
Galaxy color-magnitude diagram
Encyclopedia
Absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
, luminosity
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
, and mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of galaxies. A preliminary description of the three areas of this diagram was made in 2003 by Eric F. Bell et al. from the COMBO-17 survey that clarified the bimodal distribution of red and blue galaxies as seen in analysis of Sloan Digital Sky Survey
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-filter imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project was named after the Alfred P...
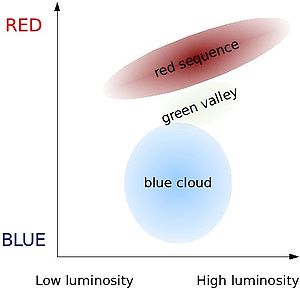
data and even in de Vaucouleurs' 1961 analyses of galaxy morphology Noticed in this diagram are three main features: the red sequence, the green valley, and the blue cloud. The red sequence includes most red galaxies which are generally elliptical galaxies
Elliptical galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars...
. The blue cloud includes most blue galaxies which are generally spirals
Spiral galaxy
A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as...
. In between the two distributions is an underpopulated space known as the green valley which includes a number of red spirals. Unlike the comparable Hertzsprung–Russell diagram for star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, galaxy properties are not necessarily completely determined by their location on the color-magnitude diagram. The diagram also shows considerable evolution through time. The red sequence earlier in evolution
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
was more constant in color across magnitudes and the blue cloud was not as uniformly distributed but showed sequence progression.

