
Force density
Encyclopedia
In fluid mechanics
, the force density is the negative gradient
of pressure. It has the physical dimensions of force per unit volume
. Force density is a vector field
representing the flux
density of the hydrostatic force within the bulk of a fluid
. Force density is represented by the symbol f, and given by the following equation, where P is the pressure
:
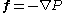 .
.
The net force on a differental volume element
dV of the fluid is:
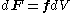
Thus, the force density at a point in a fluid, divided by the density
, is the acceleration
of the fluid at that point.
Fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the study of fluids and the forces on them. Fluid mechanics can be divided into fluid statics, the study of fluids at rest; fluid kinematics, the study of fluids in motion; and fluid dynamics, the study of the effect of forces on fluid motion...
, the force density is the negative gradient
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
of pressure. It has the physical dimensions of force per unit volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
. Force density is a vector field
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
representing the flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
density of the hydrostatic force within the bulk of a fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
. Force density is represented by the symbol f, and given by the following equation, where P is the pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
:
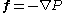 .
.The net force on a differental volume element
Volume element
In mathematics, a volume element provides a means for integrating a function with respect to volume in various coordinate systems such as spherical coordinates and cylindrical coordinates...
dV of the fluid is:
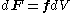
Thus, the force density at a point in a fluid, divided by the density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
, is the acceleration
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
of the fluid at that point.

