
History of the alphabet
Encyclopedia
The origins of the alphabet
are unknown, but there are several theories as to how it developed. One popular proposal — the Proto-Sinaitic theory — is that the history of the alphabet began in Ancient Egypt
, more than a millennium into the history of writing
. Under this theory, the alphabet was invented to represent the language of Semitic
workers in Egypt (see Middle Bronze Age alphabets
), and was at least influenced by the alphabetic principles of the Egyptian hieratic
script. If correct, nearly all alphabets in the world today either descend directly from this development or were inspired by its design.
The most widely used alphabet today is the Latin alphabet
. It derives from the Greek
, the first true alphabet in that it consistently assigns letters to both consonant
s and vowel
s. The Greek alphabet in turn was derived from the Phoenician alphabet
, which was an abjad
– a system where each symbol usually stands for a consonant.
and Egyptian hieroglyphs
. Both were well known in the part of the Middle East that produced the first widely used alphabet, the Phoenician
. There are signs that cuneiform was developing alphabetic properties in some of the languages it was adapted for, as was seen again later in the Old Persian cuneiform script
, but it now appears these developments were a sideline and not ancestral to the alphabet. The Byblos syllabary
has suggestive graphic similarities to both hieratic
Egyptian and to the Phoenician alphabet, but as it is undeciphered, little can be said about its role, if any, in the history of the alphabet.
s of their language, plus a 23rd that seems to have represented word-initial or word-final vowel
s. These glyphs were used as pronunciation guides for logogram
s, to write grammatical inflections, and, later, to transcribe loan words and foreign names. However, although alphabetic in nature, the system was not used for purely alphabetic writing except when transcribing foreign names. That is, while capable of being used as an alphabet, it was in fact nearly always used with a strong logographic component, presumably due to strong cultural attachment to the complex Egyptian script. A Semitic language is attested in Egyptian hieroglyphs from 2400 BCE, but glyphs have their Egyptian values and so were not ancestral to the alphabet. The first purely alphabetic script is thought to have been developed around 1850 BCE for Semitic
workers in the Sinai but giving mostly Egyptian glyphs Semitic values. Over the next five centuries it spread north, and all subsequent alphabets around the world have either descended from it, or been inspired by one of its descendants, with the possible exception of the Meroitic alphabet
, a 3rd century BCE adaptation of hieroglyphs in Nubia
to the south of Egypt – though even here many scholars suspect the influence of that first alphabet.
in the Sinai and date to perhaps 1850 BCE. The table below shows hypothetical prototypes of the Phoenician alphabet
in Egyptian hieroglyphs. Several correspondences have been proposed with Proto-Sinaitic letters.
This Semitic script adapted Egyptian hieroglyphs to write consonantal values based on the first sound of the Semitic name for the object depicted by the hieroglyph (the "acrophonic principle"). So, for example, the hieroglyph per ("house" in Egyptian) was used to write the sound [b] in Semitic, because [b] was the first sound in the Semitic word for "house", bayt. The script was used only sporadically, and retained its pictographic nature, for half a millennium, until adopted for governmental use in Canaan. The first Canaanite states to make extensive use of the alphabet were the Phoenicia
n city-state
s and so later stages of the Canaanite script are called Phoenician
. The Phoenician cities were maritime states at the center of a vast trade network and soon the Phoenician alphabet spread throughout the Mediterranean. Two variants of the Phoenician alphabet had major impacts on the history of writing: the Aramaic alphabet
and the Greek alphabet
. http://www.bbc.co.uk/dna/h2g2/A2451890
 The Phoenician and Aramaic alphabets, like their Egyptian prototype, represented only consonants, a system called an abjad
The Phoenician and Aramaic alphabets, like their Egyptian prototype, represented only consonants, a system called an abjad
. The Aramaic alphabet, which evolved from the Phoenician in the 7th century BCE as the official script of the Persian Empire, appears to be the ancestor of nearly all the modern alphabets of Asia:
 By at least the 8th century BCE the Greeks borrowed the Phoenician alphabet and adapted it to their own language, creating in the process the first "true" alphabet, in which vowels were accorded equal status with consonants. According to Greek legends transmitted by Herodotus
By at least the 8th century BCE the Greeks borrowed the Phoenician alphabet and adapted it to their own language, creating in the process the first "true" alphabet, in which vowels were accorded equal status with consonants. According to Greek legends transmitted by Herodotus
, the alphabet was brought from Phoenicia to Greece by Cadmos
. The letters of the Greek alphabet are the same as those of the Phoenician alphabet, and both alphabets are arranged in the same order. However, whereas separate letters for vowels would have actually hindered the legibility of Egyptian, Phoenician, or Hebrew, their absence was problematic for Greek, where vowel
s played a much more important role. The Greeks used for vowels some of the Phoenician letters representing consonants which weren't used in Greek speech. All of the names of the letters of the Phoenician alphabet started with consonants, and these consonants were what the letters represented, something called the acrophonic principle
.
However, several Phoenician consonants were absent in Greek, and thus several letter names came to be pronounced with initial vowels. Since the start of the name of a letter was expected to be the sound of the letter, in Greek these letters now stood for vowels. For example, the Greeks had no glottal stop or h, so the Phoenician letters ’alep and he became Greek alpha
and e (later renamed e psilon), and stood for the vowels /a/ and /e/ rather than the consonants /ʔ/ and /h/. As this fortunate development only provided for five or six (depending on dialect) of the twelve Greek vowels, the Greeks eventually created digraph
s and other modifications, such as ei, ou, and o (which became omega), or in some cases simply ignored the deficiency, as in long a, i, u.
Several varieties of the Greek alphabet developed. One, known as Western Greek or Chalcidian, was used west of Athens
and in southern Italy. The other variation, known as Eastern Greek
, was used in Asia Minor (also called Asian Greece i.e. present-day aegean Turkey
). The Athenians (c. 400 BC) adopted that latter variation and eventually the rest of the Greek-speaking world followed. After first writing right to left, the Greeks eventually chose to write from left to right, unlike the Phoenicians who wrote from right to left. Many Greek letters are similar to Phoenician, except the letter direction is reversed or changed, which can be the result of historical changes from right-to-left writing to boustrophedon
to left-to-right writing.
Descendants
Greek is in turn the source for all the modern scripts of Europe. The alphabet of the early western Greek dialects, where the letter eta
remained an h, gave rise to the Old Italic
and Roman alphabets. In the eastern Greek dialects, which did not have an /h/, eta stood for a vowel, and remains a vowel in modern Greek and all other alphabets derived from the eastern variants: Glagolitic
, Cyrillic
, Armenian
, Gothic
(which used both Greek and Roman letters), and perhaps Georgian
.
Although this description presents the evolution of scripts in a linear fashion, this is a simplification. For example, the Manchu alphabet
, descended from the abjad
s of West Asia, was also influenced by Korean hangul
, which was either independent (the traditional view) or derived from the abugida
s of South Asia. Georgian apparently derives from the Aramaic family, but was strongly influenced in its conception by Greek. A modified version of the Greek alphabet, using an additional half dozen demotic
hieroglyphs, was used to write Coptic
Egyptian. Then there is Cree syllabics
(an abugida
), which appears to be a fusion of Devanagari
and Pitman shorthand
developed by the missionary James Evans; the latter may be an independent invention, but likely has its ultimate origins in cursive Latin script.
 A tribe known as the Latins
A tribe known as the Latins
, who became known as the Romans, also lived in the Italian peninsula like the Western Greeks. From the Etruscans
, a tribe living in the first millennium BCE in central Italy
, and the Western Greeks, the Latins adopted writing in about the fifth century. In adopted writing from these two groups, the Latins dropped four characters from the Western Greek alphabet. They also adapted the Etruscan letter
F
, pronounced 'w,' giving it the 'f' sound, and the Etruscan S, which had three zigzag lines, was curved to make the modern S
. To represent the G
sound in Greek and the K
sound in Etruscan, the Gamma
was used. These changes produced the modern alphabet without the letters G
, J
, U
, W
, Y
, and Z
, as well as some other differences.
C
, K
, and Q
in the Roman alphabet could all be used to write both the /k/ and /g/ sounds; the Romans soon modified the letter C to make G, inserted it in seventh place, where Z
had been, to maintain the gematria
(the numerical sequence of the alphabet). Over the few centuries after Alexander the Great conquered the Eastern Mediterranean and other areas in the third century BCE, the Romans began to borrow Greek words, so they had to adapt their alphabet again in order to write these words. From the Eastern Greek alphabet, they borrowed Y
and Z
, which were added to the end of the alphabet because the only time they were used was to write Greek words.
The Anglo-Saxons
began using Roman letters to write Old English
as they converted to Christianity, following Augustine of Canterbury's
mission to Britain in the sixth century. Because the Runic
wen, which was first used to represent the sound 'w' and looked like a p that is narrow and triangular, was easy to confuse with an actual p, the 'w' sound began to be written using a double u. Because the u at the time looked like a v, the double u looked like two v's, W
was placed in the alphabet by V
. U
developed when people began to use the rounded U
when they meant the vowel u and the pointed V
when the meant the consonant V
. J
began as a variation of I
, in which a long tail was added to the final I
when there were several in a row. People began to use the J
for the consonant and the I
for the vowel by the fifteenth century, and it was fully accepted in the mid-seventeenth century.
located on Syria
’s northern coast. Tablets found there bear over one thousand cuneiform signs, but these signs are not Babylonian and there are only thirty distinct characters. About twelve of the tablets have the signs set out in alphabetic order. There are two orders found, one of which is nearly identical to the order used for Hebrew
, Greek
and Latin
, and a second order very similar to that used for Ethiopian
.
It is not known how many letters the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet
had nor what their alphabetic order was. Among its descendants, the Ugaritic alphabet
had 27 consonants, the South Arabian alphabet
s had 29, and the Phoenician alphabet
22. These scripts were arranged in two orders, an ABGDE order in Phoenician and an HMĦLQ order in the south; Ugaritic preserved both orders. Both sequences proved remarkably stable among the descendants of these scripts.
The letter names proved stable among the many descendants of Phoenician, including Samaritan
, Aramaic
, Syriac
, Hebrew
, and Greek alphabet
. However, they were abandoned in Arabic
and Latin
. The letter sequence continued more or less intact into Latin, Armenian
, Gothic
, and Cyrillic
, but was abandoned in Brahmi
, Runic
, and Arabic, although a traditional abjadi order remains or was re-introduced as an alternative in the latter.
The table is a schematic of the Phoenician alphabet and its descendants.
These 22 consonants account for the phonology of Northwest Semitic. Of the 29 consonant phonemes commonly-reconstructed for reconstructed Proto-Semitic consonants, seven are missing: the
interdental fricatives , the voiceless lateral fricatives , the voiced uvular fricative , and the distinction between uvular and pharyngeal voiceless fricatives , in Canaanite merged in . The six variant letters added in the Arabic alphabet
include these (except for , which survives as a separate phoneme in Ge'ez
):
> ;
> ;
> ;
> ;
> ;
>
script, which is unique in that, although it is clearly modeled after Arabic and perhaps other existing alphabets, it derives its letter forms from numerals. The Osmanya alphabet devised for Somali
in the 1920s
was co-official in Somalia with the Latin alphabet until 1972, and the forms of its consonants appear to be complete innovations.
Among alphabets that are not used as national scripts today, a few are clearly independent in their letter forms. The Zhuyin phonetic alphabet derives from Chinese character
s. The Santali alphabet of eastern India appears to be based on traditional symbols such as "danger" and "meeting place", as well as pictographs invented by its creator. (The names of the Santali letters are related to the sound they represent through the acrophonic principle, as in the original alphabet, but it is the final consonant or vowel of the name that the letter represents: le "swelling" represents e, while en "thresh grain" represents n.)
In early medieval Ireland, Ogham
consisted of tally marks, and the monumental inscriptions of the Old Persian Empire were written in an essentially alphabetic cuneiform script whose letter forms seem to have been created for the occasion.
derives from a prototypical Semitic abjad, for example, although this appears to be the case. And while manual alphabets are a direct continuation of the local written alphabet (both the British two-handed
and the French
/American one-handed
alphabets retain the forms of the Latin alphabet, as the Indian manual alphabet
does Devanagari
, and the Korean
does Hangul), Braille
, semaphore
, maritime signal flags
, and the Morse code
s are essentially arbitrary geometric forms. The shapes of the English Braille and semaphore letters, for example, are derived from the alphabetic order of the Latin alphabet, but not from the graphic forms of the letters themselves. Modern shorthand
also appears to be graphically unrelated. If it derives from the Latin alphabet, the connection has been lost to history.
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
are unknown, but there are several theories as to how it developed. One popular proposal — the Proto-Sinaitic theory — is that the history of the alphabet began in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
, more than a millennium into the history of writing
History of writing
The history of writing records the development of expressing language by letters or other marks. In the history of how systems of representation of language through graphic means have evolved in different human civilizations, more complete writing systems were preceded by proto-writing, systems of...
. Under this theory, the alphabet was invented to represent the language of Semitic
Semitic
In linguistics and ethnology, Semitic was first used to refer to a language family of largely Middle Eastern origin, now called the Semitic languages...
workers in Egypt (see Middle Bronze Age alphabets
Middle Bronze Age alphabets
Proto-Sinaitic is a Middle Bronze Age script attested in a very small collection of inscriptions at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula. Due to the extreme scarcity of Proto-Sinaitic signs, very little is known with certainty about the nature of the script...
), and was at least influenced by the alphabetic principles of the Egyptian hieratic
Hieratic
Hieratic refers to a cursive writing system that was used in the provenance of the pharaohs in Egypt and Nubia that developed alongside the hieroglyphic system, to which it is intimately related...
script. If correct, nearly all alphabets in the world today either descend directly from this development or were inspired by its design.
The most widely used alphabet today is the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
. It derives from the Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
, the first true alphabet in that it consistently assigns letters to both consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s and vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s. The Greek alphabet in turn was derived from the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, which was an abjad
Abjad
An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
– a system where each symbol usually stands for a consonant.
Pre-history
Two scripts are well attested from before the end of the fourth millennium BCE: Mesopotamian cuneiformCuneiform script
Cuneiform script )) is one of the earliest known forms of written expression. Emerging in Sumer around the 30th century BC, with predecessors reaching into the late 4th millennium , cuneiform writing began as a system of pictographs...
and Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
. Both were well known in the part of the Middle East that produced the first widely used alphabet, the Phoenician
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
. There are signs that cuneiform was developing alphabetic properties in some of the languages it was adapted for, as was seen again later in the Old Persian cuneiform script
Old Persian cuneiform script
Old Persian cuneiform is a semi-alphabetic cuneiform script that was the primary script for the Old Persian language. Texts written in this cuneiform were found in Persepolis, Susa, Hamadan, Armenia, and along the Suez Canal. They were mostly inscriptions from the time period of Darius the Great...
, but it now appears these developments were a sideline and not ancestral to the alphabet. The Byblos syllabary
Byblos syllabary
The Byblos syllabary, also known as the Pseudo-hieroglyphic script, Proto-Byblian, Proto-Byblic, or Byblic, is officially an undeciphered writing system, known from ten inscriptions found in Byblos. The inscriptions are engraved on bronze plates and spatulas, and carved in stone...
has suggestive graphic similarities to both hieratic
Hieratic
Hieratic refers to a cursive writing system that was used in the provenance of the pharaohs in Egypt and Nubia that developed alongside the hieroglyphic system, to which it is intimately related...
Egyptian and to the Phoenician alphabet, but as it is undeciphered, little can be said about its role, if any, in the history of the alphabet.
Predecessors
By 2700 BCE the ancient Egyptians had developed a set of some 22 hieroglyphs to represent the individual consonantConsonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s of their language, plus a 23rd that seems to have represented word-initial or word-final vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s. These glyphs were used as pronunciation guides for logogram
Logogram
A logogram, or logograph, is a grapheme which represents a word or a morpheme . This stands in contrast to phonograms, which represent phonemes or combinations of phonemes, and determinatives, which mark semantic categories.Logograms are often commonly known also as "ideograms"...
s, to write grammatical inflections, and, later, to transcribe loan words and foreign names. However, although alphabetic in nature, the system was not used for purely alphabetic writing except when transcribing foreign names. That is, while capable of being used as an alphabet, it was in fact nearly always used with a strong logographic component, presumably due to strong cultural attachment to the complex Egyptian script. A Semitic language is attested in Egyptian hieroglyphs from 2400 BCE, but glyphs have their Egyptian values and so were not ancestral to the alphabet. The first purely alphabetic script is thought to have been developed around 1850 BCE for Semitic
Semitic
In linguistics and ethnology, Semitic was first used to refer to a language family of largely Middle Eastern origin, now called the Semitic languages...
workers in the Sinai but giving mostly Egyptian glyphs Semitic values. Over the next five centuries it spread north, and all subsequent alphabets around the world have either descended from it, or been inspired by one of its descendants, with the possible exception of the Meroitic alphabet
Meroitic script
The Meroitic script is an alphabetic script originally derived from Egyptian hieroglyphs, used to write the Meroitic language of the Kingdom of Meroë/Kush. It was developed in the Napatan Period , and first appears in the 2nd century BCE. For a time, it was also possibly used to write the Nubian...
, a 3rd century BCE adaptation of hieroglyphs in Nubia
Nubia
Nubia is a region along the Nile river, which is located in northern Sudan and southern Egypt.There were a number of small Nubian kingdoms throughout the Middle Ages, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization...
to the south of Egypt – though even here many scholars suspect the influence of that first alphabet.
Semitic alphabet
The Proto-Sinaitic script of Egypt has yet to be fully deciphered. However, it may be alphabetic and probably records the Canaanite language. The oldest examples are found as graffitiGraffito (archaeology)
A Graffito , in an archaeological context, is a deliberate mark made by scratching or engraving on a large surface such as a wall. The marks may form an image or writing...
in the Sinai and date to perhaps 1850 BCE. The table below shows hypothetical prototypes of the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
in Egyptian hieroglyphs. Several correspondences have been proposed with Proto-Sinaitic letters.
| Possible Egyptian prototype | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phoenician Phoenician alphabet The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia... |
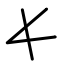 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
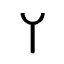 |
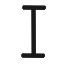 |
 |
 |
 |
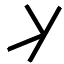 |
 |
 |
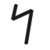 |
 |
 |
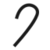 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
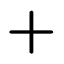 |
| Possible acrophony |
ox | bet house | gaml throwstick | digg fish | haw, hll He (letter) He is the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician , Aramaic, Hebrew , Syriac and Arabic . Its sound value is a voiceless glottal fricative .... hurrah |
waw Waw (letter) Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic .... hook |
zen, ziqq Zayin Zayin is the seventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic , Hebrew , Syriac and Perso-Arabic alphabet... handcuff |
courtyard | wheel | yad Yodh Yodh is the tenth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Yud , Syriac and Arabic... arm |
kap Kaph Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet... hand |
lamd Lamedh Lamed or Lamedh is the twelfth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Lamed and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is .The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Lambda , Latin L, and Cyrillic Л.-Origins:... goad |
mem Mem Mem is the thirteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic... water |
nun Nun (letter) Nun is the fourteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . It is the third letter in Thaana , pronounced as "noonu"... large fish |
samek fish | eye | bend | plant | qup monkey | head | šananuma SIMS - Last name :* Andrew Sims, American rapper, member of the Doomtree collective* Ashton Sims, Australian rugby league footballer* Charles Sims , British painter* Christopher A. Sims, American economist* Ernie Sims, NFL linebacker... bow |
taw Taw (letter) Taw, Tav or Taf is the twenty-second and last letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Taw and Arabic alphabet .Its original sound value is .... signature |
This Semitic script adapted Egyptian hieroglyphs to write consonantal values based on the first sound of the Semitic name for the object depicted by the hieroglyph (the "acrophonic principle"). So, for example, the hieroglyph per ("house" in Egyptian) was used to write the sound [b] in Semitic, because [b] was the first sound in the Semitic word for "house", bayt. The script was used only sporadically, and retained its pictographic nature, for half a millennium, until adopted for governmental use in Canaan. The first Canaanite states to make extensive use of the alphabet were the Phoenicia
Phoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
n city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
s and so later stages of the Canaanite script are called Phoenician
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
. The Phoenician cities were maritime states at the center of a vast trade network and soon the Phoenician alphabet spread throughout the Mediterranean. Two variants of the Phoenician alphabet had major impacts on the history of writing: the Aramaic alphabet
Aramaic alphabet
The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels....
and the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
. http://www.bbc.co.uk/dna/h2g2/A2451890
Descendants of the Aramaic abjad

Abjad
An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
. The Aramaic alphabet, which evolved from the Phoenician in the 7th century BCE as the official script of the Persian Empire, appears to be the ancestor of nearly all the modern alphabets of Asia:
- The modern Hebrew alphabetHebrew alphabetThe Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
started out as a local variant of Imperial Aramaic. (The original Hebrew alphabet has been retained by the SamaritansSamaritan alphabetThe Samaritan alphabet is used by the Samaritans for religious writings, including the Samaritan Pentateuch, writings in Samaritan Hebrew, and for commentaries and translations in Samaritan Aramaic and occasionally Arabic....
.) - The Arabic alphabetArabic alphabetThe Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
descended from Aramaic via the Nabataean alphabet of what is now southern JordanJordanJordan , officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan , Al-Mamlaka al-Urduniyya al-Hashemiyya) is a kingdom on the East Bank of the River Jordan. The country borders Saudi Arabia to the east and south-east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north and the West Bank and Israel to the west, sharing...
. - The Syriac alphabetSyriac alphabetThe Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
used after the 3rd century CE evolved, through Pahlavi and SogdianSogdian alphabetThe Sogdian alphabet was originally used for the Sogdian language, a language in the Iranian family used by the people of Sogdiana. The alphabet is derived from Syriac, the descendant script of the Aramaic alphabet. The Sogdian alphabet is one of three scripts used to write the Sogdian language,...
, into the alphabets of northern Asia, such as OrkhonOrkhon scriptThe Old Turkic script is the alphabet used by the Göktürk and other early Turkic Khanates from at least the 7th century to record the Old Turkic language. It was later used by the Uyghur Empire...
(probably), UyghurUyghur alphabetUyghur is a Turkic language spoken in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, administered by China, by the Uyghur people. It is a language with a long literary tradition, and has been written using numerous writing systems through time...
, MongolianMongolian alphabetMany alphabets have been devised for the Mongolian language over the centuries, and from a variety of scripts. The oldest, called simply the Mongolian script, has been the predominant script during most of Mongolian history, and is still in active use today in the Inner Mongolia region of China...
, and ManchuManchu alphabetThe Manchu alphabet was used for recording the now near-extinct Manchu language; a similar script is used today by the Xibe people, who speak a language descended from Manchu...
. - The Georgian alphabetGeorgian alphabetThe Georgian alphabet is the writing system used to write the Georgian language and other Kartvelian languages , and occasionally other languages of the Caucasus such as Ossetic and Abkhaz during the 1940s...
is of uncertain provenance, but appears to be part of the Persian-Aramaic (or perhaps the Greek) family.
Greek alphabet
Adoption
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
, the alphabet was brought from Phoenicia to Greece by Cadmos
Cadmus
Cadmus or Kadmos , in Greek mythology was a Phoenician prince, the son of king Agenor and queen Telephassa of Tyre and the brother of Phoenix, Cilix and Europa. He was originally sent by his royal parents to seek out and escort his sister Europa back to Tyre after she was abducted from the shores...
. The letters of the Greek alphabet are the same as those of the Phoenician alphabet, and both alphabets are arranged in the same order. However, whereas separate letters for vowels would have actually hindered the legibility of Egyptian, Phoenician, or Hebrew, their absence was problematic for Greek, where vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s played a much more important role. The Greeks used for vowels some of the Phoenician letters representing consonants which weren't used in Greek speech. All of the names of the letters of the Phoenician alphabet started with consonants, and these consonants were what the letters represented, something called the acrophonic principle
Acrophony
Acrophony is the naming of letters of an alphabetic writing system so that a letter's name begins with the letter itself. For example, Greek letter names are acrophonic: the names of the letters α, β, γ, δ, are spelled with the respective letters: ....
.
However, several Phoenician consonants were absent in Greek, and thus several letter names came to be pronounced with initial vowels. Since the start of the name of a letter was expected to be the sound of the letter, in Greek these letters now stood for vowels. For example, the Greeks had no glottal stop or h, so the Phoenician letters ’alep and he became Greek alpha
Alpha (letter)
Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 1. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Aleph...
and e (later renamed e psilon), and stood for the vowels /a/ and /e/ rather than the consonants /ʔ/ and /h/. As this fortunate development only provided for five or six (depending on dialect) of the twelve Greek vowels, the Greeks eventually created digraph
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used to write one phoneme or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined...
s and other modifications, such as ei, ou, and o (which became omega), or in some cases simply ignored the deficiency, as in long a, i, u.
Several varieties of the Greek alphabet developed. One, known as Western Greek or Chalcidian, was used west of Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
and in southern Italy. The other variation, known as Eastern Greek
History of the Greek alphabet
The history of the Greek alphabet starts with the adoption of Phoenician letter forms and continues to the present day. This article concentrates on the early period, before the codification of the now-standard Greek alphabet....
, was used in Asia Minor (also called Asian Greece i.e. present-day aegean Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
). The Athenians (c. 400 BC) adopted that latter variation and eventually the rest of the Greek-speaking world followed. After first writing right to left, the Greeks eventually chose to write from left to right, unlike the Phoenicians who wrote from right to left. Many Greek letters are similar to Phoenician, except the letter direction is reversed or changed, which can be the result of historical changes from right-to-left writing to boustrophedon
Boustrophedon
Boustrophedon , is a type of bi-directional text, mostly seen in ancient manuscripts and other inscriptions. Every other line of writing is flipped or reversed, with reversed letters. Rather than going left-to-right as in modern English, or right-to-left as in Arabic and Hebrew, alternate lines in...
to left-to-right writing.
Descendants
Greek is in turn the source for all the modern scripts of Europe. The alphabet of the early western Greek dialects, where the letter eta
Eta (letter)
Eta ) is the seventh letter of the Greek alphabet. Originally denoting a consonant /h/, its sound value in the classical Attic dialect of Ancient Greek was a long vowel , raised to in medieval Greek, a process known as itacism.In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 8...
remained an h, gave rise to the Old Italic
Old Italic alphabet
Old Italic refers to several now extinct alphabet systems used on the Italian Peninsula in ancient times for various Indo-European languages and non-Indo-European languages...
and Roman alphabets. In the eastern Greek dialects, which did not have an /h/, eta stood for a vowel, and remains a vowel in modern Greek and all other alphabets derived from the eastern variants: Glagolitic
Glagolitic alphabet
The Glagolitic alphabet , also known as Glagolitsa, is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. The name was not coined until many centuries after its creation, and comes from the Old Slavic glagolъ "utterance" . The verb glagoliti means "to speak"...
, Cyrillic
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
, Armenian
Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet is an alphabet that has been used to write the Armenian language since the year 405 or 406. It was devised by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader, and contained originally 36 letters. Two more letters, օ and ֆ, were added in the Middle Ages...
, Gothic
Gothic alphabet
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet for writing the Gothic language, created in the 4th century by Ulfilas for the purpose of translating the Christian Bible....
(which used both Greek and Roman letters), and perhaps Georgian
Georgian alphabet
The Georgian alphabet is the writing system used to write the Georgian language and other Kartvelian languages , and occasionally other languages of the Caucasus such as Ossetic and Abkhaz during the 1940s...
.
Although this description presents the evolution of scripts in a linear fashion, this is a simplification. For example, the Manchu alphabet
Manchu alphabet
The Manchu alphabet was used for recording the now near-extinct Manchu language; a similar script is used today by the Xibe people, who speak a language descended from Manchu...
, descended from the abjad
Abjad
An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel....
s of West Asia, was also influenced by Korean hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
, which was either independent (the traditional view) or derived from the abugida
Abugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
s of South Asia. Georgian apparently derives from the Aramaic family, but was strongly influenced in its conception by Greek. A modified version of the Greek alphabet, using an additional half dozen demotic
Demotic
Demotic may refer to:*Demotic Greek, a variety of the Greek language*Demotic , a script and stage of the Egyptian language...
hieroglyphs, was used to write Coptic
Coptic alphabet
The Coptic alphabet is the script used for writing the Coptic language. The repertoire of glyphs is based on the Greek alphabet augmented by letters borrowed from the Demotic and is the first alphabetic script used for the Egyptian language...
Egyptian. Then there is Cree syllabics
Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics
Canadian Aboriginal syllabic writing, or simply syllabics, is a family of abugidas used to write a number of Aboriginal Canadian languages of the Algonquian, Inuit, and Athabaskan language families....
(an abugida
Abugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
), which appears to be a fusion of Devanagari
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
and Pitman shorthand
Pitman Shorthand
Pitman shorthand is a system of shorthand for the English language developed by Englishman Sir Isaac Pitman , who first presented it in 1837. Like most systems of shorthand, it is a phonetic system; the symbols do not represent letters, but rather sounds, and words are, for the most part, written...
developed by the missionary James Evans; the latter may be an independent invention, but likely has its ultimate origins in cursive Latin script.
Latin alphabet

Latins
"Latins" refers to different groups of people and the meaning of the word changes for where and when it is used.The original Latins were an Italian tribe inhabiting central and south-central Italy. Through conquest by their most populous city-state, Rome, the original Latins culturally "Romanized"...
, who became known as the Romans, also lived in the Italian peninsula like the Western Greeks. From the Etruscans
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
, a tribe living in the first millennium BCE in central Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, and the Western Greeks, the Latins adopted writing in about the fifth century. In adopted writing from these two groups, the Latins dropped four characters from the Western Greek alphabet. They also adapted the Etruscan letter
Etruscan language
The Etruscan language was spoken and written by the Etruscan civilization, in what is present-day Italy, in the ancient region of Etruria and in parts of Lombardy, Veneto, and Emilia-Romagna...
F
F
F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club...
, pronounced 'w,' giving it the 'f' sound, and the Etruscan S, which had three zigzag lines, was curved to make the modern S
S
S is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent...
. To represent the G
G
G is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,...
sound in Greek and the K
K
K is the eleventh letter of the English and basic modern Latin alphabet.-History and usage:In English, the letter K usually represents the voiceless velar plosive; this sound is also transcribed by in the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA....
sound in Etruscan, the Gamma
Gamma
Gamma is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Gimel . Letters that arose from Gamma include the Roman C and G and the Cyrillic letters Ge Г and Ghe Ґ.-Greek:In Ancient Greek, gamma represented a...
was used. These changes produced the modern alphabet without the letters G
G
G is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,...
, J
J
Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography representing the sound .While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic...
, U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
, W
W
W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V...
, Y
Y
Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound...
, and Z
Z
Z is the twenty-sixth and final letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Name and pronunciation:In most dialects of English, the letter's name is zed , reflecting its derivation from the Greek zeta but in American English, its name is zee , deriving from a late 17th century English dialectal...
, as well as some other differences.
C
C
Ĉ or ĉ is a consonant in Esperanto orthography, representing the sound .Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for all four of its postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets...
, K
K
K is the eleventh letter of the English and basic modern Latin alphabet.-History and usage:In English, the letter K usually represents the voiceless velar plosive; this sound is also transcribed by in the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA....
, and Q
Q
Q is the seventeenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History :The Semitic sound value of Qôp was , a sound common to Semitic languages, but not found in English or most Indo-European ones...
in the Roman alphabet could all be used to write both the /k/ and /g/ sounds; the Romans soon modified the letter C to make G, inserted it in seventh place, where Z
Z
Z is the twenty-sixth and final letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Name and pronunciation:In most dialects of English, the letter's name is zed , reflecting its derivation from the Greek zeta but in American English, its name is zee , deriving from a late 17th century English dialectal...
had been, to maintain the gematria
Gematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
(the numerical sequence of the alphabet). Over the few centuries after Alexander the Great conquered the Eastern Mediterranean and other areas in the third century BCE, the Romans began to borrow Greek words, so they had to adapt their alphabet again in order to write these words. From the Eastern Greek alphabet, they borrowed Y
Y
Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound...
and Z
Z
Z is the twenty-sixth and final letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Name and pronunciation:In most dialects of English, the letter's name is zed , reflecting its derivation from the Greek zeta but in American English, its name is zee , deriving from a late 17th century English dialectal...
, which were added to the end of the alphabet because the only time they were used was to write Greek words.
The Anglo-Saxons
Anglo-Saxons
Anglo-Saxon is a term used by historians to designate the Germanic tribes who invaded and settled the south and east of Great Britain beginning in the early 5th century AD, and the period from their creation of the English nation to the Norman conquest. The Anglo-Saxon Era denotes the period of...
began using Roman letters to write Old English
Old English language
Old English or Anglo-Saxon is an early form of the English language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in parts of what are now England and southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century...
as they converted to Christianity, following Augustine of Canterbury's
Augustine of Canterbury
Augustine of Canterbury was a Benedictine monk who became the first Archbishop of Canterbury in the year 597...
mission to Britain in the sixth century. Because the Runic
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
wen, which was first used to represent the sound 'w' and looked like a p that is narrow and triangular, was easy to confuse with an actual p, the 'w' sound began to be written using a double u. Because the u at the time looked like a v, the double u looked like two v's, W
W
W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V...
was placed in the alphabet by V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
. U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
developed when people began to use the rounded U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
when they meant the vowel u and the pointed V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
when the meant the consonant V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
. J
J
Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography representing the sound .While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic...
began as a variation of I
I
I is the ninth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:In Semitic, the letter may have originated in a hieroglyph for an arm that represented a voiced pharyngeal fricative in Egyptian, but was reassigned to by Semites, because their word for "arm" began with that sound...
, in which a long tail was added to the final I
I
I is the ninth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:In Semitic, the letter may have originated in a hieroglyph for an arm that represented a voiced pharyngeal fricative in Egyptian, but was reassigned to by Semites, because their word for "arm" began with that sound...
when there were several in a row. People began to use the J
J
Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography representing the sound .While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic...
for the consonant and the I
I
I is the ninth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:In Semitic, the letter may have originated in a hieroglyph for an arm that represented a voiced pharyngeal fricative in Egyptian, but was reassigned to by Semites, because their word for "arm" began with that sound...
for the vowel by the fifteenth century, and it was fully accepted in the mid-seventeenth century.
Letter names and sequence of some alphabets
The order of the letters of the alphabet is attested from the fourteenth century BCE, in a place called UgaritUgarit
Ugarit was an ancient port city in the eastern Mediterranean at the Ras Shamra headland near Latakia, Syria. It is located near Minet el-Beida in northern Syria. It is some seven miles north of Laodicea ad Mare and approximately fifty miles east of Cyprus...
located on Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
’s northern coast. Tablets found there bear over one thousand cuneiform signs, but these signs are not Babylonian and there are only thirty distinct characters. About twelve of the tablets have the signs set out in alphabetic order. There are two orders found, one of which is nearly identical to the order used for Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
, Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
and Latin
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, and a second order very similar to that used for Ethiopian
Ge'ez alphabet
Ge'ez , also called Ethiopic, is a script used as an abugida for several languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea but originated in an abjad used to write Ge'ez, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian and Eritrean Orthodox Church...
.
It is not known how many letters the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet
Proto-Sinaitic alphabet
Proto-Sinaitic is a Middle Bronze Age script attested in a very small collection of inscriptions at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula. Due to the extreme scarcity of Proto-Sinaitic signs, very little is known with certainty about the nature of the script...
had nor what their alphabetic order was. Among its descendants, the Ugaritic alphabet
Ugaritic alphabet
The Ugaritic script is a cuneiform abjad used from around 1400 BCE for Ugaritic, an extinct Northwest Semitic language, and discovered in Ugarit , Syria, in 1928. It has 30 letters...
had 27 consonants, the South Arabian alphabet
South Arabian alphabet
The ancient Yemeni alphabet branched from the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet in about the 9th century BC. It was used for writing the Yemeni Old South Arabic languages of the Sabaean, Qatabanian, Hadramautic, Minaean, Himyarite, and proto-Ge'ez in Dʿmt...
s had 29, and the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
22. These scripts were arranged in two orders, an ABGDE order in Phoenician and an HMĦLQ order in the south; Ugaritic preserved both orders. Both sequences proved remarkably stable among the descendants of these scripts.
The letter names proved stable among the many descendants of Phoenician, including Samaritan
Samaritan alphabet
The Samaritan alphabet is used by the Samaritans for religious writings, including the Samaritan Pentateuch, writings in Samaritan Hebrew, and for commentaries and translations in Samaritan Aramaic and occasionally Arabic....
, Aramaic
Aramaic alphabet
The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels....
, Syriac
Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
, Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
, and Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
. However, they were abandoned in Arabic
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
and Latin
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
. The letter sequence continued more or less intact into Latin, Armenian
Armenian alphabet
The Armenian alphabet is an alphabet that has been used to write the Armenian language since the year 405 or 406. It was devised by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, an Armenian linguist and ecclesiastical leader, and contained originally 36 letters. Two more letters, օ and ֆ, were added in the Middle Ages...
, Gothic
Gothic alphabet
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet for writing the Gothic language, created in the 4th century by Ulfilas for the purpose of translating the Christian Bible....
, and Cyrillic
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
, but was abandoned in Brahmi
Brāhmī script
Brāhmī is the modern name given to the oldest members of the Brahmic family of scripts. The best-known Brāhmī inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in north-central India, dated to the 3rd century BCE. These are traditionally considered to be early known examples of Brāhmī writing...
, Runic
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
, and Arabic, although a traditional abjadi order remains or was re-introduced as an alternative in the latter.
The table is a schematic of the Phoenician alphabet and its descendants.
| nr. | Reconstruction | IPA International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic... |
value | Ugaritic Ugaritic alphabet The Ugaritic script is a cuneiform abjad used from around 1400 BCE for Ugaritic, an extinct Northwest Semitic language, and discovered in Ugarit , Syria, in 1928. It has 30 letters... |
Phoenician Phoenician alphabet The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia... |
Hebrew Hebrew alphabet The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two... |
Arabic Arabic alphabet The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has... |
Greek Greek alphabet The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega... |
Latin Latin alphabet The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome... |
Cyrillic Cyrillic alphabet The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School... |
Runic Runic alphabet The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | "ox" | /ʔ/ | 1 | 𐎀 | 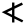 |
Α | A A A is the first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is similar to the Ancient Greek letter Alpha, from which it derives.- Origins :... |
А | ᚨ Ansuz rune The a-rune , Younger Futhark was probably called *ansuz in Proto-Germanic, to which the Norse name Æsir is attributed.The shape of the rune is likely from Neo-Etruscan a , like Latin A ultimately from Phoenician aleph.... |
||
| 2 | "house" | /b/ | 2 | 𐎁 | 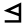 |
Β Beta (letter) Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative .... |
B B B is the second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is used to represent a variety of bilabial sounds , most commonly a voiced bilabial plosive.-History:... |
В, Б | ᛒ | ||
| 3 | "throwstick" | /ɡ/ | 3 | 𐎂 | 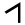 |
Γ | C C Ĉ or ĉ is a consonant in Esperanto orthography, representing the sound .Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for all four of its postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets... , G G G is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,... |
Г | ᚲ | ||
| 4 | "door" / "fish" | /d/ | 4 | 𐎄 | 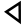 |
Δ | D D D is the fourth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History :The Semitic letter Dâlet may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are various Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek, and Latin, the letter represented ; in the... |
Д | |||
| 5 | "window" / "jubilation Hallel Hallel is a Jewish prayer—a verbatim recitation from Psalms 113–118, which is used for praise and thanksgiving that is recited by observant Jews on Jewish holidays.-Holy days:... " |
/h/ | 5 | 𐎅 | 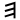 |
Ε | E E E is the fifth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is the most commonly used letter in the Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Hungarian, Latin, Norwegian, Spanish, and Swedish languages.-History:... |
Е, Є | |||
| 6 | "hook" | /β/ | 6 | 𐎆 | 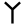 |
, Υ | F F F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club... , V V V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details.... , Y Y Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound... |
У | ᚢ | ||
| 7 | "weapon" / "manacle" | /z/ | 7 | 𐎇 | 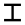 |
Ζ | Z Z Z is the twenty-sixth and final letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Name and pronunciation:In most dialects of English, the letter's name is zed , reflecting its derivation from the Greek zeta but in American English, its name is zee , deriving from a late 17th century English dialectal... |
З | |||
| 8 | "thread" / "fence"? | /ħ/ / /x/ | 8 | 𐎈 |  |
Η | H H H .) is the eighth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The Semitic letter ⟨ח⟩ most likely represented the voiceless pharyngeal fricative . The form of the letter probably stood for a fence or posts.... |
И | ᚺ | ||
| 9 | "wheel" | /tˤ/ | 9 | 𐎉 |  |
Θ | Ѳ | ||||
| 10 | "arm" | /j/ | 10 | 𐎊 | 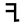 |
Ι | I I I is the ninth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:In Semitic, the letter may have originated in a hieroglyph for an arm that represented a voiced pharyngeal fricative in Egyptian, but was reassigned to by Semites, because their word for "arm" began with that sound... |
І | ᛁ | ||
| 11 | "hand" | /k/ | 20 | 𐎋 | 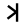 |
Κ | K K K is the eleventh letter of the English and basic modern Latin alphabet.-History and usage:In English, the letter K usually represents the voiceless velar plosive; this sound is also transcribed by in the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA.... |
К | |||
| 12 | "goad" | /l/ | 30 | 𐎍 | 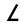 |
Λ | L L Ł or ł, described in English as L with stroke, is a letter of the Polish, Kashubian, Sorbian, Łacinka , Łatynka , Wilamowicean, Navajo, Dene Suline, Inupiaq, Zuni, Hupa, and Dogrib alphabets, several proposed alphabets for the Venetian language, and the ISO 11940 romanization of the Thai alphabet... |
Л | ᛚ | ||
| 13 | "waters" | /m/ | 40 | 𐎎 | 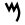 |
Μ | M M M is the thirteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem, via the Greek Mu . Semitic Mem probably originally pictured water... |
М | |||
| 14 | "snake" / "fish" | /n/ | 50 | 𐎐 | 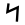 |
Ν | N N N is the fourteenth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History of the forms :One of the most common hieroglyphs, snake, was used in Egyptian writing to stand for a sound like English ⟨J⟩, because the Egyptian word for "snake" was djet... |
Н | |||
| 15 | "support" / "fish" ? | /s/ | 60 | 𐎒 | 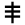 |
– | Ξ, (Χ) | (X X X is the twenty-fourth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Uses:In mathematics, x is commonly used as the name for an independent variable or unknown value. The usage of x to represent an independent or unknown variable can be traced back to the Arabic word šay شيء = “thing,” used in Arabic... ) |
Ѯ, (Х) | ||
| 16 | "eye" | /ʕ/ | 70 | 𐎓 |  |
Ο | O O O is the fifteenth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.The letter was derived from the Semitic `Ayin , which represented a consonant, probably , the sound represented by the Arabic letter ع called `Ayn. This Semitic letter in its original form seems to have been inspired by a... |
О | |||
| 17 | "mouth" / "corner" | /p/ | 80 | 𐎔 | 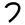 |
Π | P P P is the sixteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Usage:In English and most other European languages, P is a voiceless bilabial plosive. Both initial and final Ps can be combined with many other discrete consonants in English words... |
П | |||
| 18 | "plant" | /sˤ/ | 90 | 𐎕 | 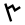 |
Ц, Ч | |||||
| 19 | "cord"? | /kˤ/ | 100 | 𐎖 | 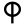 |
Q Q Q is the seventeenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History :The Semitic sound value of Qôp was , a sound common to Semitic languages, but not found in English or most Indo-European ones... |
Ҁ | ||||
| 20 | "head" | /r/ / /ɾ/ | 200 | 𐎗 | 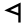 |
Ρ | R R R is the eighteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The original Semitic letter may have been inspired by an Egyptian hieroglyph for tp, "head". It was used for by Semites because in their language, the word for "head" was rêš . It developed into Greek Ρ and Latin R... |
Р | ᚱ | ||
| 21 | "tooth" / "sun Shamash Shamash was a native Mesopotamian deity and the sun god in the Akkadian, Assyrian and Babylonian pantheons. Shamash was the god of justice in Babylonia and Assyria, corresponding to Sumerian Utu... " |
/ʃ/ | 300 | 𐎌 |  |
Σ | S S S is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent... |
С, Ш | ᛊ | ||
| 22 | "mark" | /t/ | 400 | 𐎚 |  |
Τ | T T T is the 20th letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second most common letter in the English language.- History :Taw was the last letter of the Western Semitic and Hebrew alphabets... |
Т | ᛏ | ||
These 22 consonants account for the phonology of Northwest Semitic. Of the 29 consonant phonemes commonly-reconstructed for reconstructed Proto-Semitic consonants, seven are missing: the
interdental fricatives , the voiceless lateral fricatives , the voiced uvular fricative , and the distinction between uvular and pharyngeal voiceless fricatives , in Canaanite merged in . The six variant letters added in the Arabic alphabet
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
include these (except for , which survives as a separate phoneme in Ge'ez
Ge'ez alphabet
Ge'ez , also called Ethiopic, is a script used as an abugida for several languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea but originated in an abjad used to write Ge'ez, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian and Eritrean Orthodox Church...
):
> ;
> ;
> ;
> ;
> ;
>
Graphically independent alphabets
The only modern national alphabet that has not been graphically traced back to the Canaanite alphabet is the MaldivianThaana
Thaana, Taana or Tāna is the modern writing system of the Divehi language spoken in the Maldives. Taana has characteristics of both an abugida and a true alphabet , with consonants derived from indigenous and Arabic numerals, and vowels derived from the vowel diacritics of the Arabic abjad...
script, which is unique in that, although it is clearly modeled after Arabic and perhaps other existing alphabets, it derives its letter forms from numerals. The Osmanya alphabet devised for Somali
Somali language
The Somali language is a member of the East Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family. Its nearest relatives are Afar and Oromo. Somali is the best documented of the Cushitic languages, with academic studies beginning before 1900....
in the 1920s
1920s
File:1920s decade montage.png|From left, clockwise: Third Tipperary Brigade Flying Column No. 2 under Sean Hogan during the Irish Civil War; Prohibition agents destroying barrels of alcohol in accordance to the 18th amendment, which made alcoholic beverages illegal throughout the entire decade; In...
was co-official in Somalia with the Latin alphabet until 1972, and the forms of its consonants appear to be complete innovations.
Among alphabets that are not used as national scripts today, a few are clearly independent in their letter forms. The Zhuyin phonetic alphabet derives from Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s. The Santali alphabet of eastern India appears to be based on traditional symbols such as "danger" and "meeting place", as well as pictographs invented by its creator. (The names of the Santali letters are related to the sound they represent through the acrophonic principle, as in the original alphabet, but it is the final consonant or vowel of the name that the letter represents: le "swelling" represents e, while en "thresh grain" represents n.)
In early medieval Ireland, Ogham
Ogham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
consisted of tally marks, and the monumental inscriptions of the Old Persian Empire were written in an essentially alphabetic cuneiform script whose letter forms seem to have been created for the occasion.
Alphabets in other media
Changes to a new writing medium sometimes caused a break in graphical form, or make the relationship difficult to trace. It is not immediately obvious that the cuneiform Ugaritic alphabetUgaritic alphabet
The Ugaritic script is a cuneiform abjad used from around 1400 BCE for Ugaritic, an extinct Northwest Semitic language, and discovered in Ugarit , Syria, in 1928. It has 30 letters...
derives from a prototypical Semitic abjad, for example, although this appears to be the case. And while manual alphabets are a direct continuation of the local written alphabet (both the British two-handed
Two-handed manual alphabet
Several manual alphabets in use around the world employ two hands for some or all of the letters.- BANZSL alphabet :This alphabet is used in the BANZSL group of sign languages. It has been used in British Sign Language and Auslan since at least the 19th century, and in New Zealand Sign Language...
and the French
French Sign Language
French Sign Language is the sign language of the deaf in the nation of France. According to Ethnologue, it has 50,000 to 100,000 native signers....
/American one-handed
American Sign Language alphabet
The American Manual Alphabet is a manual alphabet that augments the vocabulary of American Sign Language when spelling individual letters of a word is the preferred or only option, such as with proper names or the titles of works...
alphabets retain the forms of the Latin alphabet, as the Indian manual alphabet
Indian Sign Language
Indo-Pakistani Sign Language is the predominant sign language variety in South Asia, used by at least several hundred thousand deaf signers...
does Devanagari
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
, and the Korean
Korean manual alphabet
The Korean manual alphabet is used by the Deaf in South Korea who speak Korean Sign Language. It is a one-handed alphabet that mimics the shapes of the letters in hangul, and is used when signing Korean as well as being integrated into KSL.-Consonants:...
does Hangul), Braille
Braille
The Braille system is a method that is widely used by blind people to read and write, and was the first digital form of writing.Braille was devised in 1825 by Louis Braille, a blind Frenchman. Each Braille character, or cell, is made up of six dot positions, arranged in a rectangle containing two...
, semaphore
Flag semaphore
Semaphore Flags is the system for conveying information at a distance by means of visual signals with hand-held flags, rods, disks, paddles, or occasionally bare or gloved hands. Information is encoded by the position of the flags; it is read when the flag is in a fixed position...
, maritime signal flags
International maritime signal flags
The system of international maritime signal flags is one system of flag signals representing individual letters of the alphabet in signals to or from ships...
, and the Morse code
Morse code
Morse code is a method of transmitting textual information as a series of on-off tones, lights, or clicks that can be directly understood by a skilled listener or observer without special equipment...
s are essentially arbitrary geometric forms. The shapes of the English Braille and semaphore letters, for example, are derived from the alphabetic order of the Latin alphabet, but not from the graphic forms of the letters themselves. Modern shorthand
Shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed or brevity of writing as compared to a normal method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek stenos and graphē or graphie...
also appears to be graphically unrelated. If it derives from the Latin alphabet, the connection has been lost to history.
See also
- History of writingHistory of writingThe history of writing records the development of expressing language by letters or other marks. In the history of how systems of representation of language through graphic means have evolved in different human civilizations, more complete writing systems were preceded by proto-writing, systems of...
- List of inventors of writing systems
- List of languages by first written accounts
- History of the Arabic alphabetHistory of the Arabic alphabetThe history of the Arabic alphabet shows that this abjad has changed since it arose. It is thought that the Arabic alphabet is a derivative of the Nabataean variation of the Aramaic alphabet, which descended from the Phoenician alphabet, which among others gave rise to the Hebrew alphabet and the...
- History of the Latin alphabetHistory of the Latin alphabetThe Latin alphabet is the main writing system in use in the Western world and is the most widely used alphabet writing system in the world. Being the standard script of the English language it is often referred to simply as "the alphabet" in English...
- History of the Hebrew alphabetHistory of the Hebrew alphabet-History:According to contemporary scholars, the original Hebrew script developed alongside others in the region during the course of the late second and first millennia BCE; it is closely related to the Phoenician script, which itself probably gave rise to the use of alphabetic writing in Greece...
- History of the Greek alphabetHistory of the Greek alphabetThe history of the Greek alphabet starts with the adoption of Phoenician letter forms and continues to the present day. This article concentrates on the early period, before the codification of the now-standard Greek alphabet....
- Runic alphabetRunic alphabetThe runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
Further reading
- Peter T. Daniels, William Bright (eds.), 1996. The World's Writing Systems, ISBN 0-19-507993-0.
- David DiringerDavid DiringerDavid Diringer was a British linguist, palaeographer and writer. He was the author of several well-known books about writing systems.- Bibliography :* The Alphabet: A Key to the History of Mankind; ISBN 81-215-0748-0...
, History of the Alphabet, 1977, ISBN 0-905418-12-3. - Stephen R. Fischer, A History of Writing 2005 Reaktion Books CN 136481
- Joel M. Hoffman, In the Beginning: A Short History of the Hebrew Language, 2004, ISBN 0-8147-3654-8.
- Robert K. Logan, The Alphabet Effect: The Impact of the Phonetic Alphabet on the Development of Western Civilization, New York: William Morrow and Company, Inc., 1986.
- Joseph Naveh, Early History of the Alphabet: an Introduction to West Semitic Epigraphy and Palaeography (Magnes Press – Hebrew University, Jerusalem, 1982)
- Barry B. Powell, Homer and Origin of the Greek Alphabet, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1991.
- B.L. Ullman, "The Origin and Development of the Alphabet," American Journal of Archaeology 31, No. 3 (Jul., 1927): 311-328.
External links
- Animated examples of how the English alphabet evolved by Robert Fradkin, University of Maryland
- The Greek alphabet on h2g2H2g2h2g2 is a British-based collaborative online encyclopedia project engaged in the construction of, in its own words, "an unconventional guide to life, the universe, and everything", in the spirit of the fictional publication The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy from the science fiction comedy series...
- The Development of the Western Alphabet on h2g2H2g2h2g2 is a British-based collaborative online encyclopedia project engaged in the construction of, in its own words, "an unconventional guide to life, the universe, and everything", in the spirit of the fictional publication The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy from the science fiction comedy series...
- Site by Micheal W. Palmer about the Greek alphabet
- "The Alphabet – its creation and development" on BBC Radio 4BBC Radio 4BBC Radio 4 is a British domestic radio station, operated and owned by the BBC, that broadcasts a wide variety of spoken-word programmes, including news, drama, comedy, science and history. It replaced the BBC Home Service in 1967. The station controller is currently Gwyneth Williams, and the...
’s In Our TimeIn Our Time (BBC Radio 4)In Our Time is a live BBC radio discussion series exploring the history of ideas, presented by Melvyn Bragg since 15 October 1998.. It is one of BBC radio's most successful discussion programmes, acknowledged to have "transformed the landscape for serious ideas at peak listening time"...
featuring Eleanor Robson, Alan Millard, Rosalind Thomas

