
Hammett acidity function
Encyclopedia
The Hammett acidity function (H0) is a measure of acidity that is used for very concentrated solutions of strong acid
s, including superacid
s. It was proposed by the physical organic chemist Louis Plack Hammett
and is the best-known acidity function
used to extend the measure of acidity beyond the dilute aqueous solutions for which the pH
scale is useful.
In highly concentrated solutions, simple approximations such as the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
are no longer valid due to the variations of the activity coefficient
s. The Hammett acidity function is used in fields such as physical organic chemistry
for the study of acid-catalyzed reactions, because some of these reactions use acids in very high concentrations, or even neat (pure).
in concentrated solutions. It is defined using an equation analogous to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
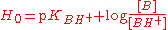
where pKBH+ is −log(K) for the dissociation of BH+, which is the conjugate acid
of a very weak base B, with a very negative pKBH+ In this way the H0 scale may be extended to negative values. Hammett originally used a series of aniline
s with electron-withdrawing groups for the bases.
Hammett also pointed out the equivalent form
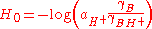
where a is the activity, and the γ are thermodynamic activity coefficients. In dilute aqueous solution (pH 0-14) the predominant acid species is H3O+ and the activity coefficients are close to unity, so H0 is approximately equal to the pH. However beyond this pH range, the effective hydrogen-ion activity changes much more rapidly than the concentration. This is often due to changes in the nature of the acid species; for example in concentrated sulfuric acid
, the predominant acid species ("H+") is not H3O+ but rather H3SO4+ which is a much stronger acid. The value H0 = -12 for pure sulfuric acid must not be interpreted as pH = -12 (which would imply an impossibly high H3O+ concentration of 10+12 mol/L in ideal solution). Instead it means that the acid species present (H3SO4+) has a protonating ability equivalent to H3O+ at a fictitious (ideal) concentration of 1012 mol/L, as measured by its ability to protonate weak bases.
Although the Hammett acidity function is the best known acidity function
, other acidity functions have been developed by authors such as Arnett, Cox, Katrizky, Yates, and Stevens.
(18.4 M) has a H0 value of −12, and pyrosulfuric acid has H0 ~ −15. Take note that the Hammett acidity function clearly avoids water in its equation. It is a generalization of the pH scale—in a dilute aqueous solution (where B is H2O), pH is very nearly equal to H0. By using a solvent-independent quantitative measure of acidity, the implications of the leveling effect are eliminated, and it becomes possible to directly compare the acidities of different substances (e.g. using pKa, HF is weaker than HCl in water but stronger than HCl in glacial acetic acid; however, pure HF is "stronger" than HCl because the H0 of pure HF is higher than that of pure HCl.)
H0 for some concentrated acids:
For mixtures (e.g., partly diluted acids in water), the acidity function depends on the composition of the mixture and has to be determined empirically. Graphs of H0 vs mole fraction can be found in the literature for many acids.
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
s, including superacid
Superacid
According to the classical definition superacid is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid, which has a Hammett acidity function of −12. According to the modern definition, superacid is a medium, in which the chemical potential of the proton is higher than in pure...
s. It was proposed by the physical organic chemist Louis Plack Hammett
Louis Plack Hammett
Louis Plack Hammett was an American physical chemist. He is known for the Hammett equation, which relates reaction rates to equilibrium constants for certain classes of organic reactions involving substituted aromatic compounds...
and is the best-known acidity function
Acidity function
An acidity function is a measure of the acidity of a medium or solvent system, usually expressed in terms of its ability to donate protons to a solute . The pH scale is by far the most commonly used acidity function, and is ideal for dilute aqueous solutions...
used to extend the measure of acidity beyond the dilute aqueous solutions for which the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
scale is useful.
In highly concentrated solutions, simple approximations such as the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
In chemistry, the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation describes the derivation of pH as a measure of acidity in biological and chemical systems...
are no longer valid due to the variations of the activity coefficient
Activity coefficient
An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed...
s. The Hammett acidity function is used in fields such as physical organic chemistry
Physical organic chemistry
Physical organic chemistry is the study of the interrelationships between structure and reactivity in organic molecules. It can be seen as the study of organic chemistry using tools of physical chemistry such as chemical equilibrium, chemical kinetics, thermochemistry, and quantum chemistry...
for the study of acid-catalyzed reactions, because some of these reactions use acids in very high concentrations, or even neat (pure).
Definition
The Hammett acidity function, H0, can replace the pHPH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
in concentrated solutions. It is defined using an equation analogous to the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
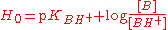
where pKBH+ is −log(K) for the dissociation of BH+, which is the conjugate acid
Conjugate acid
Within the Brønsted–Lowry acid-base theory , a conjugate acid is the acid member, HX, of a pair of two compounds that transform into each other by gain or loss of a proton. A conjugate acid can also be seen as the chemical substance that releases, or donates, a proton in the forward chemical...
of a very weak base B, with a very negative pKBH+ In this way the H0 scale may be extended to negative values. Hammett originally used a series of aniline
Aniline
Aniline, phenylamine or aminobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine. Being a precursor to many industrial chemicals, its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane...
s with electron-withdrawing groups for the bases.
Hammett also pointed out the equivalent form
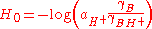
where a is the activity, and the γ are thermodynamic activity coefficients. In dilute aqueous solution (pH 0-14) the predominant acid species is H3O+ and the activity coefficients are close to unity, so H0 is approximately equal to the pH. However beyond this pH range, the effective hydrogen-ion activity changes much more rapidly than the concentration. This is often due to changes in the nature of the acid species; for example in concentrated sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
, the predominant acid species ("H+") is not H3O+ but rather H3SO4+ which is a much stronger acid. The value H0 = -12 for pure sulfuric acid must not be interpreted as pH = -12 (which would imply an impossibly high H3O+ concentration of 10+12 mol/L in ideal solution). Instead it means that the acid species present (H3SO4+) has a protonating ability equivalent to H3O+ at a fictitious (ideal) concentration of 1012 mol/L, as measured by its ability to protonate weak bases.
Although the Hammett acidity function is the best known acidity function
Acidity function
An acidity function is a measure of the acidity of a medium or solvent system, usually expressed in terms of its ability to donate protons to a solute . The pH scale is by far the most commonly used acidity function, and is ideal for dilute aqueous solutions...
, other acidity functions have been developed by authors such as Arnett, Cox, Katrizky, Yates, and Stevens.
Typical values
On this scale, pure H2SO4Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
(18.4 M) has a H0 value of −12, and pyrosulfuric acid has H0 ~ −15. Take note that the Hammett acidity function clearly avoids water in its equation. It is a generalization of the pH scale—in a dilute aqueous solution (where B is H2O), pH is very nearly equal to H0. By using a solvent-independent quantitative measure of acidity, the implications of the leveling effect are eliminated, and it becomes possible to directly compare the acidities of different substances (e.g. using pKa, HF is weaker than HCl in water but stronger than HCl in glacial acetic acid; however, pure HF is "stronger" than HCl because the H0 of pure HF is higher than that of pure HCl.)
H0 for some concentrated acids:
- Fluoroantimonic acidFluoroantimonic acidFluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride in various ratios. The 1:1 combination forms the strongest known superacid, which has been demonstrated to protonate even hydrocarbons to afford carbocations and H2....
(1990): −31.3 - Magic acidMagic acidMagic acid , is a superacid consisting of a mixture, most commonly in a 1:1 molar ratio, of fluorosulfonic acid and antimony pentafluoride...
(1974): −19.2 - Carborane superacid (1969): −18.0
- Fluorosulfuric acidFluorosulfuric acidFluorosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3F. It is one of the strongest acids commercially available and is a superacid. The formula HFSO3 emphasizes its relationship to sulfuric acid, H2SO4; HSO3F is a tetrahedral molecule.-Chemical properties:Fluorosulfuric acid is a...
(1944): −15.1 - Triflic acid (1940): −14.1
- Sulfuric acidSulfuric acidSulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
−12.0
For mixtures (e.g., partly diluted acids in water), the acidity function depends on the composition of the mixture and has to be determined empirically. Graphs of H0 vs mole fraction can be found in the literature for many acids.

