
Full aerodynamic force
Encyclopedia
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
force arises from two causes:
- the forceSurface forceSurface force denoted fs is the force that acts across an internal or external surface element in a material body. Surface force can be decomposed in to two perpendicular components: pressure and stress forces....
due to the pressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
on the surface of the body, and - the force due to viscosityViscosityViscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
, also known as skin friction.
When an airfoil
Airfoil
An airfoil or aerofoil is the shape of a wing or blade or sail as seen in cross-section....
(or a wing
Wing
A wing is an appendage with a surface that produces lift for flight or propulsion through the atmosphere, or through another gaseous or liquid fluid...
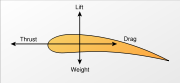
) is moving relative to the air it generates an aerodynamic in a direction at an angle with the direction of relative motion. This aerodynamic force is commonly resolved into two components:
- drag is the force component parallel to the direction of relative motion,
- liftLift (force)A fluid flowing past the surface of a body exerts a surface force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the surface force parallel to the flow direction...
is the force component perpendicular to the direction of relative motion.
The force created by a propeller
Propeller (aircraft)
Aircraft propellers or airscrews convert rotary motion from piston engines or turboprops to provide propulsive force. They may be fixed or variable pitch. Early aircraft propellers were carved by hand from solid or laminated wood with later propellers being constructed from metal...
or a jet engine
Jet engine
A jet engine is a reaction engine that discharges a fast moving jet to generate thrust by jet propulsion and in accordance with Newton's laws of motion. This broad definition of jet engines includes turbojets, turbofans, rockets, ramjets, pulse jets...
is called thrust
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's second and third laws. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on that system....
and it is also an aerodynamic force (since it also acts on the surrounding air). The aerodynamic force on a powered airplane is commonly resolved into three components: thrust, lift and drag.
The remaining other force acting on a glider or powered airplane during flight is its weight
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force on the object due to gravity. Its magnitude , often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus:...
. Note that weight is a body force
Body force
A body force is a force that acts throughout the volume of a body, in contrast to contact forces.Gravity and electromagnetic forces are examples of body forces. Centrifugal and Coriolis forces can also be viewed as body forces.This can be put into contrast to the classical definition of surface...
, and it is not an aerodynamic force.

