was presented in Kauffman and Levin (1987). The model as it is currently known first appeared in Kauffman and Weinberger (1989).
) landscapes, was presented in Kauffman and Levin (1987). The model as it is currently known first appeared in Kauffman and Weinberger (1989).
One of the reasons why the model has attracted wide attention in optimisation
is that it is a particularly simple instance of a so-called Np-complete problem
, consisting of every string (chosen from a given alphabet) of length . For each string in this search space, a scalar
. For each string in this search space, a scalar
value (called the fitness
) is defined. If a distance metric
is defined between strings, the resulting structure is a landscape.
Fitness values are defined according to the specific incarnation of the model, but the key feature of the NK model is that the fitness of a given string is the sum of contributions from each locus
is the sum of contributions from each locus 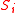 in the string:
in the string:
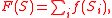
and the contribution from each locus in general depends on the value of other loci:
other loci:

where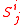 are the other loci upon which the fitness of
are the other loci upon which the fitness of 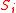 depends.
depends.
Hence, the fitness function is a mapping
is a mapping
between strings of length K + 1 and scalar values. In a particular implementation of the NK model, the scalar values corresponding to each string are often chosen randomly.
strings. Consider an NK model with N = 5, K = 1. Here, the fitness of a string is given by the sum of individual fitness contributions from each of 5 loci. Each fitness contribution depends on the local locus value and one other. We will employ the convention that , so that each locus is affected by its neighbour, and
, so that each locus is affected by its neighbour, and 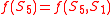 for cyclicity. If we choose, for example, the fitness function f(0, 0) = 0; f(0, 1) = 1; f(1, 0) = 2; f(1, 1) = 0, the fitness values of two example strings are:
for cyclicity. If we choose, for example, the fitness function f(0, 0) = 0; f(0, 1) = 1; f(1, 0) = 2; f(1, 1) = 0, the fitness values of two example strings are:


in the NK model, or how much other loci affect the fitness contribution of a given locus. With K = 0, the fitness of a given string is a simple sum of individual contributions of loci: for nontrivial fitness functions, a global optimum
is present and easy to locate (the genome of all 0s if f(0) > f(1), or all 1s if f(1) > f(0)). For nonzero K, the fitness of a string is a sum of fitnesses of substrings, which may interact to frustrate
the system (consider how to achieve optimal fitness in the example above). Increasing K thus increases the ruggedness of the fitness landscape.
and pleiotropy
in evolutionary biology, and combinatorial optimisation.
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
described by its primary inventor Stuart Kauffman
Stuart Kauffman
Stuart Alan Kauffman is an American theoretical biologist and complex systems researcher concerning the origin of life on Earth...
as a "tunably rugged" fitness landscape. "tunable ruggedness" captures the intuition that both the overall size of the landscape and the number of its local "hills and valleys" can be adjusted via changes to its two parameters,
 and
and  , defined below. The NK model has found application in a wide variety of fields, most notably
, defined below. The NK model has found application in a wide variety of fields, most notablythe theoretical study of evolutionary biology, immunology
Immunology
Immunology is a broad branch of biomedical science that covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all organisms. It deals with the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders ; the...
, optimisation
Combinatorial optimization
In applied mathematics and theoretical computer science, combinatorial optimization is a topic that consists of finding an optimal object from a finite set of objects. In many such problems, exhaustive search is not feasible...
and complex systems
Complex systems
Complex systems present problems in mathematical modelling.The equations from which complex system models are developed generally derive from statistical physics, information theory and non-linear dynamics, and represent organized but unpredictable behaviors of systems of nature that are considered...
.
An early version of the model, which considered only the smoothest (
 ) and most rugged (
) and most rugged ( ) landscapes, was presented in Kauffman and Levin (1987). The model as it is currently known first appeared in Kauffman and Weinberger (1989).
) landscapes, was presented in Kauffman and Levin (1987). The model as it is currently known first appeared in Kauffman and Weinberger (1989).One of the reasons why the model has attracted wide attention in optimisation
Combinatorial optimization
In applied mathematics and theoretical computer science, combinatorial optimization is a topic that consists of finding an optimal object from a finite set of objects. In many such problems, exhaustive search is not feasible...
is that it is a particularly simple instance of a so-called Np-complete problem
Mathematical Detail
The NK model defines a combinatorial search spaceSearch space
Search space may refer to one of the following.*In optimization, the domain of the function to be optimized*In search algorithms of computer science, the set of all possible solutions...
, consisting of every string (chosen from a given alphabet) of length
 . For each string in this search space, a scalar
. For each string in this search space, a scalarScalar
Scalar may refer to:*Scalar , a quantity used to multiply vectors in the context of vector spaces*Scalar , a quantity which is independent of specific classes of coordinate systems...
value (called the fitness
Fitness
Fitness may relate to:* Physical fitness, a general state of good health, usually as a result of exercise and nutrition * Cardiorespiratory fitness...
) is defined. If a distance metric
Metric (mathematics)
In mathematics, a metric or distance function is a function which defines a distance between elements of a set. A set with a metric is called a metric space. A metric induces a topology on a set but not all topologies can be generated by a metric...
is defined between strings, the resulting structure is a landscape.
Fitness values are defined according to the specific incarnation of the model, but the key feature of the NK model is that the fitness of a given string
 is the sum of contributions from each locus
is the sum of contributions from each locus 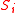 in the string:
in the string:
and the contribution from each locus in general depends on the value of
 other loci:
other loci:
where
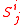 are the other loci upon which the fitness of
are the other loci upon which the fitness of 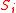 depends.
depends.Hence, the fitness function
 is a mapping
is a mappingMap (mathematics)
In most of mathematics and in some related technical fields, the term mapping, usually shortened to map, is either a synonym for function, or denotes a particular kind of function which is important in that branch, or denotes something conceptually similar to a function.In graph theory, a map is a...
between strings of length K + 1 and scalar values. In a particular implementation of the NK model, the scalar values corresponding to each string are often chosen randomly.
Example
For simplicity, we will work with binaryBinary
- Mathematics :* Binary numeral system, a representation for numbers using only two digits * Binary function, a function in mathematics that takes two arguments- Computing :* Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text...
strings. Consider an NK model with N = 5, K = 1. Here, the fitness of a string is given by the sum of individual fitness contributions from each of 5 loci. Each fitness contribution depends on the local locus value and one other. We will employ the convention that
 , so that each locus is affected by its neighbour, and
, so that each locus is affected by its neighbour, and 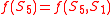 for cyclicity. If we choose, for example, the fitness function f(0, 0) = 0; f(0, 1) = 1; f(1, 0) = 2; f(1, 1) = 0, the fitness values of two example strings are:
for cyclicity. If we choose, for example, the fitness function f(0, 0) = 0; f(0, 1) = 1; f(1, 0) = 2; f(1, 1) = 0, the fitness values of two example strings are:

Tunable topology
The value of K controls the degree of epistasisEpistasis
In genetics, epistasis is the phenomenon where the effects of one gene are modified by one or several other genes, which are sometimes called modifier genes. The gene whose phenotype is expressed is called epistatic, while the phenotype altered or suppressed is called hypostatic...
in the NK model, or how much other loci affect the fitness contribution of a given locus. With K = 0, the fitness of a given string is a simple sum of individual contributions of loci: for nontrivial fitness functions, a global optimum
Global optimum
In mathematics, a global optimum is a selection from a given domain which yields either the highest value or lowest value , when a specific function is applied. For example, for the function...
is present and easy to locate (the genome of all 0s if f(0) > f(1), or all 1s if f(1) > f(0)). For nonzero K, the fitness of a string is a sum of fitnesses of substrings, which may interact to frustrate
Geometrical frustration
In condensed matter physics, the term geometrical frustration means a phenomenon in which the geometrical properties of the crystal lattice or the presence of conflicting atomic forces forbid simultaneous minimization of the interaction energies acting at a given site.This may lead to highly...
the system (consider how to achieve optimal fitness in the example above). Increasing K thus increases the ruggedness of the fitness landscape.
Applications
The NK model has found use in many fields, including in the study of spin glasses, epistasisEpistasis
In genetics, epistasis is the phenomenon where the effects of one gene are modified by one or several other genes, which are sometimes called modifier genes. The gene whose phenotype is expressed is called epistatic, while the phenotype altered or suppressed is called hypostatic...
and pleiotropy
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy occurs when one gene influences multiple phenotypic traits. Consequently, a mutation in a pleiotropic gene may have an effect on some or all traits simultaneously...
in evolutionary biology, and combinatorial optimisation.

