Flora family
Encyclopedia
The Flora family of asteroids
is a large grouping of S-type
asteroid
s in the inner main belt, whose origin and properties are relatively poorly understood at present. Roughly 4-5% of all main belt asteroids belong to this family.
Because of its poorly defined boundaries, and the location of Flora itself near the edge, this asteroid group has also sometimes been called the Ariadne family, when Flora did not make it into the group during an analysis (e.g. the WAM analysis by Zappala 1995).
The Flora family of asteroids may be the source of the K/T impactor, the likely culprit in the extinction of the dinosaurs.
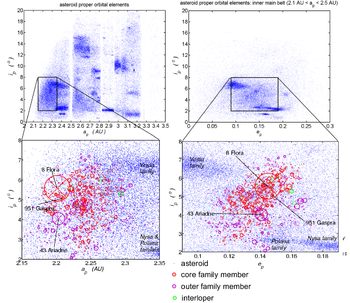 The largest member is 8 Flora
The largest member is 8 Flora
, which meaures 140 km in diameter
, and comprises about 80% of the total family mass. Nevertheless, the parent body was almost certainly disrupted by the impact/s that formed the family, and Flora is probably a gravitational aggregate of most of the pieces. 43 Ariadne
makes up much of the remaining mass (about a further 9%), with the remaining family members being fairly small, below 30 km in diameter.
A noticeable fraction of the parent body has been lost from the family since the original impact, presumably due to later processes such as e.g. secondary collisions. For example, it has been estimated that Flora contains only about 57% of the parent body's mass (Tanga 1999), but about 80% of the mass in the present family.
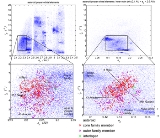
The Flora family is very broad and gradually fades into the background population (which is particularly dense in this part of space) in such a way that its boundaries are very poorly defined. There are also several non-uniformities or lobes within the family, one cause of which may have been later secondary collisions between family members. Hence, it is a classical example of a so-called 'asteroid clan' (see asteroid family
). Curiously, the largest members, 8 Flora
and 43 Ariadne
, are located near the edge of the family. The reason for this unusual mass distribution within the family is unknown at present.
951 Gaspra
, a medium-sized core family member was visited by the Galileo spacecraft
on its way to Jupiter
, and is one of the most extensively studied asteroids. Studies of Gaspra suggests that the family's age is of the order of 200 million years (indicated by the crater density), and that the parent body was at least partially differentiated
(indicated by the high abundance of olivine
) (Veverka 1994).
The Flora family members are considered good candidates for being the parent bodies of the L chondrite
meteorites (Nesvorny 2002), which contribute about 38% of all meteorites impacting the Earth. This theory is supported by the family's location close to the unstable zone of the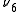 secular resonance
secular resonance
, and because the spectral properties of family members are consistent with being the parent bodies of this meteorite type.
The Flora family was one of the five original Hirayama families
that were first identified. It has a high number of early discovered members both because S-type asteroids tend to have high albedo, and because it is the closest major asteroid grouping to Earth
.
lie in the approximate ranges
! !! ap
!! ep !! ip
>
min
2.17 AU
0.109
2.4°
max
2.33 AU
0.168
6.9°
The boundaries of the family are, however, very indistinct. At the present epoch
, the range of osculating
orbital elements
of these core members is
Zappala's 1995 analysis found 604 core members, and 1027 in a wider group. A search of a recent proper element database (AstDys)for 96944 minor planet
s in 2005 yielded 7438 objects lying within the rectangular-shaped region defined by the first table above. However, this also includes parts of the Vesta
and Nysa
families in the corners so that a more likely membership estimate is 4000-5000 objects (by eye). This means that the Flora family represents 4-5% of all main belt asteroids.
(S
) that dominates the inner main belt overall. The few interlopers that have been identified are all small (Florczak et al. 1998, and also by inspection of the PDS asteroid taxonomy data set for non S-type members.) They include 298 Baptistina
, 422 Berolina
, 2093 Genichesk
, 2259 Sofievka
(the largest, with a 21 km diameter), 2952 Lilliputia
, 3533 Toyota
, 3850 Peltier
, 3875 Staehle
, 4278 Harvey
, 4396 Gressmann
, and 4750 Mukai
.
Asteroid family
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions...
is a large grouping of S-type
S-type asteroid
S-type asteroids are of a stony composition, hence the name. Approximately 17% of asteroids are of this type, making it the second most common after the C-type.-Characteristics:...
asteroid
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
s in the inner main belt, whose origin and properties are relatively poorly understood at present. Roughly 4-5% of all main belt asteroids belong to this family.
Because of its poorly defined boundaries, and the location of Flora itself near the edge, this asteroid group has also sometimes been called the Ariadne family, when Flora did not make it into the group during an analysis (e.g. the WAM analysis by Zappala 1995).
The Flora family of asteroids may be the source of the K/T impactor, the likely culprit in the extinction of the dinosaurs.
Characteristics

8 Flora
8 Flora is a large, bright main-belt asteroid. It is the innermost large asteroid: no asteroid closer to the Sun has a diameter above 25 kilometres or two-elevenths that of Flora itself, and not until the tiny 149 Medusa was discovered was a single asteroid orbiting at a closer mean distance...
, which meaures 140 km in diameter
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle. The diameters are the longest chords of the circle...
, and comprises about 80% of the total family mass. Nevertheless, the parent body was almost certainly disrupted by the impact/s that formed the family, and Flora is probably a gravitational aggregate of most of the pieces. 43 Ariadne
43 Ariadne
43 Ariadne is a fairly large and bright main-belt asteroid. It is the second-largest member of the Flora asteroid family. It was discovered by N. R. Pogson on April 15, 1857, and named after the Greek heroine Ariadne.-Characteristics:...
makes up much of the remaining mass (about a further 9%), with the remaining family members being fairly small, below 30 km in diameter.
A noticeable fraction of the parent body has been lost from the family since the original impact, presumably due to later processes such as e.g. secondary collisions. For example, it has been estimated that Flora contains only about 57% of the parent body's mass (Tanga 1999), but about 80% of the mass in the present family.
The Flora family is very broad and gradually fades into the background population (which is particularly dense in this part of space) in such a way that its boundaries are very poorly defined. There are also several non-uniformities or lobes within the family, one cause of which may have been later secondary collisions between family members. Hence, it is a classical example of a so-called 'asteroid clan' (see asteroid family
Asteroid family
An asteroid family is a population of asteroids that share similar proper orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination. The members of the families are thought to be fragments of past asteroid collisions...
). Curiously, the largest members, 8 Flora
8 Flora
8 Flora is a large, bright main-belt asteroid. It is the innermost large asteroid: no asteroid closer to the Sun has a diameter above 25 kilometres or two-elevenths that of Flora itself, and not until the tiny 149 Medusa was discovered was a single asteroid orbiting at a closer mean distance...
and 43 Ariadne
43 Ariadne
43 Ariadne is a fairly large and bright main-belt asteroid. It is the second-largest member of the Flora asteroid family. It was discovered by N. R. Pogson on April 15, 1857, and named after the Greek heroine Ariadne.-Characteristics:...
, are located near the edge of the family. The reason for this unusual mass distribution within the family is unknown at present.
951 Gaspra
951 Gaspra
951 Gaspra is an S-type asteroid that orbits very close to the inner edge of the asteroid belt. Gaspra was the first asteroid ever to be closely approached when it was visited by the Galileo spacecraft, which flew by on its way to Jupiter on 29 October 1991.-Characteristics:Apart from a multitude...
, a medium-sized core family member was visited by the Galileo spacecraft
Galileo spacecraft
Galileo was an unmanned spacecraft sent by NASA to study the planet Jupiter and its moons. Named after the astronomer and Renaissance pioneer Galileo Galilei, it was launched on October 18, 1989 by the Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-34 mission...
on its way to Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
, and is one of the most extensively studied asteroids. Studies of Gaspra suggests that the family's age is of the order of 200 million years (indicated by the crater density), and that the parent body was at least partially differentiated
Planetary differentiation
In planetary science, planetary differentiation is the process of separating out different constituents of a planetary body as a consequence of their physical or chemical behaviour, where the body develops into compositionally distinct layers; the denser materials of a planet sink to the center,...
(indicated by the high abundance of olivine
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
) (Veverka 1994).
The Flora family members are considered good candidates for being the parent bodies of the L chondrite
L chondrite
The L type ordinary chondrites are the second most common type of meteorite, accounting for approximately 35% of all those catalogued, and 40% of the ordinary chondrites....
meteorites (Nesvorny 2002), which contribute about 38% of all meteorites impacting the Earth. This theory is supported by the family's location close to the unstable zone of the
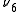 secular resonance
secular resonanceSecular resonance
A secular resonance is a type of orbital resonance.Secular resonances occur when the precession of two orbits is synchronised . A small body in secular resonance with a much larger one will precess at the same rate as the large body...
, and because the spectral properties of family members are consistent with being the parent bodies of this meteorite type.
The Flora family was one of the five original Hirayama families
Hirayama families
A Hirayama family of asteroids is a group of minor planets that share similar orbital elements, such as semimajor axis, eccentricity, and orbital inclination...
that were first identified. It has a high number of early discovered members both because S-type asteroids tend to have high albedo, and because it is the closest major asteroid grouping to Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
.
Location and size
A HCM numerical analysis (Zappala 1995) determined a large group of 'core' family members, whose proper orbital elementsProper orbital elements
The proper orbital elements of an orbit are constants of motion of an object in space that remain practically unchanged over an astronomically long timescale...
lie in the approximate ranges
Semi-major axis
The major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter, a line that runs through the centre and both foci, its ends being at the widest points of the shape...
!! ep !! ip
Inclination
Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit...
>
Astronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
The boundaries of the family are, however, very indistinct. At the present epoch
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity, such as celestial coordinates, or elliptical orbital elements of a celestial body, where these are subject to perturbations and vary with time...
, the range of osculating
Osculating orbit
In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space is the gravitational Kepler orbit In astronomy, and in particular in astrodynamics, the osculating orbit of an object in space (at a given moment of time) is the gravitational Kepler orbit In astronomy,...
orbital elements
Orbital elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used...
of these core members is
| a Semi-major axis The major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter, a line that runs through the centre and both foci, its ends being at the widest points of the shape... | e | i Inclination Inclination in general is the angle between a reference plane and another plane or axis of direction.-Orbits:The inclination is one of the six orbital parameters describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit... |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| min | 2.17 AU Astronomical unit An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance.... |
0.053 | 1.6° |
| max | 2.33 AU | 0.224 | 7.7° |
Zappala's 1995 analysis found 604 core members, and 1027 in a wider group. A search of a recent proper element database (AstDys)for 96944 minor planet
Minor planet
An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid...
s in 2005 yielded 7438 objects lying within the rectangular-shaped region defined by the first table above. However, this also includes parts of the Vesta
Vesta family
The Vesta or Vestian family of asteroids is a large and prominent grouping of mostly V-type asteroids in the inner asteroid belt in the vicinity of 4 Vesta...
and Nysa
Nysa family
The Nysa or Nysian asteroids are a group of asteroids in the Main Belt orbiting the sun between 2.41 and 2.5 AU. Asteroids in this family have eccentricities between 0.12 and 0.21 and inclinations of 1.4 to 4.3...
families in the corners so that a more likely membership estimate is 4000-5000 objects (by eye). This means that the Flora family represents 4-5% of all main belt asteroids.
Interlopers
Because of the high background density of asteroids in this part of space, one might expect that a great number of interlopers (asteroids unrelated to the collision that formed the family) would be present. However, few have been identified. This is because interlopers are hard to distinguish from family members because the family is of the same spectral typeAsteroid spectral types
Asteroids are assigned a type based on spectral shape, color, and sometimes albedo. These types are thought to correspond to an asteroid's surface composition...
(S
S-type asteroid
S-type asteroids are of a stony composition, hence the name. Approximately 17% of asteroids are of this type, making it the second most common after the C-type.-Characteristics:...
) that dominates the inner main belt overall. The few interlopers that have been identified are all small (Florczak et al. 1998, and also by inspection of the PDS asteroid taxonomy data set for non S-type members.) They include 298 Baptistina
298 Baptistina
298 Baptistina is a main belt asteroid, part of the Baptistina family of asteroids. It was discovered on September 9, 1890 by Auguste Charlois of Nice. The reason for its name is unknown. It measures around 13–30 km in diameter. Although it has an orbit similar to the Flora family...
, 422 Berolina
422 Berolina
422 Berolina is a typical Main belt asteroid.It was discovered by G. Witt on October 8, 1896 in Berlin. It was first of his two asteroid discoveries. The other was the famous asteroid 433 Eros....
, 2093 Genichesk
2093 Genichesk
2093 Genichesk is a main-belt asteroid discovered on April 28, 1971 by T. M. Smirnova at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory.- External links :*...
, 2259 Sofievka
2259 Sofievka
2259 Sofievka is a main-belt asteroid discovered on July 19, 1971 by B. Burnasheva at Nauchnyj.- External links :*...
(the largest, with a 21 km diameter), 2952 Lilliputia
2952 Lilliputia
2952 Lilliputia is a main-belt asteroid discovered on September 22, 1979 by N. Chernykh at Nauchnyj.- External links :*...
, 3533 Toyota
3533 Toyota
3533 Toyota is a main-belt asteroid discovered on October 30, 1986 by Kenzo Suzuki and Takeshi Urata at Toyota.- External links :*...
, 3850 Peltier
3850 Peltier
3850 Peltier is a Main belt asteroid. It was discovered on October 7, 1986 at Anderson Mesa by Ted Bowell who named it in honor of the American astronomer Leslie Peltier....
, 3875 Staehle
3875 Staehle
3875 Staehle is a main-belt asteroid discovered on May 17, 1988 by E. F. Helin at Palomar.- External links :*...
, 4278 Harvey
4278 Harvey
4278 Harvey is a main-belt asteroid discovered on September 22, 1982 by Ted Bowell at Flagstaff.-External links:*...
, 4396 Gressmann
4396 Gressmann
4396 Gressmann is a main-belt asteroid discovered on May 3, 1981 by Ted Bowell at Flagstaff.- External links :*...
, and 4750 Mukai
4750 Mukai
4750 Mukai is a main-belt asteroid discovered on December 15, 1990 by Tetsuya Fujii and Kazuro Watanabe at Kitami Observatory.- External links :*...
.

