
Hill yield criteria
Encyclopedia
Rodney Hill
has developed several yield criteria for anisotropic plastic deformations. The earliest version was a straightforward extension of the von Mises yield criterion and had a quadratic form. This model was later generalized by allowing for an exponent m. Variations of these criteria are in wide use for metals, polymers, and certain composites.
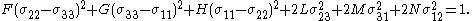
Here F, G, H, L, M, N are constants that have to be determined experimentally and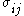 are the stresses. The quadratic Hill yield criterion depends only on the deviatoric stresses and is pressure independent. It predicts the same yield stress in tension and in compression.
are the stresses. The quadratic Hill yield criterion depends only on the deviatoric stresses and is pressure independent. It predicts the same yield stress in tension and in compression.
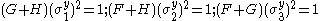
where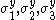 are the normal yield stresses with respect to the axes of anisotropy. Therefore we have
are the normal yield stresses with respect to the axes of anisotropy. Therefore we have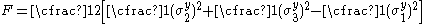
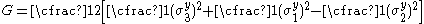
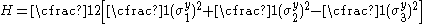
Similarly, if are the yield stresses in shear (with respect to the axes of anisotropy), we have
are the yield stresses in shear (with respect to the axes of anisotropy), we have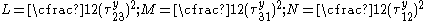
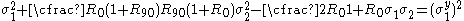
where the principal stresses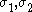 are assumed to be aligned with the axes of anisotropy with
are assumed to be aligned with the axes of anisotropy with 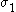 in the rolling direction and
in the rolling direction and 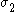 perpendicular to the rolling direction,
perpendicular to the rolling direction, 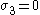 ,
, 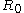 is the R-value
is the R-value
in the rolling direction, and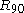 is the R-value
is the R-value
perpendicular to the rolling direction.
For the special case of transverse isotropy we have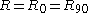 and we get
and we get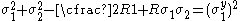
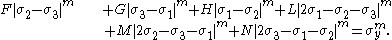
where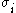 are the principal stresses (which are aligned with the directions of anisotropy),
are the principal stresses (which are aligned with the directions of anisotropy), 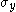 is the yield stress, and F, G, H, L, M, N are constants. The value of m is determined by the degree of anisotropy of the material and must be greater than 1 to ensure convexity of the yield surface.
is the yield stress, and F, G, H, L, M, N are constants. The value of m is determined by the degree of anisotropy of the material and must be greater than 1 to ensure convexity of the yield surface.
 being the plane of symmetry, the generalized Hill yield criterion reduces to (with
being the plane of symmetry, the generalized Hill yield criterion reduces to (with 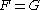 and
and 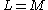 )
)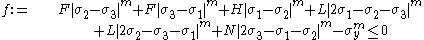
The R-value or Lankford coefficient
can be determined by considering the situation where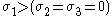 . The R-value is then given by
. The R-value is then given by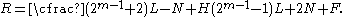
Under plane stress conditions and with some assumptions, the generalized Hill criterion can take several forms.
Rodney Hill
Rodney Hill FRS was an applied mathematician and a former Professor of Mechanics of Solids at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge....
has developed several yield criteria for anisotropic plastic deformations. The earliest version was a straightforward extension of the von Mises yield criterion and had a quadratic form. This model was later generalized by allowing for an exponent m. Variations of these criteria are in wide use for metals, polymers, and certain composites.
Quadratic Hill yield criterion
The quadratic Hill yield criterion. has the form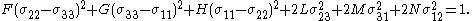
Here F, G, H, L, M, N are constants that have to be determined experimentally and
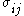 are the stresses. The quadratic Hill yield criterion depends only on the deviatoric stresses and is pressure independent. It predicts the same yield stress in tension and in compression.
are the stresses. The quadratic Hill yield criterion depends only on the deviatoric stresses and is pressure independent. It predicts the same yield stress in tension and in compression.Expressions for F, G, H, L, M, N
If the axes of material anisotropy are assumed to be orthogonal, we can write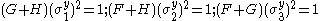
where
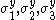 are the normal yield stresses with respect to the axes of anisotropy. Therefore we have
are the normal yield stresses with respect to the axes of anisotropy. Therefore we have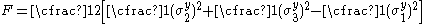
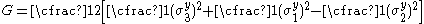
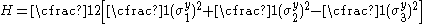
Similarly, if
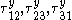 are the yield stresses in shear (with respect to the axes of anisotropy), we have
are the yield stresses in shear (with respect to the axes of anisotropy), we have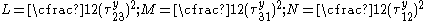
Quadratic Hill yield criterion for plane stress
The quadratic Hill yield criterion for thin rolled plates (plane stress conditions) can be expressed as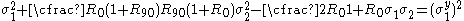
where the principal stresses
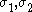 are assumed to be aligned with the axes of anisotropy with
are assumed to be aligned with the axes of anisotropy with 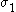 in the rolling direction and
in the rolling direction and 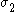 perpendicular to the rolling direction,
perpendicular to the rolling direction, 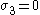 ,
, 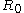 is the R-value
is the R-valueLankford coefficient
The Lankford coefficient is a measure of the plastic anisotropy of a rolled sheet metal. This scalar quantity is used extensively as an indicator of the formability of recrystallized low-carbon steel sheets....
in the rolling direction, and
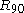 is the R-value
is the R-valueLankford coefficient
The Lankford coefficient is a measure of the plastic anisotropy of a rolled sheet metal. This scalar quantity is used extensively as an indicator of the formability of recrystallized low-carbon steel sheets....
perpendicular to the rolling direction.
For the special case of transverse isotropy we have
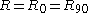 and we get
and we get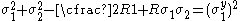
| Derivation of Hill's criterion for plane stress |
|---|
For the situation where the principal stresses are aligned with the directions of anisotropy we have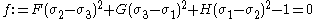 where 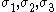 are the principal stresses. If we assume an associated flow rule we have are the principal stresses. If we assume an associated flow rule we have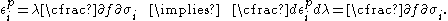 This implies that 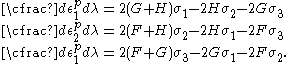 For plane stress 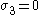 , which gives , which gives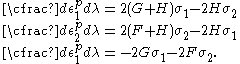 The R-value Lankford coefficient The Lankford coefficient is a measure of the plastic anisotropy of a rolled sheet metal. This scalar quantity is used extensively as an indicator of the formability of recrystallized low-carbon steel sheets.... 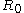 is defined as the ratio of the in-plane and out-of-plane plastic strains under uniaxial stress is defined as the ratio of the in-plane and out-of-plane plastic strains under uniaxial stress 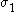 . The quantity . The quantity 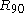 is the plastic strain ratio under uniaxial stress is the plastic strain ratio under uniaxial stress 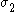 . Therefore, we have . Therefore, we have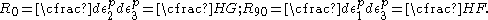 Then, using 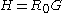 and and 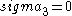 , the yield condition can be written as , the yield condition can be written as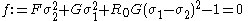 which in turn may be expressed as  This is of the same form as the required expression. All we have to do is to express 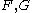 in terms of in terms of 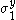 . Recall that, . Recall that,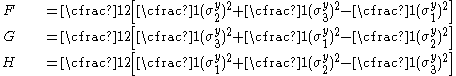 We can use these to obtain 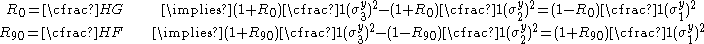 Solving for 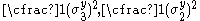 gives us gives us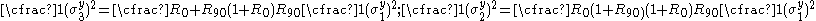 Plugging back into the expressions for 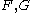 leads to leads to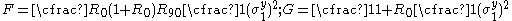 which implies that 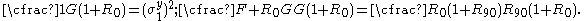 Therefore the plane stress form of the quadratic Hill yield criterion can be expressed as 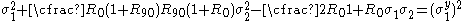 |
Generalized Hill yield criterion
The generalized Hill yield criterion has the form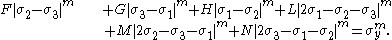
where
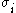 are the principal stresses (which are aligned with the directions of anisotropy),
are the principal stresses (which are aligned with the directions of anisotropy), 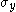 is the yield stress, and F, G, H, L, M, N are constants. The value of m is determined by the degree of anisotropy of the material and must be greater than 1 to ensure convexity of the yield surface.
is the yield stress, and F, G, H, L, M, N are constants. The value of m is determined by the degree of anisotropy of the material and must be greater than 1 to ensure convexity of the yield surface.Generalized Hill yield criterion for plane stress
For transversely isotropic materials with being the plane of symmetry, the generalized Hill yield criterion reduces to (with
being the plane of symmetry, the generalized Hill yield criterion reduces to (with 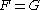 and
and 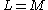 )
)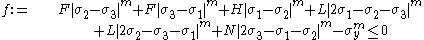
The R-value or Lankford coefficient
Lankford coefficient
The Lankford coefficient is a measure of the plastic anisotropy of a rolled sheet metal. This scalar quantity is used extensively as an indicator of the formability of recrystallized low-carbon steel sheets....
can be determined by considering the situation where
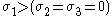 . The R-value is then given by
. The R-value is then given by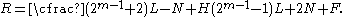
Under plane stress conditions and with some assumptions, the generalized Hill criterion can take several forms.
- Case 1:
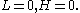
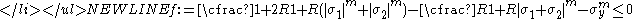
- Case 2:
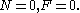
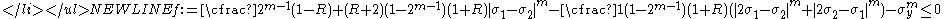
- Case 3:
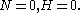
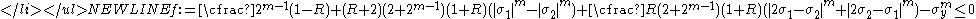
- Case 4:
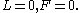
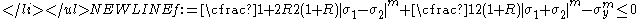
- Case 5:
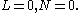 . This is the Hosford yield criterionHosford yield criterionThe Hosford yield criterion is a function that is used to determine whether a material has undergone plastic yielding under the action of stress.- Hosford yield criterion for isotropic plasticity :...
. This is the Hosford yield criterionHosford yield criterionThe Hosford yield criterion is a function that is used to determine whether a material has undergone plastic yielding under the action of stress.- Hosford yield criterion for isotropic plasticity :...
.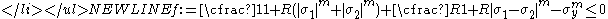
- Care must be exercised in using these forms of the generalized Hill yield criterion because the yield surfaces become concave (sometimes even unbounded) for certain combinations of
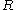 and
and 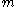 .
.
Hill 1993 yield criterion
In 1993, Hill proposed another yield criterion for plane stress problems with planar anisotropy. The Hill93 criterion has the form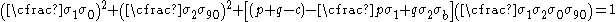
where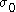 is the uniaxial tensile yield stress in the rolling direction,
is the uniaxial tensile yield stress in the rolling direction, 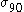 is the uniaxial tensile yield stress in the direction normal to the rolling direction,
is the uniaxial tensile yield stress in the direction normal to the rolling direction, 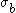 is the yield stress under uniform biaxial tension, and
is the yield stress under uniform biaxial tension, and 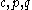 are parameters defined as
are parameters defined as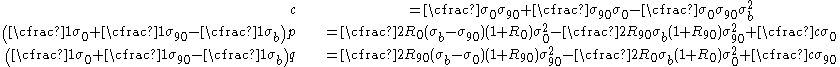
and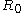 is the R-value for uniaxial tension in the rolling direction, and
is the R-value for uniaxial tension in the rolling direction, and 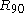 is the R-value for uniaxial tension in the in-plane direction perpendicular to the rolling direction.
is the R-value for uniaxial tension in the in-plane direction perpendicular to the rolling direction.
Extensions of Hill's yield criteria
The original versions of Hill's yield criteria were designed for material that did not have pressure-dependent yield surfaces which are needed to model polymerPolymerA polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
s and foamFoam-Definition:A foam is a substance that is formed by trapping gas in a liquid or solid in a divided form, i.e. by forming gas regions inside liquid regions, leading to different kinds of dispersed media...
s.
The Caddell-Raghava-Atkins yield criterion
An extension that allows for pressure dependence is Caddell-Raghava-Atkins (CRA) model which has the form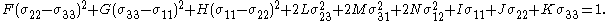
The Deshpande-Fleck-Ashby yield criterion
Another pressure-dependent extension of Hill's quadratic yield criterion which has a form similar to the Bresler Pister yield criterionBresler Pister yield criterionThe Bresler-Pister yield criterion is a function that was originally devised to predict the strength of concrete under multiaxial stress states...
is the Deshpande, Fleck and Ashby (DFA) yield criterion for honeycomb structuresHoneycomb structuresHoneycomb structures are natural or man-made structures that have the geometry of a honeycomb to allow the minimization of the amount of used material to reach minimal weight and minimal material cost. The geometry of honeycomb structures can vary widely but the common feature of all such...
(used in sandwich compositeSandwich structured compositeA sandwich-structured composite is a special class of composite materials that is fabricated by attaching two thin but stiff skins to a lightweight but thick core...
construction). This yield criterion has the form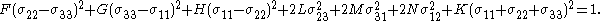
External links
- Care must be exercised in using these forms of the generalized Hill yield criterion because the yield surfaces become concave (sometimes even unbounded) for certain combinations of
- Case 5:
- Case 4:
- Case 3:
- Case 2:

