
Grantha
Encyclopedia
Grantha script is an ancient script that was widely used between the 6th century and the 19th century CE to write classical Sanskrit
and Manipravalam
by Tamil speakers in Southern India, particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala, and is still in restricted use in traditional vedic schools (veda pāṭhaśālā). It evolved from the ancient Brāhmī script
and is therefore classified under the Brahmic family of scripts
. The Ancient Pallava Variant has been used as far as South East Asia, giving rise to the various South-East Asian script
Grantha, is developed from the Southern Variant of Brahmi in Tamil Nadu. South Asian Scripts such as Mon, Lao, Javanese
, Khmer
and Thai are either direct or indirect derivations from the Pallava Variant of Grantha Script. Malayalam Script
is a direct descendant of Grantha Script. Tulu Script
and Sinhala Script were probably influenced by Grantha Script.
The rising popularity of the Devanagari
script for Sanskrit, and the political pressure created by the Tanittamil Iyakkam
for its complete replacement by the modern Tamil script
led to its gradual disuse and abandonment in Tamil Nadu in the early 20th century.
, grantha literally 'a knot'. is a word that was used for books, and the script used to write them. This stems from the practice of binding inscribed palm leaves using a length of thread held by knots. Although Sanskrit
is now mostly written in the Devanagari
script, the Grantha script was widely used to write Sanskrit in the Tamil
-speaking parts of South Asia
until the 19th century. Scholars believe that the Grantha script was used when the Vedas
were first put into writing around the 5th century CE. In the early 20th century, it began to be replaced by the Devanagari script in religious and scholarly texts, and the normal Tamil script
(with the use of diacritic
s) in popular texts.
The Grantha script was also historically used for writing Tamil–Sanskrit Manipravalam
, a blend of Tamil and Sanskrit which was used in the exegesis of Sanskrit texts. This evolved into a fairly complex writing system which required that Tamil words be written in the Tamil vatteluthu and Sanskrit words be written in the Grantha script. By the 15th century, this had evolved to the point that both scripts would be used within the same word – if the root was derived from Sanskrit it would be written in the Grantha script, but any Tamil suffixes which were added to it would be written using the Tamil vatteluthu. This system of writing went out of use when Manipravalam declined in popularity, but it was customary to use the same convention in printed editions of texts originally written in Manipravalam until the middle of the 20th century.
In modern times, the Grantha script is used in certain religious contexts by orthodox Tamil-speaking Hindus
. Most notably, they use the script to write a child's name for the first time during the naming ceremony, and to write the Sanskrit portion of wedding invitations and announcements of a person's last rites. It is also used in many religious almanacs to print traditional formulaic summaries of the coming year.
Archaic and Ornamental variety of Grantha constitute what is referred as Pallava Grantha. They were used by the Pallava in their Inscriptions. The Ornamental variety was too complex and ornate, hence this form could not have been possibly used in day to day writing and may have used only for Inscriptions. Mamallapuram Inscriptions, Tiruchirapalli
Rock Cut Cave Inscriptions, Kailasantha Inscription come under this type.
The Tulu-Malayalam script is called Transitional Grantha. Currently two varieties are used: Brahmanic, or square, and Jain, or round. The Tulu-Malayalam script is a variety of Grantha dating from the 8th or 9th century AD. The modern Tamil script is also derived from Grantha.http://www.britannica.com/eb/topic-608729/Tulu-Malayalam-script
This type of Grantha was used by Cholas approximately from 650 CE to 950 CE. Inscription of later Pallavas and Pandiyan Nedunchezhiyan are also examples for this variety of Grantha Script.
Inscriptions of the Imperial Thanjavur Cholas are an example for Medieval Grantha. This variety was in Vogue from 950 CE to 1250 CE.
Grantha in the present form descended from later Pandyas and the Vijayanagara
rulers. The Modern form of Grantha is very similar to the Modern Tamil Script
.
encoding for Grantha does not yet exist. The font used in the following tables is e-Grantamil taken from INDOLIPI.
The below glyps denote the late form of Grantha Script, which can be noticed by its similarity with the Modern Tamil Script.

As with other Abugida
scripts Grantha consonant signs have the inherent vowel
/a/. Its absence is marked with Virāma:

For other vowels diacritic
s are used:

Sometimes ligatures of consonants with vowel diacritic
s may be found, e.g.:

There are also a few special consonant forms with Virāma:
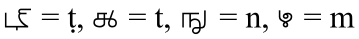

Ligatures are normally preferred whenever they exist. If no ligatures exist, "stacked" forms of consonants are written, just as in Kannada and Telugu, with the lowest member of the stack being the only "live" consonant and the other members all being vowelless. Note that ligatures may be used as members of stacks also.

Special forms:
 ⟨ya⟩ when final in a cluster, and
⟨ya⟩ when final in a cluster, and  ⟨ra⟩ when non-initial become
⟨ra⟩ when non-initial become 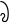 and
and  respectively. These are often called "ya-phalaa" and "ra-vattu" in other Indic scripts.
respectively. These are often called "ya-phalaa" and "ra-vattu" in other Indic scripts.
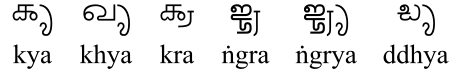
 ⟨ra⟩ as initial component of a cluster becomes
⟨ra⟩ as initial component of a cluster becomes 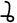 (called Reph as in other Indic scripts) and is shifted to the end of the cluster but placed before any "ya-phalaa".
(called Reph as in other Indic scripts) and is shifted to the end of the cluster but placed before any "ya-phalaa".

into Latin (ISO 15919
) and Devanāgarī
scripts.
Example 1: Taken from Kālidāsa
's Kumārasambhavam
Example 2: St. John 3:16
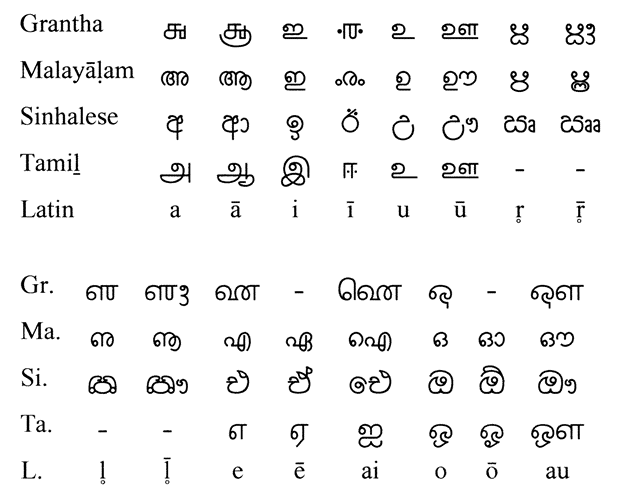
Note: As in Devanāgarī ⟨e⟩ and ⟨o⟩ in Grantha stand for [eː] and [oː]. Originally also Malayāḷam
and Tamiḻ
scripts did not distinguish long and short ⟨e⟩ and ⟨o⟩, though both languages have the phonemes /e/ /eː/ and /o/ /oː/. The addition of extra signs for /eː/ and /oː/ is attributed to the Italian missionary Constanzo Beschi
(1680–1774).
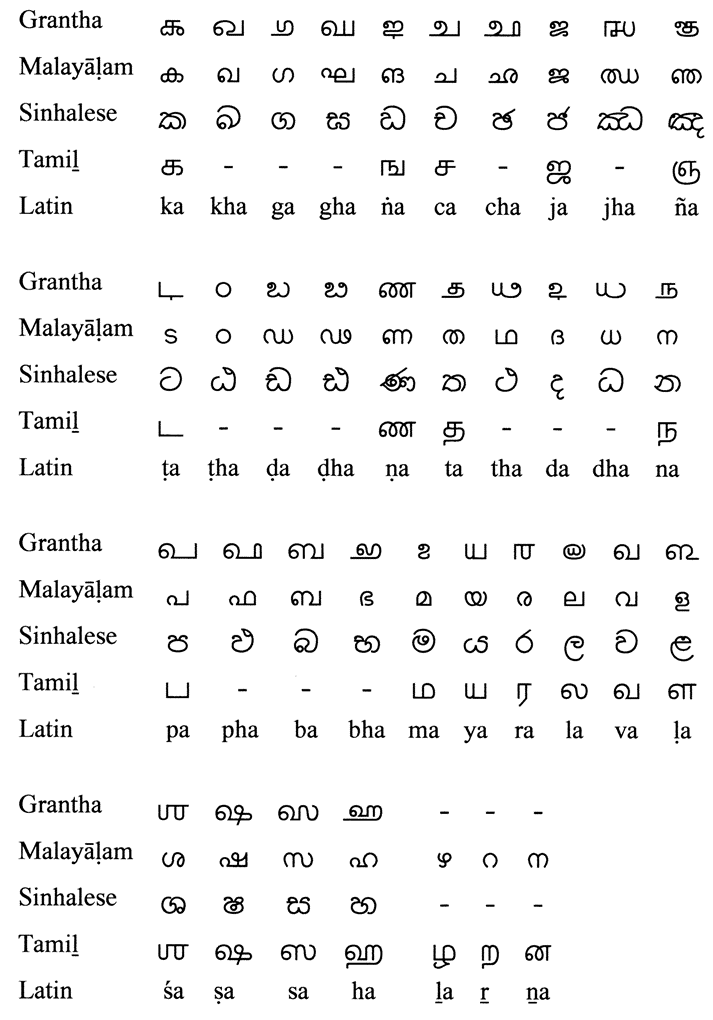
The Tamiḻ letters ஜ ஶ ஷ ஸ ஹ and the ligature க்ஷ ⟨kṣa⟩ are called "Grantha letters" and not Tamil, as they were introduced from Grantha into the Tamiḻ script to render non-Tamil words(Sanskrit, Pali
in early days now it is used to many other languages). The letters ழ ற ன and the corresponding sounds occur only in Dravidian languages
.
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
and Manipravalam
Manipravalam
Manipravalam was a literary style used in medieval liturgical texts in South India, which used an admixture of Tamil and Sanskrit. Manipravalam is termed a mixture of Sanskrit and Tamil...
by Tamil speakers in Southern India, particularly in Tamil Nadu and Kerala, and is still in restricted use in traditional vedic schools (veda pāṭhaśālā). It evolved from the ancient Brāhmī script
Brāhmī script
Brāhmī is the modern name given to the oldest members of the Brahmic family of scripts. The best-known Brāhmī inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in north-central India, dated to the 3rd century BCE. These are traditionally considered to be early known examples of Brāhmī writing...
and is therefore classified under the Brahmic family of scripts
Brahmic family of scripts
The Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
. The Ancient Pallava Variant has been used as far as South East Asia, giving rise to the various South-East Asian script
Grantha, is developed from the Southern Variant of Brahmi in Tamil Nadu. South Asian Scripts such as Mon, Lao, Javanese
Javanese script
The Javanese alphabet, natively known as Hanacaraka or Carakan , known by the Sundanese people as Cacarakan is the pre-colonial script used to write the Javanese language....
, Khmer
Khmer script
The Khmer script is an alphasyllabary script used to write the Khmer language . It is also used to write Pali among the Buddhist liturgy of Cambodia and Thailand....
and Thai are either direct or indirect derivations from the Pallava Variant of Grantha Script. Malayalam Script
Malayalam script
The Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write the Malayalam language—which is the principal language of the Indian state of Kerala, spoken by 36 million people in the world. Like many other Indic scripts, it is an abugida, or a writing system that is partially “alphabetic” and...
is a direct descendant of Grantha Script. Tulu Script
Tulu Script
The Tulu script The Tulu script The Tulu script (Tulu: —written in Tulu script, is the original script of the Tulu language. It evolved from the Grantha script. It bears partial similarity to the Malayalam script, which also evolved from the Grantha....
and Sinhala Script were probably influenced by Grantha Script.
The rising popularity of the Devanagari
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
script for Sanskrit, and the political pressure created by the Tanittamil Iyakkam
Tanittamil Iyakkam
The Thanittamil Iyakkam is a movement of linguistic purism in Tamil literature attempting to emulate the "unadulterated Tamil language" of the Sangam period, avoiding Sanskrit, Persian and English loanwords. It was notably initiated by the writings of Maraimalai Adigal and Paventhar ...
for its complete replacement by the modern Tamil script
Tamil script
The Tamil script is a script that is used to write the Tamil language as well as other minority languages such as Badaga, Irulas, and Paniya...
led to its gradual disuse and abandonment in Tamil Nadu in the early 20th century.
History
In SanskritSanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
, grantha literally 'a knot'. is a word that was used for books, and the script used to write them. This stems from the practice of binding inscribed palm leaves using a length of thread held by knots. Although Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
is now mostly written in the Devanagari
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
script, the Grantha script was widely used to write Sanskrit in the Tamil
Tamil language
Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
-speaking parts of South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
until the 19th century. Scholars believe that the Grantha script was used when the Vedas
Vedas
The Vedas are a large body of texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism....
were first put into writing around the 5th century CE. In the early 20th century, it began to be replaced by the Devanagari script in religious and scholarly texts, and the normal Tamil script
Tamil script
The Tamil script is a script that is used to write the Tamil language as well as other minority languages such as Badaga, Irulas, and Paniya...
(with the use of diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s) in popular texts.
The Grantha script was also historically used for writing Tamil–Sanskrit Manipravalam
Manipravalam
Manipravalam was a literary style used in medieval liturgical texts in South India, which used an admixture of Tamil and Sanskrit. Manipravalam is termed a mixture of Sanskrit and Tamil...
, a blend of Tamil and Sanskrit which was used in the exegesis of Sanskrit texts. This evolved into a fairly complex writing system which required that Tamil words be written in the Tamil vatteluthu and Sanskrit words be written in the Grantha script. By the 15th century, this had evolved to the point that both scripts would be used within the same word – if the root was derived from Sanskrit it would be written in the Grantha script, but any Tamil suffixes which were added to it would be written using the Tamil vatteluthu. This system of writing went out of use when Manipravalam declined in popularity, but it was customary to use the same convention in printed editions of texts originally written in Manipravalam until the middle of the 20th century.
In modern times, the Grantha script is used in certain religious contexts by orthodox Tamil-speaking Hindus
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
. Most notably, they use the script to write a child's name for the first time during the naming ceremony, and to write the Sanskrit portion of wedding invitations and announcements of a person's last rites. It is also used in many religious almanacs to print traditional formulaic summaries of the coming year.
Pallava Grantha
Archaic and Ornamental variety of Grantha constitute what is referred as Pallava Grantha. They were used by the Pallava in their Inscriptions. The Ornamental variety was too complex and ornate, hence this form could not have been possibly used in day to day writing and may have used only for Inscriptions. Mamallapuram Inscriptions, Tiruchirapalli
Tiruchirapalli
Tiruchirappalli ) , also called Tiruchi or Trichy , is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Tiruchirappalli District. It is the fourth largest municipal corporation in Tamil Nadu and also the fourth largest urban agglomeration in the state...
Rock Cut Cave Inscriptions, Kailasantha Inscription come under this type.
Transitional Grantha
The Tulu-Malayalam script is called Transitional Grantha. Currently two varieties are used: Brahmanic, or square, and Jain, or round. The Tulu-Malayalam script is a variety of Grantha dating from the 8th or 9th century AD. The modern Tamil script is also derived from Grantha.http://www.britannica.com/eb/topic-608729/Tulu-Malayalam-script
This type of Grantha was used by Cholas approximately from 650 CE to 950 CE. Inscription of later Pallavas and Pandiyan Nedunchezhiyan are also examples for this variety of Grantha Script.
Medieval Grantha
Inscriptions of the Imperial Thanjavur Cholas are an example for Medieval Grantha. This variety was in Vogue from 950 CE to 1250 CE.
Modern Grantha
Grantha in the present form descended from later Pandyas and the Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara is in Bellary District, northern Karnataka. It is the name of the now-ruined capital city "which was regarded as the second Rome" that surrounds modern-day Hampi, of the historic Vijayanagara empire which extended over the southern part of India....
rulers. The Modern form of Grantha is very similar to the Modern Tamil Script
Tamil script
The Tamil script is a script that is used to write the Tamil language as well as other minority languages such as Badaga, Irulas, and Paniya...
.
Grantha Encoding
A UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
encoding for Grantha does not yet exist. The font used in the following tables is e-Grantamil taken from INDOLIPI.
The below glyps denote the late form of Grantha Script, which can be noticed by its similarity with the Modern Tamil Script.
Consonants

As with other Abugida
Abugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
scripts Grantha consonant signs have the inherent vowel
Inherent vowel
An inherent vowel is part of an abugida script. It is the vowel sound which is used with each unmarked or basic consonant symbol....
/a/. Its absence is marked with Virāma:

For other vowels diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s are used:

Sometimes ligatures of consonants with vowel diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s may be found, e.g.:

There are also a few special consonant forms with Virāma:
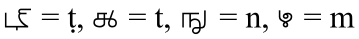
Consonant Clusters
Grantha has two ways of representing consonant clusters. Sometimes, consonants in a cluster may form ligatures.
Ligatures are normally preferred whenever they exist. If no ligatures exist, "stacked" forms of consonants are written, just as in Kannada and Telugu, with the lowest member of the stack being the only "live" consonant and the other members all being vowelless. Note that ligatures may be used as members of stacks also.

Special forms:
 ⟨ya⟩ when final in a cluster, and
⟨ya⟩ when final in a cluster, and  ⟨ra⟩ when non-initial become
⟨ra⟩ when non-initial become 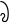 and
and  respectively. These are often called "ya-phalaa" and "ra-vattu" in other Indic scripts.
respectively. These are often called "ya-phalaa" and "ra-vattu" in other Indic scripts.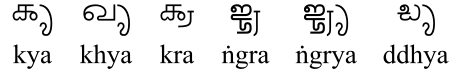
 ⟨ra⟩ as initial component of a cluster becomes
⟨ra⟩ as initial component of a cluster becomes  (called Reph as in other Indic scripts) and is shifted to the end of the cluster but placed before any "ya-phalaa".
(called Reph as in other Indic scripts) and is shifted to the end of the cluster but placed before any "ya-phalaa".
Text Samples
The Grantha text of each sample is followed by a transliterationTransliteration
Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
into Latin (ISO 15919
ISO 15919
ISO 15919 Transliteration of Devanagari and related Indic scripts into Latin characters is an international standard for the transliteration of Indic scripts to the Latin alphabet formed in 2001...
) and Devanāgarī
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
scripts.
Example 1: Taken from Kālidāsa
Kalidasa
Kālidāsa was a renowned Classical Sanskrit writer, widely regarded as the greatest poet and dramatist in the Sanskrit language...
's Kumārasambhavam
- astyuttarasyāṁ diśi devatātmā himālayo nāma nagādhirājaḥ.
- pūrvāparau toyanidhī vagāhya sthitaḥ pr̥thivyā iva mānadaṇḍaḥ.
- अस्त्युत्तरस्यां दिशि देवतात्मा हिमालयो नाम नगाधिराजः।
- पूर्वापरौ तोयनिधी वगाह्य स्थितः पृथिव्या इव मानदण्डः॥
Example 2: St. John 3:16
- By comparing the old print from 1886 with the modern version given below one may see the difficulties the typesetter had with Grantha.
- yata īśvaro jagatītthaṁ prema cakāra yannijamekajātaṁ
- putraṁ dadau tasmin viśvāsī sarvamanuṣyo yathā
- na vinaśyānantaṁ jīvanaṁ lapsyate.
- यत ईश्वरो जगतीत्थं प्रेम चकार यन्निजमेकजातं
- पुत्रं ददौ तस्मिन् विश्वासी सर्वमनुष्यो यथा
- न विनश्यानन्तं जीवनं लप्स्यते।
Vowel signs

Note: As in Devanāgarī ⟨e⟩ and ⟨o⟩ in Grantha stand for [eː] and [oː]. Originally also Malayāḷam
Malayalam script
The Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write the Malayalam language—which is the principal language of the Indian state of Kerala, spoken by 36 million people in the world. Like many other Indic scripts, it is an abugida, or a writing system that is partially “alphabetic” and...
and Tamiḻ
Tamil script
The Tamil script is a script that is used to write the Tamil language as well as other minority languages such as Badaga, Irulas, and Paniya...
scripts did not distinguish long and short ⟨e⟩ and ⟨o⟩, though both languages have the phonemes /e/ /eː/ and /o/ /oː/. The addition of extra signs for /eː/ and /oː/ is attributed to the Italian missionary Constanzo Beschi
Constanzo Beschi
Constanzo Beschi, also known under his Tamil name of Vīramāmunivar or Constantine Joseph Beschi was an Italian Jesuit priest, Missionary in South India, and renowned poet in the Tamil language.-Early years and formation:Born in Castiglione delle Stiviere, Mantova, Italy, a place very close to...
(1680–1774).
Consonant signs

The Tamiḻ letters ஜ ஶ ஷ ஸ ஹ and the ligature க்ஷ ⟨kṣa⟩ are called "Grantha letters" and not Tamil, as they were introduced from Grantha into the Tamiḻ script to render non-Tamil words(Sanskrit, Pali
Páli
- External links :* *...
in early days now it is used to many other languages). The letters ழ ற ன and the corresponding sounds occur only in Dravidian languages
Dravidian languages
The Dravidian language family includes approximately 85 genetically related languages, spoken by about 217 million people. They are mainly spoken in southern India and parts of eastern and central India as well as in northeastern Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Iran, and...
.
External links
- Quick facts about Grantha at AncientScripts.com
- Article at Omniglot
- Tamil Nadu Archeological Department – Grantha Webpage
- more about
- Digitized Grantha Books
- Software package with Grantha OpenType font and typewriter for Grantha and Manipravalam for Win XP, Vista, Win 7
- Online Tutorial for Grantha Script


