
George Pocock (inventor)
Encyclopedia
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
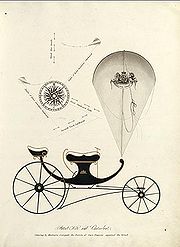
schoolteacher and inventor of the "Charvolant", a kite
Kite
A kite is a tethered aircraft. The necessary lift that makes the kite wing fly is generated when air flows over and under the kite's wing, producing low pressure above the wing and high pressure below it. This deflection also generates horizontal drag along the direction of the wind...
-drawn carriage
Carriage
A carriage is a wheeled vehicle for people, usually horse-drawn; litters and sedan chairs are excluded, since they are wheelless vehicles. The carriage is especially designed for private passenger use and for comfort or elegance, though some are also used to transport goods. It may be light,...
.
Pocock was interested in kites from an early age, and experimented with pulling loads using kite power, gradually progressing from small stones to planks and large loads. He taught at a school in Prospect Place, Bristol
Bristol
Bristol is a city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, with an estimated population of 433,100 for the unitary authority in 2009, and a surrounding Larger Urban Zone with an estimated 1,070,000 residents in 2007...
and continued his experiments with his pupils. By 1820 he had determined that in combination they could support considerable weight and began experimenting with man-lifting kite
Man-lifting kite
A man-lifting kite is a kite designed to lift a person from the ground. Historically, man-lifting kites have been used chiefly for reconnaissance and entertainment. Interest in their development declined with the advent of powered flight at the beginning of the 20th century.-Early history:The first...
s. In 1825, he used a 30-foot (9 m) kite with a chair rig to lift his daughter, Martha (the future mother of cricket
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of 11 players on an oval-shaped field, at the centre of which is a rectangular 22-yard long pitch. One team bats, trying to score as many runs as possible while the other team bowls and fields, trying to dismiss the batsmen and thus limit the...
er W.G. Grace) over 270 feet (82 m) into the air. Later the same year and continuing to use his family as subjects, he lifted his son to the top of a cliff outside Bristol; his son briefly dismounted from the chair at the top of the 200-foot (60 m) cliff and then concluded the test by releasing a clip on the kite line which allowed him to slide down the line in the chair and return to earth.
Having concluded that kites were capable of lifting humans, he turned again to experimenting with them as a way of pulling loads, this time as a method of pulling vehicles. Using kites in various arrangements he determined that a small number of large kites were capable of pulling a carriage with passengers.

Mail coach
In Great Britain, the mail coach or post coach was a horse-drawn carriage that carried mail deliveries, from 1784. In Ireland, the first mail coach began service from Dublin in 1789. The coach was drawn by four horses and had seating for four passengers inside. Further passengers were later allowed...
, which at the time was the fastest passenger transport. On another trip, a Charvolant passed the coach of the Duke of Gloucester
Prince William Frederick, Duke of Gloucester and Edinburgh
Prince William, Duke of Gloucester and Edinburgh was a member of the British Royal Family, a great-grandson of George II and nephew of George III.-Early life:...
, a breach of etiquette that was considered so rude that the occupants had to stop to let the Duke pass them.
Four control lines to the kite provided a method of steering; these lines were paid out or drawn in from large spools mounted on the front of the carriage. Large wheels allowed the carriage to utilise the power from the kites effectively. In addition to controlling the kites, the driver had to steer the carriage by means of a T-bar which controlled the direction of the front wheels, and was responsible for the brake, an iron bar mounted on the carriage which dug into the road when the lever was pulled. Controlling the Charvolant was difficult, and this may have been why it never became successful commercially, even though it escaped the toll
Toll road
A toll road is a privately or publicly built road for which a driver pays a toll for use. Structures for which tolls are charged include toll bridges and toll tunnels. Non-toll roads are financed using other sources of revenue, most typically fuel tax or general tax funds...
s levied on the roads for horse-drawn carriages: tolls were applied according to the number of horses and since the Charvolant had none it incurred no charge.
Pocock advocated other uses for kites in his book, including auxiliary sail power for ships (similar to modern traction kites), a means of dropping anchor and effecting rescues from shipwreck
Shipwreck
A shipwreck is what remains of a ship that has wrecked, either sunk or beached. Whatever the cause, a sunken ship or a wrecked ship is a physical example of the event: this explains why the two concepts are often overlapping in English....
s. He also used his book to advertise other of his inventions, including a celestial globe for viewing the stars that a teacher and pupils could stand inside.

