
Gothic alphabet
Encyclopedia
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet
for writing the Gothic language
, created in the 4th century by Ulfilas
(or Wulfila) for the purpose of translating the Christian Bible.
The alphabet is essentially an uncial form of the Greek alphabet
, with a few additional letters to account for Gothic phonology: Latin
F
, two Runic
letters to distinguish the /j/ and /w/ glides
from vocalic /i/ and /u/, and the ƕair letter to express the Gothic labiovelar.
for this purpose, as it was heavily connected with heathen
beliefs and customs. Also, the Greek-based script probably helped to integrate the Gothic nation into the dominant Greco-Roman
culture around the Black Sea
. The individual letters, however, still bear names derived from those of their Runic equivalents.
In past centuries, some authors asserted that Greek-like letters were already in use among Germanic tribes long before Ulfilas. Johannes Aventinus
(c. 1525) even ascribed them to the mythical progenitor Tuisto, claiming the Greeks had really stolen the idea from them, and not the Phoenicians. Such theories enjoy no scholarly support today, as all available evidence traces the development of alphabetic writing to the Middle East, although there is some testimony by classical Roman sources, as well as a few assorted tombstones, indicating that Greek letters were sometimes used in Germany, in addition to Gaul, by the time of Julius Caesar (1st century BC).
are not used in current English: the Runic þ
(representing /θ
/), and ƕ
(representing /xʷ
/).
As with the Greek alphabet, Gothic letters were also assigned numerical values. When used as numerals, letters were written either between two dots (•𐌹𐌱• = 12) or with an overline (𐌹𐌱 = 12). Two letters, 𐍁 (90) and 𐍊 (900), have no phonetic value.
The letter names are recorded in a 9th century manuscript of Alcuin
(Codex Vindobonensis 795
). Most of them seem to be Gothic forms of names also appearing in the rune poem
s. The names are given in their attested forms followed by the reconstructed Gothic forms and their meanings.
Most of the letters have been taken over directly from the Greek alphabet
, though a few have been created and/or modified from Latin or Runic letters to express unique phonological features of Gothic. These are:
𐍂 (r), 𐍃 (s) and 𐍆 (f) appear to be derived from their Latin equivalents rather than from the Greek, although the equivalent Runic letters (ᚱ
, ᛋ
and ᚠ), assumed to have been part of the Gothic futhark, likely played some role in this choice.
𐍇 (x) is only used in proper names and loanwords containing Greek Χ
(xristus "Christ", galiugaxristus "Pseudo-Christ", zaxarias "Zacharias", aivxaristia "eucharist").
Regarding the letters' numeric values, most correspond to those of the Greek numerals
. Gothic 𐌵 takes the place of Ϝ
(6), 𐌾 takes the place of ξ (60), 𐌿 that of Ο
(70), and 𐍈 that of ψ
(700).
include a trema placed on 𐌹 i, transliterated as ï, in general applied to express diaeresis
, the Interpunct
(·) and colon
(:) as well as overline
s to indicate sigla
(such as xaus for xristaus) and numerals.

Standard in March, 2001 with the release of version 3.1.
The Unicode block for Gothic is U+10330–U+1034F in the Supplementary Multilingual Plane. As older software that uses UCS-2 (the predecessor of UTF-16) assumes that all Unicode codepoints can be expressed as 16 bit
numbers (U+FFFF or lower, the Basic Multilingual Plane), problems may be encountered using the Gothic alphabet Unicode range and others outside of the Basic Multilingual Plane.
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
for writing the Gothic language
Gothic language
Gothic is an extinct Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizable Text corpus...
, created in the 4th century by Ulfilas
Ulfilas
Ulfilas, or Gothic Wulfila , bishop, missionary, and Bible translator, was a Goth or half-Goth and half-Greek from Cappadocia who had spent time inside the Roman Empire at the peak of the Arian controversy. Ulfilas was ordained a bishop by Eusebius of Nicomedia and returned to his people to work...
(or Wulfila) for the purpose of translating the Christian Bible.
The alphabet is essentially an uncial form of the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
, with a few additional letters to account for Gothic phonology: Latin
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
F
F
F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club...
, two Runic
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
letters to distinguish the /j/ and /w/ glides
Semivowel
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:...
from vocalic /i/ and /u/, and the ƕair letter to express the Gothic labiovelar.
Origin
Ulfilas is thought to have consciously chosen to avoid the use of the older Runic alphabetRunic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
for this purpose, as it was heavily connected with heathen
Germanic paganism
Germanic paganism refers to the theology and religious practices of the Germanic peoples of north-western Europe from the Iron Age until their Christianization during the Medieval period...
beliefs and customs. Also, the Greek-based script probably helped to integrate the Gothic nation into the dominant Greco-Roman
Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman culture, or the term Greco-Roman , when used as an adjective, as understood by modern scholars and writers, refers to those geographical regions and countries that culturally were directly, protractedly and intimately influenced by the language, culture,...
culture around the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
. The individual letters, however, still bear names derived from those of their Runic equivalents.
In past centuries, some authors asserted that Greek-like letters were already in use among Germanic tribes long before Ulfilas. Johannes Aventinus
Johannes Aventinus
Johannes Aventinus was a Bavarian historian and philologist. He wrote Annals of Bavaria, a valuable record of the early history of Germany...
(c. 1525) even ascribed them to the mythical progenitor Tuisto, claiming the Greeks had really stolen the idea from them, and not the Phoenicians. Such theories enjoy no scholarly support today, as all available evidence traces the development of alphabetic writing to the Middle East, although there is some testimony by classical Roman sources, as well as a few assorted tombstones, indicating that Greek letters were sometimes used in Germany, in addition to Gaul, by the time of Julius Caesar (1st century BC).
The letters
Below is a table of the Gothic alphabet. Two letters used in its transliterationTransliteration
Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
are not used in current English: the Runic þ
Thorn (letter)
Thorn or þorn , is a letter in the Old English, Old Norse, and Icelandic alphabets, as well as some dialects of Middle English. It was also used in medieval Scandinavia, but was later replaced with the digraph th. The letter originated from the rune in the Elder Fuþark, called thorn in the...
(representing /θ
Voiceless dental fricative
The voiceless dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English speakers as the 'th' in thing. Though rather rare as a phoneme in the world's inventory of languages, it is encountered in some of the most widespread and influential...
/), and ƕ
Hwair
Hwair is the name of , the Gothic letter expressing the or sound . Hwair is also the name of the Latin ligature .-Name:...
(representing /xʷ
Voiceless velar fricative
The voiceless velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The sound was part of the consonant inventory of Old English and can still be found in some dialects of English, most notably in Scottish English....
/).
As with the Greek alphabet, Gothic letters were also assigned numerical values. When used as numerals, letters were written either between two dots (•𐌹𐌱• = 12) or with an overline (𐌹𐌱 = 12). Two letters, 𐍁 (90) and 𐍊 (900), have no phonetic value.
The letter names are recorded in a 9th century manuscript of Alcuin
Alcuin
Alcuin of York or Ealhwine, nicknamed Albinus or Flaccus was an English scholar, ecclesiastic, poet and teacher from York, Northumbria. He was born around 735 and became the student of Archbishop Ecgbert at York...
(Codex Vindobonensis 795
Codex Vindobonensis 795
The Codex Vindobonensis 795 is a 9th century manuscript.It contains letters and treatises by Alcuin, including a discussion of the Gothic alphabet.It also contains a description of the Anglo-Saxon futhorc....
). Most of them seem to be Gothic forms of names also appearing in the rune poem
Rune poem
The Rune Poems are three poems that list the letters of runic alphabets while providing an explanatory poetic stanza for each letter. Three different poems have been preserved: the Anglo-Saxon Rune Poem, the Norwegian Rune Poem, and the Icelandic Rune Poem.The Icelandic and Norwegian poems list 16...
s. The names are given in their attested forms followed by the reconstructed Gothic forms and their meanings.
| Letter | Translit. | Compare | Gothic name | PGmc rune name | IPA | Numeric value | XML entity Numeric character reference A numeric character reference is a common markup construct used in SGML and other SGML-related markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represent a single character from the Universal Character Set of Unicode... |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 𐌰 | a | Α | aza < ans "god Æsir In Old Norse, áss is the term denoting a member of the principal pantheon in Norse paganism. This pantheon includes Odin, Frigg, Thor, Baldr and Tyr. The second pantheon comprises the Vanir... " or asks "ash" |
*ansuz Ansuz rune The a-rune , Younger Futhark was probably called *ansuz in Proto-Germanic, to which the Norse name Æsir is attributed.The shape of the rune is likely from Neo-Etruscan a , like Latin A ultimately from Phoenician aleph.... |
a | 1 | 𐌰 | |
| 𐌱 | b | Β Beta (letter) Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative .... |
bercna < *bairka "birch Birch Birch is a tree or shrub of the genus Betula , in the family Betulaceae, closely related to the beech/oak family, Fagaceae. The Betula genus contains 30–60 known taxa... " |
*berkanan Berkanan *Berkanan is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the b rune , meaning "birch". In the Younger Futhark it is called Bjarken in the Icelandic rune poem and Bjarkan in the Norwegian rune poem. In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem it is called beorc... |
/oiced bilabial plosive | 2 | 𐌱 | |
| 𐌲 | g | Γ | geuua < giba "gift" | *gebō Gyfu Gyfu is the name for the g-rune in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem, meaning "gift" or "generosity":The corresponding letter of the Gothic alphabet is g, called giba. The same rune also appears in the Elder Futhark, with a suggested Proto-Germanic name *gebô "gift". J. H... |
/oiced velar plosive | 3 | 𐌲 | |
| 𐌳 | d | Δ | daaz < dags "day" | *dagaz Dagaz The d rune is called Daeg "day" in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem. The corresponding letter of the Gothic alphabet d is called dags. This rune stave is also part of the Elder Futhark, with a reconstructed Proto-Germanic name *dagaz.... |
/oiced alveolar plosive | 4 | 𐌳 | |
| 𐌴 | e | Ε | eyz < aiƕs "horse" or eivs "yew Taxus baccata Taxus baccata is a conifer native to western, central and southern Europe, northwest Africa, northern Iran and southwest Asia. It is the tree originally known as yew, though with other related trees becoming known, it may be now known as the English yew, or European yew.-Description:It is a small-... " |
*eihwaz Eihwaz Eiwaz or Eihaz was a Proto-Germanic word for "yew", and the reconstructed name of the rune .... |
e | 5 | 𐌴 | |
| 𐌵 | q | Π Pi (letter) Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe , Coptic pi , and Gothic pairthra .The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:... |
quetra < *qairþra ? or quairna "millstone" | (see *perþō Peorð ' is the rune denoting the sound p in the Elder Futhark runic alphabet, in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem named peorð. It does not appear in the Younger Futhark. In the poem, it is glossed with the enigmatic:... ) |
kʷ | 6 | 𐌵 | |
| 𐌶 | z | Ζ | ezec < ezec (?) | (see *algiz Algiz The Algiz is part of the ancient Nordic and Anglo-Saxon runic alphabet, often equated to the modern day z, however was traditionally pronounced yr. The letter has come to symbolize many neo-pagan religions and is often worn as a pendant... ) |
z | 7 | 𐌶 | |
| 𐌷 | h | H H H .) is the eighth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The Semitic letter ⟨ח⟩ most likely represented the voiceless pharyngeal fricative . The form of the letter probably stood for a fence or posts.... |
haal < *hagal or *hagls "hail" | *haglaz Haglaz *Haglaz or *Hagalaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the h-rune , meaning "hail" .In the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, it is continued as haegl and in the Younger Futhark as hagall The corresponding Gothic letter is h, named hagl.The Elder Futhark letter has two variants, single-barred and... |
h, x | 8 | 𐌷 | |
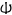 |
𐌸 | þ, th | Θ | thyth < þiuþ "good" or þaurnus "thorn" | *thurisaz | θ | 9 | 𐌸 |
| 𐌹 | i | Ι | iiz < *eis "ice" | *īsaz Isaz *Isaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the i-rune , meaning "ice". In the Younger Futhark it is called Iss in Icelandic and isa in Old Norse. As rune of the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, it is called is.... |
i | 10 | 𐌹 | |
| 𐌺 | k | Κ | chozma < *kusma or kōnja "pine sap" | *kaunan Kaunan The k-rune is called Kaun in both the Norwegian and Icelandic rune poems, meaning "ulcer". The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name is *Kaunan. It is also known as Kenaz , based on its Anglo-Saxon name.The Elder Futhark shape is likely directly based on Old Italic c / Latin C... |
k | 20 | 𐌺 | |
| 𐌻 | l | Λ | laaz < *lagus "sea, lake" | *laguz Laguz *Laguz or *Laukaz is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the l-rune , *laguz meaning "water" or "lake" and *laukaz meaning "leek". In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem, it is called lagu "ocean". In the Younger Futhark, the rune is called lögr "waterfall" in Icelandic and logr "water" in Norse.The... |
l | 30 | 𐌻 | |
| 𐌼 | m | Μ | manna < manna "man" | *mannaz Man (word) The term man and words derived from it can designate any or even all of the human race regardless of their sex or age... |
m | 40 | 𐌼 | |
| 𐌽 | n | Ν | noicz < nauþs "need" | *naudiz Naudiz Abdul Rahman Pazhwak was an Afghan poet and diplomat. He was educated in Afghanistan and started out his career as a journalist, but eventually joined the foreign ministry. During the 1950s he became ambassador to the United Nations, and served as president of the UN General Assembly from 1966 to... |
n | 50 | 𐌽 | |
| 𐌾 | j | ᛃ | gaar < jēr "year" | *jēran | j | 60 | 𐌾 | |
| 𐌿 | u | ᚢ | uraz < *ūrus "aurochs Aurochs The aurochs , the ancestor of domestic cattle, were a type of large wild cattle which inhabited Europe, Asia and North Africa, but is now extinct; it survived in Europe until 1627.... " |
*ūruz Ur (rune) The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the Elder Futhark u rune is *Ūruz meaning "wild ox" or *Ûram "water". It may have been derived from the Raetic alphabet character u as it is similar in both shape and sound value... |
u | 70 | 𐌿 | |
| 𐍀 | p | Π Pi (letter) Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe , Coptic pi , and Gothic pairthra .The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:... |
pertra < *pairþa ? | *perþō Peorð ' is the rune denoting the sound p in the Elder Futhark runic alphabet, in the Anglo-Saxon rune poem named peorð. It does not appear in the Younger Futhark. In the poem, it is glossed with the enigmatic:... |
p | 80 | 𐍀 | |
| 𐍁 | Ϙ | 90 | 𐍁 | |||||
| 𐍂 | r | R R R is the eighteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The original Semitic letter may have been inspired by an Egyptian hieroglyph for tp, "head". It was used for by Semites because in their language, the word for "head" was rêš . It developed into Greek Ρ and Latin R... |
reda < *raida "wagon" | *raidō Raidô Kate Thornton is an English journalist and television presenter. Early in her career, she was notable for her articles at the Daily Mirror and for her role as editor of Smash Hits magazine... |
r | 100 | 𐍂 | |
| 𐍃 | s | S S S is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent... |
sugil < sauïl or sōjil "sun" | *sôwilô Sowilo rune *Sowilō or *sæwelō is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the s-rune, meaning "sun". The name is attested for the same rune in all three rune poems... |
s | 200 | 𐍃 | |
| 𐍄 | t | Τ | tyz < *tius "the god Týr" | *tīwaz Tiwaz rune The t-rune is named after Týr, and was identified with this god. The reconstructed Proto-Germanic name is *Tîwaz or *Teiwaz.-Rune poems:Tiwaz is mentioned in all three rune poems... |
t | 300 | 𐍄 | |
| 𐍅 | w | Υ | uuinne < vinja "field, pasture" or vinna "pain" | *wunjō Wynn Wynn is a letter of the Old English alphabet, where it is used to represent the sound .... |
/oiced labio-velar approximant | 400 | 𐍅 | |
| 𐍆 | f | F F F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club... |
fe < faihu "cattle, wealth" | *fehu | f | 500 | 𐍆 | |
| 𐍇 | x | Χ | enguz < *iggus or *iggvs "the god Yngvi Yngvi Yngvi, Yngvin, Ingwine, Inguin are names that relate to an older theonym Ing and which appears to have been the older name for the god Freyr .... " |
*ingwaz Yngvi Yngvi, Yngvin, Ingwine, Inguin are names that relate to an older theonym Ing and which appears to have been the older name for the god Freyr .... |
x or h | 600 | 𐍇 | |
| 𐍈 | ƕ, hw | Θ | uuaer < *ƕair "kettle" | - | xʷ | 700 | 𐍈 | |
| 𐍉 | o | Ω, ᛟ | utal < *ōþal "ancestral land" | *ōþala | o | 800 | 𐍉 | |
| 𐍊 | Ϡ | 900 | 𐍊 |
Most of the letters have been taken over directly from the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
, though a few have been created and/or modified from Latin or Runic letters to express unique phonological features of Gothic. These are:
- 𐌵 (q; derived by inverting Greek 𐍀Pi (letter)Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe , Coptic pi , and Gothic pairthra .The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:...
/p/, perhaps due to similarity in the Gothic names: pairþa vs. qairþa) - 𐌸 (þ; derived from Greek ΦPhi (letter)Phi , pronounced or sometimes in English, and in modern Greek, is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greek, it represents , a voiceless labiodental fricative. In Ancient Greek it represented , an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive...
/f/ with phonetic reassignment) - 𐌾 (j; derived from Latin GGG is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,...
/g/ with possible influence from Runic ᛃ /j/) - 𐌿 (u; derived from Runic ᚢ /u/)
- 𐍈 (ƕ; derived from Greek ΘThetaTheta is the eighth letter of the Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician letter Teth...
/θ/ with phonetic reassignment) - 𐍉 (o; derived either from Greek Ω or from Runic ᛟ)
𐍂 (r), 𐍃 (s) and 𐍆 (f) appear to be derived from their Latin equivalents rather than from the Greek, although the equivalent Runic letters (ᚱ
Raidô
Kate Thornton is an English journalist and television presenter. Early in her career, she was notable for her articles at the Daily Mirror and for her role as editor of Smash Hits magazine...
, ᛋ
Sowilo rune
*Sowilō or *sæwelō is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the s-rune, meaning "sun". The name is attested for the same rune in all three rune poems...
and ᚠ), assumed to have been part of the Gothic futhark, likely played some role in this choice.
𐍇 (x) is only used in proper names and loanwords containing Greek Χ
Chi (letter)
Chi is the 22nd letter of the Greek alphabet, pronounced as in English.-Greek:-Ancient Greek:Its value in Ancient Greek was an aspirated velar stop .-Koine Greek:...
(xristus "Christ", galiugaxristus "Pseudo-Christ", zaxarias "Zacharias", aivxaristia "eucharist").
Regarding the letters' numeric values, most correspond to those of the Greek numerals
Greek numerals
Greek numerals are a system of representing numbers using letters of the Greek alphabet. They are also known by the names Ionian numerals, Milesian numerals , Alexandrian numerals, or alphabetic numerals...
. Gothic 𐌵 takes the place of Ϝ
Digamma
Digamma is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet which originally stood for the sound /w/ and later remained in use only as a numeral symbol for the number "6"...
(6), 𐌾 takes the place of ξ (60), 𐌿 that of Ο
Omicron
Omicron is the 15th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 70. It is rarely used in mathematics because it is indistinguishable from the Latin letter O and easily confused with the digit 0...
(70), and 𐍈 that of ψ
Psi (letter)
Psi is the 23rd letter of the Greek alphabet and has a numeric value of 700. In both Classical and Modern Greek, the letter indicates the combination /ps/ . The letter was adopted into the Old Italic alphabet, and its shape is continued into the Algiz rune of the Elder Futhark...
(700).
Diacritics and punctuation
Diacritics and punctuation used in the Codex ArgenteusCodex Argenteus
The Codex Argenteus, "Silver Book", is a 6th century manuscript, originally containing bishop Ulfilas's 4th century translation of the Bible into the Gothic language. Of the original 336 folios, 188—including the Speyer fragment discovered in 1970—have been preserved, containing the...
include a trema placed on 𐌹 i, transliterated as ï, in general applied to express diaeresis
Hiatus (linguistics)
In phonology, hiatus or diaeresis refers to two vowel sounds occurring in adjacent syllables, with no intervening consonant. When two adjacent vowel sounds occur in the same syllable, the result is instead described as a diphthong....
, the Interpunct
Interpunct
An interpunct —also called an interpoint—is a small dot used for interword separation in ancient Latin script, which also appears in some modern languages as a stand-alone sign inside a word. It is present in Unicode as code point ....
(·) and colon
Colon (punctuation)
The colon is a punctuation mark consisting of two equally sized dots centered on the same vertical line.-Usage:A colon informs the reader that what follows the mark proves, explains, or lists elements of what preceded the mark....
(:) as well as overline
Overline
An overline or overbar or overscore , refers to the typographical feature of a line drawn immediately above the text, for example used to indicate medieval sigla. Specifically, a line drawn over one symbol is a macron, and a line over a collection of symbols is a vinculum...
s to indicate sigla
Sigla
Sigła is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Aleksandrów, within Biłgoraj County, Lublin Voivodeship, in eastern Poland. It lies approximately east of Aleksandrów, south-east of Biłgoraj, and south of the regional capital Lublin....
(such as xaus for xristaus) and numerals.

Unicode
The Gothic alphabet was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in March, 2001 with the release of version 3.1.
The Unicode block for Gothic is U+10330–U+1034F in the Supplementary Multilingual Plane. As older software that uses UCS-2 (the predecessor of UTF-16) assumes that all Unicode codepoints can be expressed as 16 bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
numbers (U+FFFF or lower, the Basic Multilingual Plane), problems may be encountered using the Gothic alphabet Unicode range and others outside of the Basic Multilingual Plane.
See also
- BlackletterBlackletterBlackletter, also known as Gothic script, Gothic minuscule, or Textura, was a script used throughout Western Europe from approximately 1150 to well into the 17th century. It continued to be used for the German language until the 20th century. Fraktur is a notable script of this type, and sometimes...
- Gothic languageGothic languageGothic is an extinct Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizable Text corpus...
- Help:Gothic Unicode Fonts
- Rune poemRune poemThe Rune Poems are three poems that list the letters of runic alphabets while providing an explanatory poetic stanza for each letter. Three different poems have been preserved: the Anglo-Saxon Rune Poem, the Norwegian Rune Poem, and the Icelandic Rune Poem.The Icelandic and Norwegian poems list 16...
- Runic alphabetRunic alphabetThe runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...

