
City-state
Encyclopedia

Local government
Local government refers collectively to administrative authorities over areas that are smaller than a state.The term is used to contrast with offices at nation-state level, which are referred to as the central government, national government, or federal government...
.
Historical city-states
Historical examples include the oldest known SumerSumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ian cities of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
(burned city in Sis tan and Blochestan in Iran and Babylon in old Iranian empire] and Ur
Ur
Ur was an important city-state in ancient Sumer located at the site of modern Tell el-Muqayyar in Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate...
), the Phoenicia
Phoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
in cities of Canaan
Canaan
Canaan is a historical region roughly corresponding to modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and the western parts of Jordan...
(such as Tyre and Sidon
Sidon
Sidon or Saïda is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate of Lebanon, on the Mediterranean coast, about 40 km north of Tyre and 40 km south of the capital Beirut. In Genesis, Sidon is the son of Canaan the grandson of Noah...
), the Berber
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
city-states of the Garamantes
Garamantes
The Garamantes were a Saharan people who used an elaborate underground irrigation system, and founded a prosperous Berber kingdom in the Fezzan area of modern-day Libya, in the Sahara desert. They were a local power in the Sahara between 500 BC and 700 AD.There is little textual information about...
, the city-states of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
(the poleis such as Athens
Classical Athens
The city of Athens during the classical period of Ancient Greece was a notable polis of Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Hippias...
, Sparta
Sparta
Sparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
, Thebes
Thebes, Greece
Thebes is a city in Greece, situated to the north of the Cithaeron range, which divides Boeotia from Attica, and on the southern edge of the Boeotian plain. It played an important role in Greek myth, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus and others...
, and Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
), the Roman Republic
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
which grew from a city-state into a great power
Historical powers
Historical powers include great powers, nations, or empires in history.The term "Great power" represent the most important world powers. In a modern context, recognised great powers came about first in Europe during the post-Napoleonic era. The formalization of the division between small powers and...
, the Maya
Maya civilization
The Maya is a Mesoamerican civilization, noted for the only known fully developed written language of the pre-Columbian Americas, as well as for its art, architecture, and mathematical and astronomical systems. Initially established during the Pre-Classic period The Maya is a Mesoamerican...
of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a region and culture area in the Americas, extending approximately from central Mexico to Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica, within which a number of pre-Columbian societies flourished before the Spanish colonization of the Americas in the 15th and...
(including sites such as Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site built by the Maya civilization located in the northern center of the Yucatán Peninsula, in the Municipality of Tinúm, Yucatán state, present-day Mexico....
and El Mirador
El Mirador
El Mirador is a large pre-Columbian Mayan settlement, located in the north of the modern department of El Petén, Guatemala.-Discovery:El Mirador was first discovered in 1926, and was photographed from the air in 1930, but the remote site deep in the jungle had little more attention paid to it until...
), the central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
n cities along the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
, Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
and many others and Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
n city-state of Ragusa (Dubrovnik)
Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa or Republic of Dubrovnik was a maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik in Dalmatia , that existed from 1358 to 1808...
.
Within the transalpine part of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
the Free Imperial Cities
Free Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, a free imperial city was a city formally ruled by the emperor only — as opposed to the majority of cities in the Empire, which were governed by one of the many princes of the Empire, such as dukes or prince-bishops...
enjoyed a considerable autonomy, buttressed legally by the Lübeck law
Lübeck law
The Lübeck law was the constitution of a municipal form of government developed at Lübeck in Schleswig-Holstein after it was made a free city in 1226. The law provides for self-government. It replaced the personal rule of tribal monarchs descending from ancient times or the rule of the regional...
which was emulated by many other cities. Some cities — though also members of different confederacies
Confederation
A confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
at that time — officially became sovereign city-states in the 19th century — such as the Canton of Basel City (1833–48), the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen
Bremen (state)
The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen is the smallest of Germany's 16 states. A more informal name, but used in some official contexts, is Land Bremen .-Geography:...
(1806–11 and again 1813–71), the Free City of Frankfurt upon Main
Free City of Frankfurt
For almost five centuries, the German city of Frankfurt am Main was a city-state within two major Germanic states:*The Holy Roman Empire as the Free Imperial City of Frankfurt...
(1815–66), the Canton of Geneva
Canton of Geneva
The Republic and Canton of Geneva is the French speaking westernmost canton or state of Switzerland, surrounded on almost all sides by France. As is the case in several other Swiss cantons The Republic and Canton of Geneva is the French speaking westernmost canton or state of Switzerland,...
(1813–48), the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg
Hamburg
-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
(1806–11 and again 1814–71) and the Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck (1806–11 and again 1813–71). Another city-state, though lacking sovereignty, was West Berlin
West Berlin
West Berlin was a political exclave that existed between 1949 and 1990. It comprised the western regions of Berlin, which were bordered by East Berlin and parts of East Germany. West Berlin consisted of the American, British, and French occupation sectors, which had been established in 1945...
(1948–90), being a state legally not belonging to any other state, but ruled by the Western Allies
Western Allies
The Western Allies were a political and geographic grouping among the Allied Powers of the Second World War. It generally includes the United Kingdom and British Commonwealth, the United States, France and various other European and Latin American countries, but excludes China, the Soviet Union,...
. They allowed — notwithstanding their overlordship as occupant powers — its internal organisation as one state simultaneously being a city, officially called Berlin (West). Though West Berlin held close ties to the West German Federal Republic of Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, it was legally never part of it. A number of the aforementioned city-states — though partly with altered borders — continue to exist as city-states within today's Federal Republic of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and today's Swiss Confederation (see below: 'Cities that are component states of federations').
Among the most well-known periods of city-state culture in human history include ancient Greek city-states, and the merchant city-states of Renaissance Italy
Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance began the opening phase of the Renaissance, a period of great cultural change and achievement in Europe that spanned the period from the end of the 13th century to about 1600, marking the transition between Medieval and Early Modern Europe...
, who organised themselves in small independent centres. The success of small regional units coexisting as autonomous
Autonomy
Autonomy is a concept found in moral, political and bioethical philosophy. Within these contexts, it is the capacity of a rational individual to make an informed, un-coerced decision...
actors in loose geographical and cultural unity, as in Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
or Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, often prevented their amalgamation
Amalgamation (politics)
A merger or amalgamation in a political or administrative sense is the combination of two or more political or administrative entities such as municipalities , counties, districts, etc. into a single entity. This term is used when the process occurs within a sovereign entity...
into larger national units. However, such small political entities often survived only for short periods because they lacked the resources to defend themselves against incursions by larger states. Thus they inevitably gave way to larger organisations of society, including the empire
Empire
The term empire derives from the Latin imperium . Politically, an empire is a geographically extensive group of states and peoples united and ruled either by a monarch or an oligarchy....
and the nation state.
Contemporary city-states
Today there are only a handful of cities that exercise authority akin to a sub-regional state, and even fewer that are sovereign stateSovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
s in their own right.
Monaco
The Principality of MonacoMonaco
Monaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
is an independent city-state. Monaco-Ville
Monaco-Ville
Monaco-Ville is one of Monaco's administrative divisions located on a rocky headland that extends into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the four traditional quarters of Monaco, the others being La Condamine, Monte Carlo, and Fontvieille. However, in modern administrative terms it is one of ten...
(the ancient fortified city) and Monaco's well-known area Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo is an administrative area of the Principality of Monaco....
are districts of a continuous urban zone, not distinct cities, though they were three separate municipalities (communes) until 1917. The Principality of Monaco and the city of Monaco (each having specific powers) govern the same territory. On 28 June 1919, a treaty
Treaty
A treaty is an express agreement under international law entered into by actors in international law, namely sovereign states and international organizations. A treaty may also be known as an agreement, protocol, covenant, convention or exchange of letters, among other terms...
was signed providing for limited French protection over Monaco. The treaty, part of the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
, established that Monegasque
Monégasque
Monégasque may refer to:* Monégasque dialect, the local Ligurian dialect of Monaco* Something of, from, or related to Monaco, a small sovereign city-state located in southwestern Europe...
policy would be aligned with French political, military, and economic interests. Only in 1993 did Monaco become a member of the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
, with full voting rights. In 2002, a new treaty between France and Monaco clarifies that if there are no heirs to carry on the dynasty
Dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers considered members of the same family. Historians traditionally consider many sovereign states' history within a framework of successive dynasties, e.g., China, Ancient Egypt and the Persian Empire...
, the principality
Principality
A principality is a monarchical feudatory or sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a monarch with the title of prince or princess, or by a monarch with another title within the generic use of the term prince....
will remain an independent nation rather than revert to France (which were the terms of the previous arrangement). Monaco's military defence, however, is still the responsibility of France. Monaco did not receive its first foreign ambassador
Ambassador
An ambassador is the highest ranking diplomat who represents a nation and is usually accredited to a foreign sovereign or government, or to an international organization....
, the French ambassador, until 16 February 2006.
Singapore
Singapore is an island city-state in Southeast AsiaSoutheast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. About 5 million people live and work within 700 square kilometres (270.3 sq mi), making Singapore the 3rd-most-densely populated country in the world. The entire island functions as a single metropolitan area
Metropolitan area
The term metropolitan area refers to a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories, sharing industry, infrastructure, and housing. A metropolitan area usually encompasses multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighborhoods, townships,...
. The city centre near the south of the island is surrounded by satellite town
Satellite town
A satellite town or satellite city is a concept in urban planning that refers essentially to smaller metropolitan areas which are located somewhat near to, but are mostly independent of, larger metropolitan areas.-Characteristics:...
s, parks, reservoirs and industrial estates, which are connected to the centre and each other by a dense network of roads, expressways and metro
Rapid transit
A rapid transit, underground, subway, elevated railway, metro or metropolitan railway system is an electric passenger railway in an urban area with a high capacity and frequency, and grade separation from other traffic. Rapid transit systems are typically located either in underground tunnels or on...
railway lines dubbed MRT
Mass Rapid Transit (Singapore)
The Mass Rapid Transit or MRT is a rapid transit system that forms the backbone of the railway system in Singapore, spanning the entire city-state. The initial section of the MRT, between Yio Chu Kang Station and Toa Payoh Station, opened in 1987 establishing itself as the second-oldest metro...
by locals. Singapore has a highly centralised, unitary government
Unitary state
A unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
with a unicameral legislature (the City Council
City Council of Singapore
The City Council of Singapore, or the Municipal Council before 1951, was the administrative council of Singapore responsible for the provision of water, electricity, gas, roads and bridges and street lighting. It was abolished upon Singapore's secession from Malaysia in 1965...
and the Rural Board were abolished in the 1960s). While there are town council
Town council
A town council is a democratically elected form of government for small municipalities or civil parishes. A council may serve as both the representative and executive branch....
s and mayors in Singapore, these are essentially property managers
Property management
Property management is the operation, control of ususally on behalf of an owner, and oversight of commercial, industrial or residential real estate as used in its most broad terms. Management indicates a need to be cared for, monitored and accountability given for its usable life and condition...
in charge of the maintenance of public housing
Public housing
Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is owned by a government authority, which may be central or local. Social housing is an umbrella term referring to rental housing which may be owned and managed by the state, by non-profit organizations, or by a combination of the...
within their constituency boundaries. They do not represent local authorities with any legislative or executive
Executive (government)
Executive branch of Government is the part of government that has sole authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state bureaucracy. The division of power into separate branches of government is central to the idea of the separation of powers.In many countries, the term...
autonomy from the national government.
Prior to the 19th century, Singapore was a minor part of various regional empires, including Srivijaya
Srivijaya
Srivijaya was a powerful ancient thalassocratic Malay empire based on the island of Sumatra, modern day Indonesia, which influenced much of Southeast Asia. The earliest solid proof of its existence dates from the 7th century; a Chinese monk, I-Tsing, wrote that he visited Srivijaya in 671 for 6...
, Majapahit, Malacca
Malacca Sultanate
Established by the Malay ruler Parameswara, the Sultanate of Malacca was first a Hindu kingdom in 1402 and later became Muslim following the marriage of the princess of Pasai in 1409. Centered in the modern town of Malacca, the sultanate bordered the Ayutthaya Kingdom of Siam in the north to...
and Johor
Johor Sultanate
The Sultanate of Johor was founded by Malaccan Sultan Mahmud Shah's son, Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah II in 1528. Johor was part of the Malaccan Sultanate before the Portuguese conquered Malacca's capital in 1511...
. From 1826 to the Battle of Singapore
Battle of Singapore
The Battle of Singapore was fought in the South-East Asian theatre of the Second World War when the Empire of Japan invaded the Allied stronghold of Singapore. Singapore was the major British military base in Southeast Asia and nicknamed the "Gibraltar of the East"...
in 1942, Singapore was the capital of the Straits Settlements
Straits Settlements
The Straits Settlements were a group of British territories located in Southeast Asia.Originally established in 1826 as part of the territories controlled by the British East India Company, the Straits Settlements came under direct British control as a crown colony on 1 April 1867...
, a British colony that included the Settlements of Malacca
Malacca
Malacca , dubbed The Historic State or Negeri Bersejarah among locals) is the third smallest Malaysian state, after Perlis and Penang. It is located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, on the Straits of Malacca. It borders Negeri Sembilan to the north and the state of Johor to the south...
and Penang
Penang
Penang is a state in Malaysia and the name of its constituent island, located on the northwest coast of Peninsular Malaysia by the Strait of Malacca. It is bordered by Kedah in the north and east, and Perak in the south. Penang is the second smallest Malaysian state in area after Perlis, and the...
along the Straits of Malacca. After the Second World War, Singapore was hived off as a separate colony while the other two Settlements joined the Malay States to form the Federation of Malaya
Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya is the name given to a federation of 11 states that existed from 31 January 1948 until 16 September 1963. The Federation became independent on 31 August 1957...
. In 1963, Singapore merged with Malaya, Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
and Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
to form Malaysia. However, because of a number of problems
Singapore in Malaysia
On 16 September 1963, which was also Lee Kuan Yew's 40th birthday, Singapore merged with the Federation of Malaya alongside Sabah and Sarawak to form Malaysia...
, Singapore was expelled from the federation in 1965, becoming an independent republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
.
Since 1965, Singapore rapidly industrialised and modernised, becoming one of the four "Asian Tigers
East Asian Tigers
The Four Asian Tigers or Asian Dragons is a term used in reference to the highly developed economies of Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan. These nations and areas were notable for maintaining exceptionally high growth rates and rapid industrialization between the early 1960s and 1990s...
". In addition to the substantial absolute and per-capita size of its economy
Economy of Singapore
Singapore has a highly developed state capitalist mixed economy; the state owns stakes in firms that comprise perhaps 60% of the GDP through entities such as the sovereign wealth fund Temasek...
, Singapore maintains a significant armed forces
Singapore Armed Forces
The Singapore Armed Forces is the military arm of the Total Defence of the Republic of Singapore; as well as the military component of the Ministry of Defence. The SAF comprises three branches: the Singapore Army, the Republic of Singapore Air Force and the Republic of Singapore Navy...
. It ranks highly in terms of defence spending and troop size.
Despite its small land area, Singapore has a population, economy and armed forces that place it in a similar league to small, but full-fledged nations like New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
and the Nordic countries
Nordic countries
The Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic which consists of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories, the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland...
(i.e., Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
and Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
), rather than semi-dependent microstates. Singapore also maintains a diplomatic corps
Diplomatic corps
The diplomatic corps or corps diplomatique is the collective body of foreign diplomats accredited to a particular country or body.The diplomatic corps may, in certain contexts, refer to the collection of accredited heads of mission who represent their countries in another state or country...
and has memberships in international organizations such as the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
Singapore places emphasis on self-sufficiency in basic needs, like water. The government also stockpiles other key resources, such as sand and oil. In this way, Singapore tries to avoid overdependence economically, politically or militarily on larger entities. Accordingly, Singapore may represent the most-complete contemporary example of a city-state, meeting the full definitions of both a city
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
and a fully sovereign
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
state.
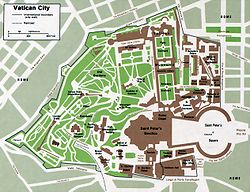
Vatican City
Until 1870, the city of RomeRome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
had been controlled by the pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
as part of his Papal States
Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
. When King Victor Emmanuel II
Victor Emmanuel II of Italy
Victor Emanuel II was king of Sardinia from 1849 and, on 17 March 1861, he assumed the title King of Italy to become the first king of a united Italy since the 6th century, a title he held until his death in 1878...
seized the city in 1870, Pope Pius IX
Pope Pius IX
Blessed Pope Pius IX , born Giovanni Maria Mastai-Ferretti, was the longest-reigning elected Pope in the history of the Catholic Church, serving from 16 June 1846 until his death, a period of nearly 32 years. During his pontificate, he convened the First Vatican Council in 1869, which decreed papal...
refused to recognize the newly formed Kingdom of Italy
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
. Because he could not travel without effectively acknowledging the authority of the king, Pius IX and his successors each claimed to be a "Prisoner in the Vatican
Prisoner in the Vatican
A prisoner in the Vatican or prisoner of the Vatican is how Pope Pius IX described himself following the capture of Rome by the armed forces of the Kingdom of Italy on 20 September 1870. Part of the process of Italian unification, the city's capture ended the millennial temporal rule of the popes...
", unable to leave the 0.44 km² (0.169884949780715 sq mi) papal enclave once they had ascended the papal thrones.
The impasse
Roman Question
thumb|300px|The breach of [[Porta Pia]], on the right, in a contemporaneous photograph.The Roman Question was a political dispute between the Italian Government and the Papacy from 1861 to 1929....
was resolved in 1929 by the Lateran Treaties
Lateran treaties
The Lateran Treaty is one of the Lateran Pacts of 1929 or Lateran Accords, three agreements made in 1929 between the Kingdom of Italy and the Holy See, ratified June 7, 1929, ending the "Roman Question"...
negotiated by the World War 2 Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
between King Victor Emmanuel III and Pope Pius XI
Pope Pius XI
Pope Pius XI , born Ambrogio Damiano Achille Ratti, was Pope from 6 February 1922, and sovereign of Vatican City from its creation as an independent state on 11 February 1929 until his death on 10 February 1939...
. Under this treaty, the Vatican was recognized as an independent state, with the Pope as its head. The Vatican City State
Vatican City
Vatican City , or Vatican City State, in Italian officially Stato della Città del Vaticano , which translates literally as State of the City of the Vatican, is a landlocked sovereign city-state whose territory consists of a walled enclave within the city of Rome, Italy. It has an area of...
has its own citizenship
Citizenship
Citizenship is the state of being a citizen of a particular social, political, national, or human resource community. Citizenship status, under social contract theory, carries with it both rights and responsibilities...
, diplomatic corps
Diplomatic corps
The diplomatic corps or corps diplomatique is the collective body of foreign diplomats accredited to a particular country or body.The diplomatic corps may, in certain contexts, refer to the collection of accredited heads of mission who represent their countries in another state or country...
, flag
Flag of the Vatican City
The flag of Vatican City was adopted on June 7, 1929, the year Pope Pius XI signed the Lateran Treaty with Italy, creating a new independent state governed by the Holy See...
, and postage stamp
Postage stamp
A postage stamp is a small piece of paper that is purchased and displayed on an item of mail as evidence of payment of postage. Typically, stamps are made from special paper, with a national designation and denomination on the face, and a gum adhesive on the reverse side...
s. With a population of less than 1,000 (mostly all Priests) it is by far the smallest sovereign country in the world.
Non-sovereign city-states
Some cities or urban areas, while not sovereign states, may nevertheless enjoy such a high degree of autonomy that they function as "city-states" within the context of the sovereign state that they belong to.Trieste
After the Second World War, the UN attempted to make the Free Territory of Trieste into a city state, but it never gained real independence and in 1954 its territory was divided between Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia refers to three political entities that existed successively on the western part of the Balkans during most of the 20th century....
.
Cities that are component states of federations
Some cities or metropolitan areas are component states of federationFederation
A federation , also known as a federal state, is a type of sovereign state characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central government...
s. Examples include:
- ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
- Buenos AiresBuenos AiresBuenos Aires is the capital and largest city of Argentina, and the second-largest metropolitan area in South America, after São Paulo. It is located on the western shore of the estuary of the Río de la Plata, on the southeastern coast of the South American continent...
(formally known in English as the "Autonomous City of Buenos Aires" (coterminous with the Argentine Federal Capital) - Austrian stateStates of AustriaAustria is a federal republic made up of nine states, known in German as Länder . Since Land is also the German word for a country, the term Bundesländer is often used instead to avoid ambiguity. The Constitution of Austria uses both terms...
of ViennaViennaVienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre... - BelgianBelgiumBelgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
capital BrusselsBrusselsBrussels , officially the Brussels Region or Brussels-Capital Region , is the capital of Belgium and the de facto capital of the European Union... - BrazilBrazilBrazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
– BrasíliaBrasíliaBrasília is the capital city of Brazil. The name is commonly spelled Brasilia in English. The city and its District are located in the Central-West region of the country, along a plateau known as Planalto Central. It has a population of about 2,557,000 as of the 2008 IBGE estimate, making it the...
(coterminous with the Brazilian Federal DistrictBrazilian Federal DistrictThe Federal District is set apart for Brasília, the capital of Brazil. Located in a region called Planalto Central, or Central Plateau, the Federal District is divided in 29 administrative regions. Brasilia - place where the three branches of the Federal Government are located - is the main...
) - EthiopiaEthiopiaEthiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
n chartered citiesCharter cityA charter city is a city in which the governing system is defined by the city's own charter document rather than by state, provincial, regional or national laws. In locations where city charters are allowed by law, a city can adopt or modify its organizing charter by decision of its administration...
(astedader akababiwach) of Addis AbabaAddis AbabaAddis Ababa is the capital city of Ethiopia...
and Dire DawaDire DawaDire Dawa is one of two chartered cities in Ethiopia . This chartered city is divided administratively into two woredas, the city proper and the non-urban woreda of Gurgura.... - German statesStates of GermanyGermany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
of BerlinBerlinBerlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
, HamburgHamburg-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
and, though consisting of two separate cities, BremenBremen (state)The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen is the smallest of Germany's 16 states. A more informal name, but used in some official contexts, is Land Bremen .-Geography:... - Malaysia - Melaka (also known as Malacca)
- RussiaRussiaRussia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
n cities of MoscowMoscowMoscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
and Saint PetersburgSaint PetersburgSaint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea... - Swiss cantonCantons of SwitzerlandThe 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the federal state of Switzerland. Each canton was a fully sovereign state with its own borders, army and currency from the Treaty of Westphalia until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848...
of Basel-Stadt, though consisting of three municipalities - USA district of columbia
Federally-administered cities
A federal countryFederation
A federation , also known as a federal state, is a type of sovereign state characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central government...
may also have one or more cities that are federally administered:
- AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
- CanberraCanberraCanberra is the capital city of Australia. With a population of over 345,000, it is Australia's largest inland city and the eighth-largest city overall. The city is located at the northern end of the Australian Capital Territory , south-west of Sydney, and north-east of Melbourne...
(Australian Capital TerritoryAustralian Capital TerritoryThe Australian Capital Territory, often abbreviated ACT, is the capital territory of the Commonwealth of Australia and is the smallest self-governing internal territory...
) - IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
– National Capital Territory of Delhi and ChandigarhChandigarhChandigarh is a union territory of India that serves as the capital of two states, Haryana and Punjab. The name Chandigarh translates as "The Fort of Chandi". The name is from an ancient temple called Chandi Mandir, devoted to the Hindu goddess Chandi, in the city...
(Union TerritoriesUnion TerritoryA Union Territory is a sub-national administrative division of India, in the federal framework of governance. Unlike the states of India, which have their own elected governments, union territories are ruled directly by the federal government; the President of India appoints an Administrator or...
) - Malaysia – Kuala LumpurKuala LumpurKuala Lumpur is the capital and the second largest city in Malaysia by population. The city proper, making up an area of , has a population of 1.4 million as of 2010. Greater Kuala Lumpur, also known as the Klang Valley, is an urban agglomeration of 7.2 million...
, PutrajayaPutrajayaPutrajaya is a planned city, located 25km south of Kuala Lumpur, that serves as the federal administrative centre of Malaysia. The seat of government was shifted in 1999 from Kuala Lumpur to Putrajaya, due to the overcrowding and congestion in the Kuala Lumpur areas...
and LabuanLabuanLabuan is a federal territory in East Malaysia. It is an island off the coast of the state of Sabah. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support...
(Federal Territories) - MexicoMexicoThe United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
– Mexico CityMexico CityMexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
(being the Mexican Federal District) - NigeriaNigeriaNigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
– AbujaAbujaAbuja is the capital city of Nigeria. It is located in the centre of Nigeria, within the Federal Capital Territory . Abuja is a planned city, and was built mainly in the 1980s. It officially became Nigeria's capital on 12 December 1991, replacing Lagos...
, Federal Capital TerritoryFederal Capital TerritoryFederal Capital Territory refer to:*Australian Capital Territory*Federal Capital Territory *Federal Capital Territory... - PakistanPakistanPakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
– IslamabadIslamabadIslamabad is the capital of Pakistan and the tenth largest city in the country. Located within the Islamabad Capital Territory , the population of the city has grown from 100,000 in 1951 to 1.7 million in 2011...
(being the Islamabad Capital TerritoryIslamabad Capital TerritoryThe Islamabad Capital Territory is one of the two federal territories of Pakistan. It includes Islamabad, the capital city of Pakistan, and covers an area of 1,165.5 km² of which 906 km² is Islamabad proper...
) - United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
– Washington, D.C.Washington, D.C.Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
Washington, D.C.

Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
's government operates under authority derived from the U.S. federal government
Federal government of the United States
The federal government of the United States is the national government of the constitutional republic of fifty states that is the United States of America. The federal government comprises three distinct branches of government: a legislative, an executive and a judiciary. These branches and...
. The city (generally referred to as the District of Columbia) is run by an elected mayor and a city council
City council
A city council or town council is the legislative body that governs a city, town, municipality or local government area.-Australia & NZ:Because of the differences in legislation between the States, the exact definition of a City Council varies...
. The council is composed of 13 members: one elected from each of the eight ward
Ward (subnational entity)
A ward is a subdivision of a municipality. Wards are usually named after neighbourhoods, thoroughfares, parishes, landmarks, geographical features and in some cases historical figures connected to the area...
s and five members, including the chairman, elected at-large
At-Large
At-large is a designation for representative members of a governing body who are elected or appointed to represent the whole membership of the body , rather than a subset of that membership...
. The council conducts its work through standing committees and special committees established as needed. District schools are administered by a chancellor, who is appointed by the mayor; in addition, a superintendent of education and a board of education
Board of education
A board of education or a school board or school committee is the title of the board of directors or board of trustees of a school, local school district or higher administrative level....
are responsible for setting some educational policies. There are 37 elected Advisory Neighborhood Commission
Advisory Neighborhood Commission
thumb|right|upright|The District of Columbia is divided into 8 wards, each of which is further divided into local ANCs.Advisory Neighborhood Commissions are bodies of local government in Washington, D.C...
ers that provide the most direct access for residents to their local government. The commissioners are elected by small neighborhood districts, and their suggestions are given "great weight" by the city council and city agencies. However, the U.S. Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
has the ultimate plenary power
Plenary power
A plenary power or plenary authority is the separate identification, definition, and complete vesting of a power or powers or authority in a governing body or individual, to choose to act on a particular subject matter or area...
over the District. It has the right to review and overrule laws created locally and has often done so. The Tenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution
Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which is part of the Bill of Rights, was ratified on December 15, 1791...
, which reserves to states all rights not belonging to the federal government, does not apply to the District. Residents of the District have one non-voting representative in the U.S. Congress.
Autonomous cities in unitary states
In nations without a federal administrative structure, i.e. as unitary stateUnitary state
A unitary state is a state governed as one single unit in which the central government is supreme and any administrative divisions exercise only powers that their central government chooses to delegate...
s, cities may sometimes enjoy a greater degree of autonomy
Autonomy
Autonomy is a concept found in moral, political and bioethical philosophy. Within these contexts, it is the capacity of a rational individual to make an informed, un-coerced decision...
, e.g.:
- CeutaCeutaCeuta is an autonomous city of Spain and an exclave located on the north coast of North Africa surrounded by Morocco. Separated from the Iberian peninsula by the Strait of Gibraltar, Ceuta lies on the border of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta along with the other Spanish...
and MelillaMelillaMelilla is a autonomous city of Spain and an exclave on the north coast of Morocco. Melilla, along with the Spanish exclave Ceuta, is one of the two Spanish territories located in mainland Africa... - Hong KongHong KongHong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
- MacaoMaçãoMação is a municipality in Portugal with a total area of 400.0 km² and a total population of 7,763 inhabitants.The municipality is composed of eight parishes, and is located in the Santarém District....
- GibraltarGibraltarGibraltar is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of , it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region...
Hong Kong and Macao
Because of Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
's and Macao
Mação
Mação is a municipality in Portugal with a total area of 400.0 km² and a total population of 7,763 inhabitants.The municipality is composed of eight parishes, and is located in the Santarém District....
's long histories as colonies of the British and Portuguese
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
empires, respectively, and the unique "one-country, two-systems
One country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is an idea originally proposed by Deng Xiaoping, then Paramount Leader of the People's Republic of China , for the reunification of China during the early 1980s...
" policy, the two city-states continue to enjoy a high degree of autonomy even after their return to the China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
. Having legal systems, police forces, monetary system
Monetary system
A monetary system is anything that is accepted as a standard of value and measure of wealth in a particular region.However, the current trend is to use international trade and investment to alter the policy and legislation of individual governments. The best recent example of this policy is the...
s, customs policies
Customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting and safeguarding customs duties and for controlling the flow of goods including animals, transports, personal effects and hazardous items in and out of a country...
, immigration policies
Immigration policy
An immigration policy is any policy of a state that deals with the transit of persons across its borders into the country, but especially those that intend to work and to remain in the country. Immigration policies can range from allowing no migration at all to allowing most types of migration,...
, national sports teams, official language
Official language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
s, postal systems, academic and educational systems, and certain degrees of international representation
Diplomacy
Diplomacy is the art and practice of conducting negotiations between representatives of groups or states...
that are different or independent from the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, make their status almost equivalent to independent nations.
Further reading
- Mogens Herman HansenMogens Herman HansenMogens Herman Hansen FBA is a Danish classical philologist who is one of the leading scholars in Athenian Democracy and the Polis....
(ed.), A comparative study of thirty city-state cultures : an investigation conducted by the Copenhagen Polis Centre, Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab, 2000. (Historisk-filosofiske skrifter, 21). ISBN 87-7876-177-8. - Mogens Herman Hansen (ed.), A comparative study of six city-state cultures : an investigation, Det Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab, 2002. (Historisk-filosofiske skrifter, 27). ISBN 87-7876-316-9.

