Fluorobenzene
Encyclopedia
Fluorobenzene is the chemical compound
with the formula C6H5F, often abbreviated Ph
F. This species is a derivative
of benzene
, with a single fluorine
atom attached. Its melting point is 44 °C lower than that of benzene, indicative of the remarkable effect of fluorination on the intermolecular interactions as seen throughout organofluorine chemistry
. In contrast, the boiling points of PhF and benzene differ by only 4 °C.
According to the procedure, solid [PhN2]BF4 is heated with a flame to initiate an exothermic reaction
that affords two volatile products, PhF and BF3, which are readily separated because of their differing boiling point
s.
PhF was first reported in 1886 by O. Wallach at the University of Bonn
, who prepared the compound in two steps, starting also with a phenyldiazonium salt. The diazonium chloride was first converted to its piperidinide, which in turn was cloven using hydrofluoric acid
.
An interesting historical note: in Wallach’s era, the element fluorine was symbolized with “Fl”. Thus, his procedure is subtitled “Fluorbenzol, C6H5Fl”.
The technical synthesis is by the reaction of cyclopentadiene
with difluorocarbene
. The initially formed cyclopropane undergoes a ring expansion and subsequent elimination of hydrogen fluoride
.
Fluorination of fluorobenzene gives mainly 1,2-difluorobenzene
.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
with the formula C6H5F, often abbreviated Ph
Phenyl group
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group or phenyl ring is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5. Phenyl groups are closely related to benzene. Phenyl groups have six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the...
F. This species is a derivative
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by some chemical or physical process. In the past it was also used to mean a compound that can be imagined to arise from another compound, if one atom is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern...
of benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
, with a single fluorine
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
atom attached. Its melting point is 44 °C lower than that of benzene, indicative of the remarkable effect of fluorination on the intermolecular interactions as seen throughout organofluorine chemistry
Organofluorine chemistry
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil- and water-repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants and reagents in catalysis...
. In contrast, the boiling points of PhF and benzene differ by only 4 °C.
Preparation
On the laboratory scale, PhF is conveniently prepared by the thermal decomposition of the benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate- PhN2BF4 → PhF + BF3Boron trifluorideBoron trifluoride is the chemical compound with the formula BF3. This pungent colourless toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.-Structure and bonding:...
+ N2NitrogenNitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
According to the procedure, solid [PhN2]BF4 is heated with a flame to initiate an exothermic reaction
Exothermic reaction
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of light or heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction. Expressed in a chemical equation:-Overview:...
that affords two volatile products, PhF and BF3, which are readily separated because of their differing boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid....
s.
PhF was first reported in 1886 by O. Wallach at the University of Bonn
University of Bonn
The University of Bonn is a public research university located in Bonn, Germany. Founded in its present form in 1818, as the linear successor of earlier academic institutions, the University of Bonn is today one of the leading universities in Germany. The University of Bonn offers a large number...
, who prepared the compound in two steps, starting also with a phenyldiazonium salt. The diazonium chloride was first converted to its piperidinide, which in turn was cloven using hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a valued source of fluorine and is the precursor to numerous pharmaceuticals such as fluoxetine and diverse materials such as PTFE ....
.
- [PhN2]Cl + 2 C5H10NH → PhN=N-NC5H10 + [C5H10NH2]Cl
- PhN=N-NC5H10 + 2 HF → PhF + N2 + [C5H10NH2]F
An interesting historical note: in Wallach’s era, the element fluorine was symbolized with “Fl”. Thus, his procedure is subtitled “Fluorbenzol, C6H5Fl”.
The technical synthesis is by the reaction of cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, this cyclic diene dimerizes over the course of hours to give dicyclopentadiene via a Diels–Alder reaction...
with difluorocarbene
Difluorocarbene
Difluorocarbene is the chemical compound with formula CF2. It has a short half-life, 0.5 and 20 msec, in solution and in the gas phase, respectively...
. The initially formed cyclopropane undergoes a ring expansion and subsequent elimination of hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula HF. This colorless gas is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the aqueous form as hydrofluoric acid, and thus is the precursor to many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers . HF is widely used in the...
.
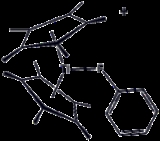
Reactions
PhF is a relatively inert compound because the C–F bond is very strong. PhF is a useful solvent for highly reactive species, but a metal complex has been crystallized.Fluorination of fluorobenzene gives mainly 1,2-difluorobenzene
1,2-Difluorobenzene
1,2-Difluorobenzene, also known as DFB, is an aromatic compound with formula C6H4F2. This colorless liquid is a solvent used in the electrochemical studies of transition metal complexes.- Synthesis :...
.


.png)