
Germinoma
Encyclopedia
A germinoma is a type of germ cell tumor
which is not differentiated upon examination. It may be benign
or malignant
.
in the brain
that has a histology
identical to two other tumors: dysgerminoma in the ovary
and seminoma in the testis
. Since 1994, MeSH
has defined germinoma as "a malignant
neoplasm of the germinal
tissue
of the gonad
s; mediastinum
; or pineal region" and within its scope included both dysgerminoma and seminoma. Collectively, these are the seminomatous or germinomatous tumors.
differentiation, whereas nongerminomatous germ cell tumors
display a variety of differentiation. Like other germ cell tumors, germinomas can undergo malignant transformation.
with vesicular nuclei
and clear or finely granular cytoplasm
that is eosinophilic
.
On gross examination, the external surface is smooth and bosselated (knobby), and the interior is soft, fleshy and either cream-coloured, gray, pink or tan. Microscopic examination typically reveals uniform cells that resemble primordial germ cells. Typically, the stroma
contains lymphocyte
s and about 20% of patients have sarcoid-like granuloma
s.
has been noted in approximately 22% of cases at time of diagnosis. Males are approximately twice as commonly affected in developing germinomas. Germinomas are most commonly diagnosed between the age of 10 and 21.
Often serum and spinal fluid tumor marker
s of AFP
and beta-HCG are tested. Pure germinomas are not associated with these markers. Nongerminomatous germ cell tumors may be associated with increased markers such as AFP with yolk sac tumors as well as embryonic cell carcinomas and immature teratomas
and beta-HCG which occur in choriocarcinoma
s. In 1-15% of germinonas a low level of beta-HCG may be produced. Although controversial, there are some thoughts that HCG-secreting germinomas are more aggressive than nonsecreting ones.
is the most common type of malignant
germ cell
ovarian cancer
. Dysgerminoma usually occurs in adolescence
and early adult life; about 5% occur in pre-pubertal children. Dysgerminoma is extremely rare after age 50. Dysgerminoma occurs in both ovaries in 10% of patients and, in a further 10%, there is microscopic tumor in the other ovary.
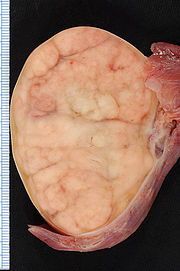 Seminoma is the second most common testicular cancer
Seminoma is the second most common testicular cancer
; the most common is mixed, which may contain seminoma.
Abnormal gonad
s (due to gonadal dysgenesis
and androgen insensitivity syndrome
) have a high risk of developing a dysgerminoma. Most dysgerminomas are associated with elevated serum lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), which is sometimes used as a tumor marker
.
Metastases are most often present in the lymph node
s.
s (GCTs) occurring outside the gonad
s, the most common location of intracranial germinoma is on or near the midline, often in the pineal or suprasellar areas; in 5-10% of patients with germinoma in either area, the tumor is in both areas. Like other (GCTs), germinomas can occur in other areas of the brain. Within the brain
, this tumor is most common in the hypothalamic or hypophyseal regions. In the thalamus
and basal ganglia
, germinoma is the most common GCT.
The diagnosis of an intracranial germinoma usually is based on biopsy
, because the features on neuroimaging are similar to other tumors.
Cytology
of the CSF
often is studied to detect metastasis
into the spine
. This is important for staging and radiotherapy planning.
Intracranial germinomas have a reported 90% survival to five years after diagnosis. Near total resection does not seem to influence the cure rate, so gross total resection is not necessary and can increase the risk of complications from surgery. The best results have been reported from craniospinal radiation with local tumor boost of greater than 4,000 cGy.
and radiotherapy. For this reason, with treatment patients' chances of long term survival, even cure, is excellent.
Although chemotherapy can shrink germinomas, it is not generally recommended alone unless there are contraindications to radiation possibly based on a study in the early 1990s where carboplatinum, etoposide
and bleomycin
were given to 45 germinoma patients. About half the patients relapsed. Most of these relapsed patients were recovered with radiation or additional chemotherapy.
Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
which is not differentiated upon examination. It may be benign
Benign
A benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
or malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
.
Classification
The term germinoma most often has referred to a tumorTumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
in the brain
Brain tumor
A brain tumor is an intracranial solid neoplasm, a tumor within the brain or the central spinal canal.Brain tumors include all tumors inside the cranium or in the central spinal canal...
that has a histology
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
identical to two other tumors: dysgerminoma in the ovary
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
and seminoma in the testis
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system.In the United States, between 7,500 and 8,000 diagnoses of testicular cancer are made each year. In the UK, approximately 2,000 men are diagnosed each year. Over his lifetime, a man's risk of...
. Since 1994, MeSH
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences; it can also serve as a thesaurus that facilitates searching...
has defined germinoma as "a malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
neoplasm of the germinal
Germ cell
A germ cell is any biological cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate near the gut of an embryo and migrate to the developing gonads. There, they undergo cell division of two types, mitosis and meiosis, followed by...
tissue
Tissue (biology)
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
of the gonad
Gonad
The gonad is the organ that makes gametes. The gonads in males are the testes and the gonads in females are the ovaries. The product, gametes, are haploid germ cells. For example, spermatozoon and egg cells are gametes...
s; mediastinum
Mediastinum
The mediastinum is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity...
; or pineal region" and within its scope included both dysgerminoma and seminoma. Collectively, these are the seminomatous or germinomatous tumors.
Natural history
Germinomas are thought to originate from an error of development, when certain primordial germ cells fail to migrate properly. Germinomas lack histologicHistology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
differentiation, whereas nongerminomatous germ cell tumors
Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
display a variety of differentiation. Like other germ cell tumors, germinomas can undergo malignant transformation.
Histology
The tumor is uniform in appearance, consisting of large, round cellsCell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
with vesicular nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
and clear or finely granular cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
that is eosinophilic
Eosinophilic
Eosinophilic refers to the staining of certain tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye.Eosin is an acidic dye; thus, the structure being stained is basic....
.
On gross examination, the external surface is smooth and bosselated (knobby), and the interior is soft, fleshy and either cream-coloured, gray, pink or tan. Microscopic examination typically reveals uniform cells that resemble primordial germ cells. Typically, the stroma
Thylakoid
A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as...
contains lymphocyte
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.Under the microscope, lymphocytes can be divided into large lymphocytes and small lymphocytes. Large granular lymphocytes include natural killer cells...
s and about 20% of patients have sarcoid-like granuloma
Granuloma
Granuloma is a medical term for a tiny collection of immune cells known as macrophages. Granulomas form when the immune system attempts to wall off substances that it perceives as foreign but is unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms such as bacteria and fungi as well as...
s.
Diagnosis
MetastasisMetastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
has been noted in approximately 22% of cases at time of diagnosis. Males are approximately twice as commonly affected in developing germinomas. Germinomas are most commonly diagnosed between the age of 10 and 21.
Often serum and spinal fluid tumor marker
Tumor marker
A tumor marker is a substance found in the blood, urine, or body tissues that can be elevated in cancer, among other tissue types. There are many different tumor markers, each indicative of a particular disease process, and they are used in oncology to help detect the presence of cancer...
s of AFP
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene....
and beta-HCG are tested. Pure germinomas are not associated with these markers. Nongerminomatous germ cell tumors may be associated with increased markers such as AFP with yolk sac tumors as well as embryonic cell carcinomas and immature teratomas
Teratoma
A teratoma is an encapsulated tumor with tissue or organ components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layers. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable...
and beta-HCG which occur in choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinoma
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant, trophoblastic and aggressive cancer, usually of the placenta. It is characterized by early hematogenous spread to the lungs...
s. In 1-15% of germinonas a low level of beta-HCG may be produced. Although controversial, there are some thoughts that HCG-secreting germinomas are more aggressive than nonsecreting ones.
Ovary (dysgerminoma) and testis (seminoma)
DysgerminomaDysgerminoma
A dysgerminoma is a type of germ cell tumor; it usually is malignant and usually occurs in the ovary.A tumor of the identical histology but not occurring in the ovary may be described by an alternate name: seminoma in the testis or germinoma in the central nervous system or other parts of the...
is the most common type of malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
germ cell
Germ cell
A germ cell is any biological cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate near the gut of an embryo and migrate to the developing gonads. There, they undergo cell division of two types, mitosis and meiosis, followed by...
ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
. Dysgerminoma usually occurs in adolescence
Adolescence
Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and mental human development generally occurring between puberty and legal adulthood , but largely characterized as beginning and ending with the teenage stage...
and early adult life; about 5% occur in pre-pubertal children. Dysgerminoma is extremely rare after age 50. Dysgerminoma occurs in both ovaries in 10% of patients and, in a further 10%, there is microscopic tumor in the other ovary.

Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system.In the United States, between 7,500 and 8,000 diagnoses of testicular cancer are made each year. In the UK, approximately 2,000 men are diagnosed each year. Over his lifetime, a man's risk of...
; the most common is mixed, which may contain seminoma.
Abnormal gonad
Gonad
The gonad is the organ that makes gametes. The gonads in males are the testes and the gonads in females are the ovaries. The product, gametes, are haploid germ cells. For example, spermatozoon and egg cells are gametes...
s (due to gonadal dysgenesis
Gonadal dysgenesis
Gonadal dysgenesis is a term used to describe multiple reproductive system development disorders. They are conditions of genetic origin. It is characterized by a progressive loss of primordial germ cells on the developing gonads of an embryo....
and androgen insensitivity syndrome
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
Androgen insensitivity syndrome is a condition that results in the partial or complete inability of the cell to respond to androgens. The unresponsiveness of the cell to the presence of androgenic hormones can impair or prevent the masculinization of male genitalia in the developing fetus, as...
) have a high risk of developing a dysgerminoma. Most dysgerminomas are associated with elevated serum lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), which is sometimes used as a tumor marker
Tumor marker
A tumor marker is a substance found in the blood, urine, or body tissues that can be elevated in cancer, among other tissue types. There are many different tumor markers, each indicative of a particular disease process, and they are used in oncology to help detect the presence of cancer...
.
Metastases are most often present in the lymph node
Lymph node
A lymph node is a small ball or an oval-shaped organ of the immune system, distributed widely throughout the body including the armpit and stomach/gut and linked by lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are garrisons of B, T, and other immune cells. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and act as...
s.
Intracranial germinoma
Intracranial germinoma occurs in 0.7 per million children. As with other germ cell tumorGerm cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
s (GCTs) occurring outside the gonad
Gonad
The gonad is the organ that makes gametes. The gonads in males are the testes and the gonads in females are the ovaries. The product, gametes, are haploid germ cells. For example, spermatozoon and egg cells are gametes...
s, the most common location of intracranial germinoma is on or near the midline, often in the pineal or suprasellar areas; in 5-10% of patients with germinoma in either area, the tumor is in both areas. Like other (GCTs), germinomas can occur in other areas of the brain. Within the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
, this tumor is most common in the hypothalamic or hypophyseal regions. In the thalamus
Thalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
and basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
, germinoma is the most common GCT.
The diagnosis of an intracranial germinoma usually is based on biopsy
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
, because the features on neuroimaging are similar to other tumors.
Cytology
Cell biology
Cell biology is a scientific discipline that studies cells – their physiological properties, their structure, the organelles they contain, interactions with their environment, their life cycle, division and death. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level...
of the CSF
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
often is studied to detect metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
into the spine
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
. This is important for staging and radiotherapy planning.
Intracranial germinomas have a reported 90% survival to five years after diagnosis. Near total resection does not seem to influence the cure rate, so gross total resection is not necessary and can increase the risk of complications from surgery. The best results have been reported from craniospinal radiation with local tumor boost of greater than 4,000 cGy.
Treatment and prognosis
Germinomas, like several other types of germ cell tumor, are sensitive to both chemotherapyChemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
and radiotherapy. For this reason, with treatment patients' chances of long term survival, even cure, is excellent.
Although chemotherapy can shrink germinomas, it is not generally recommended alone unless there are contraindications to radiation possibly based on a study in the early 1990s where carboplatinum, etoposide
Etoposide
Etoposide phosphate is an anti-cancer agent. It is known in the laboratory as a topoisomerase poison. Etoposide is often incorrectly referred to as a topoisomerase inhibitor in order to avoid using the term "poison" in a clinical setting...
and bleomycin
Bleomycin
Bleomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic produced by the bacterium Streptomyces verticillus. Bleomycin refers to a family of structurally related compounds. When used as an anticancer agent, the chemotherapeutical forms are primarily bleomycin A2 and B2. It works by causing breaks in DNA...
were given to 45 germinoma patients. About half the patients relapsed. Most of these relapsed patients were recovered with radiation or additional chemotherapy.
See also
- Brown-Sequard SyndromeBrown-Séquard syndromeBrown-Séquard syndrome, also known as Brown-Séquard's hemiplegia and Brown-Séquard's paralysis, is a loss of sensation and motor function that is caused by the lateral hemisection of the spinal cord...
(sections on Cavernous malformation and Germinoma) - Spermatocytic seminomaSpermatocytic seminomaSpermatocytic seminoma is a neoplasm of the testis , and classified as a germ cell tumour.The name of the tumour comes from the similarity between the small cells of the tumour and secondary spermatocytes.-Relation to seminoma:Spermatocytic seminoma is not considered a subtype of seminoma and,...
temodal (treatment)
External links
- Seminoma at University of UtahUniversity of UtahThe University of Utah, also known as the U or the U of U, is a public, coeducational research university in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. The university was established in 1850 as the University of Deseret by the General Assembly of the provisional State of Deseret, making it Utah's oldest...
- Seminoma and Germinoma at MedPix(r) at USUHS

