
History of Namibia
Encyclopedia

Colony
In politics and history, a colony is a territory under the immediate political control of a state. For colonies in antiquity, city-states would often found their own colonies. Some colonies were historically countries, while others were territories without definite statehood from their inception....
in the late nineteenth century to Namibia's independence on 21 March 1990.
From 1884, Namibia
Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia , is a country in southern Africa whose western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. It gained independence from South Africa on 21 March...
was a German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
colony: German South-West Africa
German South-West Africa
German South West Africa was a colony of Germany from 1884 until 1915, when it was taken over by South Africa and administered as South West Africa, finally becoming Namibia in 1990...
. After the First World War
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, the League of Nations mandated
League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League...
South Africa to administer the territory. Following World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
was dissolved in April 1946 and its successor, the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
, instituted a Trusteeship system to bring all of the former German colonies in Africa under UN control. South Africa objected arguing that a majority of the territory's people were content with South African rule.
Legal argument ensued over the course of the next twenty years until, in October 1966, the UN General Assembly
Unga
Unga may refer to:* Harvey Unga , American football running back* Unga, Alaska, United States* Unga , the largest land-living arthropod in the world* Unga , a traditional Scottish land measurement...
decided to end the mandate, declaring that South Africa had no other right to administer the territory and that henceforth South-West Africa was to come under the direct responsibility of the UN (Resolution 2145 XXI of 27 October 1966).
Pre-colonial history
There is a diversity of pre-modern peoples in Namibia. The most famous, BushmenBushmen
The indigenous people of Southern Africa, whose territory spans most areas of South Africa, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, Mozambique, Swaziland, Botswana, Namibia, and Angola, are variously referred to as Bushmen, San, Sho, Barwa, Kung, or Khwe...
(also called San) are generally assumed to have been the earliest inhabitants of the region comprising today's Namibia, Botswana
Botswana
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana , is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa. The citizens are referred to as "Batswana" . Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent within the Commonwealth on 30 September 1966...
and South Africa. The bushmen were hunters and gatherers with a nomadic lifestyle. The most important part of their diet consisted of fruits, nuts and roots, but they also hunted different kinds of antelope
Antelope
Antelope is a term referring to many even-toed ungulate species indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia. Antelopes comprise a miscellaneous group within the family Bovidae, encompassing those old-world species that are neither cattle, sheep, buffalo, bison, nor goats...
s. Over time, many different ethnic groups of immigrants settled in Namibia.
The north - the Ovambo and Kavango
The Ovambo, and the smaller and closely related group KavangoKavango
The Kavango people, also known as the vaKavango, reside on the Namibian side of the Namibian–Angolan border along the Kavango River. They are mainly riverine living people, but about 20% reside in the dry inland. Their livelihood is based on fishery, livestock-keeping and cropping...
, lived in northern Namibia, southern Angola
Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
and, in the case of the Kavango, western Zambia. Being settled people they had an economy based on farming, cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
and fishing
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping....
, but they also produced metal goods. Both groups belonged to the Bantu nation. They rarely ventured south to the central parts of the country, since the conditions there did not suit their farming way of life, but traded extensively their knives and agricultural implements.
Khoisan immigration - the Nama and Damara
Until about 2,000 years ago the original hunters and gatherers of the San people were the only inhabitants in Namibia. At this time the NamaNamaqua
Nama are an African ethnic group of South Africa, Namibia and Botswana. They traditionally speak the Nama language of the Khoe-Kwadi language family, although many Nama now speak Afrikaans. The Nama are the largest group of the Khoikhoi people, most of whom have largely disappeared as a group,...
(also known as Namaqua
Namaqua
Nama are an African ethnic group of South Africa, Namibia and Botswana. They traditionally speak the Nama language of the Khoe-Kwadi language family, although many Nama now speak Afrikaans. The Nama are the largest group of the Khoikhoi people, most of whom have largely disappeared as a group,...
, Khoikhoi
Khoikhoi
The Khoikhoi or Khoi, in standardised Khoekhoe/Nama orthography spelled Khoekhoe, are a historical division of the Khoisan ethnic group, the native people of southwestern Africa, closely related to the Bushmen . They had lived in southern Africa since the 5th century AD...
or Hottentots) settled around the Orange River
Orange River
The Orange River , Gariep River, Groote River or Senqu River is the longest river in South Africa. It rises in the Drakensberg mountains in Lesotho, flowing westwards through South Africa to the Atlantic Ocean...
in the south on the border between Namibia and South Africa where they kept herds of sheep and goat
Goat
The domestic goat is a subspecies of goat domesticated from the wild goat of southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the Bovidae family and is closely related to the sheep as both are in the goat-antelope subfamily Caprinae. There are over three hundred distinct breeds of...
s.
Both the San and the Nama were Khoisan
Khoisan
Khoisan is a unifying name for two ethnic groups of Southern Africa, who share physical and putative linguistic characteristics distinct from the Bantu majority of the region. Culturally, the Khoisan are divided into the foraging San and the pastoral Khoi...
peoples, and spoke languages from the Khoisan language group.
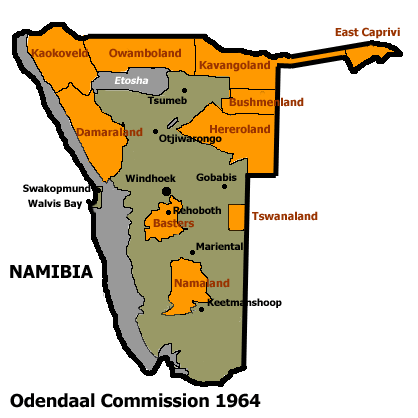
In the 9th century Damara (also known as Bergdama or Berg Damara), another Khoisan group, entered Namibia. It is unclear where they came from, but they settled in the grasslands in central Namibia, known as Damaraland
Damaraland
Damaraland was a name given to the north-central part of what later became Namibia, inhabited by the Damaras. It was bounded roughly by Ovamboland in the north, the Namib Desert in the west, the Kalahari Desert in the east, and Windhoek in the south....
.

Bantu immigration - the Herero
During the 17th century the Herero, a pastoralPastoral
The adjective pastoral refers to the lifestyle of pastoralists, such as shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasturage. It also refers to a genre in literature, art or music that depicts such shepherd life in an...
, nomadic people keeping cattle, moved into Namibia. They came from the east African lakes and entered Namibia from the northwest. First they resided in Kaokoland
Kaokoland
Kaokoland is an area in Northern Namibia, in the Kunene Region. It is one of the wildest and less populated areas in Namibia, with a population density of one person every 2 km², that is 1/4 of the national average. The most represented ethnic group is the Himba people, that accounts for...
, but in the middle of the 19th century some tribes moved farther south and into Damaraland. A number of tribes remained in Kaokoland: these were the Himba
Himba
The Himba are an ethnic group of about 20,000 to 50,000 people living in northern Namibia, in the Kunene region . Recently they have built two villages in Kamanjab which have become tourist destinations...
people, who are still there today. The Herero were said to have enslaved certain groups and displaced others such as the Bushmen
Bushmen
The indigenous people of Southern Africa, whose territory spans most areas of South Africa, Zimbabwe, Lesotho, Mozambique, Swaziland, Botswana, Namibia, and Angola, are variously referred to as Bushmen, San, Sho, Barwa, Kung, or Khwe...
to marginal areas unsuitable for their way of life.
The Oorlams
In the 19th century white farmers, mostly BoerBoer
Boer is the Dutch and Afrikaans word for farmer, which came to denote the descendants of the Dutch-speaking settlers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 18th century, as well as those who left the Cape Colony during the 19th century to settle in the Orange Free State,...
s moved farther northwards pushing the indigenous
Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are ethnic groups that are defined as indigenous according to one of the various definitions of the term, there is no universally accepted definition but most of which carry connotations of being the "original inhabitants" of a territory....
Khoisan peoples, who put up a fierce resistance, across the Orange River. Known as Oorlams, these Khoisan adopted Boer customs and spoke a language similar to Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken natively in South Africa and Namibia. It is a daughter language of Dutch, originating in its 17th century dialects, collectively referred to as Cape Dutch .Afrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , .Afrikaans was historically called Cape...
.
Armed with guns, the Oorlams caused instability as more and more came to settle in Namaqualand and eventually conflict arose between them and the Nama. Under the leadership of Jonker Afrikaner
Jonker Afrikaner
Jonker Afrikaner was the fourth Captain of the Orlam Afrikaners in South West Africa, succeeding his father, Jager Afrikaner, in 1823...
, the Oorlams used their superior weapons to take control of the best grazing land. In the 1830s Jonker Afrikaner concluded an agreement with the Nama chief Oaseb whereby the Oorlams would protect the central grasslands of Namibia from the Herero who were then pushing southwards. In return Jonker Afrikaner was recognised as overlord, received tribute from the Nama and settled at what today is Windhoek, on the borders of Herero territory. The Afrikaners soon came in conflict with the Herero who entered Damaraland from the south at about the same time as the Afrikaner started to expand farther north from Namaqualand. Both the Herero and the Afrikaner wanted to use the grasslands of Damaraland for their herds. This resulted in warfare between the Herero and the Oorlams as well as between the two of them and the Damara, who were the original inhabitants of the area. The Damara were displaced by the fighting and many were killed.
With their horses and guns, the Afrikaners proved to be militarily superior and forced the Herero to give them cattle as tribute.

Baster immigration
The last group to arrive in Namibia before the Europeans were the Basters – descendants of Boer men and African women (mostly Nama). Being Calvinist and Afrikaans-speaking, they considered themselves to be culturally more "white" than "black". As with the Oorlams, they were forced northwards by the expansion of white settlers when, in 1868, a group of about 90 families crossed the Orange RiverOrange River
The Orange River , Gariep River, Groote River or Senqu River is the longest river in South Africa. It rises in the Drakensberg mountains in Lesotho, flowing westwards through South Africa to the Atlantic Ocean...
into Namibia.
The Basters settled in central Namibia, where they founded the city Rehoboth
Rehoboth, Namibia
Rehoboth is a town of 21,000 inhabitants in central Namibia just north of the Tropic of Capricorn. Located on the B1 road, 90 kilometres south of the Namibian capital Windhoek, Rehoboth lies on a high elevation plateau with several natural hot-water springs. It receives sparse mean annual rainfall...
. In 1872 they founded the "Free Republic of Rehoboth" and adopted a constitution stating that the nation should be led by a "Kaptein" directly elected by the people, and that there should be a small parliament, or Volkraad, consisting of three directly-elected citizens.
European influence and colonisation
The first European to set foot on Namibian soil was the PortuguesePortugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
Diogo Cão
Diogo Cão
Diogo Cão was a Portuguese explorer and one of the most remarkable navigators of the Age of Discovery, who made two voyages sailing along the west coast of Africa to Namibia in the 1480s.-Early life and family:...
in 1485, who stopped briefly on the Skeleton Coast
Skeleton Coast
The Skeleton Coast is the northern part of the Atlantic Ocean coast of Namibia and south of Angola from the Kunene River south to the Swakop River, although the name is sometimes used to describe the entire Namib Desert coast...
, and raised a limestone cross there, on his exploratory mission along the west coast of Africa.
The next European to visit Namibia was also a Portuguese, Bartholomeu Dias, who stopped at what today is Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay , is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies...
and Lüderitz
Lüderitz
Lüderitz is a harbour town in south-west Namibia, lying on one of the least hospitable coasts in Africa. It is a port developed around Robert Harbour and Shark Island.- Overview :...
(which he named Angra Pequena) on his way to round the Cape of Good Hope
Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula, South Africa.There is a misconception that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa, because it was once believed to be the dividing point between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. In fact, the...
.
The inhospitable Namib Desert
Namib Desert
The Namib Desert is a desert in Namibia and southwest Angola that forms part of the Namib-Naukluft National Park, the largest game reserve in Africa. The name "Namib" is of Nama origin and means "vast place"...
constituted a formidable barrier and neither of the Portuguese explorers went far inland.
In 1793 the Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
authority in the Cape decided to take control of Walvis bay, since it was the only good deep-water harbour along the Skeleton Coast. When the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
took control of the Cape Colony
Cape Colony
The Cape Colony, part of modern South Africa, was established by the Dutch East India Company in 1652, with the founding of Cape Town. It was subsequently occupied by the British in 1795 when the Netherlands were occupied by revolutionary France, so that the French revolutionaries could not take...
in 1797, they also took over Walvis Bay. But white settlement in the area was limited, and neither the Dutch nor the British penetrated far into the country.
One of the first European groups to show interest in Namibia were the missionaries. In 1805 the London Missionary Society
London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was a non-denominational missionary society formed in England in 1795 by evangelical Anglicans and Nonconformists, largely Congregationalist in outlook, with missions in the islands of the South Pacific and Africa...
began working in Namibia, moving north from the Cape Colony. In 1811 they founded the town Bethanie in southern Namibia, where they built a church, which today is Namibia's oldest building.
In the 1840s the German Rhenish Mission Society started working in Namibia and co-operating with the London Missionary Society.
It was not until the 19th century, when European powers sought to carve up the African continent between them in the so called "Scramble for Africa
Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also known as the Race for Africa or Partition of Africa was a process of invasion, occupation, colonization and annexation of African territory by European powers during the New Imperialism period, between 1881 and World War I in 1914...
", that Europeans – Germany and Great Britain in the forefront – became interested in Namibia.
The first territorial claim on a part of Namibia came in 1878, when Britain annexed Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay , is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies...
on behalf of the Cape Colony, confirming the settlement of 1797. The annexation was an attempt to forestall German ambitions in the area, and it also guaranteed control of the good deepwater harbour on the way to the Cape Colony and other British colonies on Africa's east coast.
In 1883, a German trader, Adolf Lüderitz
Adolf Lüderitz
Franz Adolf Eduard Lüderitz was a German merchant and founder of the first German colony in Southwest Africa....
, bought Angra Pequena
Angra Pequena
Angra Pequena was a small coastal area in what is now known as Lüderitz, Namibia.First discovered by Europeans in 1487 by the Portuguese explorer Bartolomeu Dias. On April 10, 1883 Heinrich Vogelsang first landed at Angra Pequena...
from the Nama chief Joseph Fredericks. The price he paid was 10,000 Reichsmark and 260 guns.
He soon renamed the coastal area after himself, giving it the name Lüderitz. Believing that Britain was soon about to declare the whole area a protectorate, Lüderitz advised the German chancellor Otto von Bismarck
Otto von Bismarck
Otto Eduard Leopold, Prince of Bismarck, Duke of Lauenburg , simply known as Otto von Bismarck, was a Prussian-German statesman whose actions unified Germany, made it a major player in world affairs, and created a balance of power that kept Europe at peace after 1871.As Minister President of...
to claim it. In 1884 Bismarck did so, thereby establishing German South West Africa as a colony (Deutsch-Südwestafrika in German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
).
A region, the Caprivi Strip
Caprivi Strip
Caprivi, sometimes called the Caprivi Strip , Caprivi Panhandle or the Okavango Strip and formally known as Itenge, is a narrow protrusion of Namibia eastwards about , between Botswana to the south, Angola and Zambia to the north, and Okavango Region to the west. Caprivi is bordered by the...
, became a part of German South West Africa after the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty
Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty
The Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty of 1 July 1890 was an agreement between the United Kingdom and the German Empire concerning mainly territorial interests in Africa.-Terms:...
on July 1, 1890, between the United Kingdom and Germany. The Caprivi Strip in Namibia gave Germany access to the Zambezi River and thereby to German colonies in East Africa. In exchange for the island of Heligoland
Heligoland
Heligoland is a small German archipelago in the North Sea.Formerly Danish and British possessions, the islands are located in the Heligoland Bight in the south-eastern corner of the North Sea...
in the North Sea, Britain took control of the island of Zanzibar
Zanzibar
Zanzibar ,Persian: زنگبار, from suffix bār: "coast" and Zangi: "bruin" ; is a semi-autonomous part of Tanzania, in East Africa. It comprises the Zanzibar Archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of numerous small islands and two large ones: Unguja , and Pemba...
in East Africa.
German South-West Africa

Namaqua
Nama are an African ethnic group of South Africa, Namibia and Botswana. They traditionally speak the Nama language of the Khoe-Kwadi language family, although many Nama now speak Afrikaans. The Nama are the largest group of the Khoikhoi people, most of whom have largely disappeared as a group,...
. Under the leadership of the tribal chief Hendrik Witbooi
Hendrik Witbooi (Namaqua chief)
Hendrik Witbooi was a king of the Namaqua people, a sub-tribe of the Khoikhoi. He lived in present day Namibia. His face is portrayed on the obverse of all Namibian dollar banknotes.-Names:...
, nicknamed "the black Napoleon", the Namaqua put up a fierce resistance to the German occupation. Contemporary media called the conflict "The Hottentot Uprising".

In 1894 major Theodor Leutwein
Theodor Leutwein
Theodor Gotthilf Leutwein was colonial administrator of German Southwest Africa from 1894-1904. Born in Strümpfelbrunn in the Grand Duchy of Baden, he replaced Curt von François as commander of the Schutztruppe in 1894...
was appointed governor of German South-West Africa. He tried without great success to apply the principle of "colonialism without bloodshed". The protection treaty did have the effect of stabilising the situation but pockets of rebellion persisted, and were put down by an elite German regiment Schutztruppe
Schutztruppe
Schutztruppe was the African colonial armed force of Imperial Germany from the late 19th century to 1918, when Germany lost its colonies. Similar to other colonial forces, the Schutztruppe consisted of volunteer European commissioned and non-commissioned officers, medical and veterinary officers. ...
, while real peace was never achieved between the colonialists and the natives.

The settlers were encouraged by the government to appropriate land from the natives, and forced labour – hard to distinguish from slavery – was used. As a result, relations between the German settlers and the natives deteriorated.

The Herero and Namaqua wars
The ongoing local rebellions escalated in 1904 into the Herero and Namaqua WarsHerero and Namaqua Genocide
The Herero and Namaqua Genocide is considered to have been the first genocide of the 20th century. It took place between 1904 and 1907 in German South-West Africa , during the scramble for Africa...
when the Herero attacked remote farms on the countryside, killing approximately 150 Germans.
The outbreak of rebellion was considered to be a result of Theodor Leutwein's softer tactics, and he was replaced by the more notorious General Lothar von Trotha
Lothar von Trotha
Adrian Dietrich Lothar von Trotha was a German military commander widely condemned for his conduct of the Herero Wars in South-West Africa, especially for the events that led to the near-extermination of the Herero....
.
In the beginning of the war the Herero, under the leadership of chief Samuel Maharero
Samuel Maharero
Samuel Maharero was a Paramount Chief of the Herero people in German South-West Africa during their revolts and in connection with the events surrounding the Herero genocide.- Life :...
had the upper hand. With good knowledge of the terrain they had little problem in defending themselves against the Schutztruppe (initially numbering only 766). Soon the Namaqua people joined the war, again under the leadership of Hendrik Witbooi
Hendrik Witbooi
Hendrik Witbooi may refer to:* Hendrik Witbooi * Hendrik Samuel Witbooi * Hendrik Witbooi , deputy prime minister of Namibia...
.

Battle of Waterberg
The Battle of Waterberg took place on August 11, 1904 in Waterberg, German South-West Africa , and was the decisive battle in the German campaign against the Herero.-The armies:...
in 1905. Earlier von Trotha issued an ultimatum to the Herero, denying them citizenship rights and ordering them to leave the country or be killed. In order to escape, the Herero retreated into the waterless Omaheke
Omaheke
Omaheke is one of the thirteen regions of Namibia. Omaheke lies on the eastern border of Namibia and is the Western extension of the Kalahari desert. The name Omaheke is the Herero word for Sandveld. A large part of this region is known as the Sandveld...
region, a western arm of the Kalahari Desert
Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savannah in Southern Africa extending , covering much of Botswana and parts of Namibia and South Africa, as semi-desert, with huge tracts of excellent grazing after good rains. The Kalahari supports more animals and plants than a true desert...
, where many of them died of thirst. The German forces guarded every water source and were given orders to shoot any adult male Herero on sight. Only a few of them managed to escape into neighbouring British territories. These tragic events, known as the Herero and Namaqua Genocide, resulted in the death of between 24,000 and 65,000 Herero (estimated at 50% to 70% of the total Herero population) and 10,000 Nama (50% of the total Nama population). The genocide was characterized by widespread death by starvation and from consumption of well water which had been poisoned by the Germans in the Namib Desert
Namib Desert
The Namib Desert is a desert in Namibia and southwest Angola that forms part of the Namib-Naukluft National Park, the largest game reserve in Africa. The name "Namib" is of Nama origin and means "vast place"...
.
Descendants of Lothar von Trotha apologized to six chiefs of Herero royal houses for the actions of their ancestor on October 7, 2007.
South African rule
In 1915, during World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, South Africa, being a member of the British Commonwealth
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
and a former British colony, occupied the German colony of South-West Africa.
In February 1917, Mandume Ya Ndemufayo
Mandume Ya Ndemufayo
Mandume Ya Ndemufayo was the last king of the Kwanyama, a subset of the Ovambo people of southern Angola and northern Namibia...
, the last king of the Kwanyama
Kwanyama
Kwanyama or Oshikwanyama is a national language of Angola and Namibia. It is a standardized dialect of the Ovambo language, and is mutually intelligible with Ndonga, the other Ovambo dialect with a standard written form....
of Ovamboland
Ovamboland
Ovamboland was the name given by English-speaking visitors to the land occupied by the Ovambo people in what is now northern Namibia and southern Angola...
, was killed in a joint attack by South African forces for resisting South African sovereignty
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
over his people.
On December 17, 1920, South Africa undertook administration of South-West Africa under the terms of Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
and a Class C Mandate
League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administering the territory on behalf of the League...
agreement by the League Council. The Class C mandate, supposed to be used for the least developed territories, gave South Africa full power of administration and legislation over the territory, but required that South Africa promote the material and moral well-being and social progress of the people.
Following the League's supersession by the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
in 1946, South Africa refused to surrender its earlier mandate to be replaced by a United Nations Trusteeship agreement, requiring closer international monitoring of the territory's administration. Although the South African government wanted to incorporate "South-West Africa" into its territory, it never officially did so, although it was administered as the de facto 'fifth province', with the white minority having representation in the whites-only Parliament of South Africa
Parliament of South Africa
The Parliament of South Africa is South Africa's legislature and under the country's current Constitution is composed of the National Assembly and the National Council of Provinces....
. In 1959, the colonial forces in Windhoek sought to remove black residents further away from the white area of town. The residents protested and the subsequent killing of eleven protesters spawned by the Namibian War of Independence
Namibian War of Independence
See also South African Border War.The Namibian War of Independence, also known as the South African Border War, which lasted from 1966 to 1988, was a guerrilla war, which the nationalist South-West Africa People's Organization and others, fought against the apartheid government in South...
with the formation of united black opposition to South African rule as well as the township
Township (South Africa)
In South Africa, the term township and location usually refers to the urban living areas that, from the late 19th century until the end of Apartheid, were reserved for non-whites . Townships were usually built on the periphery of towns and cities...
of Katutura
Katutura
Katutura is a township of Windhoek, Khomas Region, Namibia. Katutura was created in 1961 following the forced removal of Windhoek's black population from the Old Location, which afterwards was developed into the suburb Hochland Park. Sam Nujoma Stadium, built in 2005, is located within Katutura...
.
During the 1960s, as the European powers granted independence to their colonies and trust territories in Africa, pressure mounted on South Africa to do so in Namibia, which was then South-West Africa. On the dismissal (1966) by the International Court of Justice
International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice is the primary judicial organ of the United Nations. It is based in the Peace Palace in The Hague, Netherlands...
of a complaint brought by Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
and Liberia
Liberia
Liberia , officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Sierra Leone on the west, Guinea on the north and Côte d'Ivoire on the east. Liberia's coastline is composed of mostly mangrove forests while the more sparsely populated inland consists of forests that open...
against South Africa's continued presence in the territory, the U.N. General Assembly revoked South Africa's mandate.
The struggle for independence
South-West Africa People's Organisation
The South West Africa People's Organization is a political party and former liberation movement in Namibia. It has been the governing party in Namibia since achieving independence in 1990...
's (SWAPO) military wing, the People's Liberation Army of Namibia
People's Liberation Army of Namibia
The People's Liberation Army of Namibia was the active military wing of the South West Africa People's Organization during the Namibian War of Independence. It sought independence for the territory from South African rule. PLAN launched its first attack on the South African military at...
(PLAN) began guerrilla attacks on South African forces, infiltrating the territory from bases in Zambia
Zambia
Zambia , officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west....
. The first attack of this kind was the battle at Omugulugwombashe
Omugulugwombashe
Omugulugwombashe is a settlement in the Tsandi electoral constituency in the Omusati Region of northern Namibia. The settlement features a clinic and a primary school. In Omugulugwombashe the Namibian struggle for independence started in 1966...
on August 26. After Angola became independent in 1975, SWAPO established bases in the southern part of the country. Hostilities intensified over the years, especially in Ovamboland.
In a 1971 advisory opinion, the International Court of Justice
International Court of Justice
The International Court of Justice is the primary judicial organ of the United Nations. It is based in the Peace Palace in The Hague, Netherlands...
upheld UN authority over Namibia, determining that the South African presence in Namibia was illegal and that South Africa therefore was obliged to withdraw its administration from Namibia immediately. The Court also advised UN member states to refrain from implying legal recognition or assistance to the South African presence.
In 1975, South Africa sponsored the Turnhalle Constitutional Conference
Turnhalle Constitutional Conference
The Turnhalle Constitutional Conference was a controversial conference held in Windhoek between 1975 and 1977, tasked with the development of a constitution for a self-governed Namibia under South African control...
, which sought an "internal settlement" to Namibia. Excluding SWAPO, the conference mainly included bantustan
Bantustan
A bantustan was a territory set aside for black inhabitants of South Africa and South West Africa , as part of the policy of apartheid...
leaders as well as white Namibian political parties.
International pressure
In 1977, the Western Contact GroupWestern Contact Group
The Western Contact Group , representing three of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council - France, United Kingdom and United States - and including Canada and West Germany, launched a joint diplomatic effort in 1977 to bring an internationally acceptable transition to independence...
(WCG) was formed including Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. They launched a joint diplomatic effort to bring an internationally acceptable transition to independence for Namibia. The WCG's efforts led to the presentation in 1978 of Security Council Resolution 435 for settling the Namibian problem. The settlement proposal, as it became known, was worked out after lengthy consultations with South Africa, the front-line states (Angola
Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
, Botswana
Botswana
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana , is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa. The citizens are referred to as "Batswana" . Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name after becoming independent within the Commonwealth on 30 September 1966...
, Mozambique
Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique , is a country in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west and Swaziland and South Africa to the southwest...
, Tanzania
Tanzania
The United Republic of Tanzania is a country in East Africa bordered by Kenya and Uganda to the north, Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west, and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south. The country's eastern borders lie on the Indian Ocean.Tanzania is a state...
, Zambia
Zambia
Zambia , officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west....
, and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
), SWAPO, UN officials, and the Western Contact Group. It called for the holding of elections in Namibia under UN supervision and control, the cessation of all hostile acts by all parties, and restrictions on the activities of South African and Namibian military, paramilitary, and police.
South Africa agreed to cooperate in achieving the implementation of Resolution 435. Nonetheless, in December 1978, in defiance of the UN proposal, it unilaterally held elections
South-West African legislative election, 1978
Parliamentary elections were held in South West Africa between 4 and 8 December 1978. The first multi-ethnic elections, they were won by the Democratic Turnhalle Alliance, which claimed 41 of the 50 seats. However, the elections were boycotted by SWAPO and the Namibia National Front, and were...
, which were boycotted by SWAPO and a few other political parties. South Africa continued to administer Namibia through its installed multiracial coalitions and an appointed Administrator-General. Negotiations after 1978 focused on issues such as supervision of elections connected with the implementation of the settlement proposal.
Negotiations and transition
Martti Ahtisaari
Martti Oiva Kalevi Ahtisaari is a Finnish politician, the tenth President of Finland , Nobel Peace Prize laureate and United Nations diplomat and mediator, noted for his international peace work....
who played a key role in getting the Constitutional Principles agreed in 1982 by the front-line states, SWAPO, and the Western Contact Group. This agreement created the framework for Namibia's democratic constitution. The US Government's role as mediator was both critical and disputed throughout the period, one example being the intense efforts in 1984 to obtain withdrawal of the South African Defence Force
South African Defence Force
The South African Defence Force was the South African armed forces from 1957 until 1994. The former Union Defence Force was renamed to the South African Defence Force in the Defence Act of 1957...
(SADF) from southern Angola. The so-called "Constructive Engagement
Constructive engagement
Constructive engagement was the name given to the policy of the Reagan Administration towards the apartheid regime in South Africa in the early 1980s...
" by US diplomatic interests was viewed negatively by those who supported internationally recognised independence, while to others US policy seemed to be aimed more towards restraining Soviet-Cuban influence in Angola and linking that to the issue of Namibian independence. In addition, US moves seemed to encourage the South Africans to delay independence by taking initiatives that would keep the Soviet-Cubans in Angola, such as dominating large tracts of southern Angola militarily while at the same time providing surrogate forces for the Angolan opposition movement, UNITA
UNITA
The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola is the second-largest political party in Angola. Founded in 1966, UNITA fought with the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola in the Angolan War for Independence and then against the MPLA in the ensuing civil war .The war was one...
. From , a Transitional Government of National Unity
Transitional Government of National Unity (Namibia)
The Transitional Government of National Unity was the government of Namibia from June 1985 to February 1989. The TGNU was a puppet government of Apartheid South Africa that sought moderate reform but was unable to secure recognition by the United Nations...
, backed by South Africa and various ethnic political parties, tried unsuccessfully for recognition by the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
. Finally, in 1987 when prospects for Namibian independence seemed to be improving, the fourth UN Commissioner for Namibia Bernt Carlsson
Bernt Carlsson
Bernt Wilmar Carlsson was Assistant-Secretary-General of the United Nations and United Nations Commissioner for Namibia from July 1987 until he died on Pan Am Flight 103, which was blown up over Lockerbie, Scotland on 21 December 1988.-Social democrat:A native of Stockholm, Carlsson joined the...
was appointed. Upon South Africa's relinquishing control of Namibia, Commissioner Carlsson's role would be to administer the country, formulate its framework constitution, and organize free and fair elections based upon a non-racial universal franchise.
In May 1988, a US mediation team – headed by Chester A. Crocker, US Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs – brought negotiators from Angola
Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
, Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, and South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, and observers from the Soviet Union together in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. Intense diplomatic activity characterized the next 7 months, as the parties worked out agreements to bring peace to the region and make possible the implementation of UN Security Council Resolution 435 (UNSCR 435). At the Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
/Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev is a former Soviet statesman, having served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 until 1991, and as the last head of state of the USSR, having served from 1988 until its dissolution in 1991...
summit in Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
(May 29-June 1, 1988) between leaders of the United States and the Soviet Union, it was decided that Cuban troops would be withdrawn from Angola, and Soviet military aid would cease, as soon as South Africa withdrew from Namibia. Agreements to give effect to these decisions were drawn up for signature in New York in December 1988. Cuba, South Africa, and the People's Republic of Angola agreed to a complete withdrawal of foreign troops from Angola. This agreement, known as the Brazzaville Protocol, established a Joint Monitoring Commission (JMC) with the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
as observers. The Tripartite Accord, comprising a bilateral agreement between Cuba and Angola, and a tripartite agreement between Angola, Cuba and South Africa whereby South Africa agreed to hand control of Namibia to the United Nations, were signed at UN headquarters in New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
on December 22, 1988. (UN Commissioner N°4 Bernt Carlsson
Bernt Carlsson
Bernt Wilmar Carlsson was Assistant-Secretary-General of the United Nations and United Nations Commissioner for Namibia from July 1987 until he died on Pan Am Flight 103, which was blown up over Lockerbie, Scotland on 21 December 1988.-Social democrat:A native of Stockholm, Carlsson joined the...
was not present at the signing ceremony. He was killed on flight Pan Am 103
Pan Am Flight 103
Pan Am Flight 103 was Pan American World Airways' third daily scheduled transatlantic flight from London Heathrow Airport to New York's John F. Kennedy International Airport...
which exploded over Lockerbie, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
on December 21, 1988 en route from London to New York. South African foreign minister, Pik Botha
Pik Botha
Roelof Frederik "Pik" Botha is a former South African politician who served as the country's foreign minister in the last years of the apartheid era...
, and an official delegation of 22 had a lucky escape. Their booking on Pan Am 103 was cancelled at the last minute and Pik Botha
Pik Botha
Roelof Frederik "Pik" Botha is a former South African politician who served as the country's foreign minister in the last years of the apartheid era...
, together with a smaller delegation, caught the earlier Pan Am 101 flight to New York.)
Within a month of the signing of the New York Accords, South African president P. W. Botha suffered a mild stroke, which prevented him from attending a meeting with Namibian leaders on January 20, 1989. His place was taken by acting president J. Christiaan Heunis. Botha had fully recuperated by April 1, 1989 when implementation of UNSCR 435 officially started and the South African–appointed Administrator-General, Louis Pienaar
Louis Pienaar
Louis Pienaar is a South African lawyer and former diplomat. In 1985, the apartheid government put him in charge of Namibia, in the lead-up to that country's independence in 1990...
, began the territory's transition to independence. Former UN Commissioner N°2 and now UN Special Representative Martti Ahtisaari
Martti Ahtisaari
Martti Oiva Kalevi Ahtisaari is a Finnish politician, the tenth President of Finland , Nobel Peace Prize laureate and United Nations diplomat and mediator, noted for his international peace work....
arrived in Windhoek in April 1989 to head the UN Transition Assistance Group's (UNTAG) mission.
The transition got off to a shaky start because, contrary to SWAPO President Sam Nujoma
Sam Nujoma
Samuel Daniel Shafiishuna Nujoma is a Namibian politician who was the first President of Namibia from 1990 to 2005. He led the South-West Africa People's Organisation in its long struggle against South African rule and took office as President when Namibia obtained independence on 21 March 1990...
's written assurances to the UN Secretary General to abide by a cease-fire and repatriate only unarmed Namibians, it was alleged that approximately 2,000 armed members of the People's Liberation Army of Namibia (PLAN) SWAPO's military wing, crossed the border from Angola in an apparent attempt to establish a military presence in northern Namibia. UNTAG's Martti Ahtisaari
Martti Ahtisaari
Martti Oiva Kalevi Ahtisaari is a Finnish politician, the tenth President of Finland , Nobel Peace Prize laureate and United Nations diplomat and mediator, noted for his international peace work....
took advice from British Prime Minister, Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990...
, who was visiting Southern Africa at the time, and authorized a limited contingent of South African troops to assist the South West African Police in restoring order. A period of intense fighting followed, during which 375 PLAN fighters were killed. At a hastily arranged meeting of the Joint Monitoring Commission in Mount Etjo, a game park outside Otjiwarongo
Otjiwarongo
Otjiwarongo is a city of 20,000 inhabitants in the Otjozondjupa Region of Namibia. It is the district capital of the Otjiwarongo electoral constituency and also the capital of Otjozondjupa....
, it was agreed to confine the South African forces to base and return PLAN elements to Angola. While that problem was resolved, minor disturbances in the north continued throughout the transition period.
In October 1989, under orders of the UN Security Council, Pretoria was forced to demobilize some 1,600 members of Koevoet
Koevoet
Koevoet , also known as "Operation K" and officially known as the "South West Africa Police Counter-Insurgency Unit" , was a police counter insurgency unit in South-West Africa during the 1970s and 1980s...
(Afrikaans for crowbar). The Koevoet issue had been one of the most difficult UNTAG faced. This counter-insurgency unit was formed by South Africa after the adoption of UNSCR 435, and was not, therefore, mentioned in the Settlement Proposal or related documents. The UN regarded Koevoet as a paramilitary unit which ought to be disbanded but the unit continued to deploy in the north in armoured and heavily armed convoys. In June 1989, the Special Representative told the Administrator-General that this behavior was totally inconsistent with the settlement proposal, which required the police to be lightly armed. Moreover, the vast majority of the Koevoet personnel were quite unsuited for continued employment in the South-West African Police (SWAPOL). The Security Council, in its resolution ) of August 29, therefore demanded the disbanding of Koevoet and dismantling of its command structures. South African foreign minister, Pik Botha, announced on September 28, 1989 that 1,200 ex-Koevoet members would be demobilized with effect from the following day. A further 400 such personnel were demobilized on October 30. These demobilizations were supervised by UNTAG military monitors.
The 11-month transition period ended relatively smoothly. Political prisoners were granted amnesty, discriminatory legislation was repealed, South Africa withdrew all its forces from Namibia, and some 42,000 refugees returned safely and voluntarily under the auspices of the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). Almost 98% of registered voters turned out to elect members of the Constituent Assembly. The elections were held in November 1989 and were certified as free and fair by the UN Special Representative, with SWAPO taking 57% of the vote, just short of the two-thirds necessary to have a free hand in revising the framework constitution that had been formulated not by UN Commissioner Bernt Carlsson but by the South African appointee Louis Pienaar
Louis Pienaar
Louis Pienaar is a South African lawyer and former diplomat. In 1985, the apartheid government put him in charge of Namibia, in the lead-up to that country's independence in 1990...
. The opposition Democratic Turnhalle Alliance received 29% of the vote. The Constituent Assembly held its first meeting on November 21, 1989 and resolved unanimously to use the 1982 Constitutional Principles in Namibia's new constitution.
(According to The Guardian
The Guardian
The Guardian, formerly known as The Manchester Guardian , is a British national daily newspaper in the Berliner format...
of July 26, 1991, Pik Botha told a press conference that the South African government had paid more than £20 million to at least seven political parties in Namibia to oppose SWAPO in the run-up to the 1989 elections. He justified the expenditure on the grounds that South Africa was at war with SWAPO at the time.)
Independence

Javier Pérez de Cuéllar
Javier Pérez de Cuéllar y de la Guerra is a Peruvian diplomat who served as the fifth Secretary-General of the United Nations from January 1, 1982 to December 31, 1991. He studied in Colegio San Agustín of Lima, and then at Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú. In 1995, he ran unsuccessfully...
and President of South Africa F W de Klerk, who jointly conferred formal independence on Namibia.
Sam Nujoma
Sam Nujoma
Samuel Daniel Shafiishuna Nujoma is a Namibian politician who was the first President of Namibia from 1990 to 2005. He led the South-West Africa People's Organisation in its long struggle against South African rule and took office as President when Namibia obtained independence on 21 March 1990...
was sworn in as the first President of Namibia watched by Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela served as President of South Africa from 1994 to 1999, and was the first South African president to be elected in a fully representative democratic election. Before his presidency, Mandela was an anti-apartheid activist, and the leader of Umkhonto we Sizwe, the armed wing...
(who had been released from prison shortly beforehand) and representatives from 147 countries, including 20 heads of state.
On March 1, 1994, the coastal enclave of Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay
Walvis Bay , is a city in Namibia and the name of the bay on which it lies...
and 12 offshore islands were transferred to Namibia by South Africa. This followed three years of bilateral negotiations between the two governments and the establishment of a transitional Joint Administrative Authority (JAA) in November 1992 to administer the 780 km² (301.2 sq mi) territory. The peaceful resolution of this territorial dispute was praised by the international community, as it fulfilled the provisions of the UNSCR 432 (1978), which declared Walvis Bay to be an integral part of Namibia.
Post independence

Elections in Namibia
Elections in Namibia gives information on election and election results in Namibia.Namibia elects on national level a head of state - the president - and a legislature. The president is elected for a five year term by the people. Parliament has two chambers...
held regularly. Several registered political parties are active and represented in the National Assembly, although Swapo Party has won every election since independence. The transition from the 15-year rule of President Sam Nujoma
Sam Nujoma
Samuel Daniel Shafiishuna Nujoma is a Namibian politician who was the first President of Namibia from 1990 to 2005. He led the South-West Africa People's Organisation in its long struggle against South African rule and took office as President when Namibia obtained independence on 21 March 1990...
to his successor, Hifikepunye Pohamba
Hifikepunye Pohamba
Hifikepunye Lucas Pohamba is the second and current President of Namibia. He won the 2004 and 2009 presidential elections overwhelmingly as the candidate of the South West Africa People's Organisation ruling party, taking office in March 2005. He has also been the President of SWAPO since...
in 2005 went smoothly.
Namibian government has promoted a policy of national reconciliation and issued an amnesty for those who had fought on either side during the liberation war. The civil war in Angola
Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
had a limited impact on Namibians living in the north of the country. In 1998, Namibia Defence Force (NDF) troops were sent to the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a state located in Central Africa. It is the second largest country in Africa by area and the eleventh largest in the world...
as part of a Southern African Development Community
Southern African Development Community
The Southern African Development Community is an inter-governmental organization headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana. Its goal is to further socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security cooperation among 15 southern African states...
(SADC) contingent. In August 1999, a secessionist attempt in the northeastern Caprivi region was successfully quashed.
Re-election of Sam Nujoma
Sam Nujoma won the presidential elections of 1994 with 76.34% of the votes. There was only one other candidate, Mishake MuyongoMishake Muyongo
Mishake Muyongo is a Namibian politician and former Member of Parliament who is living in exile in Denmark.Muyongo was born in Linyanti. In September 1964 Muyongo became President of the Caprivi African National Union when its leader Simbwaye was arrested and disappeared in South-African custody...
of the DTA
Democratic Turnhalle Alliance of Namibia
The Democratic Turnhalle Alliance is an amalgamation of political parties in Namibia, registered as one singular party for representation purposes. In coalition with the United Democratic Front, it formed the official opposition in Parliament until the parliamentary elections in 2009...
.
In 1998, with one year until the scheduled presidential election when Sam Nujoma would not be allowed to participate in since he had already served the two terms that the constitution allows, SWAPO amended the constitution, allowing three terms instead of two. They were able to do this since SWAPO had a two-thirds majority in both the National Assembly of Namibia
National Assembly of Namibia
The National Assembly of Namibia is the lower chamber of the country's bicameral Parliament. It has a total of 78 members. 72 members are directly elected through a system of party-list proportional representation and serve five-year terms. Six additional members are appointed by the President.The...
and the National Council
National Council of Namibia
The National Council of Namibia is the upper chamber of the country's bicameral Parliament.The 26 National Council members are chosen by regional councils, which are directly elected for a term of six-years. Each of the 13 regional councils chooses two of its members to serve on the National Council...
, which is the minimum needed to amend the constitution.
Sam Nujoma was reelected as president in 1999, winning the election, that had a 62.1% turnout
Voter turnout
Voter turnout is the percentage of eligible voters who cast a ballot in an election . After increasing for many decades, there has been a trend of decreasing voter turnout in most established democracies since the 1960s...
with 76.82%. Second was Ben Ulenga
Ben Ulenga
Benjamin Ulenga is a Namibian politician. A member of the National Assembly of Namibia, he is the President of the Congress of Democrats , an opposition political party....
from the Congress of Democrats
Congress of Democrats
The Congress of Democrats is a political party in Namibia, led by Ben Ulenga. It is an opposition party represented in the National Assembly.The party is an observer of the Socialist International.- 2004 elections :...
(COD), that won 10.49% of the votes.
Nujoma was succeeded as President of Namibia by Hifikepunye Pohamba
Hifikepunye Pohamba
Hifikepunye Lucas Pohamba is the second and current President of Namibia. He won the 2004 and 2009 presidential elections overwhelmingly as the candidate of the South West Africa People's Organisation ruling party, taking office in March 2005. He has also been the President of SWAPO since...
in 2005.
Ben Ulenga is a former SWAPO member and Deputy Minister of Environment
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
and Tourism
Tourism
Tourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes".Tourism has become a...
, and High Commissioner
High Commissioner
High Commissioner is the title of various high-ranking, special executive positions held by a commission of appointment.The English term is also used to render various equivalent titles in other languages.-Bilateral diplomacy:...
to the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
.
He left SWAPO and became one of the founding members of COD in 1998, after clashing with his party on several questions. He did not approve of the amendment to the constitution, and criticised Namibia's involvement in Congo.
Land reform
One of SWAPO's policies, that had been formulated long before the party came into power, was land reformLand reform
[Image:Jakarta farmers protest23.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Farmers protesting for Land Reform in Indonesia]Land reform involves the changing of laws, regulations or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution,...
. Namibia's colonial and Apartheid past had resulted in a situation where about 20 percent of the population owned about 75 percent of all the land.
Land was supposed to be redistributed mostly from the white minority to previously landless communities and ex-combatants. The land reform has been slow, mainly because Namibia's constitution only allows land to be bought from farmers willing to sell. Also, the price of land is very high in Namibia, which further complicates the matter.
President Sam Nujoma has been vocal in his support of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in the southern part of the African continent, between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers. It is bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia and a tip of Namibia to the northwest and Mozambique to the east. Zimbabwe has three...
and its president Robert Mugabe
Robert Mugabe
Robert Gabriel Mugabe is the President of Zimbabwe. As one of the leaders of the liberation movement against white-minority rule, he was elected into power in 1980...
. During the land crisis in Zimbabwe, where the government by force confiscated white farmers' land using violent methods, fears arose among the white minority and the western world that the same method would be used in Namibia. This has not been the case so far.

Involvement in conflicts in Angola and DRC
In 1999 Namibia signed a mutual defence pact with its northern neighbour AngolaAngola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola , is a country in south-central Africa bordered by Namibia on the south, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the north, and Zambia on the east; its west coast is on the Atlantic Ocean with Luanda as its capital city...
.
This affected the Angolan Civil War
Angolan Civil War
The Angolan Civil War was a major civil conflict in the Southern African state of Angola, beginning in 1975 and continuing, with some interludes, until 2002. The war began immediately after Angola became independent from Portugal in November 1975. Prior to this, a decolonisation conflict had taken...
that had been ongoing since Angola's independence in 1975. Both being leftist movements, SWAPO wanted to support the ruling party MPLA in Angola to fight the rebel movement UNITA
UNITA
The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola is the second-largest political party in Angola. Founded in 1966, UNITA fought with the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola in the Angolan War for Independence and then against the MPLA in the ensuing civil war .The war was one...
, whose stronghold was in southern Angola. The defence pact allowed Angolan troops to use Namibian territory when attacking UNITA.
The Angolan civil war resulted in a large number of Angolan refugees coming to Namibia. At its peak in 2001 there were over 30,000 Angolan refugees in Namibia. The calmer situation in Angola has made it possible for many of them to return to their home with the help of UNHCR, and in 2004 only 12,600 remained in Namibia.
Most of them reside in the refugee camp
Refugee camp
A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees. Hundreds of thousands of people may live in any one single camp. Usually they are built and run by a government, the United Nations, or international organizations, or NGOs.Refugee camps are generally set up in an impromptu...
Osire
Osire
Osire is a refugee camp in central Namibia, situated 200 km north of the capital Windhoek on the main road C30 from Gobabis to Otjiwarongo. Established in 1992 the refugee population of Osire stood at 6.500 in 2010 after having reached a peak of 20.000 in 1998...
north of Windhoek
Windhoek
Windhoek is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around above sea level. The 2001 census determined Windhoek's population was 233,529...
.
Namibia also intervened in the Second Congo War
Second Congo War
The Second Congo War, also known as Coltan War and the Great War of Africa, began in August 1998 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo , and officially ended in July 2003 when the Transitional Government of the Democratic Republic of the Congo took power; however, hostilities continue to this...
, sending troops in support of the Democratic Republic of Congo's president Laurent-Désiré Kabila
Laurent-Désiré Kabila
Laurent-Désiré Kabila was President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo from May 17, 1997, when he overthrew Mobutu Sese Seko, until his assassination by his bodyguards on January 18, 2001...
.
The Caprivi conflict
The Caprivi conflict was an armed conflict between the Caprivi Liberation ArmyCaprivi Liberation Army
Caprivi Liberation Army is a Namibian rebel and separatist group which was established in 1994 to separate the Caprivi Strip, a region mainly inhabited by the Lozi people. It operates only in the Caprivi strip.-Background:...
(CLA), a rebel group working for the secession of the Caprivi Strip
Caprivi Strip
Caprivi, sometimes called the Caprivi Strip , Caprivi Panhandle or the Okavango Strip and formally known as Itenge, is a narrow protrusion of Namibia eastwards about , between Botswana to the south, Angola and Zambia to the north, and Okavango Region to the west. Caprivi is bordered by the...
, and the Namibian government. It started in 1994 and had its peak in the early hours of August 2, 1999 when CLA launched an attack in Katima Mulilo
Katima Mulilo
Katima Mulilo is the capital of the Caprivi Strip, Namibia's far north–east extension into central Southern Africa. It comprises two electoral constituencies, Katima Mulilo Rural and Katima Mulilo Urban...
, the provincial capital of the Caprivi Region. Forces of the Namibian government struck back and arrested a number of alleged CLA supporters. The Caprivi conflict has led to the longest and largest trial in the history of Namibia, the Caprivi treason trial
Caprivi treason trial
The Caprivi treason trial is a trial in which the Government of Namibia indicted 132 people for allegedly participating in the Caprivi conflict on the side of the Caprivi Liberation Army in a period between 1992 and 2002...
.
See also
- History of AfricaHistory of AfricaThe history of Africa begins with the prehistory of Africa and the emergence of Homo sapiens in East Africa, continuing into the present as a patchwork of diverse and politically developing nation states. Agriculture began about 10,000 BCE and metallurgy in about 4000 BCE. The history of early...
- History of Southern Africa
- Politics of NamibiaPolitics of NamibiaPolitics of Namibia takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Namibia is both head of state and head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in...
- List of Presidents of Namibia
General
- The African Activist Archive Project website has material on the struggle for independence and support in the U.S. for that struggle produced by many U.S. organizations including National Namibia Concerns, the Lawyers' Committee for Civil Rights Under Law, and the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America(and predecessor organizations). Other organizations on the Archive with significant material on Namibia include the American Committee on Africa, Episcopal Churchpeople for Southern Africa, and the Washington Office on Africa (available on the Browse page).

