
Elliptical galaxy
Encyclopedia

Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s. They can be the result of two galaxies colliding.
Elliptical galaxies are one of the three main classes of galaxy originally described by American astronomer Edwin Hubble
Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble was an American astronomer who profoundly changed the understanding of the universe by confirming the existence of galaxies other than the Milky Way - our own galaxy...
in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae, along with spiral
Spiral galaxy
A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as...
and lenticular galaxies.
Elliptical galaxies are (together with lenticular galaxies) also called "early-type" galaxies (ETG), due to their location in the Hubble sequence.
Most elliptical galaxies are composed of older, low-mass stars
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star undergoes a sequence of radical changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from only a few million years to trillions of years .Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single...
, with a sparse interstellar medium
Interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, dust, and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space...
and minimal star formation
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
activity. They are surrounded by large numbers of globular cluster
Globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is...
s. Elliptical galaxies are believed to make up approximately 10–15% of galaxies in the local Universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
but are not the dominant type of galaxy in the universe overall. They are preferentially found close to the centers of galaxy cluster
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a compact cluster of galaxies. Basic difference between a galaxy group and a galaxy cluster is that there are many more galaxies in a cluster than in a group. Also, galaxies in a cluster are more compact and have higher velocity dispersion. One of the key features of cluster is...
s and are less common in the early Universe.
General characteristics
Elliptical galaxies are characterized by several properties that make them distinct from other classes of galaxy. The motion of stars in elliptical galaxies is predominantly radial, unlike the disks of spiral galaxiesSpiral galaxy
A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as...
, which are dominated by rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
. Furthermore, there is very little interstellar matter (neither gas nor dust), which results in low rates of star formation
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
, few open star clusters
Open cluster
An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist...
, and few young stars; rather elliptical galaxies are dominated by old stellar populations, giving them red colours. Large elliptical galaxies typically have an extensive system of globular cluster
Globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is...
s.
The dynamical properties of elliptical galaxies and the bulges
Bulge (astronomy)
In astronomy, a bulge is a tightly packed group of stars within a larger formation. The term almost exclusively refers to the central group of stars found in most spiral galaxies...
of disk galaxies
Disc galaxy
Disc galaxies are galaxies which have discs, a flattened circular volume of stars. These galaxies may, or may not include a central non-disc-like region .Disc galaxy types include* spiral galaxies** barless spiral galaxies...
are similar,
suggesting that they are formed by the same physical processes, although this remains controversial. The luminosity profiles of both elliptical galaxies and bulges are well fit by Sersic's law
Sersic profile
The Sérsic profile is a mathematical function that describes how the intensity I of a galaxy varies with distance R from its center. It is a generalization of de Vaucouleurs' law. J. L...
.
Elliptical galaxies are preferentially found in galaxy clusters and in compact groups of galaxies.
Star formation
This traditional portrait of elliptical galaxies paints them as galaxies where star formationStar formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
has finished after the initial burst, leaving them to shine with only their aging stars. Very little star formation
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
is thought to occur, because of the lack of gas, dust, and space. In general, they appear yellow-red, which is in contrast to the distinct blue tinge of a typical spiral galaxy
Spiral galaxy
A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as...
, a colour emanating largely from the young, hot stars in its spiral arms.
Sizes and shapes
Elliptical galaxies vary greatly in both size and mass, from as little as a tenth of a kiloparsec to over 100 kiloparsecs, and from 107 to nearly 1013 solar masses. This range is much broader for this galaxy type than for any other. The smallest, the Dwarf elliptical galaxiesDwarf elliptical galaxy
Dwarf elliptical galaxies, or dEs, are elliptical galaxies that are much smaller than others. They are classified as dE, and are quite common in galaxy groups and clusters, and are usually companions to other galaxies.- Examples :...
, may be no larger than a typical globular cluster
Globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is...
, but contain a considerable amount of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
not present in clusters. Most of these small galaxies may not be related to other ellipticals.
The Hubble classification of elliptical galaxies contains an integer that describes how elongated the galaxy image is.
The classification is determined by the ratio of the major (a) to the minor (b) axes of the galaxy's isophotes:
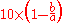
Thus for a spherical galaxy with a equal to b, the number
is 0, and the Hubble type is E0. The limit is about E7, which is believed to be due to a bending instability
Firehose instability
The firehose instability is a dynamical instability of thin or elongated galaxies. The instability causes the galaxy to buckle or bend in a direction perpendicular to its long axis. After the instability has run its course, the galaxy is less elongated than before...
that causes flatter galaxies to puff up. The most common shape is close to E3. Hubble recognized that his shape classification depends both on the intrinsic shape of the galaxy, as well as the angle with which the galaxy is observed. Hence, some galaxies with Hubble type E0 are actually elongated.
There are two physical types of ellipticals; the "boxy" giant ellipticals, whose shapes result from random motion which is greater in some directions than in others (anisotropic random motion), and the "disky" normal and low luminosity ellipticals, which have nearly isotropic random velocities but are flattened due to rotation.
Dwarf elliptical galaxies
Dwarf elliptical galaxy
Dwarf elliptical galaxies, or dEs, are elliptical galaxies that are much smaller than others. They are classified as dE, and are quite common in galaxy groups and clusters, and are usually companions to other galaxies.- Examples :...
have properties that are intermediate between those of regular elliptical galaxies and globular clusters. Dwarf spheroidal galaxies appear to be a distinct class: their properties are more similar to those of irregulars and late spiral-type galaxies.
At the large end of the elliptical spectrum, there is further division, beyond Hubble classification. Beyond gE giant ellipticals, lies D-galaxies and cD-galaxies
Type-cD galaxy
The type-cD galaxy is a galaxy morphology classification, a subtype of type-D giant elliptical galaxy, and has a large halo of stars. They can be found near the centres of some rich galaxy clusters...
. These are similar to their smaller brethren, but more diffuse, with larger haloes. Some even appear more akin to lenticular galaxies.
Evolution
Current thinking is that an elliptical galaxy may be the result of a long process where two galaxies of comparable mass, of any type, collide and mergeGalaxy merger
Galaxy mergers can occur when two galaxies collide. They are the most violent type of galaxy interaction. Although galaxy mergers do not involve stars or star systems actually colliding, due to the vast distances between stars in most circumstances, the gravitational interactions between galaxies...
.
Such major galactic mergers are thought to have been common at early times, but may carry on more infrequently today. Minor galactic mergers involve two galaxies of very different masses, and are not limited to giant ellipticals. For example, our own Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
galaxy is known to be "ingesting" a couple of small galaxies right now. The Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
galaxy, is also, depending upon an unknown tangential component, on a collision course in 4-5 billion years with the Andromeda Galaxy
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Andromeda. It is also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, and is often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. Andromeda is the nearest spiral galaxy to the...
. It has been theorized that an elliptical galaxy will result from a merger of the two spirals.
Every bright elliptical galaxy is believed to contain a supermassive black hole
Supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole is the largest type of black hole in a galaxy, in the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses. Most, and possibly all galaxies, including the Milky Way, are believed to contain supermassive black holes at their centers.Supermassive black holes have...
at its center. The mass of the black hole is tightly correlated with the mass of the galaxy, via the M-sigma relation
M-sigma relation
The M-sigma relation is an empirical correlation between the stellar velocity dispersion \sigma of a galaxy bulge and the mass M of the supermassive black hole atthe galaxy's center.The relation can be expressed mathematically as...
. It is believed that black holes may play an important role in limiting the growth of elliptical galaxies in the early universe by inhibiting star formation
Star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense parts of molecular clouds collapse into a ball of plasma to form a star. As a branch of astronomy star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium and giant molecular clouds as precursors to the star formation process and the study of young...
.
Examples
- M32
- M49
- M59
- M60 (NGC 4649)
- M87 (NGC 4486)
- M89
- M105 (NGC 3379)
- Maffei 1Maffei 1Maffei 1 is a giant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is the closest giant elliptical galaxy to the Milky Way. Once believed to be a member of the Local Group, it is now known to belong to the IC 342/Maffei Group...
, the closest giant elliptical galaxy. - Centaurus A (NGC 5128)Centaurus ACentaurus A is a prominent galaxy in the constellation of Centaurus. There is considerable debate in the literature regarding the galaxy's fundamental properties such as its Hubble type and distance...
, a radio galaxyRadio galaxyRadio galaxies and their relatives, radio-loud quasars and blazars, are types of active galaxy that are very luminous at radio wavelengths, with luminosities up to 1039 W between 10 MHz and 100 GHz. The radio emission is due to the synchrotron process...
, elliptical/lenticular disputed.
See also
- Firehose instabilityFirehose instabilityThe firehose instability is a dynamical instability of thin or elongated galaxies. The instability causes the galaxy to buckle or bend in a direction perpendicular to its long axis. After the instability has run its course, the galaxy is less elongated than before...
- Galaxy color-magnitude diagramGalaxy color-magnitude diagramThe Galaxy color-magnitude diagram shows the relationship between absolute magnitude, luminosity, and mass of galaxies. A preliminary description of the three areas of this diagram was made in 2003 by Eric F. Bell et al...
- Galaxy morphological classification
- Hubble sequenceHubble sequenceThe Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies invented by Edwin Hubble in 1926. It is often known colloquially as the Hubble tuning-fork diagram because of the shape in which it is traditionally represented....
- Lenticular galaxyLenticular galaxyA lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy which is intermediate between an elliptical galaxy and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. Lenticular galaxies are disk galaxies which have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing...
- M-sigma relationM-sigma relationThe M-sigma relation is an empirical correlation between the stellar velocity dispersion \sigma of a galaxy bulge and the mass M of the supermassive black hole atthe galaxy's center.The relation can be expressed mathematically as...
- Osipkov-Merritt modelOsipkov-Merritt modelOsipkov–Merritt models are mathematical representations of spherical stellar systems...
- Sersic profileSersic profileThe Sérsic profile is a mathematical function that describes how the intensity I of a galaxy varies with distance R from its center. It is a generalization of de Vaucouleurs' law. J. L...
External links
- Elliptical Galaxies, SEDS Messier pages
- Elliptical Galaxies

