
R
Encyclopedia
R is the eighteenth letter
of the basic modern Latin alphabet
.
The original Semitic
letter may have been inspired by an Egyptian hieroglyph for tp, "head". It was used for /r/ by Semites because in their language, the word for "head" was rêš
(also the name of the letter). It developed into Greek Ρ
(rhô) and Latin R. It is likely that some Etruscan and Western Greek forms of the letter added the extra stroke to distinguish it from a later form of the letter P.
The minuscule (lower-case) form of r developed through several variations on the capital form. In handwriting it was common not to close the bottom of the loop but continue into the leg, saving an extra pen stroke. The loop-leg stroke shortened into the simple arc used today. Another minuscule, r rotunda
(ꝛ), kept the loop-leg stroke but dropped the vertical stroke, although it fell out of use around the 18th century.
. Mathematicians use R or (an R in blackboard bold
(an R in blackboard bold
, displayed as in Unicode) for set of all real numbers.
R represents a rhotic consonant
in many languages, as shown in the table below. The International Phonetic Alphabet uses several variations of the letter to represent the different rhotic consonants; [r] represents the alveolar trill
.
Other languages may use the letter r in their alphabets (or Latin transliterations schemes) to represent rhotic consonants different from the alveolar trill. In Haitian Creole, it represents a sound so weak that it is often written interchangeably with w, e.g. Kweyol for Kreyol.
In William Shakespeare
's Romeo and Juliet
, such a reference is made by Juliet's nurse in Act 2, scene 4, when she calls the letter R "the dog's name." The reference is also found in Ben Jonson
's English Grammar.
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Letter (alphabet)
A letter is a grapheme in an alphabetic system of writing, such as the Greek alphabet and its descendants. Letters compose phonemes and each phoneme represents a phone in the spoken form of the language....
of the basic modern Latin alphabet
Basic modern Latin alphabet
The International Organization for Standardization basic Latin alphabet consists of the following 26 letters:By the 1960s it became apparent to the computer and telecommunications industries in the First World that a non-proprietary method of encoding characters was needed...
.
History
| Egyptian hieroglyph tp |
Phoenician resh Resh Resh is the twentieth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is one of a number of rhotic consonants: usually or , but also or in Hebrew.... |
Etruscan R | Greek Rho Rho (letter) Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"... |
Later Etruscan R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
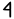 |
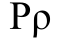 |
The original Semitic
Semitic
In linguistics and ethnology, Semitic was first used to refer to a language family of largely Middle Eastern origin, now called the Semitic languages...
letter may have been inspired by an Egyptian hieroglyph for tp, "head". It was used for /r/ by Semites because in their language, the word for "head" was rêš
Res
Shareese Renée Ballard, better known by her stage name Res , is a female singer from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Her musical style is a blend of indie pop, soul, and rock...
(also the name of the letter). It developed into Greek Ρ
Rho (letter)
Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"...
(rhô) and Latin R. It is likely that some Etruscan and Western Greek forms of the letter added the extra stroke to distinguish it from a later form of the letter P.
The minuscule (lower-case) form of r developed through several variations on the capital form. In handwriting it was common not to close the bottom of the loop but continue into the leg, saving an extra pen stroke. The loop-leg stroke shortened into the simple arc used today. Another minuscule, r rotunda
R rotunda
The r rotunda , "rounded r," is an old letter variant found in full script-like typefaces, especially blackletters. Between the Middle Ages and today, many ways of writing alphabetical characters were lost. Besides a variety of ligatures, conjoined letters, scribal abbreviations, swash characters,...
(ꝛ), kept the loop-leg stroke but dropped the vertical stroke, although it fell out of use around the 18th century.
Usage
In science, the letter R is a symbol for the gas constantGas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
. Mathematicians use R or
 (an R in blackboard bold
(an R in blackboard boldBlackboard bold
Blackboard bold is a typeface style that is often used for certain symbols in mathematical texts, in which certain lines of the symbol are doubled. The symbols usually denote number sets...
, displayed as in Unicode) for set of all real numbers.
R represents a rhotic consonant
Rhotic consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet...
in many languages, as shown in the table below. The International Phonetic Alphabet uses several variations of the letter to represent the different rhotic consonants; [r] represents the alveolar trill
Alveolar trill
The alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R...
.
| Alveolar trill Alveolar trill The alveolar trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar trills is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r. It is commonly called the rolled R, rolling R, or trilled R... [r] |
Listen | some dialects of British English British English British English, or English , is the broad term used to distinguish the forms of the English language used in the United Kingdom from forms used elsewhere... or in emphatic speech, standard Dutch Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... , Finnish Finnish language Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a... , Galician Galician language Galician is a language of the Western Ibero-Romance branch, spoken in Galicia, an autonomous community located in northwestern Spain, where it is co-official with Castilian Spanish, as well as in border zones of the neighbouring territories of Asturias and Castile and León.Modern Galician and... , German German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... in some dialects, Hungarian Hungarian language Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe.... , Icelandic Icelandic language Icelandic is a North Germanic language, the main language of Iceland. Its closest relative is Faroese.Icelandic is an Indo-European language belonging to the North Germanic or Nordic branch of the Germanic languages. Historically, it was the westernmost of the Indo-European languages prior to the... , Italian Italian language Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia... , Czech Czech language Czech is a West Slavic language with about 12 million native speakers; it is the majority language in the Czech Republic and spoken by Czechs worldwide. The language was known as Bohemian in English until the late 19th century... , Lithuanian Lithuanian language Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they... , Latin, Norwegian Norwegian language Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Norway, where it is the official language. Together with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants .These Scandinavian languages together with the Faroese language... , Polish Polish language Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries... , Catalan Catalan language Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island... , Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... (traditional form), Romanian Romanian language Romanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova... , Russian Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... , Scots Scots language Scots is the Germanic language variety spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster . It is sometimes called Lowland Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Celtic language variety spoken in most of the western Highlands and in the Hebrides.Since there are no universally accepted... , Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... and Albanian Albanian language Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece... 'rr', Swedish Swedish language Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish... , Welsh Welsh language Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa... |
| Alveolar approximant [ɹ] | Listen | English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... (most varieties), Dutch Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... in some Dutch dialects (in specific positions of words), Swedish Swedish language Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish... , Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... in some dialects (in specific positions of words), Faroese Faroese language Faroese , is an Insular Nordic language spoken by 48,000 people in the Faroe Islands and about 25,000 Faroese people in Denmark and elsewhere... , Sicilian Sicilian language Sicilian is a Romance language. Its dialects make up the Extreme-Southern Italian language group, which are spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands; in southern and central Calabria ; in the southern parts of Apulia, the Salento ; and Campania, on the Italian mainland, where it is... |
| Alveolar flap / Alveolar tap Alveolar tap The alveolar flap or tap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar flaps is .-Definition:... [ɾ] |
Listen | Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... , Catalan Catalan language Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island... , Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... and Albanian Albanian language Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece... 'r', Turkish Turkish language Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,... , Dutch Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... , Italian Italian language Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia... , Venetian Venetian language Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia... , Galician Galician language Galician is a language of the Western Ibero-Romance branch, spoken in Galicia, an autonomous community located in northwestern Spain, where it is co-official with Castilian Spanish, as well as in border zones of the neighbouring territories of Asturias and Castile and León.Modern Galician and... , Leonese Leonese language The Leonese language is the endonym term used to refer to all vernacular Romance dialects of the Astur-Leonese linguistic group in the Spanish provinces of León and Zamora; Astur-Leonese also includes the dialects... |
| Voiced retroflex fricative [ʐ] | Listen | Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... used as an allophone of /r/ in some South American accents; Mandarin Chinese Standard Mandarin Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore.... (in pinyin Pinyin Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into... ); Vietnamese Vietnamese language Vietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam... (southern dialects) |
| Retroflex approximant [ɻ] | Listen | some varieties of American English American English American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States.... ; Mandarin Chinese Standard Mandarin Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore.... (in pinyin Pinyin Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into... ); and Gutnish |
| Retroflex flap [ɽ] | Listen | sometimes in Scottish English Scottish English Scottish English refers to the varieties of English spoken in Scotland. It may or may not be considered distinct from the Scots language. It is always considered distinct from Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic language.... |
| Uvular trill Uvular trill The uvular trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a small capital R... [ʀ] |
Listen | German German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... stage standard; some Dutch Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... dialects (in Brabant and Limburg, and some city dialects in The Netherlands), Swedish Swedish language Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish... in Southern Sweden, Norwegian Norwegian language Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Norway, where it is the official language. Together with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants .These Scandinavian languages together with the Faroese language... in western and southern parts |
| Voiced uvular fricative [ʁ] | Listen | German German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... , Danish Danish language Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language... , French French language French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts... , some European Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... 'rr' |
| Voiceless uvular fricative [χ] | Listen | some Brazilian Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... 'rr' |
| Voiceless glottal fricative Voiceless glottal fricative The voiceless glottal transition, commonly called a "fricative", is a type of sound used in some spoken languages which patterns like a fricative or approximant consonant phonologically, but often lacks the usual phonetic characteristics of a consonant... [h] |
Listen | some Brazilian Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... 'rr' |
Other languages may use the letter r in their alphabets (or Latin transliterations schemes) to represent rhotic consonants different from the alveolar trill. In Haitian Creole, it represents a sound so weak that it is often written interchangeably with w, e.g. Kweyol for Kreyol.
Shape
The letter R is the only letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet in which the uppercase has a closed section and the lowercase does not.Dog's letter
The letter R is sometimes referred to as the littera canina (canine letter). This phrase has Latin origins: the Latin R was trilled to sound like a growling dog. A good example of a trilling R is the Spanish word for dog, perro.In William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon"...
's Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet is a tragedy written early in the career of playwright William Shakespeare about two young star-crossed lovers whose deaths ultimately unite their feuding families. It was among Shakespeare's most popular archetypal stories of young, teenage lovers.Romeo and Juliet belongs to a...
, such a reference is made by Juliet's nurse in Act 2, scene 4, when she calls the letter R "the dog's name." The reference is also found in Ben Jonson
Ben Jonson
Benjamin Jonson was an English Renaissance dramatist, poet and actor. A contemporary of William Shakespeare, he is best known for his satirical plays, particularly Volpone, The Alchemist, and Bartholomew Fair, which are considered his best, and his lyric poems...
's English Grammar.
Related letters and other similar characters
- Ρ ρ/ : Greek letter RhoRho (letter)Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"...
- Р р : Cyrillic letter ErEr (Cyrillic)Er is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the alveolar trill , like the "rolled" sound in the Scottish pronunciation of ⟨r⟩ in "curd".-History:...
- Я я : Cyrillic letter YaYa (Cyrillic)Ya is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet, the civil script variant of Old Cyrillic Little Yus . Among modern Slavonic languages it is used by Russian, Belarusian, Ukrainian and Bulgarian to represent both the combination in initial or post-vocalic position and after a palatalised consonant; in...
- ℛ : Script capital R
Computing codes
| character | R | r | ||
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER R | LATIN SMALL LETTER R |
||
| character encoding | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
82 | 0052 | 114 | 0072 |
| UTF-8 UTF-8 UTF-8 is a multibyte character encoding for Unicode. Like UTF-16 and UTF-32, UTF-8 can represent every character in the Unicode character set. Unlike them, it is backward-compatible with ASCII and avoids the complications of endianness and byte order marks... |
82 | 52 | 114 | 72 |
| Numeric character reference Numeric character reference A numeric character reference is a common markup construct used in SGML and other SGML-related markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represent a single character from the Universal Character Set of Unicode... |
R | R | r | r |
| EBCDIC EBCDIC Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code is an 8-bit character encoding used mainly on IBM mainframe and IBM midrange computer operating systems.... family |
217 | D9 | 153 | 99 |
| ASCII ASCII The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text... 1 |
82 | 52 | 114 | 72 |
1 and all encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.

