
Hepteract
Encyclopedia
| 7-cube Hepteract |
|
|---|---|
Orthogonal projection inside Petrie polygon Petrie polygon In geometry, a Petrie polygon for a regular polytope of n dimensions is a skew polygon such that every consecutive sides belong to one of the facets... The central orange vertex is doubled |
|
| Type | Regular 7-polytope 7-polytope In seven-dimensional geometry, a 7-polytope is a polytope contained by 6-polytope facets. Each 5-polytope ridge being shared by exactly two 6-polytope facets.... |
| Family | hypercube Hypercube In geometry, a hypercube is an n-dimensional analogue of a square and a cube . It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length.An... |
| Schläfli symbol | {4,35} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram Coxeter-Dynkin diagram In geometry, a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is a graph with numerically labeled edges representing the spatial relations between a collection of mirrors... |
|
| 6-faces | 14 {4,34} Hexeract In geometry, a 6-cube is a six-dimensional hypercube with 64 vertices, 192 edges, 240 square faces, 160 cubic cells, 60 tesseract 4-faces, and 12 5-cube 5-faces.... |
| 5-faces | 84 {4,33} Penteract In five dimensional geometry, a 5-cube is a name for a five dimensional hypercube with 32 vertices, 80 edges, 80 square faces, 40 cubic cells, and 10 tesseract hypercells.... |
| 4-faces | 280 {4,3,3} Tesseract In geometry, the tesseract, also called an 8-cell or regular octachoron or cubic prism, is the four-dimensional analog of the cube. The tesseract is to the cube as the cube is to the square. Just as the surface of the cube consists of 6 square faces, the hypersurface of the tesseract consists of 8... |
| Cells | 560 {4,3} Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
| Faces | 672 {4} Square (geometry) In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles... |
| Edges | 448 |
| Vertices | 128 |
| Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
6-simplex |
| Petrie polygon Petrie polygon In geometry, a Petrie polygon for a regular polytope of n dimensions is a skew polygon such that every consecutive sides belong to one of the facets... |
tetradecagon |
| Coxeter group Coxeter group In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example... |
C7, [35,4] |
| Dual | 7-orthoplex |
| Properties | convex Convex polytope A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set of points in the n-dimensional space Rn... |
In geometry
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a 7-cube is a seven-dimensional
Seven-dimensional space
In physics and mathematics, a sequence of n numbers can also be understood as a location in n-dimensional space. When n = 7, the set of all such locations is called 7-dimensional Euclidean space...
hypercube
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an n-dimensional analogue of a square and a cube . It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length.An...
with 128 vertices
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
, 448 edge
Edge (geometry)
In geometry, an edge is a one-dimensional line segment joining two adjacent zero-dimensional vertices in a polygon. Thus applied, an edge is a connector for a one-dimensional line segment and two zero-dimensional objects....
s, 672 square faces
Face (geometry)
In geometry, a face of a polyhedron is any of the polygons that make up its boundaries. For example, any of the squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube...
, 560 cubic cells, 280 tesseract
Tesseract
In geometry, the tesseract, also called an 8-cell or regular octachoron or cubic prism, is the four-dimensional analog of the cube. The tesseract is to the cube as the cube is to the square. Just as the surface of the cube consists of 6 square faces, the hypersurface of the tesseract consists of 8...
4-faces
Hypercell
In geometry, a hypercell is a descriptive term for an element of a polytope or tessellation, usually representing an element one dimension higher than a cell. The most generally accepted term is 4-face because it contains a 4-dimensional interior...
, 84 penteract
Penteract
In five dimensional geometry, a 5-cube is a name for a five dimensional hypercube with 32 vertices, 80 edges, 80 square faces, 40 cubic cells, and 10 tesseract hypercells....
5-faces, and 14 hexeract
Hexeract
In geometry, a 6-cube is a six-dimensional hypercube with 64 vertices, 192 edges, 240 square faces, 160 cubic cells, 60 tesseract 4-faces, and 12 5-cube 5-faces....
6-faces.
It can be named by its Schläfli symbol {4,35}, being composed of 3 6-cubes around each 5-face. It can be called a hepteract, derived from combining the name tesseract
Tesseract
In geometry, the tesseract, also called an 8-cell or regular octachoron or cubic prism, is the four-dimensional analog of the cube. The tesseract is to the cube as the cube is to the square. Just as the surface of the cube consists of 6 square faces, the hypersurface of the tesseract consists of 8...
(the 4-cube) with hepta for seven (dimensions) in Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
. It can also be called a regular tetradeca-7-tope or tetradecaexon, being a 7 dimensional polytope
7-polytope
In seven-dimensional geometry, a 7-polytope is a polytope contained by 6-polytope facets. Each 5-polytope ridge being shared by exactly two 6-polytope facets....
constructed from 14 regular facets.
Related polytopes
It is a part of an infinite family of polytopes, called hypercubeHypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an n-dimensional analogue of a square and a cube . It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length.An...
s. The dual of a Hepteract can be called a 7-orthoplex, and is a part of the infinite family of cross-polytope
Cross-polytope
In geometry, a cross-polytope, orthoplex, hyperoctahedron, or cocube is a regular, convex polytope that exists in any number of dimensions. The vertices of a cross-polytope are all the permutations of . The cross-polytope is the convex hull of its vertices...
s.
Applying an alternation operation, deleting alternating vertices of the hepteract, creates another uniform polytope
Uniform polytope
A uniform polytope is a vertex-transitive polytope made from uniform polytope facets of a lower dimension. Uniform polytopes of 2 dimensions are the regular polygons....
, called a demihepteract
Demihepteract
In geometry, a demihepteract or 7-demicube is a uniform 7-polytope, constructed from the 7-hypercube with alternated vertices deleted...
, (part of an infinite family called demihypercubes), which has 14 demihexeract
Demihexeract
In geometry, a 6-demicube or demihexteract is a uniform 6-polytope, constructed from a 6-cube with alternate vertices deleted. It is part of a dimensionally infinite family of uniform polytopes called demihypercubes....
ic and 64 6-simplex 6-faces.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a hepteract centered at the origin and edge length 2 are- (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1)
while the interior of the same consists of all points (x0, x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6) with -1 < xi < 1.
Projections
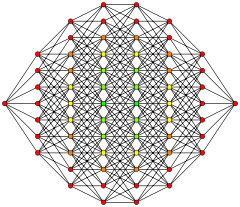 This hypercube graph is an orthogonal projection. This oriention shows columns of vertices positioned a vertex-edge-vertex distance from one vertex on the left to one vertex on the right, and edges attaching adjacent columns of vertices. The number of vertices in each column represents rows in Pascal's triangle Pascal's triangle In mathematics, Pascal's triangle is a triangular array of the binomial coefficients in a triangle. It is named after the French mathematician, Blaise Pascal... , being 1:7:21:35:35:21:7:1. |
Petrie polygon, skew orthographic projection |
 Another orthogonal projection |
Hepteract 7D simple rotation through 2Pi with 7D perspective projection to 3D.
External links
- Multi-dimensional Glossary: hypercube Garrett Jones
- Rotation of 7D-Cube www.4d-screen.de

