Genetic recombination
Encyclopedia
Genetic recombination is a process by which a molecule of nucleic acid
(usually DNA
, but can also be RNA
) is broken and then joined to a different one. Recombination can occur between similar
molecules of DNA, as in homologous recombination
, or dissimilar molecules, as in non-homologous end joining
. Recombination is a common method of DNA repair
in both bacteria
and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, recombination also occurs in meiosis
, where it facilitates chromosomal crossover
. The crossover process leads to offspring's having different combinations of genes from those of their parents, and can occasionally produce new chimeric
allele
s. In organisms with an adaptive immune system
, a type of genetic recombination called V(D)J recombination
helps immune cells rapidly diversify to recognize and adapt to new pathogen
s. The shuffling of genes brought about by genetic recombination is thought to have many advantages, as it is a major engine of genetic variation
and also allows sexually reproducing organisms to avoid Muller's ratchet
, in which the genome
s of an asexual
population
accumulate deleterious mutations
in an irreversible manner.
In genetic engineering
, recombination can also refer to artificial and deliberate recombination of disparate pieces of DNA, often from different organisms, creating what is called recombinant DNA
. A prime example of such a use of genetic recombination is gene targeting
, which can be used to add, delete or otherwise change an organism's genes. This technique is important to biomedical research
ers as it allows them to study the effects of specific genes. Techniques based on genetic recombination are also applied in protein engineering
to develop new proteins of biological interest.
Genetic recombination is catalyzed
by many different enzyme
s, called recombinases. RecA
, the chief recombinase found in Escherichia coli
, is responsible for the repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). In yeast and other eukaryotic organisms there are two recombinases required for repairing DSBs. The RAD51
protein is required for mitotic
and meiotic
recombination, whereas the DMC1
protein is specific to meiotic recombination.
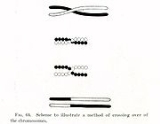
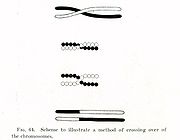 Chromosomal crossover refers to recombination between the paired chromosome
Chromosomal crossover refers to recombination between the paired chromosome
s inherited from each of one's parents, generally occurring during meiosis
. During prophase I the four available chromatid
s are in tight formation with one another. While in this formation, homologous
sites on two chromatids can mesh with one another, and may exchange genetic information.
Because recombination can occur with small probability at any location along chromosome, the frequency of recombination between two locations depends on their distance. Therefore, for genes sufficiently distant on the same chromosome the amount of crossover is high enough to destroy the correlation between alleles.
Tracking the movement of genes during crossovers has proven quite useful to geneticists. Because two genes that are close together are less likely to become separated than genes that are farther apart, geneticists can deduce roughly how far apart two genes are on a chromosome if they know the frequency of the crossovers. Geneticists can also use this method to infer the presence of certain genes. Genes that typically stay together during recombination are said to be linked. One gene in a linked pair can sometimes be used as a marker to deduce the presence of another gene. This is typically used in order to detect the presence of a disease-causing gene.
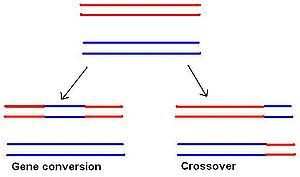 In gene conversion, a section of genetic material is copied from one chromosome to another, without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency during meiotic
In gene conversion, a section of genetic material is copied from one chromosome to another, without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency during meiotic
division and at low frequency in somatic cells. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. It is one of the ways a gene may be mutated. Gene conversion may lead to non-Mendelian inheritance
and has often been recorded in fungal crosses.
. This is referred to as nonhomologous recombination or nonhomologous end joining
.
perform genetic recombination, called immunoglobulin class switching
. It is a biological mechanism that changes an antibody
from one class to another, for example, from an isotype called IgM
to an isotype called IgG.
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biological molecules essential for life, and include DNA and RNA . Together with proteins, nucleic acids make up the most important macromolecules; each is found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information...
(usually DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, but can also be RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
) is broken and then joined to a different one. Recombination can occur between similar
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
molecules of DNA, as in homologous recombination
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks...
, or dissimilar molecules, as in non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. NHEJ is referred to as "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homologous recombination, which requires a homologous sequence to guide...
. Recombination is a common method of DNA repair
DNA repair
DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1...
in both bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
and eukaryotes. In eukaryotes, recombination also occurs in meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
, where it facilitates chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs during prophase I of meiosis in a process called synapsis. Synapsis begins before the synaptonemal complex develops, and is not completed...
. The crossover process leads to offspring's having different combinations of genes from those of their parents, and can occasionally produce new chimeric
Chimera (genetics)
A chimera or chimaera is a single organism that is composed of two or more different populations of genetically distinct cells that originated from different zygotes involved in sexual reproduction. If the different cells have emerged from the same zygote, the organism is called a mosaic...
allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
s. In organisms with an adaptive immune system
Adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogenic growth. Thought to have arisen in the first jawed vertebrates, the adaptive or "specific" immune system is activated by the “non-specific” and evolutionarily older innate...
, a type of genetic recombination called V(D)J recombination
V(D)J recombination
VJ recombination, also known as somatic recombination, is a mechanism of genetic recombination in the early stages of immunoglobulin and T cell receptors production of the immune system...
helps immune cells rapidly diversify to recognize and adapt to new pathogen
Pathogen
A pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
s. The shuffling of genes brought about by genetic recombination is thought to have many advantages, as it is a major engine of genetic variation
Genetic variation
Genetic variation, variation in alleles of genes, occurs both within and among populations. Genetic variation is important because it provides the “raw material” for natural selection. Genetic variation is brought about by mutation, a change in a chemical structure of a gene. Polyploidy is an...
and also allows sexually reproducing organisms to avoid Muller's ratchet
Muller's ratchet
In evolutionary genetics, Muller's ratchet is the process by which the genomes of an asexual population accumulate deleterious mutations in an irreversible manner....
, in which the genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
s of an asexual
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
accumulate deleterious mutations
Genetic deletion
In genetics, a deletion is a mutation in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is missing. Deletion is the loss of genetic material. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome...
in an irreversible manner.
In genetic engineering
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA or synthetic genes into the organism of interest...
, recombination can also refer to artificial and deliberate recombination of disparate pieces of DNA, often from different organisms, creating what is called recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA molecules are DNA sequences that result from the use of laboratory methods to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms...
. A prime example of such a use of genetic recombination is gene targeting
Gene targeting
Gene targeting is a genetic technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene. The method can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, and introduce point mutations. Gene targeting can be permanent or conditional...
, which can be used to add, delete or otherwise change an organism's genes. This technique is important to biomedical research
Biomedical research
Biomedical research , in general simply known as medical research, is the basic research, applied research, or translational research conducted to aid and support the body of knowledge in the field of medicine...
ers as it allows them to study the effects of specific genes. Techniques based on genetic recombination are also applied in protein engineering
Protein engineering
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles....
to develop new proteins of biological interest.
Genetic recombination is catalyzed
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
by many different enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s, called recombinases. RecA
RecA
RecA is a 38 kilodalton Escherichia coli protein essential for the repair and maintenance of DNA. RecA has a structural and functional homolog in every species in which it has been seriously sought and serves as an archetype for this class of homologous DNA repair proteins...
, the chief recombinase found in Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms . Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes can cause serious food poisoning in humans, and are occasionally responsible for product recalls...
, is responsible for the repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). In yeast and other eukaryotic organisms there are two recombinases required for repairing DSBs. The RAD51
RAD51
RAD51 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assist in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA and yeast Rad51...
protein is required for mitotic
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
and meiotic
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
recombination, whereas the DMC1
DMC1 (gene)
Meiotic recombination protein DMC1/LIM15 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DMC1 gene.-Interactions:DMC1 has been shown to interact with RAD51.-Further reading:...
protein is specific to meiotic recombination.
Chromosomal crossover

Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
s inherited from each of one's parents, generally occurring during meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
. During prophase I the four available chromatid
Chromatid
A chromatid is one of the two identical copies of DNA making up a duplicated chromosome, which are joined at their centromeres, for the process of cell division . They are called sister chromatids so long as they are joined by the centromeres...
s are in tight formation with one another. While in this formation, homologous
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
sites on two chromatids can mesh with one another, and may exchange genetic information.
Because recombination can occur with small probability at any location along chromosome, the frequency of recombination between two locations depends on their distance. Therefore, for genes sufficiently distant on the same chromosome the amount of crossover is high enough to destroy the correlation between alleles.
Tracking the movement of genes during crossovers has proven quite useful to geneticists. Because two genes that are close together are less likely to become separated than genes that are farther apart, geneticists can deduce roughly how far apart two genes are on a chromosome if they know the frequency of the crossovers. Geneticists can also use this method to infer the presence of certain genes. Genes that typically stay together during recombination are said to be linked. One gene in a linked pair can sometimes be used as a marker to deduce the presence of another gene. This is typically used in order to detect the presence of a disease-causing gene.
Gene conversion

Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
division and at low frequency in somatic cells. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. It is one of the ways a gene may be mutated. Gene conversion may lead to non-Mendelian inheritance
Non-mendelian inheritance
Non-Mendelian inheritance is a general term that refers to any pattern of inheritance in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel’s laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inheritance, each parent...
and has often been recorded in fungal crosses.
Nonhomologous recombination
Recombination can occur between DNA sequences that contain no sequence homologyHomology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
. This is referred to as nonhomologous recombination or nonhomologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. NHEJ is referred to as "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homologous recombination, which requires a homologous sequence to guide...
.
In B cells
B cells of the immune systemImmune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
perform genetic recombination, called immunoglobulin class switching
Immunoglobulin class switching
Immunoglobulin class switching is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of antibody from one class to another, for example, from an isotype called IgM to an isotype called IgG...
. It is a biological mechanism that changes an antibody
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
from one class to another, for example, from an isotype called IgM
IGM
IGM as an acronym or abbreviation can refer to:* Immunoglobulin M , the primary antibody against A and B antigens on red blood cells* International Grandmaster, a chess ranking* intergalactic medium* Intragroup medium - see: Intracluster medium...
to an isotype called IgG.
See also
- Recombination frequency
- Recombination hotspotRecombination hotspotRecombination hotspots are small regions in the genome of sexually reproducing organisms that exhibit highly elevated rates of meiotic recombination. The peak recombination rate within hotspots can be hundreds or thousands of times that of the surrounding region. The PRDM9 protein is suspected to...
- Four-gamete test
- independent assortment

