
Former Yugoslavia
Encyclopedia
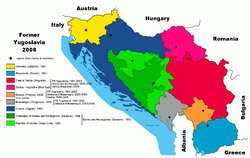
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was the Yugoslav state that existed from the abolition of the Yugoslav monarchy until it was dissolved in 1992 amid the Yugoslav Wars. It was a socialist state and a federation made up of six socialist republics: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia,...
.
The unity of Yugoslavia had been severed by the Yugoslav Wars
Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of wars, fought throughout the former Yugoslavia between 1991 and 1995. The wars were complex: characterized by bitter ethnic conflicts among the peoples of the former Yugoslavia, mostly between Serbs on the one side and Croats and Bosniaks on the other; but also...
of the 1990s. Remembrance of the time of the joint state and its perceived positive attributes is referred to as Yugo-nostalgia
Yugo-nostalgia
Yugo-nostalgia is a little-studied psychological and cultural phenomenon occurring among citizens of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia...
(Jugonostalgija). People who identify with the former Yugoslav state may self-identify as Yugoslavs
Yugoslavs
Yugoslavs is a national designation used by a minority of South Slavs across the countries of the former Yugoslavia and in the diaspora...
.
The territory of the former Yugoslavia is roughly coterminous with the geographical region of the Western Balkans; in the EU's definition of the term, the Western Balkans excludes Slovenia but includes Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
.
Successor states
These countries are, listed geographically from northwest to southeast:Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
(1991 to present) Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
(1991 to present) Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina , sometimes called Bosnia-Herzegovina or simply Bosnia, is a country in Southern Europe, on the Balkan Peninsula. Bordered by Croatia to the north, west and south, Serbia to the east, and Montenegro to the southeast, Bosnia and Herzegovina is almost landlocked, except for the...
(1992 to present) Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro was a country in southeastern Europe, formed from two former republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia : Serbia and Montenegro. Following the breakup of Yugoslavia, it was established in 1992 as a federation called the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia...
(1992 to 2006)
-
-
 MontenegroMontenegroMontenegro Montenegrin: Crna Gora Црна Гора , meaning "Black Mountain") is a country located in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast and Albania to the...
MontenegroMontenegroMontenegro Montenegrin: Crna Gora Црна Гора , meaning "Black Mountain") is a country located in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast and Albania to the...
(2006 to present) -
 SerbiaSerbiaSerbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
SerbiaSerbiaSerbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
(2006 to present) -
 KosovoKosovoKosovo is a region in southeastern Europe. Part of the Ottoman Empire for more than five centuries, later the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija within Serbia...
KosovoKosovoKosovo is a region in southeastern Europe. Part of the Ottoman Empire for more than five centuries, later the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija within Serbia...
(2008 to present) Republic of MacedoniaRepublic of MacedoniaMacedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
(1991 to present)
-
Relations with the European Union
Slovenia is the only country of the former Yugoslavia in the EU. Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro and Serbia are official candidates, while Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo have not submitted an application but are nevertheless recognized as "potential candidates" for a possible future enlargement of the European UnionFuture enlargement of the European Union
The future enlargement of the European Union is theoretically open to any European country which is democratic, operates a free market and is willing and able to implement all previous European Union law...
.
All states of the former Yugoslavia, with the exception of the disputed Autonomous Province of Kosovo, have subscribed to the Stabilisation and Association Process
Stabilisation and Association process
In talks with countries who have expressed a wish to join the European Union, the EU typically concludes Association Agreements in exchange for commitments to political, economic, trade, or human rights reform in that country...
with the EU.
EULEX (European Union Rule of Law Mission in Kosovo) is a deployment of EU police and civilian resources to Kosovo in an attempt to restore rule of law and combat the widespread organized crime.
Demographics
The last Yugoslavian census took place in 1991. At that point, the country's total population was at 22.4 millionThe CIA Factbook has estimates for the populations of Yugoslavia's successor states as of July 2011 which amount to a total population of 23.0 million.
Net population growth over the two decades between 1991 and 2011 was thus practically zero (below 0.1% p.a. on average).
Broken down by territory:
| Republic/province/country | 1991 | 2011 | growth rate p.a. (avg) |
growth rate (2011 est.) |
| Bosnia and Herzegowina | 4,377,000 | 4,622,000 | +0.18% | +0.01% |
| Croatia Croatia Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ... |
4,784,000 | 4,484,000 | -0.22% | -0.08% |
| Republic of Macedonia Republic of Macedonia Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991... |
2,034,000 | 2,077,000 | +0.07% | +0.25% |
| Montenegro Montenegro Montenegro Montenegrin: Crna Gora Црна Гора , meaning "Black Mountain") is a country located in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast and Albania to the... |
615,000 | 662,000 | +0.25% | -0.71% |
| Kosovo Kosovo Kosovo is a region in southeastern Europe. Part of the Ottoman Empire for more than five centuries, later the Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija within Serbia... |
1,956,000 | 1,826,000 | -0.23% | N/A |
| Serbia proper plus Vojvodina Vojvodina Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad... |
7,579,000 | 7,310,000 | -0.12% | -0.47% |
| Slovenia Slovenia Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of... |
1,913,000 | 2,000,000 | +0.15% | -0.16% |
| total | 22,400,000 | 23,000,000 | +0.09% | N/A |
The successor states of Yugoslavia continue to have a population growth rate that is close to zero or negative. This is mostly due to emigration.
Ethno-linguistically, the majority of the former Yugoslavia is South Slavic, speaking a dialect continuum clustered around the Serbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian language
Serbo-Croatian or Serbo-Croat, less commonly Bosnian/Croatian/Serbian , is a South Slavic language with multiple standards and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro...
, Slovene and Macedonian
Macedonian language
Macedonian is a South Slavic language spoken as a first language by approximately 2–3 million people principally in the region of Macedonia but also in the Macedonian diaspora...
. Other larger ethnic groups include Albanians
Albanians
Albanians are a nation and ethnic group native to Albania and neighbouring countries. They speak the Albanian language. More than half of all Albanians live in Albania and Kosovo...
(mostly in Kosovo), Hungarians (mostly in Vojvodina
Vojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
), Roma and other minorities.
Emigration
The small or negative population growth in the former Yugoslavia reflects a high level of emigrationEmigration
Emigration is the act of leaving one's country or region to settle in another. It is the same as immigration but from the perspective of the country of origin. Human movement before the establishment of political boundaries or within one state is termed migration. There are many reasons why people...
. Even before the breakup of the country, during the 1960s and 1970s, Yugoslavia was one of the most important "sending societies" of international migration. Emigration intensified during and after the Yugoslav Wars
Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of wars, fought throughout the former Yugoslavia between 1991 and 1995. The wars were complex: characterized by bitter ethnic conflicts among the peoples of the former Yugoslavia, mostly between Serbs on the one side and Croats and Bosniaks on the other; but also...
, during the 1990s to 2000s. An important receiving society was Switzerland
Immigration from the former Yugoslavia to Switzerland
There was substantial immigration to Switzerland from Former Yugoslavia during the 1990s and 2000s.While moderate numbers of Yugoslav citizens had residence in Switzerland during the 1980s,...
, target of an estimated total of 500,000 migrants, who now account for more than 6% of total Swiss population.
Similar numbers emigrated to Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and to North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
.
Of an estimated 2.5 million refugees created by the Yugoslav Wars
Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of wars, fought throughout the former Yugoslavia between 1991 and 1995. The wars were complex: characterized by bitter ethnic conflicts among the peoples of the former Yugoslavia, mostly between Serbs on the one side and Croats and Bosniaks on the other; but also...
, more than a million resettled in Canada.
Close to 120,000 refugees from former Yugoslavia were registered in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
during 1991 to 2002, and
67,000 migrants from the former Yugoslavia were registered in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
during 1991 to 2001.

