
Gamma Ray Burst Coordinates Network
Encyclopedia
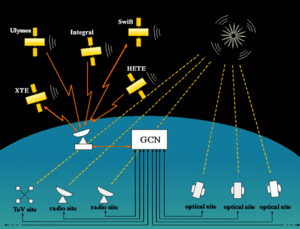
GCN has its origins in the BATSE COordinates DIstribution NEtwork (BACODINE). The Burst And Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) was a scientific instrument on the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (CGRO), and BACODINE monitored the BATSE real-time telemetry from CGRO. The first function of BACODINE was calculating the right ascension
Right ascension
Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:...
(RA) and declination
Declination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
(dec) locations for GRBs that it detected, and distributing those locations to sites around the world in real-time. Since the de-orbiting of the CGRO, this function of BACODINE is no longer operational. The second function of BACODINE was collecting right ascension and declination locations of GRBs detected by spacecraft other than CGRO, and then distributing that information. With this functionality, the original BACODINE name was changed to the more general name GCN.
GCN data flow
The GCN data flow starts when gamma-rays from a GRB hit a detector on a spacecraft. The spacecraft sends the GRB location information down to a ground station, which in turn relays it to the GCN at the NASANASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
Goddard Space Flight Center
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center is a major NASA space research laboratory established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center. GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors, and is located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, USA. GSFC,...
. At GFSC the location information is processed by GCN with custom hardware and software, and then Notices are sent to users via socket connection
Inter-process communication
In computing, Inter-process communication is a set of methods for the exchange of data among multiple threads in one or more processes. Processes may be running on one or more computers connected by a network. IPC methods are divided into methods for message passing, synchronization, shared...
E-mail
Electronic mail, commonly known as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Some early email systems required that the author and the recipient both be online at the...
, and pager
Pager
A pager is a simple personal telecommunications device for short messages. A one-way numeric pager can only receive a message consisting of a few digits, typically a phone number that the user is then requested to call...
s. Those users may then schedule follow-up observations of the GRB, and send refined information about the GRB back to the GCN.
In the case of Swift
Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission
The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission consists of a robotic spacecraft called Swift, which was launched into orbit on 20 November 2004, 17:16:00 UTC on a Delta II 7320-10C expendable launch vehicle. Swift is managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and was developed by an international...
, the GRB location information follows the same path, except it is transmitted from Swift up to a TDRS
TDRS
A Tracking and Data Relay Satellite is a type of communications satellite that forms part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System used by NASA and other United States government agencies for communications to and from independent "User Platforms" such as satellites, balloons, aircraft,...
satellite, and then down to the White Sands Complex (WSC). From WSC, the location information is sent to GSFC via a domestic communications satellite (DOMSAT).
GCN Notices
The following spacecraft, and instruments where noted, are sources of real-time GCN information:- High Energy Transient ExplorerHigh Energy Transient ExplorerThe High Energy Transient Explorer was an American astronomical satellite with international participation . The prime objective of HETE was to carry out the first multiwavelength study of gamma-ray bursts with UV, X-ray, and gamma-ray instruments mounted on a single, compact spacecraft...
(WMM and SXC) - INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory (INTEGRALINTEGRALThe European Space Agency's INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory is an operational Earth satellite, launched in 2002 for detecting some of the most energetic radiation that comes from space. It is the most sensitive gamma ray observatory ever launched.INTEGRAL is an ESA mission in...
) - InterPlanetary NetworkInterPlanetary NetworkThe InterPlanetary Network is a group of spacecraft equipped with gamma ray burst detectors. By timing the arrival of a burst at several spacecraft, its precise location can be found. The farther apart the detectors, or the greater the timing precision of each detector, the more precise the GRB...
(IPN) Position Notices from WINDWINDThe Global Geospace Science WIND satellite is a NASA science spacecraft launched at 04:31:00 EST on November 1, 1994 from launch pad 17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Merritt Island, Florida aboard a McDonnell Douglas Delta II 7925-10 rocket. WIND was designed and manufactured by Martin...
(Konus) and UlyssesUlysses probeUlysses is a decommissioned robotic space probe that was designed to study the Sun as a joint venture of NASA and the European Space Agency . The spacecraft was originally named Odysseus, because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to near Solar distance...
. - Rossi X-ray Timing ExplorerRossi X-ray Timing ExplorerThe Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer is a satellite that observes the time structure of astronomical X-ray sources. The RXTE has three instruments—the Proportional Counter Array, the High-Energy X-ray Timing Experiment , and one instrument called the All Sky Monitor...
(PCA and ASM) - SwiftSwift Gamma-Ray Burst MissionThe Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission consists of a robotic spacecraft called Swift, which was launched into orbit on 20 November 2004, 17:16:00 UTC on a Delta II 7320-10C expendable launch vehicle. Swift is managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and was developed by an international...
provides data products not previously available from prior missions, including spectra, images, and lightcurves.
Past spacecraft and instruments that participated in GCN include Array of Low Energy X-ray Imaging Sensors
Array of Low Energy X-ray Imaging Sensors
The Array of Low Energy X-ray Imaging Sensors X-ray telescopes feature curved mirrors whose multilayer coatings reflect and focus low-energy X-rays or extreme ultraviolet light the way optical telescopes focus visible light...
(ALEXIS), BeppoSAX
BeppoSAX
BeppoSAX was an Italian–Dutch satellite for X-ray astronomy which played a crucial role in resolving the origin of gamma-ray bursts , the most energetic events known in the universe...
, the Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL) on CGRO, and the X-Ray/Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (XGRS) on NEAR Shoemaker
NEAR Shoemaker
The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker , renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene M. Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a...
.
GCN Circulars
The GCN system has the capability to receive and distribute timely information on GRBs called GCN Circulars. Users e-mail their reports to a central location and then those reports will be automatically sent to an e-mail distribution list. This list of Circular recipients is completely separate from the list of Notice recipients. The GCN Observation Report Circulars allow the GRB follow-up community to make optimum use of limited resources, such as labor and telescope time, by communicating what has already been done or will soon be done.Future plans for GCN
To maximize the utility of the GCN system, GCN will make whatever modifications are necessary to incorporate and distribute GRB location information from new spacecraft and instruments as they become active. GCN will also expand its operations to include information about any astrophysical transients, including non-GRBs such as the extreme-ultravioletUV astronomy
Ultraviolet astronomy is generally used to refer to observations of electromagnetic radiation at ultraviolet wavelengths between approximately 10 and 320 nanometres; shorter wavelengths—higher energy photons—are studied by X-ray astronomy and gamma ray astronomy...
transients detected by the ALEXIS spacecraft. Future spacecraft that will be distributing GRB locations via GCN include AGILE
AGILE (spacecraft)
AGILE is an X-ray and Gamma ray astronomical satellite of the Italian Space Agency .ASI has made contact with AGILE: signals from it have been acquired by the ground station at the Broglio Space Centre near Malindi, Kenya and it has been placed in a sun-pointing mode....
and Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope , formerly referred to as the “Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope ”, is a space observatory being used to perform gamma-ray astronomy observations from low Earth orbit...
.

