
Geography of Vanuatu
Encyclopedia
Vanuatu
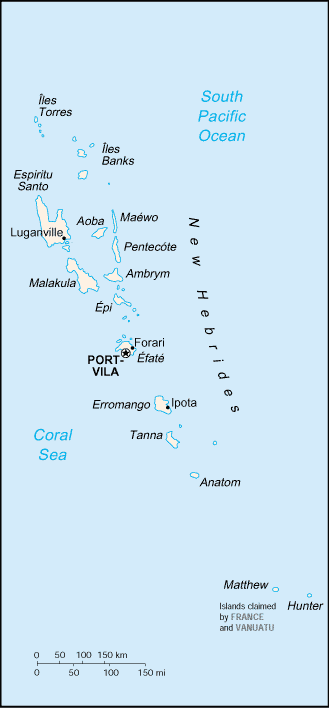
Vanuatu , officially the Republic of Vanuatu , is an island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is some east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, west of Fiji, and southeast of the Solomon Islands, near New Guinea.Vanuatu was...
(formerly called New Hebrides
New Hebrides
New Hebrides was the colonial name for an island group in the South Pacific that now forms the nation of Vanuatu. The New Hebrides were colonized by both the British and French in the 18th century shortly after Captain James Cook visited the islands...
) is a nation and group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. It is composed of over 80 islands with 2,528 km of coastline and a total surface area of 14,760 km², making it slightly larger than the state of Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
.
Vanuatu's geographic coordinates are 16°00′S 167°00′E. It is part of Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
. Its immediate neighbours include the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
and New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
, and Australasia
Australasia
Australasia is a region of Oceania comprising Australia, New Zealand, the island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term was coined by Charles de Brosses in Histoire des navigations aux terres australes...
is the closest continent.
Vanuatu is a mountainous archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
of volcanic origin with narrow coastal plain
Coastal plain
A coastal plain is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a seacoast and separated from the interior by other features. One of the world's longest coastal plains is located in eastern South America. The southwestern coastal plain of North America is notable for its species diversity...
s. The highest of all the mountains is Mount Tabwemasana
Mount Tabwemasana
Located on the isolated west coast of Espiritu Santo, Mount Tabwemasana is not only the highest peak in Vanuatu, but also one of the highest mountains in the Pacific. At , Tabwemasana towers above the surrounding mountains and provides fantastic views toward the Coral Sea in East...
at 1,877 meters. Its tropical climate is moderated by southeast trade winds, and its natural resources include, hardwood
Hardwood
Hardwood is wood from angiosperm trees . It may also be used for those trees themselves: these are usually broad-leaved; in temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen.Hardwood contrasts with softwood...
forests, and fish. As of 1993, 75% of its land area is covered by forests and woodland, 10% is devoted to crops, and a further 2% each to permanent pastures and other arable land. Natural hazards include tropical cyclone
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
s or typhoons from January to April and volcanic activity which sometimes causes minor earthquakes.
A majority of the population does not have access to a potable
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
and reliable supply of water. Deforestation
Deforestation
Deforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
is another major concern on the islands. Vanuatu is party to a number of international agreements, including agreements on Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea , also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty, is the international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea , which took place from 1973 through 1982...
, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, and Ship Pollution.
Closely tied to the Law of the Sea, Vanuatu lays maritime claim to 24 nautical miles (nm) of contiguous zone, 12 nm of territorial sea, and 200 nm of continental shelf and exclusive economic zone.

