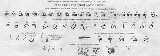
Javanese script
Encyclopedia
The Javanese alphabet, natively known as Hanacaraka or Carakan , known by the Sundanese people
as Cacarakan is the pre-colonial script used to write the Javanese language
.
As of 2008 Javanese is difficult to render on a computer, though the script was added to Unicode
in version 5.2.
are modern variants of the old Kawi script, a Brahmic script introduced to Java along with Hinduism and Buddhism. Kawi is first attested in a legal document from 804 CE
. It was widely used in literature and translations from Sanskrit from the tenth century; by the seventeenth, the script is identified as carakan. A Latin orthography based on Dutch
was introduced in 1926, revised in 1972–1973, and has largely supplanted the carakan.
Currently, there are no newspapers or magazines being printed in the Javanese script. However it is still taught in most elementary school
and some junior high school as of compulsory subject in Javanese language areas.
. Each of the twenty letter represents a syllable with a consonant (or a "zero consonant
") and the inherent vowel 'a' which is pronounced as ɔ in open position. Various diacritic
s placed around the letter indicate a different vowel than [ɔ], a final consonant, or a foreign pronunciation.
Letters have subscript forms used to transcribe consonant cluster
s. Some have "capital" forms used in proper names. However, every letter in the name is capitalized, not just the first.
Punctuation includes a comma; period; a mark that covers the colon, quotations, and indicates numerals; and marks to introduce a chapter, poem, song, or letter.

Each symbol consists of n-shapes and u-shapes. n-shapes come in two sizes: small and large (twice the size of a small). u-shapes come in three sizes: small, medium (1.5x) and large (2.5x). For example, the character 'h' consists of a small n-shape, followed by a large u-shape and two large n-shapes. This format is closely followed in hand-writing and is no longer followed in printed characters.
Javanese characters are written slanted to the side and below the line, and there are no word boundaries.
, known as sandhangan swara, are used because some diacritics can be used for two different vowels. Rules regarding the pronunciation and the context eliminate the need for a new symbol for every vowel by making the vowel predictable.
Rules regarding inherent vowels of basic characters:
1) A basic character stands for a syllable
that ends in the vowel /ɔ/ when the character is preceded by another character containing a sandhangan swara.
2) A basic character stands for a syllable
that ends in the vowel /a/ when the character is immediately followed by a character containing a sandhangan swara.
3) The first basic character of a word normally has the /ɔ/ vowel, unless it precedes two other basic characters, in which case the first basic character has the /a/ vowel.
. The four consonants are -ng, -r, -h, and -l; they are indicated by the cecak, layar, wignyan, and pengkal, respectively.
Other consonants that appear in the word-final position require the use of the basic consonant symbols and the paten (or pangku) to indicate the absence of a vowel.
For example,
/l/: blabag - board
/r/: mrana - going there
/w/: dwi - two
/y/: hyang - God
When ‘r’ or ‘y’ are the second consonant of the cluster, they are represented by diacritics “cakra” and “pengkal” respectively. However, when the consonant cluster with ‘-r’ ends with the vowel /ə/, then a different diacritic, the keret is used.
When ‘l’ or ‘w’ is the second consonant of a cluster, it is represented by the “pasangan” forms, modified consonant symbols, written under the symbol for the first consonant of the cluster.
are indicated by writing diacritic marks over similar sounding Javanese letters. On top of that, Javanese also uses special characters to write foreign names or words.
A: There are five special characters used to write non-Javanese vowels. The five vowels are represented by the following names.
B: There are five special characters used to write non-Javanese consonants. These consonants are /x/, /dʒ/, /f/, /ɣ/, and /z/.
The Javanese numeral system
has its own script but they often use the Arabic number system. In the Javanese Script, only numbers 0–9 are represented.
0 nol
1 siji
2 loro
3 telu
4 papat
5 lima
6 enem
7 pitu
8 wolu
9 sanga
When writing numbers greater than 9, simply combine the above numbers, as one would using the Arabic system. For example, to write 21, simply write the characters loro siji. Similarly, the number 90 would be the characters sanga nol.
Since some of the characters for the numbers are very similar to the characters for syllables, numbers that show up in Javanese texts are indicated by special 'numeral markers' both before and after the number. For example,
text ....... numeral marker telu siji numeral marker .......... text
Special punctuation includes:
Two special rules apply to the usage of the comma, and the period.
1.The comma is not needed after a consonant-ending word that is represented by a pangku
2.The comma is used instead of the period after a consonant-ending word that is represented by a pangku
, of which the line-by-line translation is as follows:
Hana caraka There (were) two messengers
data sawala (They) had animosity (among each other)
padha jayanya (They were) equally powerful (in fight)
maga bathanga Here are the corpses.
in detail:
hana / ana = there were/was
caraka = messenger (actually, 'one who is loyal to and trusted by someone')
data = have/has
sawala = difference (regarding a matter)
padha = same, equal
jayanya = 'their power', 'jaya' could mean 'glory' as well
maga = 'here'
bathanga = corpses
to write the Sundanese language
, but the script was simplified and called Cacarakan instead. Cacarakan differs from Carakan by omitting the dha and tha, thus only:
s are essentially typographic variants.
Standard in October, 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Javanese is U+A980–U+A9DF. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points:
Sundanese people
The Sundanese are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Indonesian island of Java. They number approximately 31 million, and are the second most populous of all the nation's ethncities. The Sundanese are predominantly Muslim...
as Cacarakan is the pre-colonial script used to write the Javanese language
Javanese language
Javanese language is the language of the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, in Indonesia. In addition, there are also some pockets of Javanese speakers in the northern coast of western Java...
.
As of 2008 Javanese is difficult to render on a computer, though the script was added to Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
in version 5.2.
History
Javanese and BalineseBalinese script
The Balinese alphabet is an abugida that was used to write the Balinese language, an Austronesian language spoken by about three million people on the Indonesian island of Bali. The use of the Balinese script has mostly been replaced by the Roman alphabet. Although it is learned in school, few...
are modern variants of the old Kawi script, a Brahmic script introduced to Java along with Hinduism and Buddhism. Kawi is first attested in a legal document from 804 CE
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
. It was widely used in literature and translations from Sanskrit from the tenth century; by the seventeenth, the script is identified as carakan. A Latin orthography based on Dutch
Dutch orthography
Dutch orthography uses the Latin alphabet according to a system which has evolved to suit the needs of the Dutch language. The regular relationship of graphemes to phonemes is listed in the article on Dutch language...
was introduced in 1926, revised in 1972–1973, and has largely supplanted the carakan.
Currently, there are no newspapers or magazines being printed in the Javanese script. However it is still taught in most elementary school
Elementary school
An elementary school or primary school is an institution where children receive the first stage of compulsory education known as elementary or primary education. Elementary school is the preferred term in some countries, particularly those in North America, where the terms grade school and grammar...
and some junior high school as of compulsory subject in Javanese language areas.
Function
The Javanese script is an abugidaAbugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
. Each of the twenty letter represents a syllable with a consonant (or a "zero consonant
Zero consonant
A zero consonant, silent initial, or null-onset letter is a consonant-like letter that is not pronounced, but indicates that a word or syllable starts with a vowel...
") and the inherent vowel 'a' which is pronounced as ɔ in open position. Various diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s placed around the letter indicate a different vowel than [ɔ], a final consonant, or a foreign pronunciation.
Letters have subscript forms used to transcribe consonant cluster
Consonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word splits....
s. Some have "capital" forms used in proper names. However, every letter in the name is capitalized, not just the first.
Punctuation includes a comma; period; a mark that covers the colon, quotations, and indicates numerals; and marks to introduce a chapter, poem, song, or letter.
Form

Each symbol consists of n-shapes and u-shapes. n-shapes come in two sizes: small and large (twice the size of a small). u-shapes come in three sizes: small, medium (1.5x) and large (2.5x). For example, the character 'h' consists of a small n-shape, followed by a large u-shape and two large n-shapes. This format is closely followed in hand-writing and is no longer followed in printed characters.
Javanese characters are written slanted to the side and below the line, and there are no word boundaries.
Vowels
In Javanese, there are a total of nine vowels: /a/, /i/, /ɪ/, /e/, /ɛ/, /ə/, /o/, /ɔ/, /u/. However, only five vowel diacriticsDiacritics
diacritics is a quarterly academic journal established in 1971 at Cornell University and published by the Johns Hopkins University Press. Articles serve to review recent literature in the field of literary criticism, and have covered topics in gender studies, political theory, psychoanalysis, queer...
, known as sandhangan swara, are used because some diacritics can be used for two different vowels. Rules regarding the pronunciation and the context eliminate the need for a new symbol for every vowel by making the vowel predictable.
| Phoneme | /i/ | /ə/ | /u/ | /e/ | /o/ |
| Symbol | |||||
| Name | wulu | pepet | suku | taling | taling-tarung |
Rules regarding inherent vowels of basic characters:
1) A basic character stands for a syllable
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building...
that ends in the vowel /ɔ/ when the character is preceded by another character containing a sandhangan swara.
2) A basic character stands for a syllable
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building...
that ends in the vowel /a/ when the character is immediately followed by a character containing a sandhangan swara.
3) The first basic character of a word normally has the /ɔ/ vowel, unless it precedes two other basic characters, in which case the first basic character has the /a/ vowel.
Consonants
| ha | na | ca | ra | ka |
| da | ta | sa | wa | la |
| pa | dha | ja | ya | nya |
| ma | ga | ba | tha | nga |
Syllable-final consonants
Four special syllable-final consonants are denoted by diacriticsDiacritics
diacritics is a quarterly academic journal established in 1971 at Cornell University and published by the Johns Hopkins University Press. Articles serve to review recent literature in the field of literary criticism, and have covered topics in gender studies, political theory, psychoanalysis, queer...
. The four consonants are -ng, -r, -h, and -l; they are indicated by the cecak, layar, wignyan, and pengkal, respectively.
| - | /h/ final | /r/ final | /ŋ/ final |
| pangkon | wignyan | layar | cecak |
Other consonants that appear in the word-final position require the use of the basic consonant symbols and the paten (or pangku) to indicate the absence of a vowel.
| ha | na | ca | ra | ka |
| da | ta | sa | wa | la |
| pa | dha | ja | ya | nya |
| ma | ga | ba | tha | nga |
Aksara murda
| Symbol | na | ka | ta | sa | pa | ga | ba |
| Murda simple | |||||||
| Murda pasangan |
Consonant clusters
Only l, r, w, and y can form consonant clusters in Javanese.For example,
/l/: blabag - board
/r/: mrana - going there
/w/: dwi - two
/y/: hyang - God
When ‘r’ or ‘y’ are the second consonant of the cluster, they are represented by diacritics “cakra” and “pengkal” respectively. However, when the consonant cluster with ‘-r’ ends with the vowel /ə/, then a different diacritic, the keret is used.
When ‘l’ or ‘w’ is the second consonant of a cluster, it is represented by the “pasangan” forms, modified consonant symbols, written under the symbol for the first consonant of the cluster.
Special characters
Words borrowed from other languages such as Arabic or MalayMalay language
Malay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
are indicated by writing diacritic marks over similar sounding Javanese letters. On top of that, Javanese also uses special characters to write foreign names or words.
A: There are five special characters used to write non-Javanese vowels. The five vowels are represented by the following names.
- 1) Ali
- 2) Irawan
- 3) Umar
- 4) Eka
- 5) Oto
| Phoneme | /a/ | /i/ | /u/ | /lə/ | /rə/ | /e/ | /o/ |
| Symbol | |||||||
| Name | nga lelet | pa cerek |
B: There are five special characters used to write non-Javanese consonants. These consonants are /x/, /dʒ/, /f/, /ɣ/, and /z/.
Numbers
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 |
The Javanese numeral system
Numeral system
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers, that is a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using graphemes or symbols in a consistent manner....
has its own script but they often use the Arabic number system. In the Javanese Script, only numbers 0–9 are represented.
0 nol
1 siji
2 loro
3 telu
4 papat
5 lima
6 enem
7 pitu
8 wolu
9 sanga
When writing numbers greater than 9, simply combine the above numbers, as one would using the Arabic system. For example, to write 21, simply write the characters loro siji. Similarly, the number 90 would be the characters sanga nol.
Since some of the characters for the numbers are very similar to the characters for syllables, numbers that show up in Javanese texts are indicated by special 'numeral markers' both before and after the number. For example,
text ....... numeral marker telu siji numeral marker .......... text
Punctuation
With the introduction of the new Javanese script (carakan script), different punctuation marks were also introduced. Punctuations can be divided into two categories: primary and special. Primary punctuation includes:- 1) the commaCommaA comma is a type of punctuation mark . The word comes from the Greek komma , which means something cut off or a short clause.Comma may also refer to:* Comma , a type of interval in music theory...
“pada-lungsi”,
- 2) the periodFull stopA full stop is the punctuation mark commonly placed at the end of sentences. In American English, the term used for this punctuation is period. In the 21st century, it is often also called a dot by young people...
“pada-lingsa”,
- 3) colonColon (punctuation)The colon is a punctuation mark consisting of two equally sized dots centered on the same vertical line.-Usage:A colon informs the reader that what follows the mark proves, explains, or lists elements of what preceded the mark....
or quotation marks “pada-handhegging-celathu”, and
- 4) to introduce a new sentence or paragraph “pada-bab”.
Special punctuation includes:
- 1) the “pada-luhur” to introduce a letter to a person of lower rank;
- 2) the “pada-madya” to introduce a letter to an equal; the “pada-handhap” to introduce a letter to a person of higher rank;
- 3) the “purwa-pada” to introduce a poem; the”madya-pada” to indicate a new song in a poem;
- 4) and the “wasana-pada” to indicate the end of a poem.
Two special rules apply to the usage of the comma, and the period.
1.The comma is not needed after a consonant-ending word that is represented by a pangku
2.The comma is used instead of the period after a consonant-ending word that is represented by a pangku
Capitalization
Javanese script has seven "capital" letters called the aksara murdha that are used for the names of highly respected persons and places. The first letter of the name is usually capitalized; however, all the letters could be capitalized if possible. Also, if an aksara murdha is not available for the first letter, the second letter is capitalized. If the second letter does not have an aksara murdha either, the third letter is capitalized, and so on. Note that the capital letters are not used to indicate the beginnings of sentences.Alphabet as poem
The alphabet itself forms a poem, and a perfect pangramPangram
A pangram , or holoalphabetic sentence, is a sentence using every letter of the alphabet at least once. Pangrams have been used to display typefaces, test equipment, and develop skills in handwriting, calligraphy, and keyboarding...
, of which the line-by-line translation is as follows:
Hana caraka There (were) two messengers
data sawala (They) had animosity (among each other)
padha jayanya (They were) equally powerful (in fight)
maga bathanga Here are the corpses.
in detail:
hana / ana = there were/was
caraka = messenger (actually, 'one who is loyal to and trusted by someone')
data = have/has
sawala = difference (regarding a matter)
padha = same, equal
jayanya = 'their power', 'jaya' could mean 'glory' as well
maga = 'here'
bathanga = corpses
Modified usage by Sundanese people
Javanese script was also used by some Sundanese peopleSundanese people
The Sundanese are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Indonesian island of Java. They number approximately 31 million, and are the second most populous of all the nation's ethncities. The Sundanese are predominantly Muslim...
to write the Sundanese language
Sundanese language
Sundanese is the language of about 27 million people from the western third of Java or about 15% of the Indonesian population....
, but the script was simplified and called Cacarakan instead. Cacarakan differs from Carakan by omitting the dha and tha, thus only:
ha, na, ca, ra, ka, da, ta, sa, wa, la, pa, ja, ya, nya, ma, ga, ba, nga.
Similarities with the Balinese script
The Javanese and Balinese scriptBalinese script
The Balinese alphabet is an abugida that was used to write the Balinese language, an Austronesian language spoken by about three million people on the Indonesian island of Bali. The use of the Balinese script has mostly been replaced by the Roman alphabet. Although it is learned in school, few...
s are essentially typographic variants.
 |
 |
| Javanese script | Balinese script |
Unicode
Javanese script was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in October, 2009 with the release of version 5.2.
The Unicode block for Javanese is U+A980–U+A9DF. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points:
Further reading
There are very few items available in English about Javanese script; however, the following give some introduction:- Gallop, Annabel Teh. Golden letters: writing traditions of Indonesia = Surat emas: budaya tulis di Indonesia (with Bernard Arps). London: British Library; Jakarta: Yayasan Lontar, c1991. ISBN 9798083067
- Pigeaud, Theodore G. Th. Javanese and Balinese manuscripts and some codices written in related idioms spoken in Java and Bali: descriptive catalogue, with examples of Javanese script, introductory chapters, a general index of names and subjects Wiesbaden: Steiner, 1975. ISBN 3515019642
See also
- History of the alphabetHistory of the alphabetThe origins of the alphabet are unknown, but there are several theories as to how it developed. One popular proposal — the Proto-Sinaitic theory — is that the history of the alphabet began in Ancient Egypt, more than a millennium into the history of writing...
- The Brahmic script and its descendantsBrahmic familyThe Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
- Folk etymology relevant to Javanese etymology
- Balinese scriptBalinese scriptThe Balinese alphabet is an abugida that was used to write the Balinese language, an Austronesian language spoken by about three million people on the Indonesian island of Bali. The use of the Balinese script has mostly been replaced by the Roman alphabet. Although it is learned in school, few...
, a very similar script used in the neighbouring island of BaliBaliBali is an Indonesian island located in the westernmost end of the Lesser Sunda Islands, lying between Java to the west and Lombok to the east...
External links
- Hanacaraka Font & Resources (in Indonesian)
- Entry on Javanese at Omniglot.com -- A guide to writing systems
- Javanese script (hanacaraka) calligraphy service in the web
- Javanese Unicode font with SIL Graphite smart font technology
- Pallawa :: Javanese Script Software
- JawaTeX :: Latex Based Javanese Script Transliterator

