
Friedman test
Encyclopedia
The Friedman test is a non-parametric
statistical test developed by the U.S.
economist Milton Friedman
. Similar to the parametric
repeated measures ANOVA, it is used to detect differences in treatments across multiple test attempts. The procedure involves ranking
each row (or block) together, then considering the values of ranks by columns. Applicable to complete block designs, it is thus a special case of the Durbin test
.
Classic examples of use are:
The Friedman test is used for one-way repeated measures analysis of variance by ranks. In its use of ranks it is similar to the Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance
by ranks.
Friedman test is widely supported by many statistical software packages
.
were proposed by Schaich and Hamerle (1984) as well as Conover (1971, 1980) in order to decide which groups are significantly different from each other, based upon the mean rank differences of the groups. These procedures are detailed in Bortz, Lienert and Boehnke (2000, pp. 275) .
Not all statistical packages support Post-hoc analysis for Friedman's test. But user contributed code exists that provides these facilities (for example in SPSS http://timo.gnambs.at/en/scripts/friedmanposthoc, and in R http://www.r-statistics.com/2010/02/post-hoc-analysis-for-friedmans-test-r-code/)
Non-parametric statistics
In statistics, the term non-parametric statistics has at least two different meanings:The first meaning of non-parametric covers techniques that do not rely on data belonging to any particular distribution. These include, among others:...
statistical test developed by the U.S.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
economist Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman was an American economist, statistician, academic, and author who taught at the University of Chicago for more than three decades...
. Similar to the parametric
Parametric statistics
Parametric statistics is a branch of statistics that assumes that the data has come from a type of probability distribution and makes inferences about the parameters of the distribution. Most well-known elementary statistical methods are parametric....
repeated measures ANOVA, it is used to detect differences in treatments across multiple test attempts. The procedure involves ranking
Ranking
A ranking is a relationship between a set of items such that, for any two items, the first is either 'ranked higher than', 'ranked lower than' or 'ranked equal to' the second....
each row (or block) together, then considering the values of ranks by columns. Applicable to complete block designs, it is thus a special case of the Durbin test
Durbin test
In the analysis of designed experiments, the Friedman test is the most common non-parametric test for complete block designs. The Durbin test is a nonparametric test for balanced incomplete designs that reduces to the Friedman test in the case of a complete block design.-Background:In a randomized...
.
Classic examples of use are:
- n wine judges each rate k different wines. Are any wines ranked consistently higher or lower than the others?
- n wines are each rated by k different judges. Are the judges' ratings consistent with each other?
- n welders each use k welding torches, and the ensuing welds were rated on quality. Do any of the torches produce consistently better or worse welds?
The Friedman test is used for one-way repeated measures analysis of variance by ranks. In its use of ranks it is similar to the Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance
Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance
In statistics, the Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance by ranks is a non-parametric method for testing whether samples originate from the same distribution. The factual null hypothesis is that the populations from which the samples originate, have the same median...
by ranks.
Friedman test is widely supported by many statistical software packages
Comparison of statistical packages
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of statistical analysis packages.-General information:Basic information about each product...
.
Method
- Given data
 , that is, a tableau with
, that is, a tableau with  rows (the blocks),
rows (the blocks), 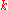 columns (the treatments) and a single observation at the intersection of each block and treatment, calculate the ranks within each block. If there are tied values, assign to each tied value the average of the ranks that would have been assigned without ties. Replace the data with a new tableau
columns (the treatments) and a single observation at the intersection of each block and treatment, calculate the ranks within each block. If there are tied values, assign to each tied value the average of the ranks that would have been assigned without ties. Replace the data with a new tableau 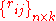 where the entry
where the entry 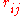 is the rank of
is the rank of 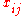 within block
within block  .
. - Find the values:
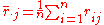
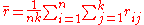
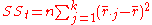 ,
,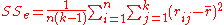
- The test statistic is given by
 . Note that the value of Q as computed above does not need to be adjusted for tied values in the data.
. Note that the value of Q as computed above does not need to be adjusted for tied values in the data. - Finally, when n or k is large (i.e. n > 15 or k > 4), the probability distributionProbability distributionIn probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of Q can be approximated by that of a chi-square distribution. In this case the p-valueP-valueIn statistical significance testing, the p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the one that was actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. One often "rejects the null hypothesis" when the p-value is less than the significance level α ,...
is given by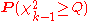 . If n or k is small, the approximation to chi-square becomes poor and the p-value should be obtained from tables of Q specially prepared for the Friedman test. If the p-value is significantStatistical significanceIn statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
. If n or k is small, the approximation to chi-square becomes poor and the p-value should be obtained from tables of Q specially prepared for the Friedman test. If the p-value is significantStatistical significanceIn statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
, appropriate post-hoc multiple comparisonsMultiple comparisonsIn statistics, the multiple comparisons or multiple testing problem occurs when one considers a set of statistical inferences simultaneously. Errors in inference, including confidence intervals that fail to include their corresponding population parameters or hypothesis tests that incorrectly...
tests would be performed.
Related tests
- When using this kind of design for a binary response, one instead uses the Cochran's Q test.
Post hoc analysis
Post-hoc testsPost-hoc analysis
Post-hoc analysis , in the context of design and analysis of experiments, refers to looking at the data—after the experiment has concluded—for patterns that were not specified a priori. It is sometimes called by critics data dredging to evoke the sense that the more one looks the more likely...
were proposed by Schaich and Hamerle (1984) as well as Conover (1971, 1980) in order to decide which groups are significantly different from each other, based upon the mean rank differences of the groups. These procedures are detailed in Bortz, Lienert and Boehnke (2000, pp. 275) .
Not all statistical packages support Post-hoc analysis for Friedman's test. But user contributed code exists that provides these facilities (for example in SPSS http://timo.gnambs.at/en/scripts/friedmanposthoc, and in R http://www.r-statistics.com/2010/02/post-hoc-analysis-for-friedmans-test-r-code/)
Secondary sources
- Kendall, M. G. Rank Correlation Methods. (1970, 4th ed.) London: Charles Griffin.
- Hollander, M., and Wolfe, D. A. Nonparametric Statistics. (1973). New York: J. Wiley.
- Siegel, Sidney, and Castellan, N. John Jr. Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. (1988, 2nd ed.) New York: McGraw-Hill.

