History of Sindh
Encyclopedia
Sindh
(Sind) is one of the provinces of Pakistan
. Sindh was home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, the Indus Valley civilization
.
is one of the most important Paleolithic site discovered in southern Sindh, few kilometers south of Hyderabad, on the right side of the Indus River
. According to the aspect and surface patina of the tools, the flint assemblages can be attributed to the Early, Middle and Late (Upper) Paleolithic periods.
At Rehri
, along the coast east of Karachi, Karachi University team has discovered a few Mesolithic
and Late Palaeolithic sites. Most of these sites have vanished during the last twenty years. Nevertheless their discovery shed new light on the prehistory of the coastal area of Lower Sindh. Scatters of flint were found in different spots, some of which were associated with Terebralia palustris mangrove shells.
The Late Palaeolithic and Mesolithic sites found by Karachi University team on the Mulri Hills
, in front of Karachi University Campus, constitute one of the most important archaeological discoveries made in Sindh during the last fifty years. The last hunter-gatherers, who left abundant traces of their passage, repeatedly inhabited the Hills. Some twenty different spots of flint tools were discovered during the surface surveys.
is located along the right bank of the Indus River
, south of Dadu. The excavations carried out by the French Archaeological Mission at the beginning of the sixties revealed a long sequence of subsequent habitation phases datable from the Copper to the Bronze Age. The typical Amri layers have been radiocarbon-dated to the second half of the fourth millennium BC and are attributed by some authors to the beginning of the Early Harappan
Civilization. At least 160 settlements attributed to the Amri Culture
, among them the Tharro Hills
, near the village of Gujo
, is one of the most famous of lower Sindh.
..
The site of Kot Diji
, near Rohri
, consists of a small mound composed of a sequence of overimposed structures and anthropogenic layers. They have been subdivided into two main complexes, the first of which belongs to the Early Harappan
, Kot Diji Culture
, and the second to the Mature Harappan Civilization.
The site of Lakhueen-jo-daro
, near Sukkur
, belongs to the Mature Harappan Civilization as indicated by the characteristics of the structural remains, material culture finds and one radiocarbon date, covers a wide area, from which a few mounds emerge. The site indicates that the origins of Sukkur are to be referred to a much older period than previously suspected.
The metropolis of Mohenjo-daro
, near Larkana
, is largest Indus city so far discovered in Sindh. The large-scale excavations carried out in the 1920s brought to light most of the architectural remains that are still currently visible. They are mainly of backed bricks with very well preserved buildings aligned along streets and lanes. Mohen-jo-daro is the largest Bronze Age city of the world. The larkana was very famous city in sindh. moen-jo-dero is 25 kilometer far from larkana.ratodero is 30 kilometer far from larkana ratodero is very big city and very famous ratodero is name of rato jalbani he was very brave and honest. he was very rich in sindh now he was dead now her tomb in 10 meter in the gold he does not give her gold to her sons,and her son was sobdar khan jalbani there was the famous story of the sindh.
Pir Shah Jurio
is a Mature Indus Civilization village along the left bank of the Hub River
. It consists of a small mound, which is nowadays partly covered by a cemetery. From its surface, typical potsherds and other finds were collected. This site is strictly connected with the sea, which is a few kilometers south of it. It was radiocarbon-dated to the third millennium BP, from a sample of Terebralia palustris shells.
The Indus Civilization site of Kot Bala
is located in the interior of the Sonmiani Bay
, along the coast of Lasbela District
, Balochistan
. It was partly excavated by Professor G. Dales of Berkeley University in the Seventies and never published in detail. This site is of great importance for its location close to the Arabian Sea. It is supposed to be one of the main harbors from which the Indus traders sailed their ships to the coasts of the Arabian Peninsula.
Sindh has been known by various names in the past, the name Sindh comes from the Indo-Aryans
. In Sanskrit, the province was called Sindhu meaning the river Sindh and the people living on its banks. The Assyrians (as early as the seventh century BCE) knew the region as Sinda, the Persians
Hindush, the Greeks
Indos, the Romans
Sindus or Indus, the Chinese
Sintu, while the Arabs dubbed it Sind. A legend claims that the Indus River
flowed from the mouth of a lion or Sinh-ka-bab.
The first known village settlements date as far back as 7000 BCE
. Permanent settlements at Mehrgarh
to the west expanded into Sindh. One of the original inhabitants of ancient Sindh were the Austro-Asiatic speaking peoples who spoke the Munda languages
. This culture blossomed over several millennia and gave rise to the Indus Valley Civilization
around 3000 BCE. The Indus Valley Civilization
spanned much of what is today Pakistan, but went into decline a few centuries prior to the invasion of the Indo-Aryans
which is still a hotly debated subject, a branch of the Indo-Iranians
, who are considered to have founded the Vedic Civilization, that existed between the Kabul river
, the Sarasvati River
and the upper Ganges river after 1500 BCE. The Vedic civilization - with much in-fighting and fighting with the locals as well as interaction with them - ultimately helped shape subsequent cultures in South Asia
.
Another group of academia, claims that the original inhabitants of Sindh, who gave rise to the Indus Valley Civilization
around 3000 BCE, were native Aryans, as Vedic literature speaks of no reference to an Aryan race outside of the South Asia. This topic is considered still unresolved.
The Indus Valley Civilization
rivaled the contemporary civilizations of Ancient Egypt
and Mesopotamia
in both size and scope numbering nearly half a million inhabitants at its height with well-planned grid cities and sewer systems. It is known that the Indus Valley Civilization traded with ancient Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt via established shipping lanes. In ancient Egypt
, the word for cotton was Sindh denoting that the bulk of that civilizations cotton was predominantly imported from the Indus Valley Civilization. Speculation remains as to how and why the civilization declined and may have been a combination of natural disasters such as deterioration in climate, flooding as well as breakdown of international trade and internecine conflicts.
Sindh was conquered by the Persian Achaemenid Empire
in the late 6th century BCE, and became a the Persian satrap
y (province) of Hindush in addition to that of Gandara
(Gandāra) centered in the Punjab
to the north. Iranian and thus also Persian
speech replaces 'S' with 'H' in many Sanskrit
ic words, resulting in 'Sindhu' being pronounced and written as 'Hindu'. They introduced the Kharoshti script and links to the west in the region.
Conquered by Macedonian Greek
armies led by Alexander the Great, after 326 BCE the region came under loose Greek control for a few decades. After Alexander's death, there was a brief period of Seleucid rule. Sindh was traded to the Mauryan Empire of Chandragupta
after a peace treaty with the Seleucids in 305 BCE.
Later, during the reign of the emperor Ashoka
the region would solidly become a Buddhist domain. Following a century of Mauryan rule which ended by 232 BCE, the region came under the Greco-Bactrians based in what is today northern Afghanistan
. Some of their rulers also converted to Buddhism and spread it in the region.
The Scythians (Saka) shattered the Greco-Bactrian kingdom. Subsequently, the Tocharian
Kushan Empire
annexed Sindh by the 1st century CE. Though the Kushans followed their own religion, they were tolerant of the local Buddhist tradition and sponsored many building projects for local beliefs.
Scythians, Kushans, Huns
and the Sassanid
Persians all exercised some degree of control in Sindh until the coming of the Muslim
Arabs in 711 CE.
The Buddhist city of Siraj-ji-Takri
is located along the western limestone terraces of the Rohri Hills in the Khairpur district
of Upper Sindh, along the road that leads to Sorah. Its ruins are still visible on the top of three different mesas, in the form of stone and mud-brick walls and small mounds, whilst other architectural remains were observed along the slopes of the hills in the 1980s. This city is not mentioned from any text dealing with the history of the Buddhist period of Sindh.
Rai Dynasty
Rai Dynasty of Rajput
s was the ruling dynasty of Sindh
from c. 489 – 632. The Rais were one of the Middle kingdoms of India
and patrons of Buddhism
even though they also established a huge temple of Shiva
in present-day Sukkur
, derived from original Shankar
, close to their capital in Al-ror
. This is consistent with the historical accounts from the times of Emperor Ashoka
and Harsha
because India
n monarchs never sponsored a state religion and usually patronized more than one faith. The influence of the Rai state to Kannauj
in the east, Makran
and Debal (Karachi
) port in the west, Surat
port in south, Kandahar
, Sistan
, Suleyman, Ferdan and Kikanan hills in the north.
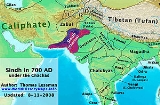
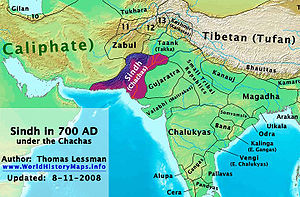 The province
The province
of Sistan
was the largest province of Persian Empire; its frontiers extended from Sindh
in east
to Balkh
(Afghanistan
) in north
east
. During the Rashidun Caliphate
, the Islamic conquest
of some parts of Sindh
was extension of the campaigns to conquer the Persian empire in 643 AD, by sending seven armies from seven different routs to different parts of empire.
Islamic force
s first entered Sindh
during the reign of Caliph Umar
, in 644] AD. It was not a full scale arrival in Sindh
, but was merely as extension of the conquests of the largest province of Persia - Sistan
and Makran
region. In 644 AD, the columns of Hakam ibn Amr, Shahab ibn Makharaq and Abdullah ibn Utban concentrated near the west bank of Indus river
and defeated the army of Raja Sahasi Rai II a Hindu
king
of Rai kingdom
of Sind, in Battle of Rasil
, his armies retreated to the estern bank of river Indus.
In response of Caliph Umar
's question about the Makran
region
, the Messenger from Makran answered:
Caliph Umar
looked at the messenger and said:
"Are you a messenger or a poet?" He replied, "Messenger".
Thereupon Caliph Umar
, after listening to the unfavorable situations for sending an army, instructed Hakim bin Amr al Taghlabi that, for the time being, Makran
should be the easternmost frontier of the Islamic empire
, and that no further attempt should be made to extend the conquests.
After the death of Caliph Umar
the areas—like other regions of Persian Empire—broke into revolt and Caliph Uthman sent forces to re-conquer them. Caliph Uthman also sent his agent Haheem ibn Jabla Abdi to investigate the matters of Hind
. On his return, he told Caliph Uthman about the cities and, listening to the miserable conditions of the region, he avoided campaigning in interior Sindh
and, like Caliph Umar
, he ordered his armies not to cross Indus river
.
; it became the easternmost province of the Umayyad Caliphate. The Arab province of Sindh is modern Pakistan
, while the lands of modern India further east were known to the Arabs as Hind. The defeat of the Hindu
ruler Dahir Rajah
was made easier due to the tension between the Buddhist majority and the ruling Hindus' fragile base of control. The Arabs redefined the region and adopted the term budd to refer to the numerous Buddhist idols they encountered, a word that remains in use today. The city of Mansura
was established as a regional capital and Arab rule lasted for nearly 3 centuries and a fusion of cultures produced much of what is today modern Sindhi society. Arab geographers, historians and travellers also sometimes called the entire area from the Arabian Sea to the Hindu Kush
as Sindh. The meaning of the word Sindhu being water (or ocean) appears to refer to the Indus river
.
 Arab
Arab
rule ended with the ascension of the Soomro
dynasty, who were local Sindhi Muslims and who controlled the province directly and as vassals from 1058 to 1249. Turkic
dynasties conquered the area by 977 CE and the region loosely became part of the Ghaznavid Empire
and then the Delhi Sultanate
which lasted until 1524. The Mughals took control the region and their rule lasted for another two centuries, while another local Sindhi Muslim group, the Samma Dynasty, challenged Mughal rule from their base at Thatta
. The Muslim
Sufis played a pivotal role in converting the millions of native people to Islam
. Sindh, though part of larger empires, continued to enjoy certain autonomy as a loyal Muslim domain and came under the rule of the Arghun Dynasty
and Turkhan or Tarkhan
dynasty from 1519 to 1625. Sindh became a vassal-state of the Afghan
Durrani Empire
by 1747. It was then ruled by Kalhora
rulers and later the Balochi
Talpurs from 1783.
 The British East India Company started its occupation of Sindh at the time when it was ruled by Balochi tribesmen of Dera Ghazi Khan. Most of them were Talpur (a branch of Laghari tribe), Laghari, Nizamani, Murree, Gopang and other Balochi tribesmen. Karachi was the first area in the province to be occupied by the British East India Company
The British East India Company started its occupation of Sindh at the time when it was ruled by Balochi tribesmen of Dera Ghazi Khan. Most of them were Talpur (a branch of Laghari tribe), Laghari, Nizamani, Murree, Gopang and other Balochi tribesmen. Karachi was the first area in the province to be occupied by the British East India Company
in 1839. Four years later, most of the province (except for the State of Khairpur) was added to the Company's domain after victories at Miani
and Dubbo. Many people helped the British in the conquest of Sindh, including a Hindu government minister of Sindh, Mirs of Khairpur, Chandio Tribesmen, and Khosa Tribesmen. General Charles Napier
is said to have reported victory to his Governor General with a Latin
one-word telegram, namely "Peccavi" – or "I have sinned (Sindh)", which is a pun
.
 Charles Napier had brought first army consisting of mostly Bengali soldiers. The Balochi ruling forces of Sindh used to attack the British led armies in the darkness of night. The Bengali soldiers could not compete in those war techniques, and they used to run away. Then, Charles Napier hired Khosa Baloch tribesman (from Dera Ghazi Khan) in his army, to fight with the ruling Balochis of Sindh, who were also originally from Dera Ghazi Khan, Punjab. Chandio Baloch Sardar brought a cavalry of 10,000 to support Charles Napier in the Miani war, but did not participate in the actual war, and his armies stood on reserve to attack in case Charles Napier lost the war. For his role, Chandio sardar got Chandka (present day Larakana, Qambar-Shahdadkot districts) as Jagir. Talpurs of Khairpur also got Khairpur state as gift from Charles Napier for non-participation in the war. The first Aga Khan
Charles Napier had brought first army consisting of mostly Bengali soldiers. The Balochi ruling forces of Sindh used to attack the British led armies in the darkness of night. The Bengali soldiers could not compete in those war techniques, and they used to run away. Then, Charles Napier hired Khosa Baloch tribesman (from Dera Ghazi Khan) in his army, to fight with the ruling Balochis of Sindh, who were also originally from Dera Ghazi Khan, Punjab. Chandio Baloch Sardar brought a cavalry of 10,000 to support Charles Napier in the Miani war, but did not participate in the actual war, and his armies stood on reserve to attack in case Charles Napier lost the war. For his role, Chandio sardar got Chandka (present day Larakana, Qambar-Shahdadkot districts) as Jagir. Talpurs of Khairpur also got Khairpur state as gift from Charles Napier for non-participation in the war. The first Aga Khan
had helped the British in the conquest of Sindh and was granted a pension as a result.
Sind was made part of British India's Bombay Presidency
in 1847 and became a separate province in 1936. During British control of Indian subcontinent, they laid railway lines in Sindh. Many barrages and canals were built to irrigate farm land in Sindh, which improved the livelihood of rural Sindhis. The first stamps in Asia, known as Scinde Dawk
, were released in 1852. The mail was carried quickly and efficiently, connecting British
administrative offices and post offices from Karachi
through Kotri and Hyderabad up to Shikkur in the north.
During the freedom struggle, the Sindh branch of Muslim League
party was established by Ghulam Muhammad Bhurgari
in 1918. Abdullah Haroon, who joined it in 1918, was elected president of the provincial Muslim League in 1920. In those days, both the Muslim League and the Indian National Congress
of Sindh held their annual sessions at the same place simultaneously and passed similar resolutions.
The Sindh assembly was the first British Indian legislature to pass the resolution in favour of Pakistan
. G. M. Syed
, an influential Sindhi activist, revolutionary, and one of the important leaders in the forefront of the provincial autonomy movement, joined the Muslim League in 1938 and presented the Pakistan resolution in the Sindh Assembly.
gained independence from foreign British
colonial rule. The province of Sindh
thus regained its self rule, lost since the defeat of Sindhi
Talpur
Amirs in the Battle of Miani
on February 17, 1843.
The first challenge faced by the Government of Sindh
was the settlement of Muslim
refugees. Nearly 7 million Muslim
s from India migrated to Pakistan while nearly equal number of Hindu
s and Sikh
s from Pakistan
migrated to India. The Muslim
refugee
s, (known as Muhajirs from India), settled mostly in urban areas of Sindh
, most of them in Karachi
and Hyderabad.
), can be regarded as Sir Syed Ahmed Khan of Sindh. He made great efforts to encourage the Sindhi people to get modern education. He built an educational institution known as Sindh-Madrsat-ul-Islam. Muhammad Ali Jinnah
went to Sindh-Madarsat-ul-Islam in Karachi, Sindh for education and, after his law education, worked in Karachi for a Sindhi (Hindu) law firm.
Education in Sindh is divided into five levels: primary
(grades one through five); middle
(grades six through eight); high
(grades nine and ten, leading to the Secondary School Certificate
); intermediate
(grades eleven and twelve, leading to a Higher Secondary School Certificate); and university
programs leading to graduate
and advanced degrees.
Primary
, middle
and high
schools are established in all parts of Sindh
providing, Sindhi
, Urdu and English
medium schools.
The college
s and universities
are established in major towns and cities of Sindh
. They provide courses leading to BA
, BSc
and Bachelor of Commerce
/ BCom/BBA
degrees. medical colleges
and engineering college
s are also established in major cities of Sindh.
There are many postgraduate
and research institute
s in Sindh
providing state-of-the-art education to Sindhi students.
has become the most industrialized and urbanized province of Pakistan
. The head offices of Pakistani companies, and regional offices of international companies, are located in Sindh. The Sindhis have been in forefront of economic development of the province. The new dams and canals have irrgated many areas that were barren and Sindh produces many agricultural products for the country and for export.
The construction of multi-billion projects like Karachi Nuclear Power Plant
, Port Qasim
and Pakistan Steel Mills
provided tens of thousands of jobs to the residents of Sindh.
, Quaid-e-Azam Muhammad Ali Jinnah
was of Sindhi background. Khan Bahadur Muhammad Ayub Khuhro
was the first Chief Minister of Sindh
, after independence of Pakistan
. Pakistan's political scene continued to be dominated by Sindhi politicians like Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
, Mumtaz Bhutto
, Benazir Bhutto
, Muhammad Khan Junejo
, Ghulam Mustafa Jatoi
, Asif Ali Zardari
, Muhammad Mian Soomro
, who served the nation as President
, Prime Minister
, Senate chairman
etc. Karachi
was chosen as the first capital of Pakistan
and it remains now as the capital of Sindh
province. In the province of Sindh, the Sindhis have always dominated the government and its various departments.
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
(Sind) is one of the provinces of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. Sindh was home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, the Indus Valley civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
.
Paleolithic and Mesolithic era
OngarOngar, Sindh
-Introduction:Ongar is a Paleolithic site located in Sindh, Pakistan, noted for flint tools.Ongar is located a few kilometers south of Hyderabad on the hills, which lie on the right side of the Indus River. At the present state of the research, Ongar is the most important Paleolithic site...
is one of the most important Paleolithic site discovered in southern Sindh, few kilometers south of Hyderabad, on the right side of the Indus River
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
. According to the aspect and surface patina of the tools, the flint assemblages can be attributed to the Early, Middle and Late (Upper) Paleolithic periods.
At Rehri
Rehri
Rehri or Rehri Goth , a 300 years old site, is one of the neighbourhoods of Bin Qasim Town in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. Rehri is located on the Arabian Sea coast and has large a community of fishermen....
, along the coast east of Karachi, Karachi University team has discovered a few Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
and Late Palaeolithic sites. Most of these sites have vanished during the last twenty years. Nevertheless their discovery shed new light on the prehistory of the coastal area of Lower Sindh. Scatters of flint were found in different spots, some of which were associated with Terebralia palustris mangrove shells.
The Late Palaeolithic and Mesolithic sites found by Karachi University team on the Mulri Hills
Mulri Hills
Mulri Hills are located in Gulshan Town, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. Latitude: 24.9166667 / Longitude: 67.1333333The late Palaeolithic and Mesolithic sites found by Karachi University archaeological team on the Mulri Hills, in front of Karachi University Campus, constitute one of the most important...
, in front of Karachi University Campus, constitute one of the most important archaeological discoveries made in Sindh during the last fifty years. The last hunter-gatherers, who left abundant traces of their passage, repeatedly inhabited the Hills. Some twenty different spots of flint tools were discovered during the surface surveys.
Copper to the Bronze Age
The mound of AmriAmri
Amri is the site of a Pre-Harappa fortified town which flourished from 3600 to 3300 BC.The site is located south of Mohenjo Daro on Hyderabad-Dadu Road about 110 kilometres north of Hyderabad in Sindh province of Pakistan. Situated near foothills of Kirthar Range of mountains, this was an...
is located along the right bank of the Indus River
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
, south of Dadu. The excavations carried out by the French Archaeological Mission at the beginning of the sixties revealed a long sequence of subsequent habitation phases datable from the Copper to the Bronze Age. The typical Amri layers have been radiocarbon-dated to the second half of the fourth millennium BC and are attributed by some authors to the beginning of the Early Harappan
Harappan
Harappan can refer to:* Aspects related to Harappa an archaeological site and city in northeast Pakistan* The Indus Valley Civilization that thrived along Indus River...
Civilization. At least 160 settlements attributed to the Amri Culture
Amri Culture
Amri Culture is attributed to Amri archaeological sites in Sindh and Balochistan provinces of Pakistan.At least 160 settlements attributed to the Amri Culture, have been discovered, mainly in Balochistan, but also in lower Sindh...
, among them the Tharro Hills
Tharro Hills
Tharro Hills are located in Sindh, Pakistan. The most important archaeological sites of Amri Culture has been discovered near Tharro Hills....
, near the village of Gujo
Gujo
Gujo is a town located in Sindh, Pakistan. The most important archaeological sites of Amri Culture has been discovered near Gujo....
, is one of the most famous of lower Sindh.
..
The site of Kot Diji
Kot Diji
The ancient site at Kot Diji was the forerunner of the Indus Civilization. The people of this site lived about 3000 BCE. The remains consist of two parts; the citadel area on high ground , and outer area...
, near Rohri
Rohri
Rohri is a town of Sukkur District, Sindh province, Pakistan. It is located at 27°40'60N 68°54'0E, on the east bank of the Indus River. Rohri town is the administrative headquarters of Rohri Taluka, a tehsil of Sukkur District with which it forms a metropolitan area...
, consists of a small mound composed of a sequence of overimposed structures and anthropogenic layers. They have been subdivided into two main complexes, the first of which belongs to the Early Harappan
Harappan
Harappan can refer to:* Aspects related to Harappa an archaeological site and city in northeast Pakistan* The Indus Valley Civilization that thrived along Indus River...
, Kot Diji Culture
Kot Diji
The ancient site at Kot Diji was the forerunner of the Indus Civilization. The people of this site lived about 3000 BCE. The remains consist of two parts; the citadel area on high ground , and outer area...
, and the second to the Mature Harappan Civilization.
The site of Lakhueen-jo-daro
Lakhueen-jo-daro
-Introduction:Lakhueen-jo-daro is an archaeological site located in Sindh, Pakistan.The site of Lakhueen-jo-daro, near Sukkur, belongs to the Matura Harappan Civilization as indicated by the characteristics of the structural remains, material culture finds and one radiocarbon date, covers a wide...
, near Sukkur
Sukkur
Sukkur, or Sakharu , formerly Aror and Bakar, is the third largest city of Sindh province, situated on the west bank of Indus River in Pakistan in Sukkur District. However, the word Sakharu in Sindhi means "superior", which the spelling of the city's name in Sindhi suggests is the origin of the...
, belongs to the Mature Harappan Civilization as indicated by the characteristics of the structural remains, material culture finds and one radiocarbon date, covers a wide area, from which a few mounds emerge. The site indicates that the origins of Sukkur are to be referred to a much older period than previously suspected.
The metropolis of Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro is an archeological site situated in what is now the province of Sindh, Pakistan. Built around 2600 BC, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, and one of the world's earliest major urban settlements, existing at the same time as the...
, near Larkana
Larkana
Larkana or Larkano is the fourth largest city in the north-western part of Sindh Province, Pakistan, and is located within Larkana District.The old name of larkano is chandka which was changed in 1901. In August 2000 Larkana celebrated its hundred years of existence...
, is largest Indus city so far discovered in Sindh. The large-scale excavations carried out in the 1920s brought to light most of the architectural remains that are still currently visible. They are mainly of backed bricks with very well preserved buildings aligned along streets and lanes. Mohen-jo-daro is the largest Bronze Age city of the world. The larkana was very famous city in sindh. moen-jo-dero is 25 kilometer far from larkana.ratodero is 30 kilometer far from larkana ratodero is very big city and very famous ratodero is name of rato jalbani he was very brave and honest. he was very rich in sindh now he was dead now her tomb in 10 meter in the gold he does not give her gold to her sons,and her son was sobdar khan jalbani there was the famous story of the sindh.
Pir Shah Jurio
Pir Shah Jurio
-Introduction:Pir Shah Jurio is an archaeological site located in Sindh, Pakistan. It was discovered by Abdur Rauf Khan.-Historical significance:...
is a Mature Indus Civilization village along the left bank of the Hub River
Hub River
Hub River is located in Lasbela, Balochistan, Pakistan. It forms the provincial boundary between Sindh and Balochistan, west of Karachi.Hub Dam is a large water storage reservoir constructed in 1981 on the River in the arid plains north of Karachi...
. It consists of a small mound, which is nowadays partly covered by a cemetery. From its surface, typical potsherds and other finds were collected. This site is strictly connected with the sea, which is a few kilometers south of it. It was radiocarbon-dated to the third millennium BP, from a sample of Terebralia palustris shells.
The Indus Civilization site of Kot Bala
Kot Bala
Kot Bala is located in Lasbela District, Balochistan, Pakistan.The Indus Civilization site of Kot Bala is located in the interior of the Sonmiani Bay, along the Lasbela coast. It was partly excavated by Professor George F. Dales of the University of California, Berkeley in the 1970s and was never...
is located in the interior of the Sonmiani Bay
Sonmiani Bay
Sonmiani Bay is located on the Arabian Sea in Lasbela District, Balochistan, Pakistan....
, along the coast of Lasbela District
Lasbela District
Lasbela is a coastal district of Balochistan province of Pakistan. It became a separate district in Kalat Division on 30 June 1954. The name is derived from the words Las which in Sanskrit signifies a settlement or lived in or lively and Bela which means "A Sea's Shore" in Sanskrit and is also the...
, Balochistan
Balochistan (Pakistan)
Balochistan is one of the four provinces or federating units of Pakistan. With an area of 134,051 mi2 or , it is the largest province of Pakistan, constituting approximately 44% of the total land mass of Pakistan. According to the 1998 population census, Balochistan had a population of...
. It was partly excavated by Professor G. Dales of Berkeley University in the Seventies and never published in detail. This site is of great importance for its location close to the Arabian Sea. It is supposed to be one of the main harbors from which the Indus traders sailed their ships to the coasts of the Arabian Peninsula.
Sindh has been known by various names in the past, the name Sindh comes from the Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan is an ethno-linguistic term referring to the wide collection of peoples united as native speakers of the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-Iranian family of Indo-European languages...
. In Sanskrit, the province was called Sindhu meaning the river Sindh and the people living on its banks. The Assyrians (as early as the seventh century BCE) knew the region as Sinda, the Persians
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
Hindush, the Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
Indos, the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
Sindus or Indus, the Chinese
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
Sintu, while the Arabs dubbed it Sind. A legend claims that the Indus River
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
flowed from the mouth of a lion or Sinh-ka-bab.
Ancient era
In ancient times, the territory of the modern Sindh province was sometimes known as Sovira (or Souveera, Sauvīra) and also as Sindhudesha, Sindhu being the original name for Indus river and the suffix 'desh' roughly corresponding to country or territory.The first known village settlements date as far back as 7000 BCE
7th millennium BC
During the 7th millennium BC, agriculture spreads from Anatolia to the Balkans.World population was essentially stable at around 5 million people, living mostly scattered across the globe in small hunting-gathering tribes...
. Permanent settlements at Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh , one of the most important Neolithic sites in archaeology, lies on the "Kachi plain" of Balochistan, Pakistan...
to the west expanded into Sindh. One of the original inhabitants of ancient Sindh were the Austro-Asiatic speaking peoples who spoke the Munda languages
Munda languages
-Anderson :Gregory Anderson's 1999 proposal is as follows. Individual languages are highlighted in italics.*North Munda **Korku**Kherwarian***Santhali***Mundari*South Munda **Kharia–Juang***Juang***Kharia...
. This culture blossomed over several millennia and gave rise to the Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
around 3000 BCE. The Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
spanned much of what is today Pakistan, but went into decline a few centuries prior to the invasion of the Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan is an ethno-linguistic term referring to the wide collection of peoples united as native speakers of the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-Iranian family of Indo-European languages...
which is still a hotly debated subject, a branch of the Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples are a linguistic group consisting of the Indo-Aryan, Iranian, Dardic and Nuristani peoples; that is, speakers of Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European language family....
, who are considered to have founded the Vedic Civilization, that existed between the Kabul river
Kabul River
Kabul River , the classical Cophes , is a 700 km long river that starts in the Sanglakh Range of the Hindu Kush Mountains in Afghanistan and ends in the Indus River near Attock, Pakistan. It is the main river in eastern Afghanistan and is separated from the watershed of the Helmand by the Unai Pass...
, the Sarasvati River
Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River is one of the chief Rigvedic rivers mentioned in ancient Hindu texts. The Nadistuti hymn in the Rigveda mentions the Sarasvati between the Yamuna in the east and the Sutlej in the west, and later Vedic texts like Tandya and Jaiminiya Brahmanas as well as the Mahabharata...
and the upper Ganges river after 1500 BCE. The Vedic civilization - with much in-fighting and fighting with the locals as well as interaction with them - ultimately helped shape subsequent cultures in South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
.
Another group of academia, claims that the original inhabitants of Sindh, who gave rise to the Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
around 3000 BCE, were native Aryans, as Vedic literature speaks of no reference to an Aryan race outside of the South Asia. This topic is considered still unresolved.
The Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
rivaled the contemporary civilizations of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
in both size and scope numbering nearly half a million inhabitants at its height with well-planned grid cities and sewer systems. It is known that the Indus Valley Civilization traded with ancient Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt via established shipping lanes. In ancient Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
, the word for cotton was Sindh denoting that the bulk of that civilizations cotton was predominantly imported from the Indus Valley Civilization. Speculation remains as to how and why the civilization declined and may have been a combination of natural disasters such as deterioration in climate, flooding as well as breakdown of international trade and internecine conflicts.
Sindh was conquered by the Persian Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
in the late 6th century BCE, and became a the Persian satrap
Satrap
Satrap was the name given to the governors of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as the Sassanid Empire and the Hellenistic empires....
y (province) of Hindush in addition to that of Gandara
Gandara
Gandara may refer to:People:*Raúl Gándara-Cartagena, long-time Ponce fire chiefPlaces:*Gandara, Samar, a Philippine municipality*Gandara, Buenos Aires, a village in Chascomús Partido, Argentina*Gándara, a river in Cantabria, Spain...
(Gandāra) centered in the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
to the north. Iranian and thus also Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
speech replaces 'S' with 'H' in many Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
ic words, resulting in 'Sindhu' being pronounced and written as 'Hindu'. They introduced the Kharoshti script and links to the west in the region.
Conquered by Macedonian Greek
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
armies led by Alexander the Great, after 326 BCE the region came under loose Greek control for a few decades. After Alexander's death, there was a brief period of Seleucid rule. Sindh was traded to the Mauryan Empire of Chandragupta
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya , was the founder of the Maurya Empire. Chandragupta succeeded in conquering most of the Indian subcontinent. Chandragupta is considered the first unifier of India and its first genuine emperor...
after a peace treaty with the Seleucids in 305 BCE.
Later, during the reign of the emperor Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
the region would solidly become a Buddhist domain. Following a century of Mauryan rule which ended by 232 BCE, the region came under the Greco-Bactrians based in what is today northern Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
. Some of their rulers also converted to Buddhism and spread it in the region.
The Scythians (Saka) shattered the Greco-Bactrian kingdom. Subsequently, the Tocharian
Tocharian
Tocharian may refer to:* Tocharians, an ancient people who inhabited the Tarim Basin in Central Asia* Tocharian languages, two Indo-European languages spoken by those people...
Kushan Empire
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire originally formed in the early 1st century AD under Kujula Kadphises in the territories of ancient Bactria on either side of the middle course of the Oxus in what is now northern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and southern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.During the 1st and early 2nd centuries...
annexed Sindh by the 1st century CE. Though the Kushans followed their own religion, they were tolerant of the local Buddhist tradition and sponsored many building projects for local beliefs.
Scythians, Kushans, Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
and the Sassanid
Sassanid Empire
The Sassanid Empire , known to its inhabitants as Ērānshahr and Ērān in Middle Persian and resulting in the New Persian terms Iranshahr and Iran , was the last pre-Islamic Persian Empire, ruled by the Sasanian Dynasty from 224 to 651...
Persians all exercised some degree of control in Sindh until the coming of the Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
Arabs in 711 CE.
The Buddhist city of Siraj-ji-Takri
Siraj-ji-Takri
Siraj-ji-Takri or Seeraj-ji-Takri is a Buddhist archaeological site located in Sindh, Pakistan. The Buddhist city of Siraj-ji-Takri is located along the western limestone terraces of the Rohri Hills in the Khairpur District of Upper Sindh, along the road that leads to Sorah...
is located along the western limestone terraces of the Rohri Hills in the Khairpur district
Khairpur District
Khairpur District is a district in the Sindh province of Pakistan. The district has an area of 15,910 square kilometres and is headquartered at the city of Khairpur.-Location:...
of Upper Sindh, along the road that leads to Sorah. Its ruins are still visible on the top of three different mesas, in the form of stone and mud-brick walls and small mounds, whilst other architectural remains were observed along the slopes of the hills in the 1980s. This city is not mentioned from any text dealing with the history of the Buddhist period of Sindh.
Rai DynastyRai DynastyThe Rai Dynasty was an Aryan dynasty of Sindh, from c. 489–690 AD. The influence of the Rai empire extended from Kashmir in the east, Makran and Debal port in the west, Surat port in south, Kandahar, Sistan, Suleyman, Ferdan and Kikanan hills in the north, ruling an area of over 600,000...
Rai Dynasty of RajputRajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
s was the ruling dynasty of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
from c. 489 – 632. The Rais were one of the Middle kingdoms of India
Middle kingdoms of India
Middle kingdoms of India refers to the political entities in India from the 3rd century BC after the decline of the Maurya Empire, and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, beginning with Simuka, from 230 BC...
and patrons of Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
even though they also established a huge temple of Shiva
Shiva
Shiva is a major Hindu deity, and is the destroyer god or transformer among the Trimurti, the Hindu Trinity of the primary aspects of the divine. God Shiva is a yogi who has notice of everything that happens in the world and is the main aspect of life. Yet one with great power lives a life of a...
in present-day Sukkur
Sukkur
Sukkur, or Sakharu , formerly Aror and Bakar, is the third largest city of Sindh province, situated on the west bank of Indus River in Pakistan in Sukkur District. However, the word Sakharu in Sindhi means "superior", which the spelling of the city's name in Sindhi suggests is the origin of the...
, derived from original Shankar
Shankar
Shankar or Shamkar is a Sanskrit noun, and means "Beneficent" or "Giver of Bliss". It generally refers to a Hindu descriptions of one of the chief gods, Lord Shiva.It may also refer to:-People:...
, close to their capital in Al-ror
Alor (Sukkur)
- History :Aror was the ancient capital of Sindh, now modern Rohri adjacent to Sukkur, Sindh, Pakistan. In 711 AD, Aror was captured by the army of Muslim general Muhammad bin Qasim. In 962 it was hit by a massive earthquake that changed the course of the Indus River...
. This is consistent with the historical accounts from the times of Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
and Harsha
Harsha
Harsha or Harsha Vardhana or Harshvardhan was an Indian emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 AD. He was the son of Prabhakara Vardhana and younger brother of Rajya Vardhana, a king of Thanesar, Haryana...
because India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n monarchs never sponsored a state religion and usually patronized more than one faith. The influence of the Rai state to Kannauj
Kannauj
Kannauj , also spelt Kanauj, is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is traditionally derived from the term Kanyakubja . Kannauj is an ancient city, in earlier times the capital...
in the east, Makran
Makran
The present day Makran is a semi-desert coastal strip in the south of Sindh, Balochistan, in Iran and Pakistan, along the coast of the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman. The present day Makran derived its name from Maka, a satrap of Achaemenid Empire....
and Debal (Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
) port in the west, Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
port in south, Kandahar
Kandahar
Kandahar is the second largest city in Afghanistan, with a population of about 512,200 as of 2011. It is the capital of Kandahar Province, located in the south of the country at about 1,005 m above sea level...
, Sistan
Sistan
Sīstān is a border region in eastern Iran , southwestern Afghanistan and northern tip of Southwestern Pakistan .-Etymology:...
, Suleyman, Ferdan and Kikanan hills in the north.
During the Rashidun Caliphate

Province
A province is a territorial unit, almost always an administrative division, within a country or state.-Etymology:The English word "province" is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French "province," which itself comes from the Latin word "provincia," which referred to...
of Sistan
Sistan
Sīstān is a border region in eastern Iran , southwestern Afghanistan and northern tip of Southwestern Pakistan .-Etymology:...
was the largest province of Persian Empire; its frontiers extended from Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
in east
East
East is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.East is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of west and is perpendicular to north and south.By convention, the right side of a map is east....
to Balkh
Balkh
Balkh , was an ancient city and centre of Zoroastrianism in what is now northern Afghanistan. Today it is a small town in the province of Balkh, about 20 kilometers northwest of the provincial capital, Mazar-e Sharif, and some south of the Amu Darya. It was one of the major cities of Khorasan...
(Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
) in north
North
North is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.North is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west.By convention, the top side of a map is north....
east
East
East is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.East is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of west and is perpendicular to north and south.By convention, the right side of a map is east....
. During the Rashidun Caliphate
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate , comprising the first four caliphs in Islam's history, was founded after Muhammad's death in 632, Year 10 A.H.. At its height, the Caliphate extended from the Arabian Peninsula, to the Levant, Caucasus and North Africa in the west, to the Iranian highlands and Central Asia...
, the Islamic conquest
Conquest (military)
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms. One example is the Norman conquest of England, which provided the subjugation of the Kingdom of England and the acquisition of the English crown by William the Conqueror in 1066...
of some parts of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
was extension of the campaigns to conquer the Persian empire in 643 AD, by sending seven armies from seven different routs to different parts of empire.
Islamic force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
s first entered Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
during the reign of Caliph Umar
Umar
`Umar ibn al-Khattāb c. 2 November , was a leading companion and adviser to the Islamic prophet Muhammad who later became the second Muslim Caliph after Muhammad's death....
, in 644] AD. It was not a full scale arrival in Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
, but was merely as extension of the conquests of the largest province of Persia - Sistan
Sistan
Sīstān is a border region in eastern Iran , southwestern Afghanistan and northern tip of Southwestern Pakistan .-Etymology:...
and Makran
Makran
The present day Makran is a semi-desert coastal strip in the south of Sindh, Balochistan, in Iran and Pakistan, along the coast of the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman. The present day Makran derived its name from Maka, a satrap of Achaemenid Empire....
region. In 644 AD, the columns of Hakam ibn Amr, Shahab ibn Makharaq and Abdullah ibn Utban concentrated near the west bank of Indus river
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
and defeated the army of Raja Sahasi Rai II a Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
king
Monarch
A monarch is the person who heads a monarchy. This is a form of government in which a state or polity is ruled or controlled by an individual who typically inherits the throne by birth and occasionally rules for life or until abdication...
of Rai kingdom
Rai Dynasty
The Rai Dynasty was an Aryan dynasty of Sindh, from c. 489–690 AD. The influence of the Rai empire extended from Kashmir in the east, Makran and Debal port in the west, Surat port in south, Kandahar, Sistan, Suleyman, Ferdan and Kikanan hills in the north, ruling an area of over 600,000...
of Sind, in Battle of Rasil
Battle of Rasil
Battle of Rasil was fought between Rai Kingdom of Sindh and Rashidun Caliphate in early 644. It was first encounter of Rashidun Caliphate with Indian subcontinent...
, his armies retreated to the estern bank of river Indus.
In response of Caliph Umar
Umar
`Umar ibn al-Khattāb c. 2 November , was a leading companion and adviser to the Islamic prophet Muhammad who later became the second Muslim Caliph after Muhammad's death....
's question about the Makran
Makran
The present day Makran is a semi-desert coastal strip in the south of Sindh, Balochistan, in Iran and Pakistan, along the coast of the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman. The present day Makran derived its name from Maka, a satrap of Achaemenid Empire....
region
Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
, the Messenger from Makran answered:
Caliph Umar
Umar
`Umar ibn al-Khattāb c. 2 November , was a leading companion and adviser to the Islamic prophet Muhammad who later became the second Muslim Caliph after Muhammad's death....
looked at the messenger and said:
"Are you a messenger or a poet?" He replied, "Messenger".
Thereupon Caliph Umar
Umar
`Umar ibn al-Khattāb c. 2 November , was a leading companion and adviser to the Islamic prophet Muhammad who later became the second Muslim Caliph after Muhammad's death....
, after listening to the unfavorable situations for sending an army, instructed Hakim bin Amr al Taghlabi that, for the time being, Makran
Makran
The present day Makran is a semi-desert coastal strip in the south of Sindh, Balochistan, in Iran and Pakistan, along the coast of the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman. The present day Makran derived its name from Maka, a satrap of Achaemenid Empire....
should be the easternmost frontier of the Islamic empire
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
, and that no further attempt should be made to extend the conquests.
After the death of Caliph Umar
Umar
`Umar ibn al-Khattāb c. 2 November , was a leading companion and adviser to the Islamic prophet Muhammad who later became the second Muslim Caliph after Muhammad's death....
the areas—like other regions of Persian Empire—broke into revolt and Caliph Uthman sent forces to re-conquer them. Caliph Uthman also sent his agent Haheem ibn Jabla Abdi to investigate the matters of Hind
Hind
The word Hind may refer to:* A female red deer* al-Hind , also Hind - The people of India or Indian subcontinent...
. On his return, he told Caliph Uthman about the cities and, listening to the miserable conditions of the region, he avoided campaigning in interior Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
and, like Caliph Umar
Umar
`Umar ibn al-Khattāb c. 2 November , was a leading companion and adviser to the Islamic prophet Muhammad who later became the second Muslim Caliph after Muhammad's death....
, he ordered his armies not to cross Indus river
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
.
Under the Umayyads, Abbasids and later dynasties
Sindh was finally conquered by Syrian Arabs led by Muhammad bin QasimMuhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim Al-Thaqafi was a Umayyad general who, at the age of 17, began the conquest of the Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River for the Umayyad Caliphate. He was born in the city of Taif...
; it became the easternmost province of the Umayyad Caliphate. The Arab province of Sindh is modern Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, while the lands of modern India further east were known to the Arabs as Hind. The defeat of the Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
ruler Dahir Rajah
Dahir
A Dahir is a Moroccan King's decree.-List of Dahirs:* August 12, 1913 - Criminal proceedings* March 11, 1915 - Education * November 17, 1915 - Creation of the 5-branch Seal of Solomon Flag of Morocco....
was made easier due to the tension between the Buddhist majority and the ruling Hindus' fragile base of control. The Arabs redefined the region and adopted the term budd to refer to the numerous Buddhist idols they encountered, a word that remains in use today. The city of Mansura
Mansura (Brahmanabad)
Mansura was the historic capital of the Arab empire in Sindh. The city now lies in Western Pakistan and is usually known as Brahmanabad in Sindh, situated about south-east of Shahdadpur railway station, and north-east of Hyderabad.-History:...
was established as a regional capital and Arab rule lasted for nearly 3 centuries and a fusion of cultures produced much of what is today modern Sindhi society. Arab geographers, historians and travellers also sometimes called the entire area from the Arabian Sea to the Hindu Kush
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a...
as Sindh. The meaning of the word Sindhu being water (or ocean) appears to refer to the Indus river
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
.

Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
rule ended with the ascension of the Soomro
Soomro
Soomro or Soomra is a Sindhi tribe in Sindh, Punjab and Balochistan, Pakistan.- History and origin :The Soomra Dynasty was established by the Soomro tribe of Sindh. The Soomra ruled Sindh from 750-1351. Following the 985 CE expulsion of the Qarmatian Muslim sect from Iraq and Egypt, the...
dynasty, who were local Sindhi Muslims and who controlled the province directly and as vassals from 1058 to 1249. Turkic
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
dynasties conquered the area by 977 CE and the region loosely became part of the Ghaznavid Empire
Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavids were a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic slave origin which existed from 975 to 1187 and ruled much of Persia, Transoxania, and the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. The Ghaznavid state was centered in Ghazni, a city in modern-day Afghanistan...
and then the Delhi Sultanate
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultanates, of Turkic origin in medieval India. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty...
which lasted until 1524. The Mughals took control the region and their rule lasted for another two centuries, while another local Sindhi Muslim group, the Samma Dynasty, challenged Mughal rule from their base at Thatta
Thatta
Thatta is a historic town of 220,000 inhabitants in the Sindh province of Pakistan, near Lake Keenjhar, the largest freshwater lake in the country. Thatta's major monuments especially its necropolis at Makli are listed among the World Heritage Sites. The Shah Jahan Mosque is also listed...
. The Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
Sufis played a pivotal role in converting the millions of native people to Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
. Sindh, though part of larger empires, continued to enjoy certain autonomy as a loyal Muslim domain and came under the rule of the Arghun Dynasty
Arghun Dynasty
The Arghun Dynasty was a dynasty of either Mongol, Turkish or Turko-Mongol ethnicity that ruled parts of Afghanistan and Pakistan in the late 15th and early 16th centuries, and would later be focused around the region of Sindh in south east Pakistan for most of the 16th century...
and Turkhan or Tarkhan
Tarkhan
Tarkhan is an ancient Central Asian title used by various Indo-European Tarkhan (Old Turkic Tarqan; Mongolian: Darkhan; ; ; ; alternative spellings Tarkan, Tarkhaan, Tarqan, Tarchan, Tarxan, Tarcan or Targan) is an ancient Central Asian title used by various Indo-European Tarkhan (Old Turkic...
dynasty from 1519 to 1625. Sindh became a vassal-state of the Afghan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
Durrani Empire
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire was a Pashtun dynasty centered in Afghanistan and included northeastern Iran, the Kashmir region, the modern state of Pakistan, and northwestern India. It was established at Kandahar in 1747 by Ahmad Shah Durrani, an Afghan military commander under Nader Shah of Persia and chief...
by 1747. It was then ruled by Kalhora
Kalhora
The Kalhora are of Sindhi origin they trace their origins to a Sindhi warrior named, Sultan Ahmad Kalhora who married a daughter of Raja Rai Dhorang Sahta, receiving much territories as dowry. Amir Fathullah Khan Kalhora, is the recognized ancestor of the dynasty. He conquered the bhangar...
rulers and later the Balochi
Baloch people
The Baloch or Baluch are an ethnic group that belong to the larger Iranian peoples. Baluch people mainly inhabit the Balochistan region and Sistan and Baluchestan Province in the southeast corner of the Iranian plateau in Western Asia....
Talpurs from 1783.
Colonial era

United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in 1839. Four years later, most of the province (except for the State of Khairpur) was added to the Company's domain after victories at Miani
Miani
Miani or Meeanee is a village in Sindh, Pakistan, six miles north of Hyderabad. It was the site of the battle of Miani, 17 February 1843, in which Sir Charles Napier defeated the ruler of Sindh and made it part of British India....
and Dubbo. Many people helped the British in the conquest of Sindh, including a Hindu government minister of Sindh, Mirs of Khairpur, Chandio Tribesmen, and Khosa Tribesmen. General Charles Napier
Charles James Napier
General Sir Charles James Napier, GCB , was a general of the British Empire and the British Army's Commander-in-Chief in India, notable for conquering the Sindh Province in what is now Pakistan.- His genealogy :...
is said to have reported victory to his Governor General with a Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
one-word telegram, namely "Peccavi" – or "I have sinned (Sindh)", which is a pun
Pun
The pun, also called paronomasia, is a form of word play which suggests two or more meanings, by exploiting multiple meanings of words, or of similar-sounding words, for an intended humorous or rhetorical effect. These ambiguities can arise from the intentional use and abuse of homophonic,...
.

Aga Khan I
Aga Khan I The Imam Hasan Ali Shah was born in 1804 in Kahak, Iran to Shah Khalil Allah, the 45th Ismaili Imam, and Bibi Sarkara, the daughter of Muhammad Sadiq Mahallati , a poet and a Ni‘mat Allahi Sufi...
had helped the British in the conquest of Sindh and was granted a pension as a result.
Sind was made part of British India's Bombay Presidency
Bombay Presidency
The Bombay Presidency was a province of British India. It was established in the 17th century as a trading post for the English East India Company, but later grew to encompass much of western and central India, as well as parts of post-partition Pakistan and the Arabian Peninsula.At its greatest...
in 1847 and became a separate province in 1936. During British control of Indian subcontinent, they laid railway lines in Sindh. Many barrages and canals were built to irrigate farm land in Sindh, which improved the livelihood of rural Sindhis. The first stamps in Asia, known as Scinde Dawk
Scinde Dawk
Scinde Dawk was a very old postal system of runners that served the Indus Valley of Sindh, an area of present-day Pakistan. The term also refers to the first postage stamps in Asia, the forerunners of the adhesive stamps used throughout India, Burma, the Straits Settlements and other areas...
, were released in 1852. The mail was carried quickly and efficiently, connecting British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
administrative offices and post offices from Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
through Kotri and Hyderabad up to Shikkur in the north.
During the freedom struggle, the Sindh branch of Muslim League
Pakistan Muslim League
The Pakistan Muslim League was founded in 1962, as a successor to the previously disbanded Muslim League in Pakistan. Unlike the original PML which ended in 1958 when General Ayub Khan banned all political parties, each subsequent Muslim League was in some way propped by the military dictators of...
party was established by Ghulam Muhammad Bhurgari
Bhurgari
Bhurgari is a Baloch tribe found in Sindh and Balochistan provinces of Pakistan....
in 1918. Abdullah Haroon, who joined it in 1918, was elected president of the provincial Muslim League in 1920. In those days, both the Muslim League and the Indian National Congress
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
of Sindh held their annual sessions at the same place simultaneously and passed similar resolutions.
The Sindh assembly was the first British Indian legislature to pass the resolution in favour of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. G. M. Syed
G. M. Syed
G. M. Syed was a political leader who pioneered the Jeay Sindh movement for the freedom of Sindh from Pakistan. He is regarded as one of the founding fathers of modern Sindhi nationalism...
, an influential Sindhi activist, revolutionary, and one of the important leaders in the forefront of the provincial autonomy movement, joined the Muslim League in 1938 and presented the Pakistan resolution in the Sindh Assembly.
Independence
On August 14, 1947 PakistanPakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
gained independence from foreign British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
colonial rule. The province of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
thus regained its self rule, lost since the defeat of Sindhi
Sindhi people
Sindhis are a Sindhi speaking socio-ethnic group of people originating from Sindh, a province Formerly of British India, now in Pakistan. Today Sindhis that live in Pakistan belong to various religious denominations including Islam, Zoroastrianism, Hinduism, Sikhism and Christianity...
Talpur
Talpur
Talpur ; is a Baloch tribe settled in Sindh. Talpurs settled in northern Sindh, spoke Sindhi language very soon their descendants and allies formed a confederacy against the Kalhora dynasty. Later, however, they enjoyed good relations with the Kalhoras and were invited by them to help organize...
Amirs in the Battle of Miani
Battle of Miani
The Battle of Miani was a battle between British forces under Sir Charles Napier and the Talpur Amirs of Sindh, Pakistan.-Background:...
on February 17, 1843.
The first challenge faced by the Government of Sindh
Government of Sindh
Government of Sindh is based in Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan. سندھ is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and is home to the Sindhis, Muhajirs, Pashtuns and a whole array of other ethnic and linguistic groups. Neighbouring regions are Balochistan to the west and north, Punjab in the north and...
was the settlement of Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
refugees. Nearly 7 million Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
s from India migrated to Pakistan while nearly equal number of Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
s and Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
s from Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
migrated to India. The Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
refugee
Refugee
A refugee is a person who outside her country of origin or habitual residence because she has suffered persecution on account of race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or because she is a member of a persecuted 'social group'. Such a person may be referred to as an 'asylum seeker' until...
s, (known as Muhajirs from India), settled mostly in urban areas of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
, most of them in Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
and Hyderabad.
Education
The foundation for modern, liberal, universal education was laid by the British colonial administration. Sindhi intelligentsia also participated in this modernisation of educational system. Hassan Ali Affandi, maternal grandfather of the present President of Pakistan (Mr. Asif Ali ZardariAsif Ali Zardari
Asif Ali Zardari is the 11th and current President of Pakistan and the Co-Chairman of the ruling Pakistan Peoples Party . He is also the widower of Benazir Bhutto, who served two nonconsecutive terms as Prime Minister....
), can be regarded as Sir Syed Ahmed Khan of Sindh. He made great efforts to encourage the Sindhi people to get modern education. He built an educational institution known as Sindh-Madrsat-ul-Islam. Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah was a Muslim lawyer, politician, statesman and the founder of Pakistan. He is popularly and officially known in Pakistan as Quaid-e-Azam and Baba-e-Qaum ....
went to Sindh-Madarsat-ul-Islam in Karachi, Sindh for education and, after his law education, worked in Karachi for a Sindhi (Hindu) law firm.
Education in Sindh is divided into five levels: primary
Primary education
A primary school is an institution in which children receive the first stage of compulsory education known as primary or elementary education. Primary school is the preferred term in the United Kingdom and many Commonwealth Nations, and in most publications of the United Nations Educational,...
(grades one through five); middle
Middle school
Middle School and Junior High School are levels of schooling between elementary and high schools. Most school systems use one term or the other, not both. The terms are not interchangeable...
(grades six through eight); high
Secondary education
Secondary education is the stage of education following primary education. Secondary education includes the final stage of compulsory education and in many countries it is entirely compulsory. The next stage of education is usually college or university...
(grades nine and ten, leading to the Secondary School Certificate
Secondary School Certificate
The Secondary School Certificate, also known as SSC, is a public examination taken by students in Bangladesh, Pakistan and in the states of Tamilnadu, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Goa in India after successfully completing at least ten years of schooling. It is followed...
); intermediate
Secondary education
Secondary education is the stage of education following primary education. Secondary education includes the final stage of compulsory education and in many countries it is entirely compulsory. The next stage of education is usually college or university...
(grades eleven and twelve, leading to a Higher Secondary School Certificate); and university
University
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
programs leading to graduate
Undergraduate education
Undergraduate education is an education level taken prior to gaining a first degree . Hence, in many subjects in many educational systems, undergraduate education is post-secondary education up to the level of a bachelor's degree, such as in the United States, where a university entry level is...
and advanced degrees.
Primary
Primary education
A primary school is an institution in which children receive the first stage of compulsory education known as primary or elementary education. Primary school is the preferred term in the United Kingdom and many Commonwealth Nations, and in most publications of the United Nations Educational,...
, middle
Middle school
Middle School and Junior High School are levels of schooling between elementary and high schools. Most school systems use one term or the other, not both. The terms are not interchangeable...
and high
Secondary education
Secondary education is the stage of education following primary education. Secondary education includes the final stage of compulsory education and in many countries it is entirely compulsory. The next stage of education is usually college or university...
schools are established in all parts of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
providing, Sindhi
Sindhi language
Sindhi is the language of the Sindh region of Pakistan that is spoken by the Sindhi people. In India, it is among 22 constitutionally recognized languages, where Sindhis are a sizeable minority. It is spoken by 53,410,910 people in Pakistan, according to the national government's Statistics Division...
, Urdu and English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
medium schools.
The college
College
A college is an educational institution or a constituent part of an educational institution. Usage varies in English-speaking nations...
s and universities
University
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
are established in major towns and cities of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
. They provide courses leading to BA
Bachelor of Arts
A Bachelor of Arts , from the Latin artium baccalaureus, is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate course or program in either the liberal arts, the sciences, or both...
, BSc
Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science is an undergraduate academic degree awarded for completed courses that generally last three to five years .-Australia:In Australia, the BSc is a 3 year degree, offered from 1st year on...
and Bachelor of Commerce
Bachelor of Commerce
A Bachelor of Commerce is an undergraduate degree in commerce and related subjects. The degree is also known as the Bachelor of Commerce and Administration, or BCA...
/ BCom/BBA
Bachelor of Business Administration
The Bachelor of Business Administration is a bachelor's degree in Commerce and business administration. In most universities, the degree is conferred upon a student after four years of full-time study in one or more areas of business concentrations; see below...
degrees. medical colleges
Medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution—or part of such an institution—that teaches medicine. Degree programs offered at medical schools often include Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine, Bachelor/Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Philosophy, master's degree, or other post-secondary...
and engineering college
Engineering college
Engineering colleges generally refer to institutes of higher education which offer an engineering course at degree level. The duration of the course is four to five years depending upon the university to which the college is affiliated. The students learn little of basic science concentrating...
s are also established in major cities of Sindh.
There are many postgraduate
Postgraduate education
Postgraduate education involves learning and studying for degrees or other qualifications for which a first or Bachelor's degree generally is required, and is normally considered to be part of higher education...
and research institute
Research institute
A research institute is an establishment endowed for doing research. Research institutes may specialize in basic research or may be oriented to applied research...
s in Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
providing state-of-the-art education to Sindhi students.
Economy
SindhSindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
has become the most industrialized and urbanized province of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. The head offices of Pakistani companies, and regional offices of international companies, are located in Sindh. The Sindhis have been in forefront of economic development of the province. The new dams and canals have irrgated many areas that were barren and Sindh produces many agricultural products for the country and for export.
The construction of multi-billion projects like Karachi Nuclear Power Plant
KANUPP
The Karachi Nuclear Power Plant, widely known as KANUPP-I, is a commercial nuclear power plant, located at Karachi, Sindh Province of Pakistan. In terms of Nuclear industry, the KANUPP-I is Pakistan's first nuclear power plant and is the first nuclear power plant in the Muslim world to be constructed...
, Port Qasim
Port Qasim
The Port Muhammad Bin Qasim , also known as Port Qasim, is a seaport in Karachi, Pakistan, on the coastline of the Arabian Sea. It is Pakistan's second busiest port, handling about 35% of the nation's cargo...
and Pakistan Steel Mills
Pakistan Steel Mills
The Pakistan Steel Mills, PSM, is the state-owned producer of long rolled steel and heavy iron products in Karachi, Sindh Province of Pakistan. The Pakistan Steel Mill is the country's largest industrial undertaking having a production capacity of 1.1 million tonnes of steel...
provided tens of thousands of jobs to the residents of Sindh.
Politics
The founding father of PakistanPakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, Quaid-e-Azam Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah was a Muslim lawyer, politician, statesman and the founder of Pakistan. He is popularly and officially known in Pakistan as Quaid-e-Azam and Baba-e-Qaum ....
was of Sindhi background. Khan Bahadur Muhammad Ayub Khuhro
Muhammad Ayub Khuhro
Khan Bahadur Muhammad Ayub Khoro was a politician from Sindh, Pakistan, who became its first Chief Minister after independence of Pakistan and subsequently serving two additional terms in the 1950s. He later became the Defence Minister in the government of PM Feroz Khan Noon, before the imposition...
was the first Chief Minister of Sindh
Chief Minister of Sindh
The Chief Minister of Sindh is elected by the Provincial Assembly of Sindh to serve as the head of the provincial government in Sindh, Pakistan. The current Chief Minister is Qaim Ali Shah, who belongs to Pakistan Peoples Party...
, after independence of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. Pakistan's political scene continued to be dominated by Sindhi politicians like Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto was 9th Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1973 to 1977, and prior to that, 4th President of Pakistan from 1971 to 1973. Bhutto was the founder of the Pakistan Peoples Party — the largest and most influential political party in Pakistan— and served as its chairman until his...
, Mumtaz Bhutto
Mumtaz Bhutto
Sardar Mumtaz Ali Khan Bhutto is the first cousin of Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto, chief of the Bhutto clan and chairman of the Sindh National Front and Sindh Qaumi Itehad...
, Benazir Bhutto
Benazir Bhutto
Benazir Bhutto was a democratic socialist who served as the 11th Prime Minister of Pakistan in two non-consecutive terms from 1988 until 1990 and 1993 until 1996....
, Muhammad Khan Junejo
Muhammad Khan Junejo
Muhammad Khan Junejo was the tenth Prime Minister of Pakistan.-Early life:He was born at Sindhri in Tharparkar of Sindh. He belongs to Sindhi Muslim Rajput family of Junejo clan. Junejo started his political career at the age of twenty one...
, Ghulam Mustafa Jatoi
Ghulam Mustafa Jatoi
Ghulam Mustafa Jatoi was a Pakistani politician, and was the Acting Prime Minister of Pakistan for 3 months, from August 6, 1990 to November 6, 1990. Ghulam Mustafa Jatoi's ancestors were mureeds of the Pir's of Sarhandi....
, Asif Ali Zardari
Asif Ali Zardari
Asif Ali Zardari is the 11th and current President of Pakistan and the Co-Chairman of the ruling Pakistan Peoples Party . He is also the widower of Benazir Bhutto, who served two nonconsecutive terms as Prime Minister....
, Muhammad Mian Soomro
Muhammad Mian Soomro
Muhammad Mian Soomro is a Pakistani politician who has been the Chairman of the Senate of Pakistan since 2003. Soomro comes from a renowned political family of Sindh that has been active in public life since 1923...
, who served the nation as President
President of Pakistan
The President of Pakistan is the head of state, as well as figurehead, of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Recently passed an XVIII Amendment , Pakistan has a parliamentary democratic system of government. According to the Constitution, the President is chosen by the Electoral College to serve a...
, Prime Minister
Prime Minister of Pakistan
The Prime Minister of Pakistan , is the Head of Government of Pakistan who is designated to exercise as the country's Chief Executive. By the Constitution of Pakistan, Pakistan has the parliamentary democratic system of government...
, Senate chairman
Chairman of the Senate of Pakistan
The current Chairman of the Senate of Pakistan is Farooq Naek since 12 March, 2009.The first Chairman of the Senate was Justice Khan Habibullah Khan Marwat.-History:...
etc. Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
was chosen as the first capital of Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and it remains now as the capital of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
province. In the province of Sindh, the Sindhis have always dominated the government and its various departments.

